Case Characteristics, Clinical Data, And Outcomes of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients In Qom Province, Iran: A Prospective Cohort Study
et al., Research Square, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-365321/v2, May 2021
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
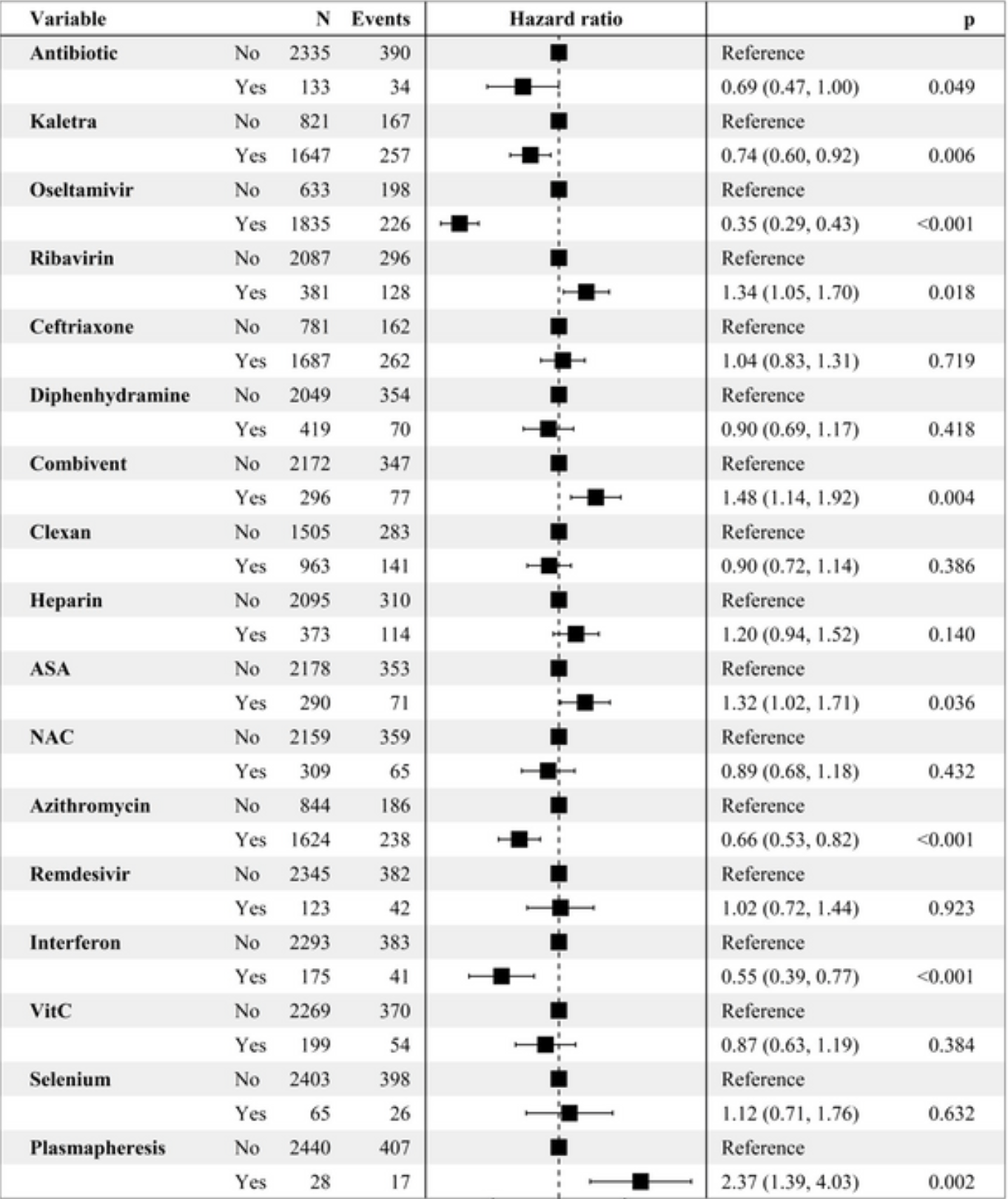
Prospective study of 2,468 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Iran, showing no significant difference with vitamin C treatment. IR.MUQ.REC.1399.013.
Although the 13% lower mortality is not statistically significant, it is consistent with the significant 18% lower mortality [9‑27%] from meta-analysis of the 45 mortality results to date.
This is the 26th of 73 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000076.
20 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0016.
|
risk of death, 13.0% lower, HR 0.87, p = 0.38, treatment 54 of 199 (27.1%), control 285 of 2,269 (12.6%), adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Pourhoseingholi et al., 26 May 2021, prospective, Iran, preprint, mean age 57.9, 11 authors, study period 2 February, 2020 - 20 July, 2020, average treatment delay 7.4 days, dosage not specified.
Case Characteristics, Clinical Data, And Outcomes of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients In Qom Province, Iran: A Prospective Cohort Study
doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-365321/v2
The outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) dates back to December 2019 in China. Iran has been one of the most virus in icted countries. The aim of this study was to report demographics, signs and symptoms, laboratory ndings, therapeutic approaches, and outcomes. This observational cohort study was performed from 20 th February 2020 to 20 th July 2020. Patients' information was recorded in their medical les. Multivariable analysis was performed to assess demographics, signs and symptoms, paraclinical data, treatments, outcomes of disease, and nding the risk factors of death subject to COVID-19. Of all 2468 participants, the mean age was 57.9±17.6 years and 56.8% of patients were male. The most signi cant comorbidities were seen among those who have Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus. 14.42% were admitted to ICU, and 17.2% died in hospital. The signi cant risk factors of death were ageing, male gender, HTN, CHF, CVA, CKD, increasing ESR, PT, WBC, liver function tests, and decreasing Oxygen saturation. Incontinent results in the case of COVID-19 outcomes and deathrelated risk factors attribute to marked differences in demographics and health care systems. The patients with hazardous risk factors must be detected urgently and monitored closely to save more lives.
Supplementary Files This is a list of supplementary les associated with this preprint. Click to download. app.docx
References
Aggarwal, Lippi, Henry, Cerebrovascular disease is associated with an increased disease severity in patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A pooled analysis of published literature, International Journal of Stroke
Arab-Mazar, Sah, Rabaan, Mapping the incidence of the COVID-19 hotspot in Iran-Implications for Travellers, Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease
Arentz, Yim, Klaff, Characteristics and outcomes of 21 critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Washington State, JAMA
Ashraf, Shokouhi, Shirali, COVID-19 in Iran, a comprehensive investigation from exposure to treatment outcomes
Audit, ICNARC report on COVID-19 in critical care
Covid, coronavirus pandemic
Cummings, Baldwin, Abrams, Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: a prospective cohort study, The Lancet
Docherty, Harrison, Green, Features of 20 133 UK patients in hospital with covid-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterisation Protocol: prospective observational cohort study
Duan, Liu, Li, Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Geleris, Sun, Platt, Observational Study of Hydroxychloroquine in Hospitalized Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Giacomo, Antonio, Cecconi, Critical care utilization for the COVID-19 outbreak in
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Baseline Characteristics and Outcomes of 1591 Patients Infected With SARS-CoV-2 Admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Karagiannidis, Mostert, Hentschker, Case characteristics, resource use, and outcomes of 10 021 patients with COVID-19 admitted to 920 German hospitals: an observational study, The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Keith, Day, Choe, The successful use of therapeutic plasma exchange for severe COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome with multiple organ failure, SAGE open medical case reports
Khoshnood, Ommi, Zali, Epidemiological Characteristics, Clinical Features, and Outcome of COVID-19 Patients in Northern Tehran, Iran; a Cross-Sectional Study, Advanced Journal of Emergency Medicine
Nile, Nile, Qiu, COVID-19: Pathogenesis, cytokine storm and therapeutic potential of interferons, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev
Novel, The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China. Zhonghua liu xing bing, xue za zhi= Zhonghua liuxingbingxue zazhi
Ranucci, Ballotta, Dedda, The procoagulant pattern of patients with COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area
Wang, Fish, Editors, Global virus outbreaks: Interferons as 1st responders, Seminars in immunology
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Jama
Yang, Yu, Xu, Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study, Lancet Respir Med
Ye, Fu, Ren, Treatment with convalescent plasma for COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China, J Med Virol
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-365321/v2",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-365321/v2",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome corona virus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) dates back to December 2019 in China. Iran has been one of the most virus inflicted countries. The aim of this study was to report demographics, signs and symptoms, laboratory findings, therapeutic approaches, and outcomes. This observational cohort study was performed from 20<jats:sup>th </jats:sup>February 2020 to 20<jats:sup>th </jats:sup>July 2020. Patients’ information was recorded in their medical files. Multivariable analysis was performed to assess demographics, signs and symptoms, paraclinical data, treatments, outcomes of disease, and finding the risk factors of death subject to COVID-19. Of all 2468 participants, the mean age was 57.9±17.6 years and 56.8% of patients were male. The most significant comorbidities were seen among those who have Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus. 14.42% were admitted to ICU, and 17.2% died in hospital. The significant risk factors of death were ageing, male gender, HTN, CHF, CVA, CKD, increasing ESR, PT, WBC, liver function tests, and decreasing Oxygen saturation. Incontinent results in the case of COVID-19 outcomes and death-related risk factors<jats:bold> </jats:bold>attribute to marked differences in demographics and health care systems. The patients with hazardous risk factors must be detected urgently and monitored closely to save more lives.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
3,
26
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"family": "Pourhoseingholi",
"given": "Mohamad Amin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Qom University of Medical Science and Health Services"
}
],
"family": "Yousefi",
"given": "Hosein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Qom University of Medical Science and Health Services"
}
],
"family": "Manesh",
"given": "Hassan Fatemi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Qom University of Medical Science and Health Services"
}
],
"family": "Motahaver",
"given": "Nima Najafian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Qom University of Medical Science and Health Services"
}
],
"family": "Heydari",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"family": "Looha",
"given": "Mehdi Azizmohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"family": "Taraghikhah",
"given": "Nazanin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Qom University of Medical Science and Health Services"
}
],
"family": "Yazdi",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Qom University of Medical Science and Health Services"
}
],
"family": "Salami",
"given": "Zahra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Qom University of Medical Science and Health Services"
}
],
"family": "Moallemi",
"given": "Elmira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Qom University of Medical Science and Health Services"
}
],
"family": "Adeli",
"given": "Seyed Hasan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-26T21:16:11Z",
"timestamp": 1622063771000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-14T10:44:35Z",
"timestamp": 1639478675000
},
"group-title": "In Review",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-20T21:50:16Z",
"timestamp": 1640037016832
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "Research Square"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
26
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-26T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1621987200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-365321/v2",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-365321/v2.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "8761",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
26
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.21203",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Research Square Platform LLC",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": [
"Case Characteristics, Clinical Data, And Outcomes of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients In Qom Province, Iran: A Prospective Cohort Study"
],
"type": "posted-content"
}
