Vitamin D and Exercise Are Major Determinants of Natural Killer Cell Activity, Which Is Age- and Gender-Specific
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.594356, Jun 2021
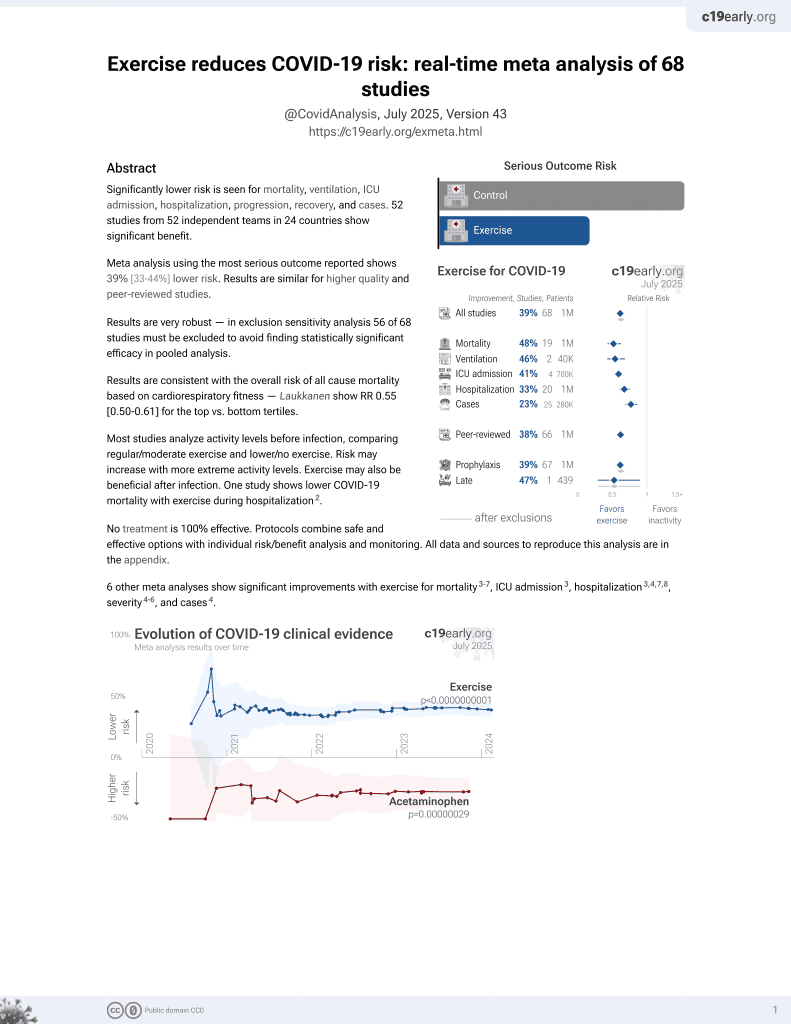
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Analysis of 2,095 patients in South Korea, showing exercise and vitamin D associated with improved natural killer cell activity.
Graydon showed that a lower frequency of natural killer cells was associated with symptomatic COVID-19 infection.
Study covers exercise and vitamin D.
Oh et al., 23 Jun 2021, retrospective, South Korea, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: sangwoon.choi@gmail.com.
Vitamin D and Exercise Are Major Determinants of Natural Killer Cell Activity, Which Is Age- and Gender-Specific
Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.594356
Background: The coronavirus-19 disease (COVID-19) pandemic reminds us of the importance of immune function, even in immunologically normal individuals. Multiple lifestyle factors are known to influence the immune function. Objective: The aim was to investigate the association between NK cell activity (NKA) and multiple factors including vitamin D, physical exercise, age, and gender. Methods: This was a cross-sectional association study using health check-up and NKA data of 2,095 subjects collected from 2016 to 2018 in a health check-up center in the Republic of Korea. NKA was measured using the interferon-g (IFN-g) stimulation method. The association of NKA with 25-(OH)-vitamin D (25(OH)D) and other factors was investigated by multiple logistic regression analysis.
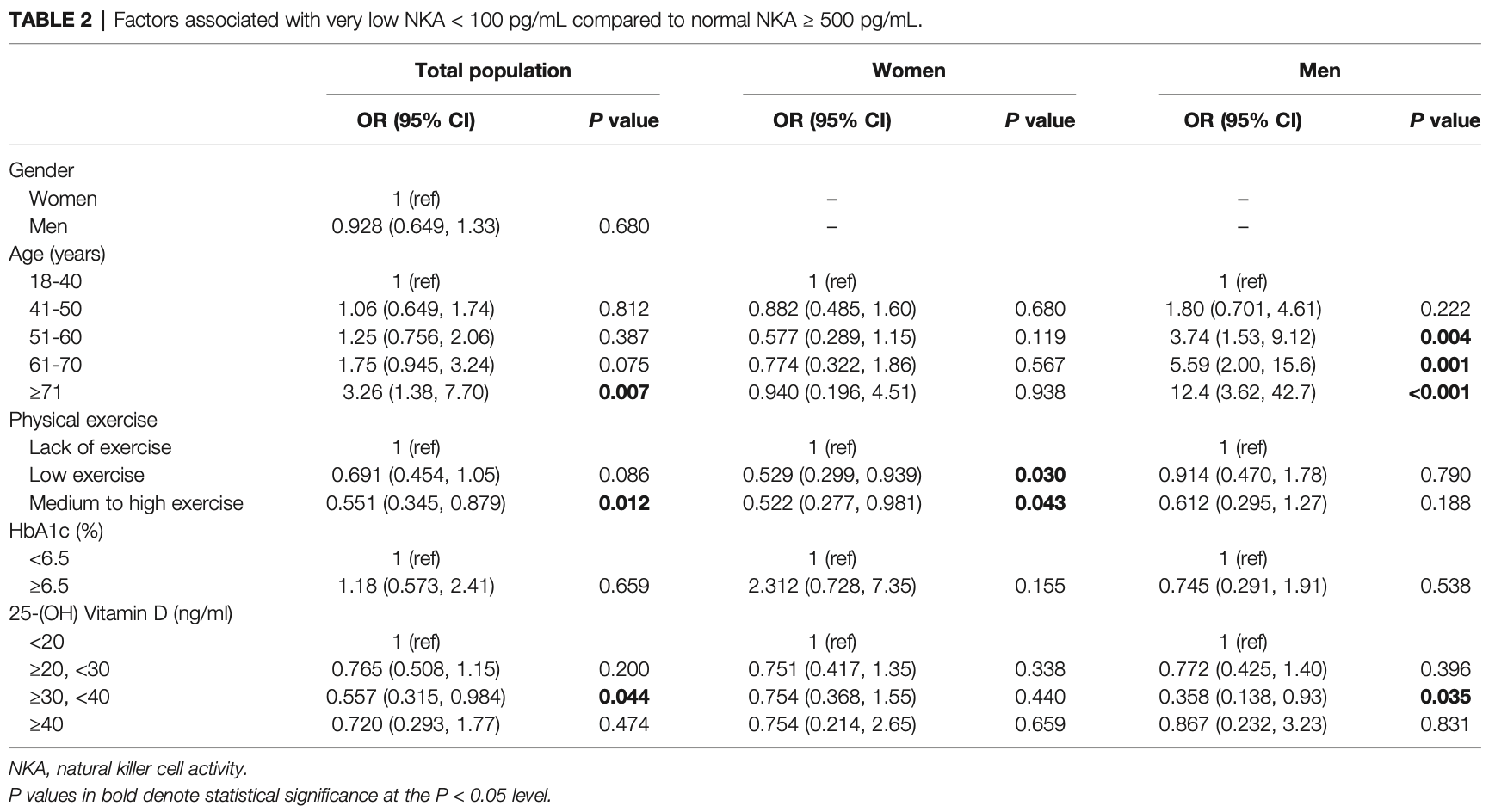
Results: The average age of subjects was 48.8 ± 11.6 years (52.9% of subjects were female). Among 2,095 subjects, 1,427 had normal NKA (NKA ≥ 500 pg IFN-g/mL), while 506 had low NKA (100 ≤ NKA < 500 pg/mL), and 162 subjects had very low NKA (NKA < 100 pg/mL). Compared to men with low 25(OH)D serum level (< 20 ng/mL), vitamin D replete men (30-39.9 ng/mL) had significantly lower risk of very low NKA (OR: 0.358; 95% CI: 0.138, 0.929; P = 0.035). In women, both low exercise (OR: 0.529; 95% CI: 0.299, 0.939; P = 0.030) and medium to high exercise (OR: 0.522; 95% CI: 0.277, 0.981; P = 0.043) decreased the risk compared to lack of physical exercise. Interestingly, in men and women older than 60 years, physical exercise significantly decreased the risk. Older-age was associated with increased risk of very low NKA in men, but not in women.
Conclusion: Physical exercise and vitamin D were associated with NKA in a genderand age-dependent manner. Age was a major risk factor of very low NKA in men but not in women.
ETHICS STATEMENT The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by CHA Bundang Medical Center. Written informed consent for participation was not required for this study in acc ordance with the national l egis lation and the institutional requirements.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS SO, SC, and S-WC contributed to the study design, data collection, study analysis, manuscript writing, critical review of the manuscript, and final approval of the manuscript submission. SH, JK, YC, JL, and KK assisted in analyzing and interpreting the data, critical review of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
Akbar, Wibowo, Pranata, Setiabudiawan, Low Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D (Vitamin D) Level Is Associated With Susceptibility to COVID-19, Severity, and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.660420
Akha, Aging and the Immune System: An Overview, J Immunol Methods, doi:10.1016/j.jim.2018.08.005
Amrein, Quraishi, Litonjua, Gibbons, Pieber et al., Evidence for a U-Shaped Relationship Between Prehospital Vitamin D Status and Mortality: A Cohort Study, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2013-3481
Barkin, Rodriguez-Suarez, Betito, Association Between Natural Killer Cell Activity and Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Study, Can J Urol
Bassatne, Basbous, Chakhtoura, El Zein, Rahme et al., The Link Between COVID-19 and (Vivid): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Metabolism, doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753
Bigley, Simpson, NK Cells and Exercise: Implications for Cancer Immunotherapy and Survivorship, Discovery Med
Bigley, Spielmann, Lavoy, Simpson, Can Exercise-Related Improvements in Immunity Influence Cancer Prevention and Prognosis in the Elderly?, Maturitas, doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2013.06.010
Blom, Lönn, Ekblom, Kallings, Väisänen et al., Lifestyle Habits and Mental Health in Light of the Two Covid-19 Pandemic Waves in Sweden, Int J Environ Res Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph18063313
Chastin, Abaraogu, Bourgois, Dall, Darnborough et al., Effects of Regular Physical Activity on the Immune System, Vaccination and Risk of Community-Acquired Infectious Disease in the General Population: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Sports Med, doi:10.1007/s40279-021-01466-1
Cormie, Zopf, Zhang, Schmitz, The Impact of Exercise on Cancer Mortality, Recurrence, and Treatment-Related Adverse Effects, Epidemiol Rev, doi:10.1093/epirev/mxx007
Delarosa, Pawelec, Peralbo, Wikby, Mariani et al., Immunological Biomarkers of Ageing in Man: Changes in Both Innate and Adaptive Immunity Are Associated With Health and Longevity, Biogerontology, doi:10.1007/s10522-006-9062-6
Despeghel, Reichel, Zander, Krüger, Weyh, Effects of a 6 Week Low-Dose Combined Resistance and Endurance Training on T Cells and Systemic Inflammation in the Elderly, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells10040843
Dixit, Can Moderate Intensity Aerobic Exercise be an Effective and Valuable Therapy in Preventing and Controlling the Pandemic of COVID-19?, Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109854
Dramém, Hentzien, Proye, Coulibaly, Demoustier-Tampère, Relation Between Vitamin D and COVID-19 in Aged People: A Systematic Review, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13041339
Duggal, Niemiro, Harridge, Simpson, Lord, Can Physical Activity Ameliorate Immunosenescence and Thereby Reduce Age-Related Multi-Morbidity?, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-019-0177-9
Ebadi, Montano-Loza, Perspective: Improving Vitamin D Status in the Management of COVID-19, Eur J Clin Nutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0661-0
Elias, Hartshorn, Rahma, Lin, Snyder-Cappione, None, Aging, Immune Senescence, and Immunotherapy: A Comprehensive Review. Semin Oncol, doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2018.08.006
Ferguson, Wikby, Maxson, Olsson, Johansson, Immune Parameters in a Longitudinal Study of a Very Old Population of Swedish People: A Comparison Between Survivors and Nonsurvivors, J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci, doi:10.1093/gerona/50A.6.B378
Fish, The X-Files in Immunity: Sex-Based Differences Predispose Immune Responses, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri2394
Fitzgerald, Exercise and the Immune System, Immunol Today, doi:10.1016/0167-5699(88)91332-1
Flanagan, Sexual Dimorphism in Biomedical Research: A Call to Analyse by Sex, Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg, doi:10.1093/trstmh/tru079
Gaksch, Jorde, Grimnes, Joakimsen, Schirmer et al., Vitamin D and Mortality: Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis of Standardized 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in 26916 Individuals From a European Consortium, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0170791
Gbd, Alcohol Collaborators. Alcohol Use and Burden for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990-2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31310-2
Giefing-Kroll, Berger, Lepperdinger, Grubeck-Loebenstein B. How Sex and Age Affect Immune Responses, Susceptibility to Infections, and Response to Vaccination, Aging Cell, doi:10.1111/acel.12326
Goronzy, Weyand, Immune Aging and Autoimmunity, Cell Mol Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s00018-012-0970-0
Gounder, Abdullah, Radzuanb, Zain, Sait et al., Effect of Aging on NK Cell Population and Their Proliferation at Ex Vivo Culture Condition, Anal Cell Pathol (Amst), doi:10.1155/2018/7871814
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence That Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Han, Ma, Wang, Wang, You, Immunological Characteristics in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Covid-19 Patients, Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), doi:10.3389/fendo.2021.596518
Hirokawa, Utsuyama, Hayashi, Kitagawa, Makinodan et al., Slower Immune System Aging in Women Versus Men in the Japanese Population, Immun Ageing, doi:10.1186/1742-4933-10-19
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Gordon, Hanley et al., Evaluation, Treatment, and Prevention of Vitamin D Deficiency: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline, J Clin Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1210/jc.2011-0385
Hupin, Roche, Gremeaux, Chatard, Oriol et al., Even a Low-Dose of Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity Reduces Mortality by 22% in Adults Aged ≥ 60 Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Br J Sports Med, doi:10.1136/bjsports-2014-094306
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Del Campo, Samouda et al., Strengthening the Immune System and Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Through Diet and Nutrition: Considerations During the COVID-19 Crisis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12061562
Imai, Matsuyama, Miyake, Suga, Nakachi, Natural Cytotoxic Activity of Peripheral-Blood Lymphocytes and Cancer Incidence: An 11-Year Follow-Up Study of a General Population, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)03231-1
Jobin, Rodriguez-Suarez, Betito, Association Between Natural Killer Cell Activity and Colorectal Cancer in High-Risk Subjects Undergoing Colonoscopy, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.06.009
Jung, Park, Park, Sohn, Lee et al., Physical Inactivity and Unhealthy Metabolic Status Are Associated With Decreased Natural Killer Cell Activity, Yonsei Med J, doi:10.3349/ymj.2018.59.4.554
Kakanis, Peake, Brenu, Simmonds, Gray et al., The Open Window of Susceptibility to Infection After Acute Exercise in Healthy Young Male Elite Athletes, Exerc Immunol Rev
Kontis, Bennett, Mathers, Li, Foreman et al., Future Life Expectancy in 35 Industrialised Countries: Projections With a Bayesian Model Ensemble, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32381-9
Koo, Shim, Yang, Lee, Kim et al., Reduction of the CD16(-)CD56bright NK Cell Subset Precedes NK Cell Dysfunction in Prostate Cancer, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0078049
Kunzmann, Coleman, Huang, Berndt, The Association of Lifetime Alcohol Use With Mortality and Cancer Risk in Older Adults: A Cohort Study, PloS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1002585
Lee, Cha, Kim, Yoon, Lee et al., A High-Throughput Assay of NK Cell Activity in Whole Blood and Its Clinical Application, Biochem Biophys Res Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.02.040
Lee, Park, Ryu, Bae, Choi et al., Natural Killer Cell Activity for IFN-Gamma Production as a Supportive Diagnostic Marker for Gastric Cancer, Oncotarget, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.19712
Lowder, Padgett, Woods, Moderate Exercise Protects Mice From Death Due to Influenza Virus, Brain Behav Immun, doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2005.04.002
Mace, Orange, Emerging Insights Into Human Health and NK Cell Biology From the Study of NK Cell Deficiencies, Immunol Rev, doi:10.1111/imr.12725
Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French, Baggerly, Garland et al., Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations ≥40 Ng/Ml Are Associated With >65% Lower Cancer Risk: Pooled Analysis of Randomized Trial and Prospective Cohort Study, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0152441
Mckechnie, Blish, The Innate Immune System: Fighting on the Front Lines or Fanning the Flames of COVID-19?, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.009
Medrano, Carrillo-Cruz, Montero, Perez-Simon, Vitamin D: Effect on Haematopoiesis and Immune System and Clinical Applications, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms19092663
Moore, Patel, Matthews, De Gonzalez, Park et al., Leisure Time Physical Activity of Moderate to Vigorous Intensity and Mortality: A Large Pooled Cohort Analysis, PloS Med, doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.1001335
Murasko, Weiner, Kaye, Decline in Mitogen Induced Proliferation of Lymphocytes With Increasing Age, Clin Exp Immunol
Neumann, Acker, Schormann, Pfreundschuh, Bittenbring, Determination of Optimum Vitamin D3 Levels for NK Cell-Mediated Rituximab-and Obinutuzumab-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity, Cancer Immunol Immunother, doi:10.1007/s00262-018-2224-y
Ng, Camous, Nyunt, Vasudev, Tan et al., Markers of T-Cell Senescence and Physical Frailty: Insights From Singapore Longitudinal Ageing Studies, NPJ Aging Mech Dis, doi:10.1038/npjamd.2015.5
Ogata, Shioi, Nakamura, Luo, Yokose, Association Between Natural Killer Cell Activity and Infection in Immunologically Normal Elderly People, Clin Exp Immunol, doi:10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01571.x
Ogata, Yokose, Tamura, Nakamura, Dan, Natural Killer Cells in the Late Decades of Human Life, Clin Immunol Immunopathol, doi:10.1006/clin.1997.4401
Oh, Lee, Kwack, Choi, Natural Killer Cell Therapy: A New Treatment Paradigm for Solid Tumors, Cancers, doi:10.3390/cancers11101534
Pawelec, Immune Parameters Associated With Mortality in the Elderly are Context-Dependent: Lessons From Sweden, Holland and Belgium, Biogerontology, doi:10.1007/s10522-017-9739-z
Pedersen, Influence of Physical Activity on the Cellular Immune System: Mechanisms of Action, Int J Sports Med, doi:10.1055/s-2007-1024746
Pedersen, Tvede, Klarlund, Christensen, Hansen et al., Indomethacin In Vitro and In Vivo Abolishes Post-Exercise Suppression of Natural Killer Cell Activity in Peripheral Blood, Int J Sports Med, doi:10.1055/s-2007-1024776
Pedersen, Ullum, NK Cell Response to Physical Activity: Possible Mechanisms of Action, Med Sci Sports Exerc, doi:10.1249/00005768-199402000-00003
Pilz, Zitterman, Trummer, Schwetz, Lerchbaum et al., Vitamin D Testing and Treatment: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence, Endocr Connect, doi:10.1530/EC-18-0432
Roberts-Thomson, Youngchaiyud, Whittingham, Mackay, Ageing, Immune Response, and Mortality, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(74)91755-3
Sabetta, Depetrillo, Cipriani, Smardin, Burns et al., Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and the Incidence of Acute Viral Respiratory Tract Infections in Healthy Adults, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011088
Salomon, Wang, Freeman, Vos, Flaxman et al., Healthy Life Expectancy for 187 Countries, 1990-2010: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden Disease Study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61690-0
Scartoni, Sant'ana, Lo, Murillo-Rodriguez, Yamamoto et al., Physical Exercise and Immune System in the Elderly: Implications and Importance in COVID-19 Pandemic Period, Front Psychol, doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2020.593903
Schmidt, Van Mackelenbergh, Wesch, Mundhenke, Physical Activity Influences the Immune System of Breast Cancer Patients, J Cancer Res Ther, doi:10.4103/0973-1482.150356
Simpson, Kunz, Agha, Graff, Exercise and the Regulation of Immune Functions, Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci, doi:10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.08.001
Song, Chang, Respiratory Allergies in the Elderly: Findings From the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging Phase I Study
Vanherwegen, Gysemans, Mathieu, Regulation of Immune Function by Vitamin D and Its Use in Diseases of Immunity, Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am, doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2017.07.010
Wayne, Rhyne, Garry, Goodwin, Cell-Mediated Immunity as a Predictor of Morbidity and Mortality in Subjects Over 60, J Gerontol, doi:10.1093/geronj/45.2.M45
Wen, Su, Tang, Le, Zhang et al., Immune Cell Profiling of COVID-19 Patients in the Recovery Stage by Single-Cell Sequencing, Cell Discovery, doi:10.1038/s41421-020-0168-9
Wikby, Johansson, Ferguson, The OCTO and NONA Immune Longitudinal Studies: A Review of 11 Years Studies of Swedish Very Old Humans, Adv Cell Aging Gerontol, doi:10.1016/S1566-3124(02)13001-X
Wikby, Maxson, Olsson, Johansson, Ferguson, Changes in CD8 and CD4 Lymphocyte Subsets, T Cell Proliferation Responses and Non-Survival in the Very Old: The Swedish Longitudinal OCTO-Immune Study, Mech Ageing Dev, doi:10.1016/S0047-6374(97)00151-6
Wilk, Rustagi, Zhao, Roque, Martinez-Colon et al., A Single-Cell Atlas of the Peripheral Immune Response in Patients With Severe COVID-19, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0944-y
Woods, Keylock, Lowder, Vieira, Zelkovich et al., Cardiovascular Exercise Training Extends Influenza Vaccine Seroprotection in Sedentary Older Adults: The Immune Function Intervention Trial, J Am Geriatr Soc, doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02563.x
Zabetakis, Lordan, Norton, Tsoupras, Covid-19: The Inflammation Link and the Role of Nutrition in Potential Mitigation, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12051466
Zemb, Bergman, Camargo, Jr, Cavalier et al., Vitamin D Deficiency and COVID-19 Pandemic, J Glob Antimicrob Resist, doi:10.1016/j.jgar.2020.05.006
Zheng, Gao, Wang, Song, Liu et al., Functional Exhaustion of Antiviral Lymphocytes in COVID-19 Patients, Cell Mol Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0402-2
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.594356",
"ISSN": [
"1664-3224"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.594356",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>The coronavirus-19 disease (COVID-19) pandemic reminds us of the importance of immune function, even in immunologically normal individuals. Multiple lifestyle factors are known to influence the immune function.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>The aim was to investigate the association between NK cell activity (NKA) and multiple factors including vitamin D, physical exercise, age, and gender.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>This was a cross-sectional association study using health check-up and NKA data of 2,095 subjects collected from 2016 to 2018 in a health check-up center in the Republic of Korea. NKA was measured using the interferon-γ (IFN-γ) stimulation method. The association of NKA with 25-(OH)-vitamin D (25(OH)D) and other factors was investigated by multiple logistic regression analysis.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>The average age of subjects was 48.8 ± 11.6 years (52.9% of subjects were female). Among 2,095 subjects, 1,427 had normal NKA (NKA ≥ 500 pg IFN-γ/mL), while 506 had low NKA (100 ≤ NKA &lt; 500 pg/mL), and 162 subjects had very low NKA (NKA &lt; 100 pg/mL). Compared to men with low 25(OH)D serum level (&lt; 20 ng/mL), vitamin D replete men (30–39.9 ng/mL) had significantly lower risk of very low NKA (OR: 0.358; 95% CI: 0.138, 0.929; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.035). In women, both low exercise (OR: 0.529; 95% CI: 0.299, 0.939; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.030) and medium to high exercise (OR: 0.522; 95% CI: 0.277, 0.981; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0.043) decreased the risk compared to lack of physical exercise. Interestingly, in men and women older than 60 years, physical exercise significantly decreased the risk. Older-age was associated with increased risk of very low NKA in men, but not in women.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Physical exercise and vitamin D were associated with NKA in a gender- and age-dependent manner. Age was a major risk factor of very low NKA in men but not in women.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fimmu.2021.594356"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Oh",
"given": "Sooyeon",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chun",
"given": "Sukyung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hwang",
"given": "Sena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "Jongseok",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cho",
"given": "Yuri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Jooho",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kwack",
"given": "KyuBum",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Choi",
"given": "Sang-Woon",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Immunology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Immunol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-23T06:21:45Z",
"timestamp": 1624429305000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-23T06:21:54Z",
"timestamp": 1624429314000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-05T13:04:16Z",
"timestamp": 1693919056122
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 12,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
23
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-23T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1624406400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.594356/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
23
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061562",
"article-title": "Strengthening the Immune System and Reducing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Through Diet and Nutrition: Considerations During the COVID-19 Crisis",
"author": "Iddir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1562",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051466",
"article-title": "Covid-19: The Inflammation Link and the Role of Nutrition in Potential Mitigation",
"author": "Zabetakis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1466",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109854",
"article-title": "Can Moderate Intensity Aerobic Exercise be an Effective and Valuable Therapy in Preventing and Controlling the Pandemic of COVID-19",
"author": "Dixit",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "109854",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "143",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpsyg.2020.593903",
"article-title": "Physical Exercise and Immune System in the Elderly: Implications and Importance in COVID-19 Pandemic Period",
"author": "Scartoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Psychol",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph18063313",
"article-title": "Lifestyle Habits and Mental Health in Light of the Two Covid-19 Pandemic Waves in Sweden, 2020",
"author": "Blom",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3313",
"journal-title": "Int J Environ Res Public Health",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/gerona/50A.6.B378",
"article-title": "Immune Parameters in a Longitudinal Study of a Very Old Population of Swedish People: A Comparison Between Survivors and Nonsurvivors",
"author": "Ferguson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "50",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0047-6374(97)00151-6",
"article-title": "Changes in CD8 and CD4 Lymphocyte Subsets, T Cell Proliferation Responses and Non-Survival in the Very Old: The Swedish Longitudinal OCTO-Immune Study",
"author": "Wikby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mech Ageing Dev",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "102",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1566-3124(02)13001-X",
"article-title": "The OCTO and NONA Immune Longitudinal Studies: A Review of 11 Years Studies of Swedish Very Old Humans",
"author": "Wikby",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Adv Cell Aging Gerontol",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10522-006-9062-6",
"article-title": "Immunological Biomarkers of Ageing in Man: Changes in Both Innate and Adaptive Immunity Are Associated With Health and Longevity",
"author": "DelaRosa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biogerontology",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10522-017-9739-z",
"article-title": "Immune Parameters Associated With Mortality in the Elderly are Context-Dependent: Lessons From Sweden, Holland and Belgium",
"author": "Pawelec",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biogerontology",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/npjamd.2015.5",
"article-title": "Markers of T-Cell Senescence and Physical Frailty: Insights From Singapore Longitudinal Ageing Studies",
"author": "Ng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "15005",
"journal-title": "NPJ Aging Mech Dis",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.02.040",
"article-title": "A High-Throughput Assay of NK Cell Activity in Whole Blood and Its Clinical Application",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biochem Biophys Res Commun",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "445",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/oncotarget.19712",
"article-title": "Natural Killer Cell Activity for IFN-Gamma Production as a Supportive Diagnostic Marker for Gastric Cancer",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Oncotarget",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2017.06.009",
"article-title": "Association Between Natural Killer Cell Activity and Colorectal Cancer in High-Risk Subjects Undergoing Colonoscopy",
"author": "Jobin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0078049",
"article-title": "Reduction of the CD16(-)CD56bright NK Cell Subset Precedes NK Cell Dysfunction in Prostate Cancer",
"author": "Koo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e78049",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Association Between Natural Killer Cell Activity and Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Study",
"author": "Barkin",
"journal-title": "Can J Urol",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/imr.12725",
"article-title": "Emerging Insights Into Human Health and NK Cell Biology From the Study of NK Cell Deficiencies",
"author": "Mace",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Immunol Rev",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "287",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(00)03231-1",
"article-title": "Natural Cytotoxic Activity of Peripheral-Blood Lymphocytes and Cancer Incidence: An 11-Year Follow-Up Study of a General Population",
"author": "Imai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "356",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cancers11101534",
"article-title": "Natural Killer Cell Therapy: A New Treatment Paradigm for Solid Tumors",
"author": "Oh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1534",
"journal-title": "Cancers (Basel)",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/clin.1997.4401",
"article-title": "Natural Killer Cells in the Late Decades of Human Life",
"author": "Ogata",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol Immunopathol",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "84",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01571.x",
"article-title": "Association Between Natural Killer Cell Activity and Infection in Immunologically Normal Elderly People",
"author": "Ogata",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Immunol",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41421-020-0168-9",
"article-title": "Immune Cell Profiling of COVID-19 Patients in the Recovery Stage by Single-Cell Sequencing",
"author": "Wen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "31",
"journal-title": "Cell Discovery",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0944-y",
"article-title": "A Single-Cell Atlas of the Peripheral Immune Response in Patients With Severe COVID-19",
"author": "Wilk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0402-2",
"article-title": "Functional Exhaustion of Antiviral Lymphocytes in COVID-19 Patients",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol Immunol",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.009",
"article-title": "The Innate Immune System: Fighting on the Front Lines or Fanning the Flames of COVID-19",
"author": "McKechnie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2021.596518",
"article-title": "Immunological Characteristics in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Covid-19 Patients",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol (Lausanne)",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1002585",
"article-title": "The Association of Lifetime Alcohol Use With Mortality and Cancer Risk in Older Adults: A Cohort Study",
"author": "Kunzmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1002585",
"journal-title": "PloS Med",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31310-2",
"article-title": "Alcohol Use and Burden for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990-2016: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "392",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"key": "B29",
"volume-title": "Assesing Alcohol Problems, A Guide for Clinicians and Researchers",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1001335",
"article-title": "Leisure Time Physical Activity of Moderate to Vigorous Intensity and Mortality: A Large Pooled Cohort Analysis",
"author": "Moore",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1001335",
"journal-title": "PloS Med",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bjsports-2014-094306",
"article-title": "Even a Low-Dose of Moderate-to-Vigorous Physical Activity Reduces Mortality by 22% in Adults Aged ≥ 60 Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Hupin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Br J Sports Med",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"key": "B32",
"volume-title": "Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(03)15268-3",
"article-title": "Appropriate Body-Mass Index for Asian Populations and Its Implications for Policy and Intervention Strategies",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "363",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19092663",
"article-title": "Vitamin D: Effect on Haematopoiesis and Immune System and Clinical Applications",
"author": "Medrano",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2663",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence That Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Influenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "988",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ecl.2017.07.010",
"article-title": "Regulation of Immune Function by Vitamin D and Its Use in Diseases of Immunity",
"author": "Vanherwegen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EC-18-0432",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Testing and Treatment: A Narrative Review of Current Evidence",
"author": "Pilz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Endocr Connect",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13041339",
"article-title": "Relation Between Vitamin D and COVID-19 in Aged People: A Systematic Review",
"author": "Dramé",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1339",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.660420",
"article-title": "Low Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D (Vitamin D) Level Is Associated With Susceptibility to COVID-19, Severity, and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Akbar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2021.154753",
"article-title": "The Link Between COVID-19 and (Vivid): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Bassatne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "154753",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0661-0",
"article-title": "Perspective: Improving Vitamin D Status in the Management of COVID-19",
"author": "Ebadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "856",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Nutr",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jgar.2020.05.006",
"article-title": "Vitamin D Deficiency and COVID-19 Pandemic",
"author": "Zemb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Glob Antimicrob Resist",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"article-title": "Evaluation, Treatment, and Prevention of Vitamin D Deficiency: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline",
"author": "Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00262-018-2224-y",
"article-title": "Determination of Optimum Vitamin D3 Levels for NK Cell-Mediated Rituximab- and Obinutuzumab-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity",
"author": "Neumann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cancer Immunol Immunother",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0011088",
"article-title": "Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and the Incidence of Acute Viral Respiratory Tract Infections in Healthy Adults",
"author": "Sabetta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e11088",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0152441",
"article-title": "Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Concentrations ≥40 Ng/Ml Are Associated With >65% Lower Cancer Risk: Pooled Analysis of Randomized Trial and Prospective Cohort Study",
"author": "McDonnell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0152441",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0170791",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and Mortality: Individual Participant Data Meta-Analysis of Standardized 25-Hydroxyvitamin D in 26916 Individuals From a European Consortium",
"author": "Gaksch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0170791",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2013-3481",
"article-title": "Evidence for a U-Shaped Relationship Between Prehospital Vitamin D Status and Mortality: A Cohort Study",
"author": "Amrein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"article-title": "NK Cells and Exercise: Implications for Cancer Immunotherapy and Survivorship",
"author": "Bigley",
"journal-title": "Discovery Med",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/0973-1482.150356",
"article-title": "Physical Activity Influences the Immune System of Breast Cancer Patients",
"author": "Schmidt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Cancer Res Ther",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/epirev/mxx007",
"article-title": "The Impact of Exercise on Cancer Mortality, Recurrence, and Treatment-Related Adverse Effects",
"author": "Cormie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "71",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol Rev",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.maturitas.2013.06.010",
"article-title": "Can Exercise-Related Improvements in Immunity Influence Cancer Prevention and Prognosis in the Elderly",
"author": "Bigley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Maturitas",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-019-0177-9",
"article-title": "Can Physical Activity Ameliorate Immunosenescence and Thereby Reduce Age-Related Multi-Morbidity",
"author": "Duggal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40279-021-01466-1",
"article-title": "Effects of Regular Physical Activity on the Immune System, Vaccination and Risk of Community-Acquired Infectious Disease in the General Population: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Chastin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Sports Med",
"key": "B54",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2005.04.002",
"article-title": "Moderate Exercise Protects Mice From Death Due to Influenza Virus",
"author": "Lowder",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav Immun",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0167-5699(88)91332-1",
"article-title": "Exercise and the Immune System",
"author": "Fitzgerald",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Immunol Today",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "9",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.08.001",
"article-title": "Exercise and the Regulation of Immune Functions",
"author": "Simpson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-2007-1024776",
"article-title": "Indomethacin In Vitro and In Vivo Abolishes Post-Exercise Suppression of Natural Killer Cell Activity in Peripheral Blood",
"author": "Pedersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Sports Med",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "11",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-2007-1024746",
"article-title": "Influence of Physical Activity on the Cellular Immune System: Mechanisms of Action",
"author": "Pedersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Sports Med",
"key": "B59",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"article-title": "The Open Window of Susceptibility to Infection After Acute Exercise in Healthy Young Male Elite Athletes",
"author": "Kakanis",
"journal-title": "Exerc Immunol Rev",
"key": "B60",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1249/00005768-199402000-00003",
"article-title": "NK Cell Response to Physical Activity: Possible Mechanisms of Action",
"author": "Pedersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Med Sci Sports Exerc",
"key": "B61",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3349/ymj.2018.59.4.554",
"article-title": "Physical Inactivity and Unhealthy Metabolic Status Are Associated With Decreased Natural Killer Cell Activity",
"author": "Jung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Yonsei Med J",
"key": "B62",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32381-9",
"article-title": "Future Life Expectancy in 35 Industrialised Countries: Projections With a Bayesian Model Ensemble",
"author": "Kontis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B63",
"volume": "389",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61690-0",
"article-title": "Healthy Life Expectancy for 187 Countries, 1990-2010: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden Disease Study 2010",
"author": "Salomon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B64",
"volume": "380",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jim.2018.08.005",
"article-title": "Aging and the Immune System: An Overview",
"author": "Sadighi Akha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Immunol Methods",
"key": "B65",
"volume": "463",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-012-0970-0",
"article-title": "Immune Aging and Autoimmunity",
"author": "Goronzy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol Life Sci",
"key": "B66",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5415/apallergy.2017.7.4.185",
"article-title": "Respiratory Allergies in the Elderly: Findings From the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging Phase I Study (2005-2006)",
"author": "Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Asia Pac Allergy",
"key": "B67",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(74)91755-3",
"article-title": "Ageing, Immune Response, and Mortality",
"author": "Roberts-Thomson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B68",
"volume": "304",
"year": "1974"
},
{
"article-title": "Decline in Mitogen Induced Proliferation of Lymphocytes With Increasing Age",
"author": "Murasko",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Immunol",
"key": "B69",
"volume": "70",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/geronj/45.2.M45",
"article-title": "Cell-Mediated Immunity as a Predictor of Morbidity and Mortality in Subjects Over 60",
"author": "Wayne",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Gerontol",
"key": "B70",
"volume": "45",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.seminoncol.2018.08.006",
"article-title": "Aging, Immune Senescence, and Immunotherapy: A Comprehensive Review",
"author": "Elias",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "187",
"journal-title": "Semin Oncol",
"key": "B71",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/7871814",
"article-title": "Effect of Aging on NK Cell Population and Their Proliferation at Ex Vivo Culture Condition",
"author": "Gounder",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7871814",
"journal-title": "Anal Cell Pathol (Amst)",
"key": "B72",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02563.x",
"article-title": "Cardiovascular Exercise Training Extends Influenza Vaccine Seroprotection in Sedentary Older Adults: The Immune Function Intervention Trial",
"author": "Woods",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Am Geriatr Soc",
"key": "B73",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10040843",
"article-title": "Effects of a 6 Week Low-Dose Combined Resistance and Endurance Training on T Cells and Systemic Inflammation in the Elderly",
"author": "Despeghel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "843",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "B74",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/acel.12326",
"article-title": "How Sex and Age Affect Immune Responses, Susceptibility to Infections, and Response to Vaccination",
"author": "Giefing-Kroll",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Aging Cell",
"key": "B75",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri2394",
"article-title": "The X-Files in Immunity: Sex-Based Differences Predispose Immune Responses",
"author": "Fish",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "B76",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/trstmh/tru079",
"article-title": "Sexual Dimorphism in Biomedical Research: A Call to Analyse by Sex",
"author": "Flanagan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "B77",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1742-4933-10-19",
"article-title": "Slower Immune System Aging in Women Versus Men in the Japanese Population",
"author": "Hirokawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "19",
"journal-title": "Immun Ageing",
"key": "B78",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2013"
}
],
"reference-count": 78,
"references-count": 78,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.594356/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Immunology",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Vitamin D and Exercise Are Major Determinants of Natural Killer Cell Activity, Which Is Age- and Gender-Specific",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "12"
}