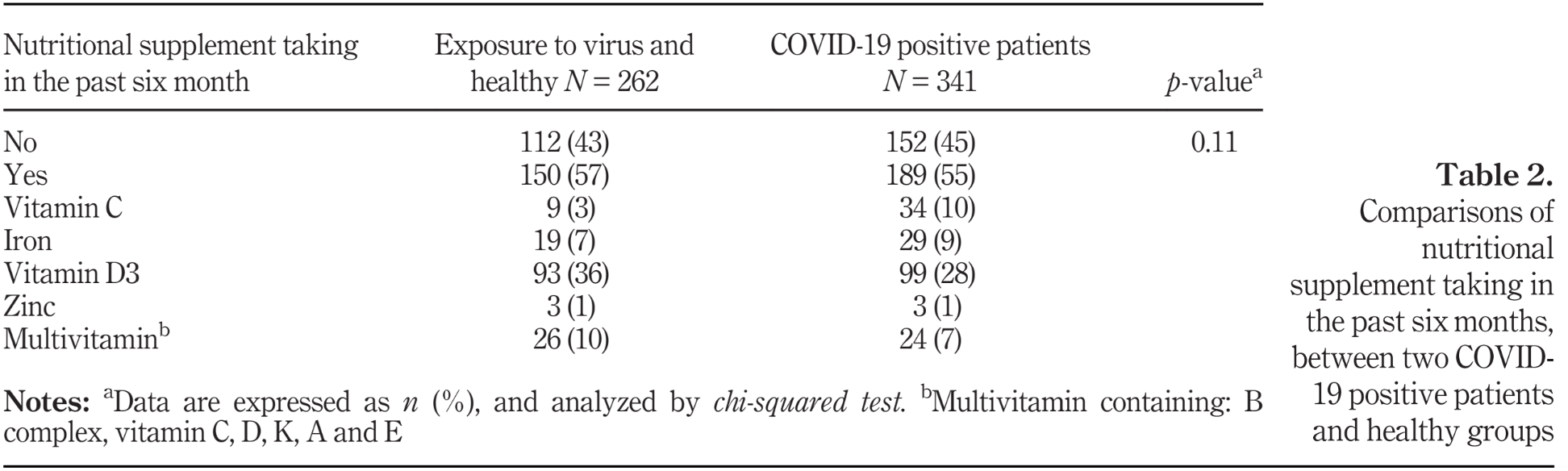
Do body mass index (BMI) and history of nutritional supplementation play a role in the severity of COVID-19? A retrospective study
et al., Nutrition & Food Science, doi:10.1108/NFS-11-2020-0421, Aug 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 603 patients in Iran, 192 taking vitamin D supplements, showing no significant difference in COVID-19 cases in unadjusted results. IR.SHOUSHTAR.REC.1399.015.
Although the 12% fewer cases is not statistically significant, it is consistent with the significant 17% fewer cases [9‑25%] from meta-analysis of the 32 cases results to date.
This is the 46th of 136 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin D, which collectively show efficacy with p<0.0000000001.
40 studies are RCTs, which show efficacy with p=0.0000001.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
Study covers vitamin C and vitamin D.
|
risk of case, 12.4% lower, RR 0.88, p = 0.09, treatment 99 of 192 (51.6%), control 242 of 411 (58.9%), NNT 14.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Mohseni et al., 4 Aug 2021, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, dosage not specified.
Are history of dietary intake and food habits of patients with clinical symptoms of COVID 19 different from healthy controls? A case–control study
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.01.021
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease that put unprecedented significant strain on clinical services and healthcare systems. The aim of the present research was to assess dietary food groups and also food habits of patients with clinical symptoms of COVID 19 and healthy controls. Methods: This caseecontrol research was carried out on 505 participants (279 subjects with clinical symptoms of COVID-19 and 226 controls), in age 18e65 years. Dietary food group's intake last year was investigated by a food frequency questionnaire. Food habits were asked by a general information questionnaire. The strength of the association between food group's intakes with the odds ratios (ORs) of COVID-19 was assessed using Logistic regression models. Results: After adjusting for physical activity in the logistic regression models, intake of dough and yogurt had a significantly protective role on occurrence of COVID19 (OR ¼ 0.62; 95% confidence interval (CI) ¼ 0.44e0.87; P ¼ 0.006) (OR ¼ 0.74; 95% CI ¼ 0.56e0.98; P ¼ 0.044), respectively. No significant differences were seen in food habits between the two groups in the last year ago. Conclusions: High risk population for COVID19, advised to consume enough amount of yogurt and dough at the time of this pandemic.
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
Ethics approval and consent to participate The protocol of study was approved, by the Medical Ethics Committee at the Shoushtar faculty of medical science according to the 2013 Helsinki Declaration (Registration No: IR.SHOUSHTAR.-REC.1399.015). All participants read and signed the consent form before their inclusion in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable. Author contributions H Mohseni and S Amini contributed significantly, in the conception and design of the research, analysis of data and interpretation, also, in the writing and critical revision of the manuscript. B Abiri, M Kalantar, B Barati and E Pirabbasi contributed to the critical revision of the manuscript. M Kaidani and F Bahrami contributed to the design of the research. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript before submitting it.
References
Ahirwar, Asia, Sakarde, Kaim, COVID-19 outbreakeDiabetes aspect and perspective, Curr Med Res Pract, doi:10.1016/j.cmrp.2020.05.005
Amini, Jafarirad, Mohseni, Ehsani, Hejazi et al., Comparison of food intake and body mass index before pregnancy between women with spontaneous abortion and women with successful pregnancy, Iran J Obstetr Gynecol Infertil
Bodnar, Wisner, Nutrition and depression: implications for improving mental health among childbearing-aged women, Biol Psychiatr
Calder, Carr, Gombart, Eggersdorfer, Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections, Nutrients
Craig, Marshall, Ostr€ Om, Bauman, Booth et al., International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity, Med Sci Sports Exerc
Cucinotta, Vanelli, WHO declares COVID-19 a pandemic, Acta Biomed: Atenei Parmensis
Galanakis, Aldawoud, Rizou, Rowan, Ibrahim, Food ingredients and active compounds against the Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic: a comprehensive review, Foods
Ghaderpour, Baveicy, Jafarirad, Relationship of constipation and irritable bowel syndrome with food intake, anthropometric measurements and eating behaviors in male students, Nutr Food Sci Res
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Del Campo, Samouda et al., Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the COVID-19 crisis, Nutrients
Infusino, Marazzato, Mancone, Fedele, Mastroianni et al., Diet supplementation, probiotics, and nutraceuticals in SARS-CoV-2 infection: a scoping review, Nutrients
Jayawardena, Sooriyaarachchi, Chourdakis, Jeewandara, Ranasinghe, Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: a review, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015
Mirmiran, Esfahani, Mehrabi, Hedayati, Azizi, Reliability and relative validity of an FFQ for nutrients in the Tehran lipid and glucose study, Publ Health Nutr
Mohseni, Amini, Abiri, Kalantar, Do body mass index (BMI) and history of nutritional supplementation play a role in the severity of COVID-19? A retrospective study, Nutr Food Sci, doi:10.1108/NFS-11-2020-0421
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Crawford, Mcginn et al., Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area, J Am Med Assoc, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6775
Rizou, Galanakis, Aldawoud, Galanakis, Safety of foods, food supply chain and environment within the COVID-19 pandemic, Trends Food Sci Technol, doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2020.06.008
Rozga, Cheng, Handu, Effects of probiotics in conditions or infections similar to COVID-19 on health outcomes: an evidence analysis center scoping review, J Acad Nutr Diet, doi:10.1016/j.jand.2020.07.016
Salonen, De Vos, Impact of diet on human intestinal microbiota and health, Annu Rev Food Sci Technol
To, Tsang, Yip, Chan, Wu et al., Consistent detection of 2019 novel coronavirus in saliva, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa149
Tuli, Halima, Ava, Islam, Unusual presentation of COVID 19-A case report, Bangladesh J
Vasheghani-Farahani, Tahmasbi, Asheri, Ashraf, Nedjat et al., The Persian, last 7-day, long form of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire: translation and validation study, Asian J Sports Med
Wang, Tang, Wei, Updated understanding of the outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in Wuhan, China, J Med Virol
Willett, Stampfer, Total energy intake: implications for epidemiologic analyses, Am J Epidemiol
Wu, Zha, Treatment strategies for reducing damages to lungs in patients with coronavirus and other infections
Zabetakis, Lordan, Norton, Tsoupras, COVID-19: the inflammation link and the role of nutrition in potential mitigation, Nutrients
Zu, Jiang, Xu, Ni, Lu, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a perspective from China, Radiology, doi:10.1148/radiol.2020200490
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1108/nfs-11-2020-0421",
"ISSN": [
"0034-6659",
"0034-6659"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/NFS-11-2020-0421",
"abstract": "<jats:sec>\n<jats:title content-type=\"abstract-subheading\">Purpose</jats:title>\n<jats:p>The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease that puts strain on health-care systems. Obesity is considered as a risk factor for the severity of infection. Hypotheses also suggested some nutritional supplements may be useful in COVID-19. This paper aims to assess the role of body mass index (BMI) and nutritional supplements on the severity of COVID-19.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec>\n<jats:title content-type=\"abstract-subheading\">Design/methodology/approach</jats:title>\n<jats:p>This research was conducted on 603 participants (in five groups including: exposure to virus and healthy, COVID-19 positive patients with severity of mild, moderate, severe and death from COVID-19), in age 18 to 65 years. Demographic data and history of nutritional supplements were asked. Anthropometric measurements were measured in a healthy group and in a patient. They were collected by referring to patients' medical records.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec>\n<jats:title content-type=\"abstract-subheading\">Findings</jats:title>\n<jats:p>The mean of BMI in groups with severity symptoms of moderate (27.57 kg/m<jats:sup>2</jats:sup>), severe (29.70 kg/m<jats:sup>2</jats:sup>) and death persons (28.13 kg/m<jats:sup>2</jats:sup>), was significantly higher than healthy (26.70 kg/m<jats:sup>2</jats:sup>) and mild symptoms (26.57 kg/m<jats:sup>2</jats:sup>) groups (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.001). The logistic regression shown, the fourth quartile of BMI was significantly associated with occurrence of COVID19, odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CI): [OR: 1.81, (95% CI: 1.13– 2.89), p-for trend = 0.55]. There was no significant difference in the percentage of vitamin C, D3, Zinc, Iron and multivitamin supplements intake, between groups, in the past six months (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.11).</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec>\n<jats:title content-type=\"abstract-subheading\">Originality/value</jats:title>\n<jats:p>This study indicated the role of higher BMI in the occurrence and severity of COVID-19. Researches are not enough to recommend consumption of nutritional supplements for the prevention of COVID-19.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1108/NFS-11-2020-0421"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mohseni",
"given": "Houra",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Amini",
"given": "Shirin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abiri",
"given": "Behnaz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalantar",
"given": "Mojtaba",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrition & Food Science",
"container-title-short": "NFS",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-13T08:18:26Z",
"timestamp": 1613204306000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-05T11:52:06Z",
"timestamp": 1628164326000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-15T09:19:50Z",
"timestamp": 1707988790992
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 7,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
27
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.emerald.com/insight/site-policies",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1611705600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/NFS-11-2020-0421/full/xml",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/NFS-11-2020-0421/full/html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "140",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1017-1027",
"prefix": "10.1108",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
27
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
4
]
]
},
"publisher": "Emerald",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.obmed.2020.100283",
"article-title": "Association of high level gene expression of ACE2 in adipose tissue with mortality of COVID-19 infection in obese patients",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Obesity Medicine",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref001",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Nutrition, immunity and Covid-19",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMJ Nutrition, Prevention and Health",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref002",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12041181",
"article-title": "Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1181",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref003",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bja.2020.07.006",
"article-title": "Body mass index and acute respiratory distress severity in patients with and without SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Anaesthesia",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref004",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1249/01.MSS.0000078924.61453.FB",
"article-title": "International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1381",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref005",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fendo.2020.00042",
"article-title": "Patterns of obesity and overweight in the iranian population: Findings of STEPs 2016",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "42",
"journal-title": "Front Endocrinol",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref006",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Obesity and inflammation: the linking mechanism and the complications",
"first-page": "851",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Archives of Medical Science",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref007",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050",
"article-title": "Vitamin D concentrations and COVID-19 infection in UK biobank",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref008",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31024-2",
"article-title": "Obesity could shift severe COVID-19 disease to younger ages",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1544",
"issue": "10236",
"journal-title": "The Lancet",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref009",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7861/clinmed.2019-coron",
"article-title": "What we know so far: COVID-19 current clinical knowledge and research",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "124",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clinical Medicine",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref010",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa415",
"article-title": "Obesity in patients younger than 60 years is a risk factor for covid-19 hospital admission",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref011",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Association of vitamin D status and other clinical characteristics with COVID-19 test results",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref012",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An official clinical practice guideline of the American thoracic society and infectious diseases society of America",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref013",
"volume": "200",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0635-2",
"article-title": "Nutritional recommendations for CoVID-19 quarantine",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "850",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "European Journal of Clinical Nutrition",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref014",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60460-8",
"article-title": "Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"issue": "9945",
"journal-title": "The Lancet",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref015",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa548",
"article-title": "Association of higher body mass index with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in younger patients",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref016",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pcd.2020.05.011",
"article-title": "Body mass index and risk of COVID‐19 across ethnic groups: analysis of UK biobank study",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref017",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32247-X",
"article-title": "Effect of interleukin-1β inhibition with canakinumab on incident lung cancer in patients with atherosclerosis: exploratory results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1833",
"issue": "10105",
"journal-title": "The Lancet",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref018",
"volume": "390",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.05.006",
"article-title": "Obesity and outcomes in COVID-19: when an epidemic and pandemic collide",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1445",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clinic Proceedings",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref019",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19 and smoking: a systematic review of the evidence",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Tobacco Induced Diseases",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref020",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The Persian, last 7-day, long form of the international physical activity questionnaire: translation and validation study",
"first-page": "106",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Asian Journal of Sports Medicine",
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref021",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"key": "key2021080511502206800_ref022",
"unstructured": "WHO (2020), “Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) situation report-198”, available at: www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200805-covid-19-sitrep-198.pdf?sfvrsn=f99d1754_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 22,
"references-count": 22,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/NFS-11-2020-0421/full/html"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Food Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Do body mass index (BMI) and history of nutritional supplementation play a role in the severity of COVID-19? A retrospective study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "51"
}
