A randomized clinical trial evaluating the immunomodulatory effect of convalescent plasma on COVID-19-related cytokine storm
et al., Internal and Emergency Medicine, doi:10.1007/s11739-021-02734-8, IRCT20200310046736N1, Apr 2021
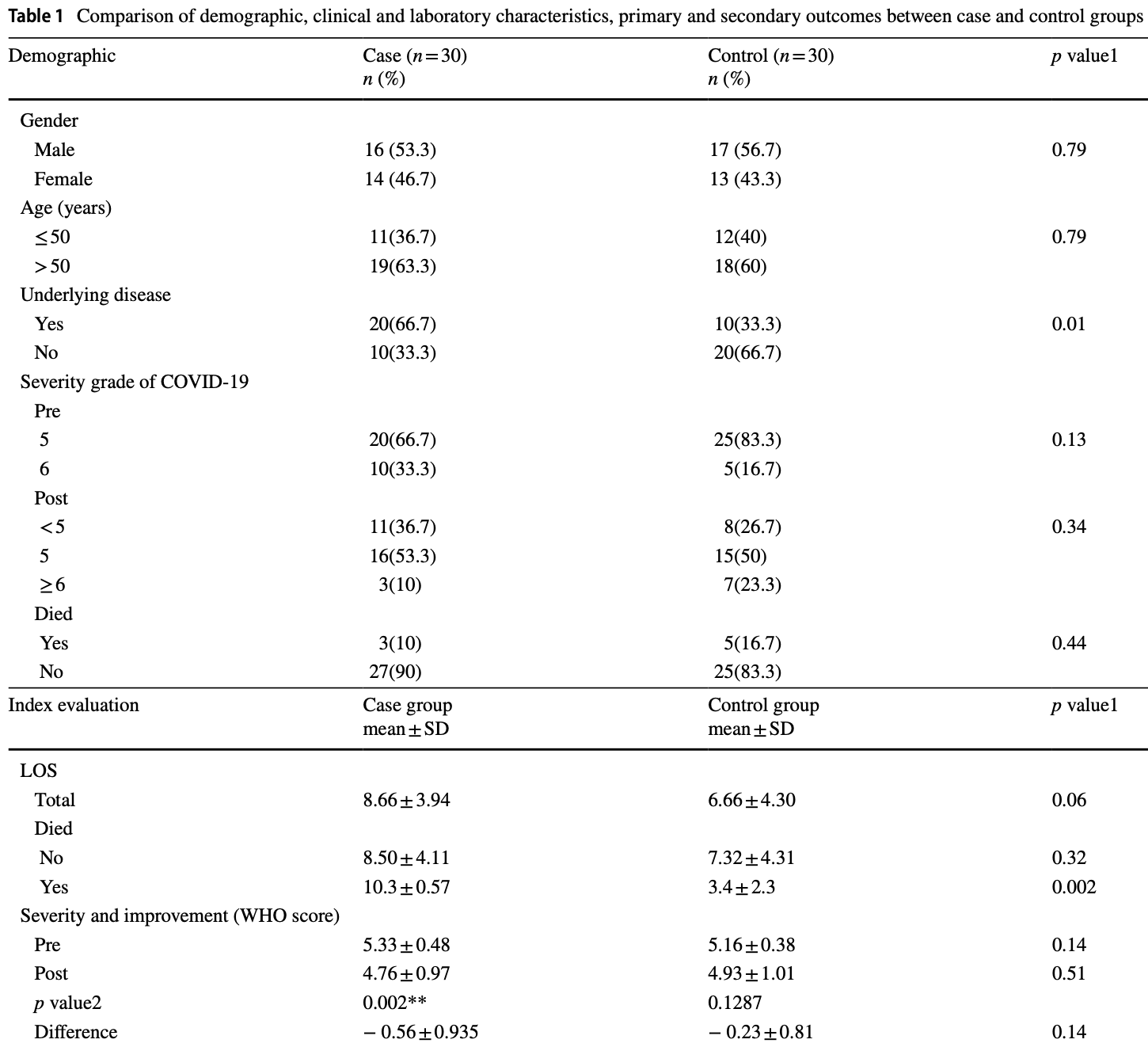
RCT 62 hospitalized patients in Iran, showing no significant difference in mortality and length of stay with convalescent plasma.
|
risk of death, 40.0% lower, RR 0.60, p = 0.71, treatment 3 of 30 (10.0%), control 5 of 30 (16.7%), NNT 15.
|
|
hospitalization time, 30.0% higher, relative time 1.30, p = 0.06, treatment 30, control 30.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Pouladzadeh et al., 10 Apr 2021, Single Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, mean age 53.5, 17 authors, study period March 2020 - May 2020, trial IRCT20200310046736N1.
Contact: msafdaryan@gmail.com, parastoomoradi40@yahoo.com.
A randomized clinical trial evaluating the immunomodulatory effect of convalescent plasma on COVID-19-related cytokine storm
Internal and Emergency Medicine, doi:10.1007/s11739-021-02734-8
Evaluating the effect of convalescent plasma (CP) on some cytokine storm indices in severe COVID-19 patients. Totally, 62 patients were randomly assigned into two groups for this clinical trial. Patients in the intervention group received one unit (500 mL) plasma on the admission day plus standard drugs while the controls merely received standard treatments. Eventually, primary and secondary outcomes were evaluated. In the CP group, compared with controls, the mean levels of lymphocytes and IL-10 significantly increased while the levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and IFN-γ decreased (p < 0.05). The length of in-hospital stay, and mortality rate did not significantly reduce in the CP group compared with controls (p > 0.05) while WHO severity scores remarkably improved (p = 0.01), despite the higher frequency of underlying diseases among the CP group (66.7%) vs. controls (33.3%). Although CP has a remarkable immunomodulatory and antiviral potential to improve the cytokine storm and disease severity in COVID-19 patients, it did not considerably affect the mortality rate.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at https:// doi. org/ 10. 1007/ s11739-021-02734-8. Author contributions MP conceptualization, supervision, investigation, and funding acquisition; MS supervision, project administration, methodology, and writing-review and editing; PE and HA methodology and resources; AGB and BS investigation; PMC investigation, data curation, writing-original draft, and writing-review and editing; AF resources and coordination of plasma donation plan; MGB and AF resources; MAJF, GAK, and MA laboratory consultation; ER, MT and FY clinical consultation; RH coordination for blood plasma separation device.
Declarations Ethical approval All the procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the national research committee and with the 2008 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This hospital-based, parallel-group and randomized controlled trial was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran with Ethical Code: IR.AJUMS.REC.1399.003 and IRCT20200310046736N1.
Authors and Affiliations
Mandana Pouladzadeh 1 • Mehdi Safdarian 2 • Peyman Eshghi
References
Abolghasemi, Eshghi, Cheraghali, Clinical efficacy of convalescent plasma for treatment of COVID-19 infections: results of a multicenter clinical study, Transfus Apher Sci
Agarwal, Mukherjee, Kumar, Chatterjee, Bhatnagar et al., Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate covid-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial, doi:10.1136/bmj.m3939
Benjamin, Mclaughlin, Plasma components: properties, differences, and uses, Transfusion
Channappanavar, Perlman, Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology, Semin Immunopathol
Chen, Liu, Liu, Analysis of clinical features of 29 patients with 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia, Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi
Chen, Wu, Guo, Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J Clin Invest
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet
Choghakabodi, Pouladzadeh, Haybar, Biological whistleblowers for silent myocardial ischemia: diagnostic and prognostic approach, Recenti Prog Med
Duan, Liu, Li, Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients, ProcNatl Acad Sci
Garraud, Heshmati, Pozzetto, Plasma therapy against infectious pathogens, as of yesterday, today and tomorrow, Transfus Clin Biol
Gharbharan, Jordans, Geurtsvankessel, Convalescent plasma for COVID-19. A randomized clinical trial, MedRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.07.01.20139857
Han, Ma, Li, Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors, Emerg Microbes Infect
Hegerova, Gooley, Sweerus, Maree, Bailey et al., Use of convalescent plasma in hospitalized patients with covid-19-case series, Blood
Hou, Huang, Immune suppressive properties of artemisinin family drugs, Pharmacol Therap
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan China, Lancet
Hung, To, Lee, Convalescent plasma treatment reduced mortality in patients with severe pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 virus infection, Clin Infect Dis
Hung, Toe, Lee, Hyperimmune IV immunoglobulin treatment: a multicenter double-blind randomized controlled trial for patients with severe 2009 influenza A (H1N1) infection, Chest
Lenzer, Covid-19: US gives emergency approval to hydroxychloroquine despite lack of evidence, BMJ
Li, Zhang, Hu, Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Lunemann, Nimmerjahn, Dalakas, Intravenous immunoglobulin in neurology-mode of action and clinical efficacy, Nat Rev Neurol
Magro, Cytokine storm: is it the only major death factor in COVID-19 patients?, Coagul role Med Hypotheses
Mair-Jenkins, Saavedra-Campos, Baillie, The effectiveness of convalescent plasma and hyperimmune immunoglobulin for the treatment of severe acute respiratory infections of viral etiology: a systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis, J Infect Dis
Michot, Albiges, Chaput, Tocilizumab, an anti-IL6 receptor antibody, to treat Covid-19-related respiratory failure: a case report, Ann Oncol
Odievre, De Marcellus, Ducou Pointe, Dramatic improvement after tocilizumab of a severe COVID-19 in a child with sickle cell disease and acute chest syndrome, Am J Hematol, doi:10.1002/ajh.25855
Piechotta, Chai, Valk, Doree, Monsef et al., Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a living systematic review, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Planitzer, Modrof, Kreil, West Nile virus neutralization by US plasma-derived immunoglobulin products, J Infect Dis
Rieder, Wengenmayer, Staudacher, Cytokine adsorption in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-03130-y
Rojas, Monsalve, Pacheco, Ebola virus disease: An emerging and re-emerging viral threat, J Autoimmun
Salazar, Perez, Ashraf, Treatment of COVID-19 patients with convalescent plasma, Am J Pathol
Simonovich, Pratx, Scibona, Beruto, Vallone et al., A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Tan, Li, Yiyang, Clinical efficacy analysis of 50 cases of corona virus disease 2019 in traditional Chinese medicine, Jilin J Chin Med
Tang, Liu, Zhang, Cytokine storm in COVID-19: the current evidence and treatment strategies, Front Immunol
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan China, JAMA
Wang, Yang, Li, Clinical features of 69 cases with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China, Clin Infect Dis
Xia, Li, Wu, Improved clinical symptoms and mortality on severe/critical COVID-19 patients utilizing convalescent plasma transfusion, Blood
Xin, Retrospective clinical analysis on treatment of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia with traditional Chinese medicine Lianhua Qingwen, Chin J Exp Tradition Med Formul
Xu, Shi, Wang, Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X
Zhang, Song, Tong, First case of COVID-19 in a patient with multiple myeloma successfully treated with tocilizumab, Blood Adv
Zhang, Xiao, Zhang, Xia, Cao et al., Coagulopathy and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11739-021-02734-8",
"ISSN": [
"1828-0447",
"1970-9366"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11739-021-02734-8",
"alternative-id": [
"2734"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "11 December 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "30 March 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "10 April 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethical approval",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "All the procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the national research committee and with the 2008 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This hospital-based, parallel-group and randomized controlled trial was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, Ahvaz, Iran with Ethical Code: IR.AJUMS.REC.1399.003 and IRCT20200310046736N1."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pouladzadeh",
"given": "Mandana",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9735-2632",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Safdarian",
"given": "Mehdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Eshghi",
"given": "Peyman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abolghasemi",
"given": "Hassan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "bavani",
"given": "Alireza Ghorbani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sheibani",
"given": "Behnam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6362-7842",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Moradi Choghakabodi",
"given": "Parastoo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Feghhi",
"given": "Abdolaziz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghafourian Boroujerdnia",
"given": "Mehri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Forouzan",
"given": "Arash",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jalali Far",
"given": "Mohammad Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaydani",
"given": "Gholam Abbas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rajaei",
"given": "Elham",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amin",
"given": "Mansour",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Torabizadeh",
"given": "Mehdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yousefi",
"given": "Farid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hadaddezfuli",
"given": "Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Internal and Emergency Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Intern Emerg Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-10T14:02:41Z",
"timestamp": 1618063361000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-02T07:19:18Z",
"timestamp": 1635837558000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100005001",
"award": [
"IR.AJUMS.REC.1399.003"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-14T10:55:04Z",
"timestamp": 1673693704195
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 32,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1618012800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1618012800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s11739-021-02734-8.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11739-021-02734-8/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s11739-021-02734-8.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2181-2191",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"author": "C Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2734_CR1",
"unstructured": "Huang C, Wang Y, Li X et al (2020) Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan China. Lancet 395:497–506",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129",
"author": "H Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1123",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "2734_CR2",
"unstructured": "Han H, Ma Q, Li C et al (2020) Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors. Emerg Microbes Infect 9(1):1123–1130",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "L Chen",
"first-page": "E005",
"journal-title": "Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi",
"key": "2734_CR3",
"unstructured": "Chen L, Liu HG, Liu W et al (2020) Analysis of clinical features of 29 patients with 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi 43:E005",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"author": "Z Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2734_CR4",
"unstructured": "Xu Z, Shi L, Wang Y et al (2020) Pathological findings of COVID-19 associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome. Lancet Respir Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30076-X",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00281-017-0629-x",
"author": "R Channappanavar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "529",
"journal-title": "Semin Immunopathol",
"key": "2734_CR5",
"unstructured": "Channappanavar R, Perlman S (2017) Pathogenic human coronavirus infections: causes and consequences of cytokine storm and immunopathology. Semin Immunopathol 39:529–539",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa272",
"author": "Z Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "769",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2734_CR6",
"unstructured": "Wang Z, Yang B, Li Q et al (2020) Clinical features of 69 cases with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China. Clin Infect Dis 71(15):769–777",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI137244",
"author": "G Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2620",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "2734_CR7",
"unstructured": "Chen G, Wu D, Guo W et al (2020) Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019. J Clin Invest 130:2620–2629",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.300",
"author": "JM Michot",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "961",
"journal-title": "Ann Oncol",
"key": "2734_CR8",
"unstructured": "Michot JM, Albiges L, Chaput N et al (2020) Tocilizumab, an anti-IL6 receptor antibody, to treat Covid-19-related respiratory failure: a case report. Ann Oncol 31:961–964",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/bloodadvances.2020001907",
"author": "X Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1307",
"journal-title": "Blood Adv",
"key": "2734_CR9",
"unstructured": "Zhang X, Song K, Tong F et al (2020) First case of COVID-19 in a patient with multiple myeloma successfully treated with tocilizumab. Blood Adv 4:1307–1310",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ajh.25855",
"author": "MH Odievre",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Am J Hematol.",
"key": "2734_CR10",
"unstructured": "Odievre MH, de Marcellus C, Le Ducou Pointe H et al (2020) Dramatic improvement after tocilizumab of a severe COVID-19 in a child with sickle cell disease and acute chest syndrome. Am J Hematol. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajh.25855",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"author": "N Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "507",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2734_CR11",
"unstructured": "Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X et al (2020) Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet 395:507–513",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"author": "D Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2734_CR12",
"unstructured": "Wang D, Hu B, Hu C et al (2020) Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan China. JAMA 323:1061–1069",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1335",
"author": "J Lenzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "m1335",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2734_CR13",
"unstructured": "Lenzer J (2020) Covid-19: US gives emergency approval to hydroxychloroquine despite lack of evidence. BMJ 369:m1335",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "2734_CR14",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019(COVID-19) Situation Report-41: Data as Reported by 10AM CET 01 March 2020. Available online at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200301-sitrep-41-covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=6768306d_2."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01708",
"author": "Y Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "2734_CR15",
"unstructured": "Tang Y, Liu J, Zhang D et al (2020) Cytokine storm in COVID-19: the current evidence and treatment strategies. Front Immunol 11:1708",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03130-y",
"author": "M Rieder",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "435",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "2734_CR16",
"unstructured": "Rieder M, Wengenmayer T, Staudacher D et al (2020) Cytokine adsorption in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Crit Care 24:435. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13054-020-03130-y",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "W Tan",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "Jilin J Chin Med",
"key": "2734_CR17",
"unstructured": "Tan W, Li S, Yiyang C et al (2020) Clinical efficacy analysis of 50 cases of corona virus disease 2019 in traditional Chinese medicine. Jilin J Chin Med 40:281–285",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Y Kai-tao",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "Chin J Exp Tradition Med Formul",
"key": "2734_CR18",
"unstructured": "Kai-tao Y, Ming-yu L, Xin L et al (2020) Retrospective clinical analysis on treatment of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia with traditional Chinese medicine Lianhua Qingwen. Chin J Exp Tradition Med Formul 26:8–12",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.07.002",
"author": "L Hou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "123",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Therap",
"key": "2734_CR19",
"unstructured": "Hou L, Huang H (2016) Immune suppressive properties of artemisinin family drugs. Pharmacol Therap 166:123–127",
"volume": "166",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiu396",
"author": "J Mair-Jenkins",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "80",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "2734_CR20",
"unstructured": "Mair-Jenkins J, Saavedra-Campos M, Baillie JK et al (2015) The effectiveness of convalescent plasma and hyperimmune immunoglobulin for the treatment of severe acute respiratory infections of viral etiology: a systematic review and exploratory meta-analysis. J Infect Dis 211:80–90",
"volume": "211",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/519392",
"author": "CB Planitzer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "435",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "2734_CR21",
"unstructured": "Planitzer CB, Modrof J, Kreil TR (2007) West Nile virus neutralization by US plasma-derived immunoglobulin products. J Infect Dis 196:435–440",
"volume": "196",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2019.102375",
"author": "M Rojas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102375",
"journal-title": "J Autoimmun",
"key": "2734_CR22",
"unstructured": "Rojas M, Monsalve DM, Pacheco Y et al (2020) Ebola virus disease: An emerging and re-emerging viral threat. J Autoimmun 106:102375",
"volume": "106",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tracli.2015.12.003",
"author": "O Garraud",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Transfus Clin Biol",
"key": "2734_CR23",
"unstructured": "Garraud O, Heshmati F, Pozzetto B et al (2016) Plasma therapy against infectious pathogens, as of yesterday, today and tomorrow. Transfus Clin Biol 23:39–44",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.10044",
"author": "L Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "460",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2734_CR24",
"unstructured": "Li L, Zhang W, Hu Y et al (2020) Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 324(5):460–470",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.transci.2020.102875",
"author": "H Abolghasemi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102875",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Transfus Apher Sci.",
"key": "2734_CR25",
"unstructured": "Abolghasemi H, Eshghi P, Cheraghali AM et al (2020) Clinical efficacy of convalescent plasma for treatment of COVID-19 infections: results of a multicenter clinical study. Transfus Apher Sci. 59(5):102875",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2004168117",
"author": "K Duan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9490",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "ProcNatl Acad Sci.",
"key": "2734_CR26",
"unstructured": "Duan K, Liu B, Li C et al (2020) Effectiveness of convalescent plasma therapy in severe COVID-19 patients. ProcNatl Acad Sci. 117(17):9490–9496",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.01.20139857",
"author": "A Gharbharan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv.",
"key": "2734_CR27",
"unstructured": "Gharbharan A, Jordans CCE, GeurtsvanKessel C et al (2020) Convalescent plasma for COVID-19. A randomized clinical trial. MedRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.07.01.20139857",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.05.014",
"author": "E Salazar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1680",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Am J Pathol",
"key": "2734_CR28",
"unstructured": "Salazar E, Perez KK, Ashraf M et al (2020) Treatment of COVID-19 patients with convalescent plasma. Am J Pathol 190(8):1680–1690",
"volume": "190",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020006964",
"author": "L Hegerova",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "759",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "2734_CR29",
"unstructured": "Hegerova L, Gooley T, Sweerus KA, Maree CL, Bailey N, Bailey M et al (2020) (2020) Use of convalescent plasma in hospitalized patients with covid-19—case series. Blood 136(6):759–762",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood.2020007079",
"author": "X Xia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "755",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "2734_CR30",
"unstructured": "Xia X, Li K, Wu L et al (2020) Improved clinical symptoms and mortality on severe/critical COVID-19 patients utilizing convalescent plasma transfusion. Blood 136(6):755–759",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "V Piechotta",
"first-page": "013600",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev.",
"key": "2734_CR31",
"unstructured": "Piechotta V, Chai KL, Valk SJ, Doree C, Monsef I, Wood EM et al (2020) Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a living systematic review. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 7(7):013600",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1537-2995.2012.03622.x",
"author": "RJ Benjamin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9S",
"issue": "Suppl. 1",
"journal-title": "Transfusion",
"key": "2734_CR32",
"unstructured": "Benjamin RJ, McLaughlin LS (2012) Plasma components: properties, differences, and uses. Transfusion 52(Suppl. 1):9S-19S",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrneurol.2014.253",
"author": "JD Lunemann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "80",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Neurol",
"key": "2734_CR33",
"unstructured": "Lunemann JD, Nimmerjahn F, Dalakas MC (2015) Intravenous immunoglobulin in neurology–mode of action and clinical efficacy. Nat Rev Neurol 11:80–89",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3939",
"author": "A Agarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2734_CR34",
"unstructured": "Agarwal A, Mukherjee A, Kumar G, Chatterjee P, Bhatnagar T, Malhotra P (2020) Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate covid-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID Trial). BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m3939",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "VA Simonovich",
"first-page": "NEJMoa2031304",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "2734_CR35",
"unstructured": "Simonovich VA, Burgos Pratx LD, Scibona P, Beruto MV, Vallone MG, Vázquez C et al (2020) A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 24:NEJMoa2031304",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "PM Choghakabodi",
"first-page": "415",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Recenti Prog Med",
"key": "2734_CR36",
"unstructured": "Choghakabodi PM, Pouladzadeh M, Haybar H et al (2020) Biological whistleblowers for silent myocardial ischemia: diagnostic and prognostic approach. Recenti Prog Med 111(7):415–425",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.12-2907",
"author": "IFN Hung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "464",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "2734_CR37",
"unstructured": "Hung IFN, Toe KKW, Lee C-K et al (2013) Hyperimmune IV immunoglobulin treatment: a multicenter double-blind randomized controlled trial for patients with severe 2009 influenza A (H1N1) infection. Chest 144(2):464–473",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciq106",
"author": "IF Hung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "447",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2734_CR38",
"unstructured": "Hung IF, To KK, Lee C-K et al (2011) Convalescent plasma treatment reduced mortality in patients with severe pandemic influenza A (H1N1) 2009 virus infection. Clin Infect Dis 52(4):447–456",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2007575",
"author": "Y Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e38",
"issue": "17",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2734_CR39",
"unstructured": "Zhang Y, Xiao M, Zhang S, Xia P, Cao W, Jiang W et al (2020) Coagulopathy and antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 382(17):e38",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109829",
"author": "G Magro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "109829",
"journal-title": "Coagul role Med Hypotheses",
"key": "2734_CR40",
"unstructured": "Magro G (2020) Cytokine storm: is it the only major death factor in COVID-19 patients? Coagul role Med Hypotheses 142:109829",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 40,
"references-count": 40,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s11739-021-02734-8"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Emergency Medicine",
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A randomized clinical trial evaluating the immunomodulatory effect of convalescent plasma on COVID-19-related cytokine storm",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "16"
}