Quantifying the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 viral load and infectiousness
et al., eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.69302, Sep 2021
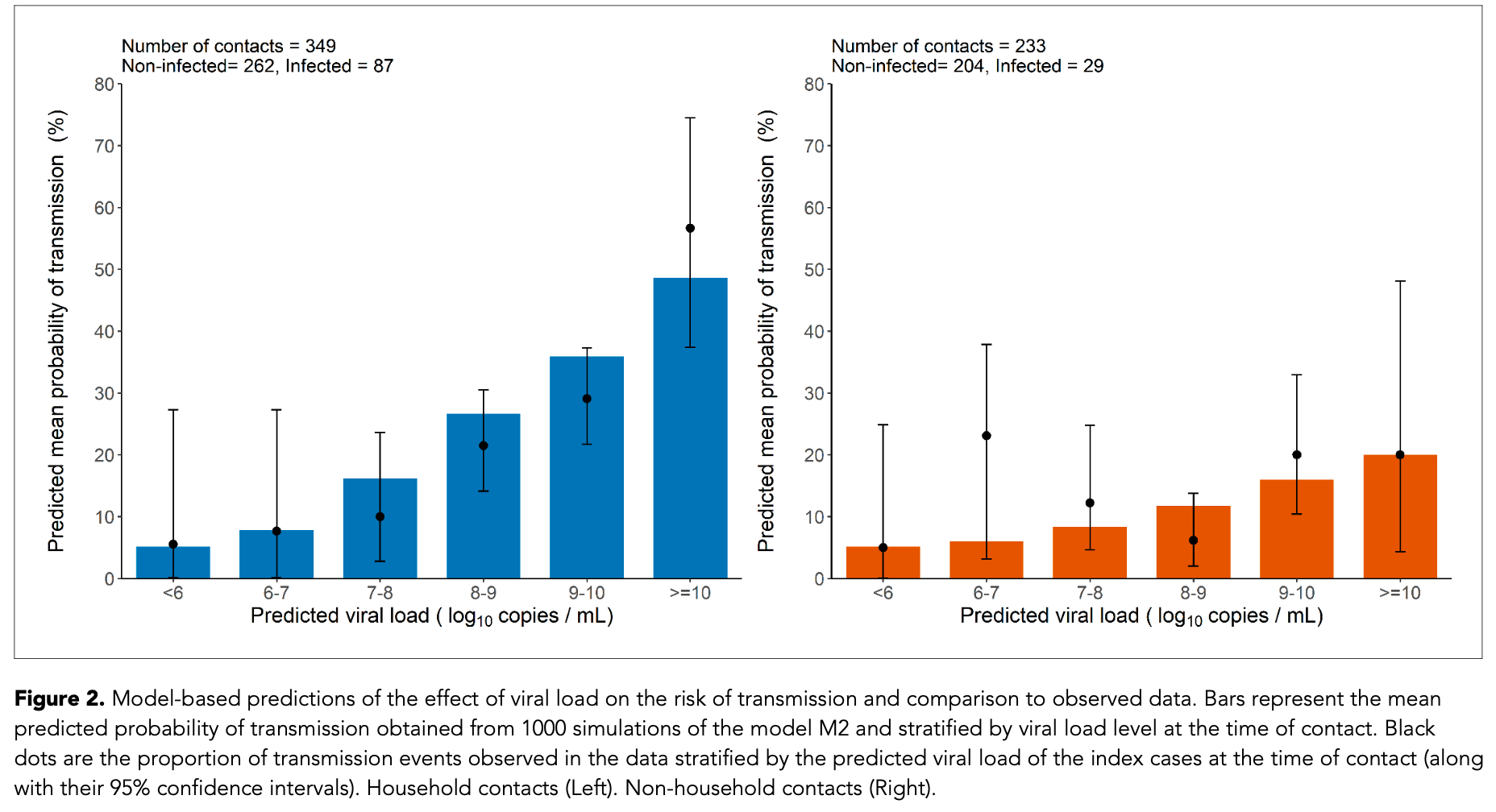
Analysis of 259 COVID-19 index cases and 582 high-risk contacts in Spain quantifying the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 viral load and transmission probability. Transmission probability increased significantly as the viral load increased. High viral load (≥10 log10 copies/mL) increased transmission probability by a factor of 10 for household contacts and 4 for non-household contacts, compared with <6 log10 copies/mL.
Marc et al., 27 Sep 2021, Spain, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: aurelien.marc@inserm.fr, jeremie.guedj@inserm.fr.
Quantifying the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 viral load and infectiousness
eLife, doi:10.7554/elife.69302
The relationship between SARS-CoV-2 viral load and infectiousness is poorly known. Using data from a cohort of cases and high-risk contacts, we reconstructed viral load at the time of contact and inferred the probability of infection. The effect of viral load was larger in household contacts than in non-household contacts, with a transmission probability as large as 48% when the viral load was greater than 10 10 copies per mL. The transmission probability peaked at symptom onset, with a mean probability of transmission of 29%, with large individual variations. The model also projects the effects of variants on disease transmission. Based on the current knowledge that viral load is increased by two-to eightfold with variants of concern and assuming no changes in the pattern of contacts across variants, the model predicts that larger viral load levels could lead to a relative increase in the probability of transmission of 24% to 58% in household contacts, and of 15% to 39% in non-household contacts.
funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Author contributions Aure ´lien Marc, Marion Kerioui, Modelling, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing -reviewing and editing; Franc ¸ois Blanquart, Formal analysis, Writing -reviewing and editing; Julie Bertrand, Formal analysis, Writing -review and editing; Oriol Mitja `, Marc Corbacho-Monne ´, Resources, Writingreview and editing; Michael Marks, Formal analysis, Resources, Writing -review and editing; Jeremie Guedj, Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Writing -reviewing and editing Ethics Clinical trial registration NCT04304053. Human subjects: The trial was supported by the crowd funding campaign YoMeCorono ( https:// www.yomecorono . com/), Generalitat de Catalunya, Zurich Seguros, Synlab Diagno ´sticos, Laboratorios Rubio ´, and Laboratorios Gebro Pharma. Laboratorios Rubio ´donated and supplied the hydroxychloroquine (Dolquine). The sponsors had no role in the conduct of the trial, the analysis, or the decision to submit the manuscript for publication. The trial protocol and subsequent amendments were approved by the institutional review board at Hospital Germans Trias i Pujol and the Spanish Agency of Medicines and Medical Devices. All the participants provided written informed consent. ( https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2021801 ).
Decision letter and Author response Decision..
References
Baccam, Beauchemin, Macken, Hayden, Perelson, Kinetics of influenza A virus infection in humans, Journal of Virology, doi:10.1128/JVI.01623-05
Bailly, Guilpain, Bouiller, Chirouze, Debi et al., BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination did not prevent an outbreak of SARS COV-2 variant 501Y.V2 in an elderly nursing home but reduced transmission and disease severity, Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciab446
Best, Guedj, Madelain, De Lamballerie, Lim et al., Zika plasma viral dynamics in nonhuman primates provides insights into early infection and antiviral strategies, PNAS, doi:10.1073/pnas.1704011114
Bi, Wu, Mei, Ye, Zou et al., Epidemiology and transmission of COVID-19 in 391 cases and 1286 of their close contacts in Shenzhen, China: a retrospective cohort study, The Lancet. Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30287-5
Boulware, Pullen, Bangdiwala, Pastick, Lofgren et al., A randomized trial of hydroxychloroquine as postexposure prophylaxis for Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2016638
Cereda, Tirani, Rovida, Demicheli, Ajelli et al., The early phase of the COVID-19 outbreak in Lombardy, Italy
Chen, Bobrovitz, Premji, Koopmans, Fisman et al., Heterogeneity in transmissibility and shedding SARS-CoV-2 via droplets and aerosols, eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.65774
Comets, Lavenu, Lavielle, Parameter estimation in nonlinear mixed effect models using saemix, an R implementation of the SAEM algorithm, Journal of Statistical Software, doi:10.18637/jss.v080.i03
Cosentino, Bernard, Ambroise, Giannoli, Guedj et al., SARS-CoV-2 viral dynamics in infections with alpha and beta variants of concern in the french community, The Journal of Infection S, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.07.031
Delyon, Lavielle, Moulines, Convergence of a stochastic approximation version of the EM algorithm, The Annals of Statistics, doi:10.1214/aos/1018031103
Edwards, Ausiello, Salzman, Devlin, Langer et al., Exhaled aerosol increases with COVID-19 infection, age, and obesity, PNAS, doi:10.1073/pnas.2021830118
Elie, Lecorche, Sofonea, Trombert-Paolantoni, Foulongne et al., Inferring SARS-CoV-2 variant within-host kinetics, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.05.26.21257835
Ferretti, Wymant, Kendall, Zhao, Nurtay et al., Quantifying SARS-CoV-2 transmission suggests epidemic control with digital contact tracing, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb6936
Golubchik, Lythgoe, Hall, Ferretti, Fryer et al., Early analysis of a potential link between viral load and the N501Y mutation in the SARS-COV-2 spike protein, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.01.12.20249080
Gonc ¸alves, Bertrand, Ke, Comets, De Lamballerie et al., Timing of antiviral treatment initiation is critical to reduce SARS-CoV-2 viral load, CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology, doi:10.1002/psp4.12543
Gonc ¸alves, Maisonnasse, Donati, Albert, Behillil et al., SARS-CoV-2 viral dynamics in non-human primates, PLOS Computational Biology, doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008785
He, Lau, Wu, Deng, Wang et al., Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19, Nature Medicine, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0869-5
Jones, Biele, Mu ¨hlemann, Veith, Schneider et al., Estimating infectiousness throughout SARS-CoV-2 infection course, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abi5273
Ke, Martinez, Smith, Gibson, Mirza et al., Daily sampling of early SARS-CoV-2 infection reveals substantial heterogeneity in infectiousness, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.07.12.21260208
Ke, Zitzmann, Ribeiro, Perelson, Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the human upper and lower respiratory tracts and their relationship with infectiousness, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.09.25.20201772
Kidd, Richter, Best, Cumley, Mirza et al., S-variant SARS-CoV-2 lineage B1.1.7 is associated with significantly higher viral loads in samples tested by ThermoFisher TaqPath RT-qPCR, The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab082
Lauer, Grantz, Bi, Jones, Zheng et al., The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application, Annals of Internal Medicine, doi:10.7326/M20-0504
Levine-Tiefenbrun, Yelin, Katz, Herzel, Golan et al., Initial report of decreased SARS-CoV-2 viral load after inoculation with the BNT162b2 vaccine, Nature Medicine, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01316-7
Liu, Liu, Plante, Plante, Xie et al., The N501Y spike substitution enhances SARS-CoV-2 transmission, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.08.434499
Madelain, Baize, Jacquot, Fizet, Barron et al., Ebola viral dynamics in nonhuman primates provides insights into virus immuno-pathogenesis and antiviral strategies, Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-018-06215-z
Maisonnasse, Guedj, Contreras, Behillil, Solas et al., Hydroxychloroquine use against SARS-CoV-2 infection in non-human primates, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2558-4
Marks, Millat-Martinez, Ouchi, Roberts, Alemany et al., Transmission of COVID-19 in 282 clusters in Catalonia, Spain: a cohort study, The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30985-3
Mcellistrem, Clancy, Buehrle, Lucas, Decker, Single dose of a mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine is associated with lower nasopharyngeal viral load among nursing home residents with asymptomatic COVID-19, Clinical Infectious Diseases
Mitja, Corbacho-Monne, Ubals, Alemany, Sun ˜er et al., A Cluster-Randomized trial of hydroxychloroquine for prevention of Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2021801
Mollan, Eron, Krajewski, Painter, Duke et al., SARS-CoV-2 infectious virus, viral RNA in nasopharyngeal swabs, and serostatus of symptomatic COVID-19 outpatients in the United States, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.05.28.21258011
Naveca, Nascimento, De Souza, Corado, Nascimento et al., COVID-19 in Amazonas, Brazil, was driven by the persistence of endemic lineages and p. 1 emergence, Nature Medicine, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01378-7
Ne ´ant, Lingas, Hingrat, Ghosn, Engelmann et al., Modeling SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and association with mortality in hospitalized patients from the French COVID cohort, PNAS, doi:10.1073/pnas.2017962118
Roquebert, Haim-Boukobza, Trombert-Paolantoni, Lecorche, Verdurme et al., SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern are associated with lower RT-PCR amplification cycles between January and march 2021 in France, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.03.19.21253971
Tang, Mao, Jones, Tan, Ji et al., Aerosol transmission of SARS-CoV-2? Evidence, prevention and control, Environment International, doi:10.1016/j.envint.2020.106039
Teyssou, Soulie, Visseaux, Lambert-Niclot, Ferre et al., The 501Y.V2 SARS-CoV-2 variant has an intermediate viral load between the 501Y.V1 and the historical variants in nasopharyngeal samples from newly diagnosed COVID-19 patients, Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.04.023
Thompson, Burgess, Naleway, Tyner, Yoon et al., Prevention and attenuation of Covid-19 with the BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccines, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107058
Van Kampen, Van De Vijver, Fraaij, Haagmans, Lamers et al., Duration and key determinants of infectious virus shedding in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19), Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20568-4
Wu, Leung, Bushman, Kishore, Niehus et al., Estimating clinical severity of COVID-19 from the transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, Nature Medicine, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0822-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7554/elife.69302",
"ISSN": [
"2050-084X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.69302",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The relationship between SARS-CoV-2 viral load and infectiousness is poorly known. Using data from a cohort of cases and high-risk contacts, we reconstructed viral load at the time of contact and inferred the probability of infection. The effect of viral load was larger in household contacts than in non-household contacts, with a transmission probability as large as 48% when the viral load was greater than 10<jats:sup>10</jats:sup> copies per mL. The transmission probability peaked at symptom onset, with a mean probability of transmission of 29%, with large individual variations. The model also projects the effects of variants on disease transmission. Based on the current knowledge that viral load is increased by two- to eightfold with variants of concern and assuming no changes in the pattern of contacts across variants, the model predicts that larger viral load levels could lead to a relative increase in the probability of transmission of 24% to 58% in household contacts, and of 15% to 39% in non-household contacts.</jats:p>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
1
]
]
},
"alternative-id": [
"10.7554/eLife.69302"
],
"article-number": "e69302",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"name": "peer_review_taxonomy"
},
"label": "Peer review transparency",
"name": "peer_review_transparency",
"value": "single anonymised"
},
{
"group": {
"name": "peer_review_taxonomy"
},
"label": "Peer review interaction",
"name": "peer_review_interaction",
"value": "other reviewer(s), editor"
},
{
"group": {
"name": "peer_review_taxonomy"
},
"label": "Peer review published",
"name": "peer_review_published",
"value": "review summaries, review reports, author/editor communication, reviewer identities reviewer opt in, editor identities"
},
{
"group": {
"name": "post_publication_commenting"
},
"label": "Post publication commenting",
"name": "post_publication_commenting",
"value": "open (sign in with ORCID iD required)"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6936-5388",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Université de Paris, IAME, INSERM",
"place": [
"Paris, France"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Marc",
"given": "Aurélien",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Université de Paris, IAME, INSERM",
"place": [
"Paris, France"
]
}
],
"family": "Kerioui",
"given": "Marion",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Université de Paris, IAME, INSERM",
"place": [
"Paris, France"
]
},
{
"name": "Centre for Interdisciplinary Research in Biology (CIRB), Collège de France, CNRS, INSERM, PSL Research University",
"place": [
"Paris, France"
]
}
],
"family": "Blanquart",
"given": "François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Université de Paris, IAME, INSERM",
"place": [
"Paris, France"
]
}
],
"family": "Bertrand",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fight AIDS and Infectious Diseases Foundation, Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol",
"place": [
"Badalona, Spain"
]
},
{
"name": "Lihir Medical Centre, International SOS",
"place": [
"Londolovit, Papua New Guinea"
]
}
],
"family": "Mitjà",
"given": "Oriol",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fight AIDS and Infectious Diseases Foundation, Hospital Universitari Germans Trias i Pujol",
"place": [
"Badalona, Spain"
]
},
{
"name": "Hospital Universitari Parc Taulí",
"place": [
"Sabadell, Spain"
]
},
{
"name": "Facultat de Medicina–Universitat de Barcelona",
"place": [
"Barcelona, Spain"
]
}
],
"family": "Corbacho-Monné",
"given": "Marc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine",
"place": [
"London, United Kingdom"
]
},
{
"name": "Hospital for Tropical Diseases",
"place": [
"London, United Kingdom"
]
},
{
"name": "Division of infection and Immunity, University College London",
"place": [
"London, United Kingdom"
]
}
],
"family": "Marks",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5534-5482",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Université de Paris, IAME, INSERM",
"place": [
"Paris, France"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Guedj",
"given": "Jeremie",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "eLife",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"elifesciences.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-27T11:11:04Z",
"timestamp": 1632741064000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-12T01:18:20Z",
"timestamp": 1697073500000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000865",
"award": [
"INV-017335"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000865",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001665",
"award": [
"ANR-20-COVI-0018"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100001665",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "French National Research Agency"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100000781",
"award": [
"ERC Starting Grant under the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100000781",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "European Research Council"
},
{
"award": [
"Crowdfunding campaign"
],
"name": "YoMeCorono"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100002809",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100002809",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Generalitat de Catalunya"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-22T10:45:31Z",
"timestamp": 1761129931754,
"version": "3.41.2"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 123,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
27
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1632700800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1632700800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1632700800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69302/elife-69302-v2.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://cdn.elifesciences.org/articles/69302/elife-69302-v2.xml",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://elifesciences.org/articles/69302",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "4374",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7554",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "eLife Sciences Publications, Ltd",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01623-05",
"article-title": "Kinetics of influenza A virus infection in humans",
"author": "Baccam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7590",
"journal-title": "Journal of Virology",
"key": "bib1",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciab446",
"article-title": "BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination did not prevent an outbreak of SARS COV-2 variant 501Y.V2 in an elderly nursing home but reduced transmission and disease severity",
"author": "Bailly",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"key": "bib2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1704011114",
"article-title": "Zika plasma viral dynamics in nonhuman primates provides insights into early infection and antiviral strategies",
"author": "Best",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8847",
"journal-title": "PNAS",
"key": "bib3",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30287-5",
"article-title": "Epidemiology and transmission of COVID-19 in 391 cases and 1286 of their close contacts in Shenzhen, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Bi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "911",
"journal-title": "The Lancet. Infectious Diseases",
"key": "bib4",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2016638",
"article-title": "A randomized trial of hydroxychloroquine as postexposure prophylaxis for Covid-19",
"author": "Boulware",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "517",
"journal-title": "New England Journal of Medicine",
"key": "bib5",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The early phase of the COVID-19 outbreak in Lombardy, Italy",
"author": "Cereda",
"key": "bib6",
"unstructured": "Cereda D, Tirani M, Rovida F, Demicheli V, Ajelli M, Poletti P, Trentini F, Guzzetta G, Marziano V, Barone A, Magoni M, Deandrea S, Diurno G, Lombardo M, Faccini M, Pan A, Bruno R, Pariani E, Grasselli G, Piatti A, Gramegna M, Baldanti F, Melegaro A, Merler S. 2020. The early phase of the COVID-19 outbreak in Lombardy, Italy. arXiv. https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.09320.",
"volume-title": "arXiv",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.65774",
"article-title": "Heterogeneity in transmissibility and shedding SARS-CoV-2 via droplets and aerosols",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "eLife",
"key": "bib7",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18637/jss.v080.i03",
"article-title": "Parameter estimation in nonlinear mixed effect models using saemix, an R implementation of the SAEM algorithm",
"author": "Comets",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Journal of Statistical Software",
"key": "bib8",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.07.031",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral dynamics in infections with alpha and beta variants of concern in the french community",
"author": "Cosentino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "The Journal of Infection",
"key": "bib9",
"volume": "S0163-4453",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1214/aos/1018031103",
"article-title": "Convergence of a stochastic approximation version of the EM algorithm",
"author": "Delyon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "94",
"journal-title": "The Annals of Statistics",
"key": "bib10",
"volume": "27",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2021830118",
"article-title": "Exhaled aerosol increases with COVID-19 infection, age, and obesity",
"author": "Edwards",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PNAS",
"key": "bib11",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.05.26.21257835",
"article-title": "Inferring SARS-CoV-2 variant within-host kinetics",
"author": "Elie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bib12",
"volume-title": "medRxiv",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb6936",
"article-title": "Quantifying SARS-CoV-2 transmission suggests epidemic control with digital contact tracing",
"author": "Ferretti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "bib13",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.01.12.20249080",
"article-title": "Early analysis of a potential link between viral load and the N501Y mutation in the SARS-COV-2 spike protein",
"author": "Golubchik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bib14",
"volume-title": "medRxiv",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/psp4.12543",
"article-title": "Timing of antiviral treatment initiation is critical to reduce SARS-CoV-2 viral load",
"author": "Gonçalves",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology",
"key": "bib15",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008785",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral dynamics in non-human primates",
"author": "Gonçalves",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLOS Computational Biology",
"key": "bib16",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0869-5",
"article-title": "Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19",
"author": "He",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "672",
"journal-title": "Nature Medicine",
"key": "bib17",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abi5273",
"article-title": "Estimating infectiousness throughout SARS-CoV-2 infection course",
"author": "Jones",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "bib18",
"volume": "373",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.09.25.20201772",
"article-title": "Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the human upper and lower respiratory tracts and their relationship with infectiousness",
"author": "Ke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bib19",
"volume-title": "medRxiv",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.07.12.21260208",
"article-title": "Daily sampling of early SARS-CoV-2 infection reveals substantial heterogeneity in infectiousness",
"author": "Ke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bib20",
"volume-title": "medRxiv",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab082",
"article-title": "S-variant SARS-CoV-2 lineage B1.1.7 is associated with significantly higher viral loads in samples tested by ThermoFisher TaqPath RT-qPCR",
"author": "Kidd",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1666",
"journal-title": "The Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"key": "bib21",
"volume": "223",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-0504",
"article-title": "The Incubation Period of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) From Publicly Reported Confirmed Cases: Estimation and Application",
"author": "Lauer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "577",
"journal-title": "Annals of Internal Medicine",
"key": "bib22",
"volume": "172",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01316-7",
"article-title": "Initial report of decreased SARS-CoV-2 viral load after inoculation with the BNT162b2 vaccine",
"author": "Levine-Tiefenbrun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "790",
"journal-title": "Nature Medicine",
"key": "bib23",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.03.08.434499",
"article-title": "The N501Y spike substitution enhances SARS-CoV-2 transmission",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bib24",
"volume-title": "bioRxiv",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-018-06215-z",
"article-title": "Ebola viral dynamics in nonhuman primates provides insights into virus immuno-pathogenesis and antiviral strategies",
"author": "Madelain",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nature Communications",
"key": "bib25",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2558-4",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine use against SARS-CoV-2 infection in non-human primates",
"author": "Maisonnasse",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "584",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "bib26",
"volume": "585",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30985-3",
"article-title": "Transmission of COVID-19 in 282 clusters in Catalonia, Spain: a cohort study",
"author": "Marks",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "629",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"key": "bib27",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Single dose of a mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccine is associated with lower nasopharyngeal viral load among nursing home residents with asymptomatic COVID-19",
"author": "McEllistrem",
"journal-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"key": "bib28",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021801",
"article-title": "A Cluster-Randomized trial of hydroxychloroquine for prevention of Covid-19",
"author": "Mitjà",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "417",
"journal-title": "New England Journal of Medicine",
"key": "bib29",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.05.28.21258011",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infectious virus, viral RNA in nasopharyngeal swabs, and serostatus of symptomatic COVID-19 outpatients in the United States",
"author": "Mollan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bib30",
"volume-title": "medRxiv",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Monolix version 2020R1",
"key": "bib31",
"unstructured": "Monolix version 2020R1. 2019. LIXOFT. Antony, France: Lixoft SAS, 2019. http://lixoft.com/products/monolix/.",
"volume-title": "Antony, France: Lixoft SAS, 2019",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01378-7",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in Amazonas, Brazil, was driven by the persistence of endemic lineages and p.1 emergence",
"author": "Naveca",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1230",
"journal-title": "Nature Medicine",
"key": "bib32",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2017962118",
"article-title": "Modeling SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and association with mortality in hospitalized patients from the French COVID cohort",
"author": "Néant",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PNAS",
"key": "bib33",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.03.19.21253971",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern are associated with lower RT-PCR amplification cycles between January and march 2021 in France",
"author": "Roquebert",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bib34",
"volume-title": "medRxiv",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.envint.2020.106039",
"article-title": "Aerosol transmission of SARS-CoV-2? Evidence, prevention and control",
"author": "Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Environment International",
"key": "bib35",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.04.023",
"article-title": "The 501Y.V2 SARS-CoV-2 variant has an intermediate viral load between the 501Y.V1 and the historical variants in nasopharyngeal samples from newly diagnosed COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Teyssou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Journal of Infection",
"key": "bib36",
"volume": "83",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2107058",
"article-title": "Prevention and attenuation of Covid-19 with the BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 vaccines",
"author": "Thompson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "320",
"journal-title": "New England Journal of Medicine",
"key": "bib37",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-20568-4",
"article-title": "Duration and key determinants of infectious virus shedding in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "van Kampen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nature Communications",
"key": "bib38",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0822-7",
"article-title": "Estimating clinical severity of COVID-19 from the transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "506",
"journal-title": "Nature Medicine",
"key": "bib39",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 39,
"references-count": 39,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "subject",
"id": "10.1101/2021.05.07.21256341",
"id-type": "doi"
},
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2021.05.07.21256341",
"id-type": "doi"
}
],
"has-review": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.7554/eLife.69302.sa1",
"id-type": "doi"
},
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.7554/eLife.69302.sa2",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://elifesciences.org/articles/69302"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Quantifying the relationship between SARS-CoV-2 viral load and infectiousness",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.69302",
"volume": "10"
}