Home pharmacological therapy in early COVID-19 to prevent hospitalization and reduce mortality: Time for a suitable proposal
et al., Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology, doi:10.1111/bcpt.13690, Dec 2021
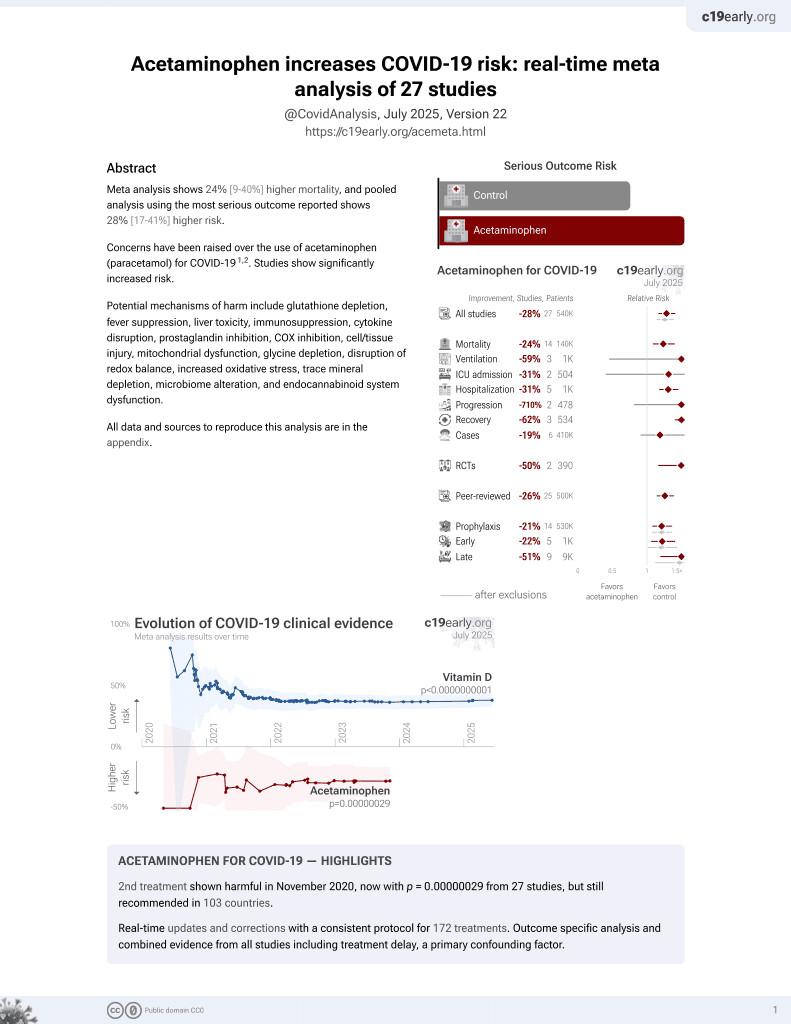
2nd treatment shown to increase risk in
November 2020, now with p = 0.00000029 from 27 studies, but still recommended in 103 countries.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Proposal for early treatment of COVID-19, including a review of potential concerns for treatment with acetaminophen and a recommendation against using acetaminophen.
Acetaminophen is also known as paracetamol, Tylenol, Panadol, Calpol, Tempra, Calprofen, Doliprane, Efferalgan, Grippostad C, Dolo, Acamol, Fevadol, Crocin, and Perfalgan.
1.
Hashemian et al., Management of critically Ill COVID-19 patients: Exploring the potential of morphine and assessing disadvantages of acetaminophen, Caspian Journal of Internal Medicine, doi:10.22088/cjim.16.2.381.
2.
Fazio et al., The Problem of Home Therapy during COVID-19 Pandemic in Italy: Government Guidelines versus Freedom of Cure?, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology Research, 6:2022, www.fortunejournals.com/articles/the-problem-of-home-therapy-during-covid19-pandemic-in-italy-government-guidelines-versus-freedom-of-cure.html.
3.
Pandolfi et al., Home pharmacological therapy in early COVID-19 to prevent hospitalization and reduce mortality: Time for a suitable proposal, Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology, doi:10.1111/bcpt.13690.
Pandolfi et al., 2 Dec 2021, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Contact: salvatore.chirumbolo@univr.it.
Home pharmacological therapy in early COVID‐19 to prevent hospitalization and reduce mortality: Time for a suitable proposal
Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology, doi:10.1111/bcpt.13690
The COVID-19 pandemic is a highly dramatic concern for mankind. In Italy, the pandemic exerted its major impact throughout the period of February to June 2020. To date, the awkward amount of more than 134,000 deaths has been reported. Yet, post-mortem autopsy was performed on a very modest number of patients who died from COVID-19 infection, leading to a first confirmation of an immune-thrombosis of the lungs as the major COVID-19 pathogenesis, likewise for SARS. Since then (June-August 2020), no targeted early therapy considering this pathogenetic issue was approached. The patients treated with early anti-inflammatory, anti-platelet, anticoagulant and antibiotic therapy confirmed that COVID-19 was an endothelial inflammation with immuno-thrombosis. Patients not treated or scarcely treated with the most proper and appropriate therapy and in the earliest, increased the hospitalization rate in the intensive care units and also mortality, due to immunethrombosis from the pulmonary capillary district and alveoli. The disease causes widespread endothelial inflammation, which can induce damage to various organs and systems. Therapy must be targeted in this consideration, and in this review, we demonstrate how early anti-inflammatory therapy may treat endothelia inflammation and immune-thrombosis caused by COVID-19, by using drugs we are going to recommend in this paper.
References
Adiletta, Baglioni, Bettoncelli, Comments on "Preventive home therapy for symptomatic patients affected by COVID-19 and followed by teleconsultations, Multidiscip Respir Med
Akhter, Quéromès, Pillai, The combination of bromelain and acetylcysteine (BromAc) synergistically inactivates SARS-CoV-2, Viruses
Albasheer, Almutairi, Almalki, Malaka, Massive arterial cerebral thrombosis in a 59-year old female patient with severe COVID-19, Cureus
Alesci, Aragona, Cicero, Lauriano, Can nutraceuticals assist treatment and improve covid-19 symptoms?, Nat Prod Res
Alkotaji, Al-Zidan, Indomethacin: can it counteract bradykinin effects in COVID-19 patients?, Curr Pharmacol Rep
Amato, Acanfora, Paoli, Amato, Preventive home therapy for symptomatic patients affected by COVID-19 and followed by teleconsultations, Multidiscip Respir Med
Amici, Caro, Ciucci, Indomethacin has a potent antiviral activity against SARS coronavirus, Antivir Ther
Atefi, Behrangi, Mozafarpoor, Seirafianpour, Peighambari et al., N-acetylcysteine and coronavirus disease 2019: may it work as a beneficial preventive and adjuvant therapy? A comprehensive review study, J Res Med Sci
Badmann, Langsch, Keogh, Brunner, Kaufmann et al., TRAIL enhances paracetamol-induced liver sinusoidal endothelial cell death in a Bim-and Bid-dependent manner, Cell Death Dis
Baghaki, Yalcin, Baghaki, Aydin, Daghan et al., COX2 inhibition in the treatment of COVID-19: review of literature to propose repositioning of celecoxib for randomized controlled studies, Int J Infect Dis
Bahrami, Daryani, Haghpanah, Effects of indomethacin on viral replication markers in asymptomatic carriers of hepatitis B: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, Am J Gastroenterol
Ball, Vijayan, Nguyen, Glutathione regulates integrin alpha (IIb)beta(3)-mediated cell adhesion under flow conditions, Thromb Haemost
Bartolini, Stabile, Bastianelli, SARS-CoV2 infection impairs the metabolism and redox function of cellular glutathione, Redox Biol
Bonaventura, Vecchié, Dagna, Endothelial dysfunction and immunothrombosis as key pathogenic mechanisms in COVID-19, Nat Rev Immunol
Campbell, Boilard, Rondina, Is there a role for the ACE2 receptor in SARS-CoV-2 interactions with platelets?, J Thromb Haemost
Cazzola, De Novellis, Bianco, Rogliani, Matera, Disputes over the production and dissemination of misinformation in the time of COVID-19, Respir Med
Chakraborty, Khan, Banerjee, Ray, Sinha, Inhibition of human blood platelet aggregation and the stimulation of nitric oxide synthesis by aspirin, Platelets
Chen, Alfajaro, Chow, Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs dampen the cytokine and antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 infection, J Virol
Chen, Alfajaro, Wei, Chow, Filler et al., Cyclooxgenase-2 is induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection but does not affect viral entry or replication, doi:10.1101/2020.09.24.312769
Chirumbolo, Nutraceuticals and dietary supplements should not be used to treat COVID-19 as pharmaceuticals, Nutrition
Chirumbolo, Simonetti, Franzini, Valdenassi, Bertossi et al., Estimating coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-caused deaths in hospitals and healthcare units: do hospital-acquired infections play a role? Comments with a proposal, Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol Mar
Chirumbolo, Valdenassi, Simonetti, Insights on the mechanisms of action of ozone in the medical therapy against COVID-19, Int Immunopharmacol
Cipolloni, Sessa, Bertozzi, Preliminary postmortem COVID-19 evidence of endothelial injury and factor VIII hyperexpression, Diagnostics
Cochener, Kling, Floch, Indométhacine (Indocollyre) versus Diclofénac (Voltarène) sur la douleur post-photoablation excimer de surface [Indomethacin (indocollyre) versus diclofenac (voltarene) for the control of pain following excimer photoablation
Consolaro, Suter, Rubis, Nurse, Pedroni et al., A hometreatment algorithmbased on anti-inflammatory drugs to prevcent hospitalization of patients with early COVID-19. A matched-cohort study (COVER 2), MedRXiv, doi:10.1101/2021.09.29.21264298
Cui, Chen, Ke, Reply to "Ibuprofen and thromboembolism in SARS-COV2, J Thromb Haemost
Czervionke, Smith, Fry, Hoak, Haycraft, Inhibition of prostacyclin by treatment of endothelium with aspirin. Correlation with platelet adherence, J Clin Invest
Dapino, Ottonello, Dallegri, The anti-inflammatory drug nimesulide inhibits neutrophil adherence to and migration across monolayers of cytokine-activated endothelial cells, Respiration
De La Cruz, Reyes, Ruiz-Moreno, Lopez-Villodres, Jebrouni et al., Differences in the in vitro antiplatelet effect of dexibuprofen, ibuprofen, and flurbiprofen in human blood, Anesth Analg
Deshotels, Xia, Sriramula, Lazartigues, Filipeanu, Angiotensin II mediates angiotensin converting enzyme type 2 internalization and degradation through an angiotensin II type I receptor-dependent mechanism, Hyper
Di Micco, Tufano, Cardillo, The impact of riskadjusted heparin regimens on the outcome of patients with COVID-19 Infection. A prospective cohort study, Viruses
Diener, Schneider, Aicher, Per-capita consumption of analgesics: a nine-country survey over 20 years, J Headache Pain
Dimova, Hoet, Dinsdale, Nemery, Acetaminophen decreases intracellular glutathione levels and modulates cytokine production in human alveolar macrophages and type II pneumocytes in vitro, Int J Biochem Cell Biol
Donno, Grattagliano, Rossi, How to treat COVID-19 patients at home in the Italian context: an expert opinion, Infect Dis Rep
Duong, Gulmez, Salvo, Usage patterns of paracetamol in France, Br J Clin Pharmacol
Egeberg, The effect of unspecific fever induction on the blood clotting system, Scand J Clin Lab Invest
Ekim, Sekeroglu, Balahoroglu, Ozkol, Ekim, Roles of the oxidative stress and ADMA in the development of deep venous thrombosis, Biochem Res Int
Elezkurtaj, Greuel, Ihlow, Causes of death and comorbidities in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Sci Rep
Erlich, Talmor, Cartin-Ceba, Gajic, Kor, Prehospitalization antiplatelet therapy is associated with a reduced incidence of acute lung injury: a population-based cohort study, Chest
Esba, Alqahtani, Thomas, Shamas, Alswaidan et al., Ibuprofen and NSAID use in COVID-19 infected patients is not associated with worse outcomes: a prospective cohort study, Infect Dis Ther
Espinosa-Díez, Miguel, Vallejo, Role of glutathione biosynthesis in endothelial dysfunction and fibrosis, Redox Biol
Essex, Li, Feinman, Miller, Platelet surface glutathione reductase-like activity, Blood
Essex, Li, Redox control of platelet aggregation, Biochemistry
Flora, Balansky, Maestra, Rationale for the use of N-acetylcysteine in both prevention and adjuvant therapy of COVID-19, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.202001807
Franco, Lillo, Rivas-Santisteban, Functional complexes of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and reninangiotensin system receptors: expression in adult but not fetal lung tissue, Int J Mol Sci
Franzini, Valdenassi, Ricevuti, Oxygen-ozone (O 2 -O 3 ) immunoceutical therapy for patients with COVID-19. Preliminary evidence reported, Int Immunopharmacol
Galati, Zanotta, Capitelli, Bocchino, A bird's eye view on the role of dendritic cells in SARS-CoV-2 infection: perspectives for immune-based vaccines, Allergy, doi:10.1111/all.15004
Galliard-Grigioni, Fehr, Reinhart, Influence of combinations of acetylsalicylic acid, acetaminophen, and diclofenac on platelet aggregation, Eur J Pharmacol
García-Alvarez, Vigil, Guidelines for clinical management of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Gac Med Mex
García-Lee, Alez-Avila, A proposal for the management of COVID-19-induced coagulopathy in adults, Gac Med Mex
Geddes, The fever paradox, New Sci, doi:10.1016/S0262-4079(20)30731-4
Gorudko, Shamova, Shishlo, Glutathionedependent regulation of platelet aggregation with neutrophils and tumor cells, Biofizika
Grosser, The pharmacology of selective inhibition of COX-2, Thromb Haemost
Grèen, Drvota, Vesterqvist, Pronounced reduction of in vivo prostacyclin synthesis in humans by acetaminophen (paracetamol), Prostaglandins
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Gurbel, Bliden, Zhu, Thromboxane inhibition during concurrent therapy with low-dose aspirin and over-thecounter naproxen sodium, J Thromb Thrombolysis
Hall, Mfone, Shallcross, Pathak, Review of pharmacotherapy trialed for management of the coronavirus disease-19, Eur J Med
Hamilos, Petousis, Parthenakis, Interaction between platelets and endothelium: from pathophysiology to new therapeutic options, Cardiovasc Diagn Ther
Hashemi, Kyani, Bathaie, The in silico mechanism of hVKOR interaction with acetaminophen and its metabolite, as well as N-acetyl cysteine: caution on application in COVID-19 patients, J Biomol Struct Dyn, doi:10.1080/07391102.2021.1910570
Hernugrahanto, Utomo, Hariman, Thromboembolic involvement and its possible pathogenesis in COVID-19 mortality: lesson from post-mortem reports, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Hinz, Cheremina, Brune, Acetaminophen (paracetamol) is a selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor in man, FASEB j
Hitzing, Böttcher, Laube, Metabolische azidose unter paracetamol-eine ungewöhnliche Nebenwirkung [Metabolic acidosis under acetaminophen intake-an unordinary side effect
Ho, Zheng, Wu, Perspective adjunctive therapies for COVID-19: beyond antiviral therapy, Int J Med Sci
Hodgman, Garrard, A review of acetaminophen poisoning, Crit Care Clin
Huang, Wang, Tan, Liu, Ni, High-dose vitamin C intravenous infusion in the treatment of patients with COVID-19: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis, Medicine
Ikeda, The effect of ibuprofen on platelet function in vivo, Keio J Med
Irani, Borchert, Craven, Gibbons, Flucloxacillin and paracetamol induced pyroglutamic acidosis, BMJ Case Rep
Jamerson, Haryadi, The use of ibuprofen to treat fever in COVID-19: a possible indirect association with worse outcome?, Med Hypotheses
Kandeil, Mostafa, Kutkat, Bioactive polyphenolic compounds showing strong antiviral activities against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, Pathogens
Kashiwagi, Shiota, Yokomizo, Inokuchi, Uchiumi et al., EP2 signaling mediates suppressive effects of celecoxib on androgen receptor expression and cell proliferation in prostate cancer, Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis
Keaveney, Peters, Way, Effects of acetaminophen on risk taking, Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci
Kelleni, Early use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in COVID-19 might reverse pathogenesis, prevent complications and improve clinical outcomes, Biomed Pharmacother
Kelleni, NSAIDs/nitazoxanide/azithromycin immunomodulatory protocol used in adult, geriatric, pediatric, pregnant, and immunocompromised COVID-19 patients: a realworld experience, Canad J Medicine
Kelleni, NSAIDs/nitazoxanide/azithromycin repurposed for COVID-19: potential mitigation of the cytokine storm interleukin-6 amplifier via immunomodulatory effects, Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther Jun
Khanfar, Qaroot, Could glutathione depletion be the Trojan horse of COVID-19 mortality?, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Knox, Lee, Moon, Cohen, Pain manifestations of COVID-19 and their association with mortality: a multicenter prospective observational study, Mayo Clin Proc
Kohlstedt, Brandes, Müller-Esterl, Busse, Fleming, Angiotensin-converting enzyme is involved in outside-in signaling in endothelial cells, Circ Res
Kohlstedt, Busse, Fleming, Signaling via the angiotensin-converting enzyme enhances the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in endothelial cells, Hypertension
Kow, Hasan, Use of low-molecular-weight heparin in COVID-19 patients, J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord
Kozer, Evans, Barr, Glutathione, glutathionedependent enzymes and antioxidant status in erythrocytes from children treated with high-dose paracetamol, Br J Clin Pharmacol
Kumar, Singh, Kumari, Identification of multipotent drugs for COVID-19 therapeutics with the evaluation of their SARS-CoV2 inhibitory activity, Comput Struct Biotechnol J
Kutti Sridharan, Kotagiri, Chandiramani, COVID-19 and avoiding ibuprofen. How good is the evidence?, Am J Ther
Lechien, Chiesa-Estomba, Place, Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of 1420 European patients with mild-to-moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J Intern Med
Liu, Huang, Li, Effect of low-dose aspirin on mortality and viral duration of the hospitalized adults with COVID-19, Medicine
Lu, Zhang, Du, SARS-CoV-2 infection in children, N Engl J Med
Malikiwi, Roufaeil, Tan, Sehgal, Indomethacin vs ibuprofen: comparison of efficacy in the setting of conservative therapeutic approach, Eur J Pediatr
Martha, Pranata, Lim, Wibowo, Akbar, Active prescription of low-dose aspirin during or prior to hospitalization and mortality in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of adjusted effect estimates, Int J Infect Dis
Martini, Rodriguez, Deguzman, Dose responses of ibuprofen in vitro on platelet aggregation and coagulation in human and pig blood samples, Mil Med
Mcintyre, Philp, Inwood, Effect of ibuprofen on platelet function in normal subjects and hemophiliac patients, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Mehta, Mazer-Amirshahi, Alkindi, Pourmand, Pharmacotherapy in COVID-19; a narrative review for emergency providers, Am J Emerg Med
Mendoza, Heard, Dart, Coma, metabolic acidosis and normal liver function in a child with a large serum acetaminophen level, Ann Emerg Med
Minich, Brown, A review of dietary (phyto)nutrients for glutathione support, Nutrients
Mitchell, Lucas, Vojnovic, Hasan, Pepper et al., Stronger inhibition by nonsteroid antiinflammatory drugs of cyclooxygenase-1 in endothelial cells than platelets offers an explanation for increased risk of thrombotic events, FASEB J
Moore, Carleton, Blin, Bosco-Levy, Droz, Does ibuprofen worsen COVID-19?, Drug Saf
Moore, No arguments for extra risk from ibuprofen in SARS-COV2 infection, Therapie. 2020b
Morthorst, Erlangsen, Nordentoft, Hawton, Hoegberg et al., Availability of paracetamol sold over the counter in Europe: a descriptive cross-sectional international survey of pack size restriction, Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol
Munsterhjelm, Munsterhjelm, Niemi, Ylikorkala, Neuvonen et al., Dose-dependent inhibition of platelet function by acetaminophen in healthy volunteers, Anesthesiology
Munsterhjelm, Niemi, Ylikorkala, Silvanto, Rosenberg, Characterization of inhibition of platelet function by paracetamol and its interaction with diclofenac in vitro, Acta Anaesthesiol Scand
Napolitano, Gambardella, Carrella, Gao, Di Bernardo, Computational drug repositioning and elucidation of mechanism of action of compounds against SARS-COV-2
O'brien, Krammer, Leary, Mastrogiannis, The effect of acetaminophen on prostacyclin production in pregnant women, Am J Obstet Gynecol
O'keefe, Newsom, Taylor, A survey of providerreported use and perceived effectiveness of medications for symptom management in telemedicine and outpatient visits for mild COVID-19, Infect Dis Ther
Ortiz-Prado, Fernandez-Naranjo, Torres-Berru, Lowe, Torres, Exceptional prices of medical and other supplies during the COVID-19 pandemic in Ecuador, Am J Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.4269/ajtmh.21-0221
Osborne, Veigulis, Arreola, Mahajan, Röösli et al., Association of mortality and aspirin prescription for COVID-19 patients at the Veterans Health Administration, PLoS ONE
Pan, Ip, Zhan, Pre-hospital antiplatelet medication use on COVID-19 disease severity, Heart Lung
Pandolfi, Chirumbolo, Home therapy of COVID-19 at the earliest may greatly prevent hospitalization, Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol, doi:10.1111/bcpt.13650
Pandolfi, Simonetti, Ricevuti, Chirumbolo, Paracetamol in the home treatment of early COVID-19 symptoms: a possible foe rather than a friend for elderly patients?, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27158
Parks, Hoak, Czervionke, Comparative effect of ibuprofen on endothelial and platelet prostaglandin synthesis, J Pharmacol Exp Ther
Peluso, Abella, Ferrer, Kucher, Sunde et al., Fever management in COVID-19 patients, Minerva Anestesiol
Pergolizzi, Varrassi, Magnusson, COVID-19 and NSAIDS: a narrative review of knowns and unknowns, Pain Ther
Pierro, Iqtadar, Khan, Potential clinical benefits of quercetin in the early stage of covid-19: results of a second, pilot, randomized, controlled and open-label clinical trial, Int J Gen Med
Poe, Corn, N-Acetylcysteine: a potential therapeutic agent for SARS-CoV-2, Med Hypotheses
Polonikov, Endogenous deficiency of glutathione as the most likely cause of serious manifestations and death in COVID-19 patients, ACS Infect Dis
Poutoglidou, Saitis, Kouvelas, Ibuprofen and COVID-19 disease: separating the myths from facts, Expert Rev Respir Med
Prasher, Sharma, Gunupuru, Targeting cyclooxygenase enzyme for the adjuvant COVID-19 therapy, Drug Dev Res
Rad, Vardanyan, Tas, Ibuprofen and thromboembolism in SARS-COV2, J Thromb Haemost
Raghav, Kamboj, Singh, Effect of some steroidal & non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on purified goat brain cathepsin L, Indian J Med Res
Ravichandran, Purna, Vijayaragavan, Kalavakollu, Gaidhane et al., Efficacy and safety of indomethacin in COVID-19 patients, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.12.14.20245266
Reese, Coleman, Chan, Blau, Callahan et al., Cyclooxygenase inhibitor use is associated with increased COVID-19 severity
Reynolds, Enquist, Biological interactions between herpesviruses and cyclooxygenase enzymes, Rev Med Virol
Robertson, Sauer, Gold, Nonas, The role of cyclooxygenase-2 in mechanical ventilation-induced lung injury, Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol
Rodríguez-Morales, Cardona-Ospina, Murillo-Muñoz, Gastroenterologists, hepatologists, COVID-19 and the use of acetaminophen, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol
Romano, Galante, Figueira, Mendes, Rodrigues, Time-trend analysis of medicine sales and shortages during COVID-19 outbreak: data from community pharmacies, Res Social Adm Pharm
Rousar, Pařík, Kucera, Bartos, Červinkov A Z, Glutathione reductase is inhibited by acetaminophen-glutathione conjugate in vitro, Physiol Res
Russell, Moss, George, Associations between immune-suppressive and stimulating drugs and novel COVID-19-a systematic review of current evidence, Ecancermedicalscience
Rybka, Kupczyk, Kędziora-Kornatowska, Glutathione-related antioxidant defense system in elderly patients treated for hypertension, Cardiovasc Toxicol
Sahai, Bhandari, Koupenova, Freedman, Godwin et al., SARS-CoV-2 receptors are expressed on human platelets and the effect of aspirin on clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients, Res Sq
Santos, Sampaio, Alzamora, The ACE2/angiotensin-(1-7)/MAS axis of the renin-angiotensin system: focus on angiotensin-(1-7), Physiol Rev
Scalise, Indiveri, Repurposing nimesulide, a potent inhibitor of the B0AT1 subunit of the SARS-CoV-2 receptor, as a therapeutic adjuvant of COVID-19, SLAS Discov
Schildknecht, Daiber, Ghisla, Cohen, Bachschmid, Acetaminophen inhibits prostanoid synthesis by scavenging the PGHS-activator peroxynitrite, FASEB J
Schmelzle, Splith, Andersen, Increased plasma levels of microparticles expressing CD39 and CD133 in acute liver injury, Transplantation
Schröer, Shenk, Inhibition of cyclooxygenase activity blocks cell-to-cell spread of human cytomegalovirus, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Schwartz, Musser, Tanaka, Inhibition of prostacyclin and thromboxane biosynthesis in healthy volunteers by single and multiple doses of acetaminophen and indomethacin, Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev
Semeraro, Colucci, The prothrombotic state associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection: pathophysiological aspects, Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis
Sepehrinezhad, Gorji, Negah, SARS-CoV-2 may trigger inflammasome and pyroptosis in the central nervous system: a mechanistic view of neurotropism, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-021-00845-4
Shader, Acetaminophen (paracetamol), COVID-19, and misleading conclusions: a commentary, J Clin Psychopharmacol
Sharif-Askari, Sharif-Askari, Mdkhana, Effect of common medications on the expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptors in liver tissue, Arch Toxicol
Shen, Zhang, Fang, SARS-CoV-2 interacts with platelets and megakaryocytes via ACE2-independent mechanism, J Hematol Oncol
Shi, Puyo, N-acetylcysteine to combat COVID-19: an evidence review, Ther Clin Risk Manag
Simões E Silva, Silveira, Ferreira, Teixeira, ACE2, angiotensin-(1-7) and Mas receptor axis in inflammation and fibrosis, Br J Pharmacol
Srivastava, Kumar, Use of aspirin in reduction of mortality of COVID-19 patients: a metanalysis, Int J Clin Pract
Steiner, Should we let fever run its course in the early stages of COVID-19?, J R Soc Med
Sun, Zhang, Li, Therapeutic mechanisms of ibuprofen, prednisone and betamethasone in osteoarthritis, Mol Med Rep
Suter, Consolaro, Pedroni, A simple, home-therapy algorithm to prevent hospitalisation for COVID-19 patients: A retrospective observational matched-cohort study, EClinicalMedicine
Taher, Lashgari, Sedighi, Rahimi-Bashar, Poorolajal et al., A pilot study on intravenous N-Acetylcysteine treatment in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome, Pharmacol Rep, doi:10.1007/s43440-021-00296-2
Terrier, Dilly, Pizzorno, Antiviral properties of the NSAID drug naproxen targeting the nucleoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus, Molecules
Valenzuela, Pedrosa, Garrido-Gil, Interactions between ibuprofen, ACE2, renin-angiotensin system, and spike protein in the lung. Implications for COVID-19, Clin Transl Med
Violi, Cammisotto, Pignatelli, Thrombosis in Covid-19 and non-Covid-19 pneumonia: role of platelets, Platelets, doi:10.1080/09537104.2021.1936478
Wastesson, Martikainen, Zoëga, Schmidt, Karlstad et al., Trends in use of paracetamol in the Nordic countries, Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol
Wessels, Hempel, Ibuprofen protects human endothelial cell prostaglandin H synthase from hydrogen peroxide, Am J Physiol
White, Faich, Whelton, Comparison of thromboembolic events in patients treated with celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 specific inhibitor, versus ibuprofen or diclofenac, Am J Cardiol
Williams, Langley, Osei-Hwediah, Wendon, Hughes, Hyaluronic acid and endothelial damage due to paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity, Liver Int
Wrotek, Soboci Nska, Kozłowski, Pawlikowska, Jędrzejewski et al., New insights into the role of glutathione in the mechanism of fever, Int J Mol Sci
Xu, Gao, Wu, Selinger, Zhou, Indomethacin has a potent antiviral activity against SARS-COV-2 in vitro and canine coronavirus in vivo, BioRXiv, doi:10.1101/2020.04.01.017624
Xu, Sriramula, Xia, Clinical relevance and role of neuronal AT 1 receptors in ADAM17-mediated ACE2 shedding in neurogenic hypertension, Circ Res
Yang, Xie, Tu, Fu, Xu et al., The signal pathways and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19. Signal Transduct, Target Ther
Yousefifard, Zali, Zarghi, Madani Neishaboori, Hosseini et al., Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in management of COVID-19; a systematic review on current evidence, Int J Clin Pract
Zahran, El-Badawy, Mahran, Mahran, Rayan, Circulating microparticles and activated platelets as novel prognostic biomarkers in COVID-19; relation to cancer, PLoS ONE
Zhang, Guo, Kim, SARS-CoV-2 hijacks folate and one-carbon metabolism for viral replication, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21903-z
Zhang, Huang, Ding, Tao, Platelet-driven coagulopathy in COVID-19 patients: in comparison to seasonal influenza cases, Exp Hematol Oncol
Zhang, Qi, Zhou, Upregulation of Nrf-2 attenuates oxidative complement activation-associated endothelial injury and apoptosis in transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy, Transplant Cell Ther
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcpt.13690",
"ISSN": [
"1742-7835",
"1742-7843"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.13690",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/bcpt.13690"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "High School of Oxygen Ozone Therapy University of Pavia Pavia Italy"
},
{
"name": "Unit of Neurosurgery Villa Mafalda Health Clinics Rome Italy"
}
],
"family": "Pandolfi",
"given": "Sergio",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1789-8307",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neurosciences, Biomedicine and Movement Sciences University of Verona Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chirumbolo",
"given": "Salvatore",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3422-2747",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Drug Science University of Pavia Pavia Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ricevuti",
"given": "Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "High School of Oxygen Ozone Therapy University of Pavia Pavia Italy"
}
],
"family": "Valdenassi",
"given": "Luigi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Direction Board Council for Nutritional an Environmental Medicine (CONEM) Mo i Rana Norway"
}
],
"family": "Bjørklund",
"given": "Geir",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "CONEM Ukraine Life Science Research Group Danylo Halytsky Lviv National Medical University Lviv Ukraine"
}
],
"family": "Lysiuk",
"given": "Roman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine Ovidius University Constanta Romania"
}
],
"family": "Doşa",
"given": "Monica Daniela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "CONEM Ukraine Pharmacognosy and Natural Product Chemistry Research Group National University of Pharmacy Kharkiv Ukraine"
}
],
"family": "Lenchyk",
"given": "Larysa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine University of Naples Federico II Naples Italy"
}
],
"family": "Fazio",
"given": "Serafino",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology",
"container-title-short": "Basic Clin Pharma Tox",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-23T05:50:37Z",
"timestamp": 1637646637000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-20T10:21:49Z",
"timestamp": 1650450109000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-26T15:52:38Z",
"timestamp": 1661529158937
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 4,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
2
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638403200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-02T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1638403200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/bcpt.13690",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1111/bcpt.13690",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/bcpt.13690",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "225-239",
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
2
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Preventive home therapy for symptomatic patients affected by COVID‐19 and followed by teleconsultations",
"author": "D'Amato G",
"first-page": "748",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Multidiscip Respir Med",
"key": "e_1_2_8_2_1",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Comments on “Preventive home therapy for symptomatic patients affected by COVID‐19 and followed by teleconsultations” by D'Amato et al",
"author": "Adiletta G",
"first-page": "757",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Multidiscip Respir Med",
"key": "e_1_2_8_3_1",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2021.106380",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/idr13010028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-021-00536-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_6_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Massive arterial cerebral thrombosis in a 59‐year old female patient with severe COVID‐19",
"author": "Albasheer OB",
"first-page": "e15553",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cureus",
"key": "e_1_2_8_7_1",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "A proposal for the management of COVID‐19‐induced coagulopathy in adults",
"author": "Ignacio‐Ibarra G",
"first-page": "201",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Gac Med Mex",
"key": "e_1_2_8_8_1",
"volume": "157",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4084/MJHID.2021.045",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcpt.13650",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.15004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-021-00845-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00679-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/diagnostics10080575",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000025876",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_15_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Thromboembolic involvement and its possible pathogenesis in COVID‐19 mortality: lesson from post‐mortem reports",
"author": "Dwiputra Hernugrahanto K",
"first-page": "1670",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "e_1_2_8_16_1",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-82862-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27158",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_18_1"
},
{
"article-title": "The in silico mechanism of hVKOR interaction with acetaminophen and its metabolite, as well as N‐acetyl cysteine: caution on application in COVID‐19 patients",
"author": "Hashemi SA",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Biomol Struct Dyn Apr",
"key": "e_1_2_8_19_1",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100941",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_20_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_8_21_1",
"unstructured": "ReeseJT ColemanB ChanL BlauH CallahanTJ CappellettiL FontanaT BradwellKR HarrisNL CasiraghiE ValentiniG KarlebachG DeerR McMurryJA HaendelMA ChuteCG PfaffE MoffittR SprattH SinghJ MungallCJ WilliamsAE RobinsonPN.Cyclooxygenase inhibitor use is associated with increased COVID‐19 severity.2021medRxiv [Preprint]. Apr 20:2021.04.13.21255438."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcpt.13003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcpt.12959",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sapharm.2020.05.024",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2005073",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13089",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.12957",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10194-008-0046-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/JCP.0000000000001345",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/scan/nsaa108",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2020.04.025",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.23736/S0375-9393.20.15195-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1165/rcmb.2011-0005OC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bcr-2020-237536",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/a-0636-2595",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annemergmed.2006.06.045",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0141076820951544",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ccc.2012.07.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.21-0221",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-021-00432-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.13557",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.12.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1034/j.1600-0676.2003.00808.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cddis.2012.185",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_45_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Could glutathione depletion be the Trojan horse of COVID‐19 mortality?",
"author": "Khanfar A",
"first-page": "12500",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "e_1_2_8_46_1",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2017.08.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_47_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21041393",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_48_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biocel.2005.03.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_49_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0262-4079(20)30731-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_50_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/00365516209051265",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_51_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40164-021-00228-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_52_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.15156",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_53_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13045-021-01082-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_54_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.10-0891",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_55_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00000542-200510000-00009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_56_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1399-6576.2005.00707.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_57_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.07.036",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_58_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.07-8506com",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_59_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/cdt.2018.07.01",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_60_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-119031/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_8_61_1",
"unstructured": "SahaiA BhandariR KoupenovaM FreedmanJ GodwinM McIntyreT ChungM IskandarJP KamranH AggarwalA KalraA BartholomewJ McCraeK ElbadawiA SvenssonL KapadiaS HaririE CameronS.SARS‐CoV‐2 receptors are expressed on human platelets and the effect of aspirin on clinical outcomes in COVID‐19 patients.2020Res Sq [Preprint]. Dec 23:rs.3.rs‐119031"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0090-6980(89)90001-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_62_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0002-9378(93)90362-M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_63_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpdd.194",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_64_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.06-8015com",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_65_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/TP.0b013e318278d3cd",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_66_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0246806",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_67_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI109379",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_68_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Comparative effect of ibuprofen on endothelial and platelet prostaglandin synthesis",
"author": "Parks WM",
"first-page": "415",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Pharmacol Exp Ther",
"key": "e_1_2_8_69_1",
"volume": "219",
"year": "1981"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpcell.1996.271.6.C1879",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_70_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Glutathione‐dependent regulation of platelet aggregation with neutrophils and tumor cells",
"author": "Gorudko IV",
"first-page": "93",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biofizika",
"key": "e_1_2_8_71_1",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/bi0205045",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_72_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2004-03-1097",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_73_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1160/TH08-02-0095",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_74_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2125.2003.01723.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_75_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/703128",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_76_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12012-010-9096-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_77_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2021.102041",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_78_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00288",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_79_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-21903-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_80_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.33549/physiolres.931744",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_81_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt1978245616",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_82_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2302/kjm.26.213",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_83_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181f7b679",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_84_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/095371032000158763",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_85_1"
},
{
"article-title": "NSAIDs/nitazoxanide/azithromycin repurposed for COVID‐19: potential mitigation of the cytokine storm interleukin‐6 amplifier via immunomodulatory effects",
"author": "Kelleni MT",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther Jun",
"key": "e_1_2_8_86_1",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ctm2.371",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_87_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40264-020-00953-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_88_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109880",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_89_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.06-6615com",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_90_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MJT.0000000000001196",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_91_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40122-020-00173-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_92_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-020-00363-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_93_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/17476348.2021.1951239",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_94_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.12159",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_95_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00023.2016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_96_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21249602",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_97_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.114.03743",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_98_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.310509",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_99_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/pcan.2013.53",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_100_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00204-020-02869-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_101_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.09.24.312769",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_8_102_1",
"unstructured": "ChenJS AlfajaroMM WeiJ ChowRD FillerRB EisenbarthSC WilenCB.Cyclooxgenase‐2 is induced by SARS‐CoV‐2 infection but does not affect viral entry or replication.2020bioRxiv [Preprint]. Sep 25:2020.09.24.312769.https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.09.24.312769"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.RES.0000107195.13573.E4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_103_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.HYP.0000150159.48992.11",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_104_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7205/MILMED-D-15-00381",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_105_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0002-9149(01)02265-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_106_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14901",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_107_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14934",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_108_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.therap.2020.07.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_109_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules26092593",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_110_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11239-017-1593-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_111_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2472555220934421",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_112_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.csbj.2021.04.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_113_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/135965350601100803",
"article-title": "Indomethacin has a potent antiviral activity against SARS coronavirus",
"author": "Amici C",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1021",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Antivir Ther",
"key": "e_1_2_8_114_1",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.519",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_115_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0810740105",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_116_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1572-0241.2005.41144.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_117_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_8_118_1",
"unstructured": "NapolitanoF GambardellaG CarrellaD GaoX diBernardoD.Computational drug repositioning and elucidation of mechanism of action of compounds against SARS‐COV‐2.2020.https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.07697v2"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of some steroidal & non‐steroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs on purified goat brain cathepsin L",
"author": "Raghav N",
"first-page": "188",
"journal-title": "Indian J Med Res",
"key": "e_1_2_8_119_1",
"volume": "98",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.01.017624",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_8_120_1",
"unstructured": "XuT GaoX WuZ SelingerDW ZhouZ.Indomethacin has a potent antiviral activity against SARS‐COV‐2 in vitro and canine coronavirus in vivo. BioRXiv (preprint) April2020https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.01.017624"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3332/ecancer.2020.1022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_121_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Indomethacin: can it counteract bradykinin effects in COVID‐19 patients?",
"author": "Alkotaji M",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Curr Pharmacol Rep",
"key": "e_1_2_8_122_1",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Indométhacine (Indocollyre) versus Diclofénac (Voltarène) sur la douleur post‐photoablation excimer de surface [Indomethacin (indocollyre) versus diclofenac (voltarene) for the control of pain following excimer photoablation]",
"author": "Cochener B",
"first-page": "555",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Fr Ophtalmol",
"key": "e_1_2_8_123_1",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ddr.21794",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_124_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00431-014-2441-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_125_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110982",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_126_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00014-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_127_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.12.14.20245266",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_8_128_1",
"unstructured": "RavichandranR PurnaP VijayaragavanS KalavakolluRT GaidhaneS KumarRK.Efficacy and safety of indomethacin in COVID‐19 patients.2020. medRxiv 12.14.20245266.https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.14.20245266"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajem.2020.04.035",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_129_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2016.6068",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_130_1"
},
{
"article-title": "The pharmacology of selective inhibition of COX‐2",
"author": "Grosser T",
"first-page": "393",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Thromb Haemost",
"key": "e_1_2_8_131_1",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000196365",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_132_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.1466",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_133_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Guidelines for clinical management of SARS‐CoV‐2 infection",
"author": "García‐Álvarez JL",
"first-page": "576",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Gac Med Mex",
"key": "e_1_2_8_134_1",
"volume": "156",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13030425",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_135_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000024544",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_136_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0246825",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_137_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.05.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_138_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Use of aspirin in reduction of mortality of COVID‐19 patients: a metanalysis",
"author": "Srivastava R",
"first-page": "e14515",
"journal-title": "Int J Clin Pract",
"key": "e_1_2_8_139_1",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Thrombosis in Covid‐19 and non‐Covid‐19 pneumonia: role of platelets",
"author": "Violi F",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Platelets",
"key": "e_1_2_8_140_1",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.hrtlng.2021.04.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_141_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2021.111494",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_142_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11092073",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_143_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Review of pharmacotherapy trialed for management of the coronavirus disease‐19",
"author": "Hall K",
"first-page": "137",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Eur J Med",
"key": "e_1_2_8_144_1",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107777",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_145_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106879",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_146_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/IJGM.S318949",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_147_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens10060758",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_148_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14786419.2021.1914032",
"article-title": "Can nutraceuticals assist treatment and improve covid‐19 symptoms?",
"author": "Alesci A",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Prod Res",
"key": "e_1_2_8_149_1",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijms.51935",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_150_1"
},
{
"article-title": "A pilot study on intravenous N‐Acetylcysteine treatment in patients with mild‐to‐moderate COVID19‐associated acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "Taher A",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep",
"key": "e_1_2_8_151_1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/TCRM.S273700",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_152_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.202001807",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_153_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109862",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_154_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Upregulation of Nrf‐2 attenuates oxidative stress‐induced complement activation‐associated endothelial injury and apoptosis in transplant‐associated thrombotic microangiopathy",
"author": "Zhang R",
"first-page": "01002",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "Transplant Cell Ther",
"key": "e_1_2_8_155_1",
"volume": "2666",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/jrms.JRMS_777_20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_156_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.09.29.21264298",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "e_1_2_8_157_1",
"unstructured": "ConsolaroE SuterF RubisN NurseR PedroniS MoroniC PastòE PaganiniMV PravettoniG CantarelliU PericoN PernaA PeracchiTS RuggenentiP RemuzziG.A home‐treatment algorithmbased on anti‐inflammatory drugs to prevcent hospitalization of patients with early COVID‐19. A matched‐cohort study (COVER 2). MedRXiv Oct 12021.https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.09.29.21264298"
},
{
"article-title": "NSAIDs/nitazoxanide/azithromycin immunomodulatory protocol used in adult, geriatric, pediatric, pregnant, and immunocompromised COVID‐19 patients: a real‐world experience",
"author": "Kelleni MT",
"first-page": "121",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Canad J Medicine",
"key": "e_1_2_8_158_1",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jvsv.2020.06.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_159_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13091720",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_8_160_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Estimating coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19)‐caused deaths in hospitals and healthcare units: do hospital‐acquired infections play a role? Comments with a proposal",
"author": "Chirumbolo S",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol Mar",
"key": "e_1_2_8_161_1",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 160,
"references-count": 160,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bcpt.13690"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology",
"Toxicology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Home pharmacological therapy in early COVID‐19 to prevent hospitalization and reduce mortality: Time for a suitable proposal",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "130"
}