Evaluation of vitamin A and E deficiency with severity of SARS-COV-2 disease: a case–control study
et al., The Egyptian Journal of Bronchology, doi:10.1186/s43168-023-00210-9, NCT05946499, Jul 2023
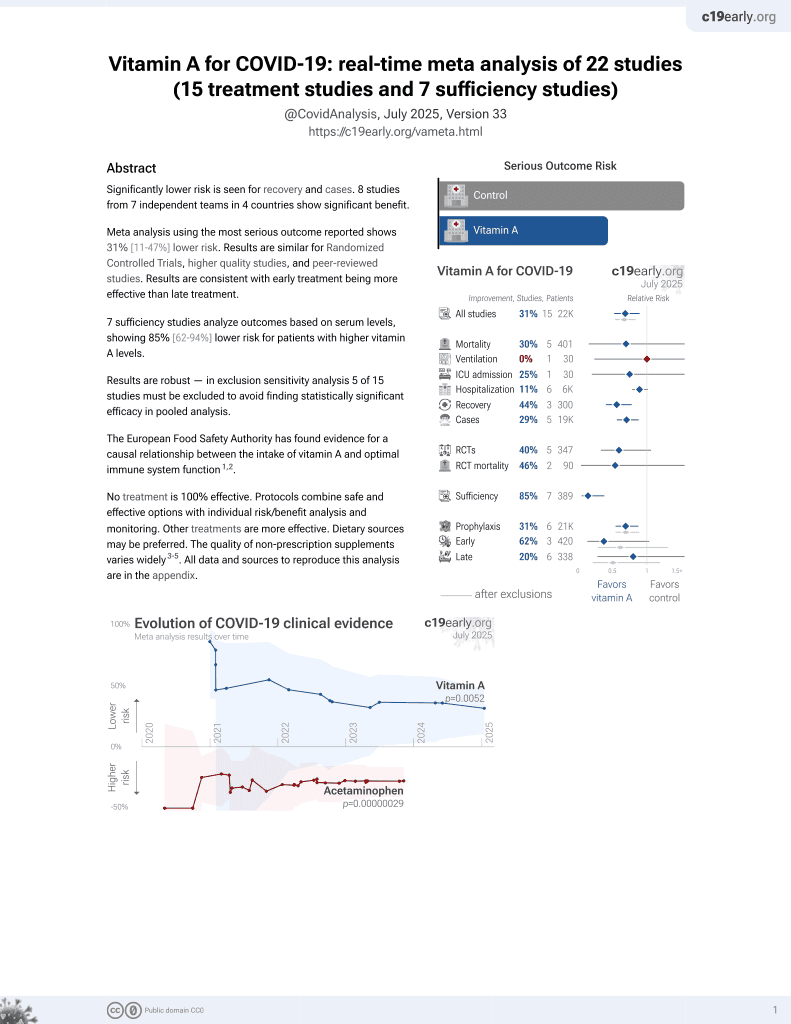
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
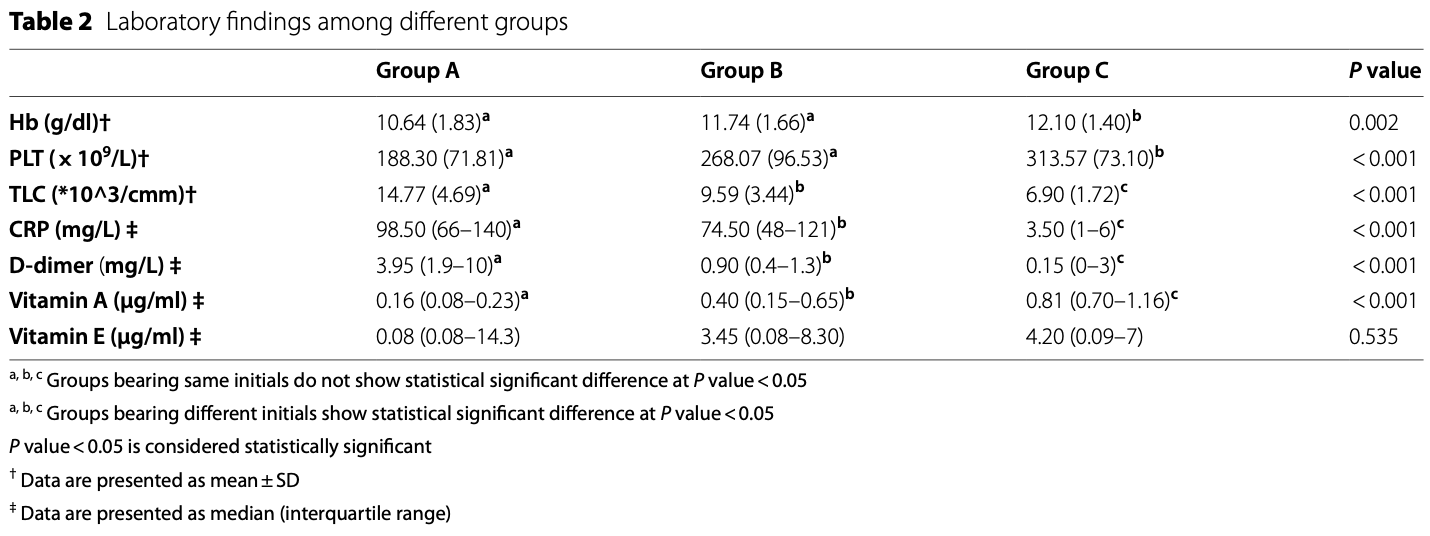
Case control study with 30 ICU COVID-19 patients, 30 hospitalized non-ICU patients, and 30 matched healthy controls, showing vitamin A levels associated with COVID-19 and severity, with ICU patient levels < hospitalized patients < healthy controls. Authors also show significantly lower risk of ARDS with vitamin A levels above 0.65µg/ml.
|
risk of ARDS, 99.7% lower, OR 0.003, p < 0.001, cutoff 0.65μg/ml, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Mandour et al., 21 Jul 2023, prospective, Egypt, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, study period September 2021 - April 2022, trial NCT05946499 (history).
Contact: balsam.sherif@kasralainy.edu.eg.
Evaluation of vitamin A and E deficiency with severity of SARS-COV-2 disease: a case–control study
The Egyptian Journal of Bronchology, doi:10.1186/s43168-023-00210-9
Background Coronavirus disease 2019 can cause severe inflammation and damage to the lungs. Vitamins A and E are essential in the enhancement of immunity and they tend to decrease in cases with inflammation. Determination of serum levels of vitamins A and E in COVID-19 patients was the aim of the study.
Methods This case-control study was carried out on 30 ICU-admitted SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals (group A), 30 ward-admitted SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals (group B) and 30 healthy controls (group C). High-performance liquid chromatography was used to measure vitamin A and E levels.
Results Median levels of vitamin A in group A [0.16 (0.08-0.23) µg/ml] were significantly lower than those in group B [0.4 (0.15-0.65) µg/ml] and in group C [0.81 (0.70-1.16) µg/ml] with P value < 0.001, while there was no significant difference between groups concerning vitamin E levels (P value = 0.535). Vitamin A deficiency showed significant correlation with lower hemoglobin levels, lower platelet counts, higher total leucocyte counts, higher C-reactive protein levels, and higher D-dimer levels. ROC curve construction showed that vitamin A level with cut off < 0.65 µg/ml increases risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) development with sensitivity 90% and specificity 83.3%. Logistic regression analysis showed that cases with vitamin A levels < 0.65 µg/ml were more prone to develop ARDS (OR = 0.003 [0.000-0.036] P < 0.001).
Conclusion Levels of vitamin A were reduced in COVID-19 patients particularly in ICU-admitted cases. This ensures the association of decreased vitamin A with disease morbidity and the importance of vitamin A supplementation as part of disease management. Trial registration Clinicaltrial.gov, NCT05946499. Registered 12 July 2023-Retrospectively registered.https:// regis ter. clini caltr ials. gov/ prs/ app/ action/ Selec tProt ocol? sid= S000D GLS& selec tacti on= Edit& uid= U0007 0DC& ts= 2& cx= gieusm.
Abbreviations
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate The study has received approval from Cairo University' s Faculty of Medicine' s research ethics committee (approval number: MS-59-2020; date: 29/4/2020). Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Aklamati, Mulenga, Dueker, Buchholz, Peerson et al., Accelerator mass spectrometry can be used to assess vitamin A metabolism quantitatively in boys in a community setting, J Nutr
Berrocal, Irriguible, Philibert, Llàcher, De Osaba et al., Zinc and vitamin a deficiency predisposes to the need for intubation and icu admission in patients with COVID-19. An observational study
Bielsa-Berrocal, Bordejé-Laguna, Tural-Llàcher, Barallat, Manresa-Domínguez, Low Levels of Few Micronutrients May Impact COVID-19 Disease Progression: an observational study on the first wave, Metabolites, doi:10.3390/metabo11090565
Biesalski, Nohr, Importance of vitamin-A for lung function and development, Mol Aspects Med
Chew, Park, Carotenoid action on the immune response, J Nutr
Cummings, Baldwin, Abrams, Jacobson, Meyer et al., Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: a prospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2
De Flora, Balansky, Maestra, Antioxidants and COVID-19, J Prev Med Hyg, doi:10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.1S3.1895
Duncan, Talwar, Mcmillan, Stefanowicz, Reilly, Quantitative data on the magnitude of the systemic inflammatory response and its effect on micronutrient status based on plasma measurements, Am J Clin Nutr
Ejaz, Alsrhani, Zafar, Javed, Junaid et al., COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients, J Infect Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014
Fadel, Morrison, Vahia, Smith, Chaudhry et al., Early short-course corticosteroids in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa601
Fiorino, Gallo, Zippi, Sabbatani, Manfredi et al., Cytokine storm in aged people with CoV-2: possible role of vitamins as therapy or preventive strategy, Aging Clin Exp Res, doi:10.1007/s40520-020-01669-y
Ghazzay, Wzs, Therapeutic effect of Vitamin A on severe COVID-19 patients, Eurasia J Biosci, doi:10.31838/SRP.2021.1.33
Giacobbe, Battaglini, Ball, Brunetti, Bruzzone et al., Bloodstream infections in critically ill patients with COVID-19, Eur J Clin Invest, doi:10.1111/eci.13319
Gieng, Green, Green, Rosales, Model-based compartmental analysis indicates a reduced mobilization of hepatic vitamin A during inflammation in rats, J Lipid Res
Glasziou, Mackerras, Vitamin A supplementation in infectious diseases: A meta-analysis, BMJ
Gorji, Ghadiri, Potential roles of micronutrient deficiency and immune system dysfunction in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic, Nutrition
Hakamifard, Soltani, Maghsoudi, Rismanbaf, Aalinezhad et al., The effect of vitamin E and vitamin C in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia; a randomized controlled clinical trial, Immunopathol Persa, doi:10.34172/ipp.2022.08
Herrero, Puchadesgimeno, García, Gómez, Ocetemochón et al., Methylprednisolone added to tocilizumab reduces mortality in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: An observational study, J Intern Med, doi:10.1111/joim.13145
Huang, Liu, Qi, Brand, Zheng, Role of Vitamin A in the Immune System, J Clin Med
Jayawardena, Sooriyaarachchi, Chourdakis, Jeewandara, Ranasinghe, Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: a review, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015
Jovic, Ali, Ibrahim, Jessop, Tarassoli et al., Could Vitamins Help in the Fight Against COVID-19?, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092550
Lewis, Meydani, Wu, Regulatory role of vitamin E in the immune system and inflammation, IUBMB Life, doi:10.1002/iub.1976
Liu, Li, Xu, Wu, Luo et al., Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with
Mcgill, Kelly, Guerra-Maupome, Winkley, Henningson et al., Vitamin A deficiency impairs the immune response to intranasal vaccination and RSV infection in neonatal calves, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-019-51684-x
Patel, Penkert, Jones, Sealy, Surman et al., Baseline serum vitamin A and D levels determine benefit of oral vitamin A&D supplements to humoral immune responses following pediatric influenza vaccination, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v11100907
Samad, Dutta, Sodunke, Fairuz, Sapkota et al., Fat-Soluble Vitamins and the Current Global Pandemic of COVID-19: Evidence-Based Efficacy from Literature Review, J Inflamm Res, doi:10.2147/JIR.S307333
Sarohan, COVID-19: endogenous retinoic acid theory and retinoic acid depletion syndrome, Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110250
Sommer, Vitamin a deficiency and clinical disease: An historical overview, J Nutr
Souza, Souza, Vitamin A for preventing secondary infections in children with measles-a systematic review, J Trop Pediatr, doi:10.1093/tropej/48.2.72.84
Stephensen, Lietz, Vitamin A in resistance to and recovery from infection: relevance to SARS-CoV2, Br J Nutr, doi:10.1017/S0007114521000246
Stephensen, Vitamin A, infection, and immune function, Annu Rev Nutr
Tanaka, Fujiwara, Torisu, Vitamin E and immune response I Enhancement of Helper T-Cell Activity by Dietary Supplementation of Vitamin E in Mice, Immunology
Tang, Liu, Zhang, Xu, Wen, Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: the current evidence and treatment strategies, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01708
Tepasse, Vollenberg, Fobker, Kabar, Schmidt et al., Vitamin A Plasma Levels in COVID-19 Patients: a prospective multicenter study and hypothesis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu13072173
Timoneda, Rodriguez-Fernandez, Zaragoza, Marin, Cabezuelo et al., Vitamin A Deficiency and the Lung
Wang, Li, Bai, Qi, Wang, Association Between Serum Vitamin A Levels and Recurrent Respiratory Tract Infections in Children, Front Pediatr, doi:10.3389/fped.2021.756217
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43168-023-00210-9",
"ISSN": [
"2314-8551"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s43168-023-00210-9",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Coronavirus disease 2019 can cause severe inflammation and damage to the lungs. Vitamins A and E are essential in the enhancement of immunity and they tend to decrease in cases with inflammation. Determination of serum levels of vitamins A and E in COVID-19 patients was the aim of the study.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>This case–control study was carried out on 30 ICU–admitted SARS-CoV-2–infected individuals (group A), 30 ward–admitted SARS-CoV-2–infected individuals (group B) and 30 healthy controls (group C). High-performance liquid chromatography was used to measure vitamin A and E levels.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Median levels of vitamin A in group A [0.16 (0.08–0.23) µg/ml] were significantly lower than those in group B [0.4 (0.15–0.65) µg/ml] and in group C [0.81 (0.70–1.16) µg/ml] with <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> value < 0.001, while there was no significant difference between groups concerning vitamin E levels (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> value = 0.535). Vitamin A deficiency showed significant correlation with lower hemoglobin levels, lower platelet counts, higher total leucocyte counts, higher C- reactive protein levels, and higher D-dimer levels. ROC curve construction showed that vitamin A level with cut off < 0.65 µg/ml increases risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) development with sensitivity 90% and specificity 83.3%. Logistic regression analysis showed that cases with vitamin A levels < 0.65 µg/ml were more prone to develop ARDS (OR = 0.003 [0.000–0.036] <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> < 0.001).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Levels of vitamin A were reduced in COVID-19 patients particularly in ICU–admitted cases. This ensures the association of decreased vitamin A with disease morbidity and the importance of vitamin A supplementation as part of disease management.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec><jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Trial registration</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Clinicaltrial.gov, NCT05946499. Registered 12 July 2023—Retrospectively registered. \n<jats:ext-link xmlns:xlink=\"http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink\" ext-link-type=\"uri\" xlink:href=\"https://register.clinicaltrials.gov/prs/app/action/SelectProtocol?sid=S000DGLS&selectaction=Edit&uid=U00070DC&ts=2&cx=gieusm\">https://register.clinicaltrials.gov/prs/app/action/SelectProtocol?sid=S000DGLS&selectaction=Edit&uid=U00070DC&ts=2&cx=gieusm</jats:ext-link>.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"210"
],
"article-number": "36",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "25 May 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "14 July 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "21 July 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The study has received approval from Cairo University's Faculty of Medicine's research ethics committee (approval number: MS-59–2020; date: 29/4/2020). Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mandour",
"given": "Iman Atef",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hussein",
"given": "Sabah Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanna",
"given": "Hany William Z.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdellatif",
"given": "Salma Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5900-5274",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fahmy",
"given": "Balsam Sherif",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Egyptian Journal of Bronchology",
"container-title-short": "Egypt J Bronchol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-21T11:02:06Z",
"timestamp": 1689937326000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-21T11:05:58Z",
"timestamp": 1689937558000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100002386",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Cairo University"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-22T04:48:15Z",
"timestamp": 1690001295881
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
21
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1689897600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1689897600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s43168-023-00210-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s43168-023-00210-9/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s43168-023-00210-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2",
"author": "MJ Cummings",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1763",
"issue": "10239",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "210_CR1",
"unstructured": "Cummings MJ, Baldwin MR, Abrams D, Jacobson SD, Meyer BJ, Balough EM et al (2020) Epidemiology, clinical course, and outcomes of critically ill adults with COVID-19 in New York City: a prospective cohort study. Lancet 395(10239):1763–1770. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31189-2. Epub 2020 May 19. PMID: 32442528; PMCID: PMC7237188",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01708",
"author": "Y Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1708",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "210_CR2",
"unstructured": "Tang Y, Liu J, Zhang D, Xu Z, Ji J, Wen C (2020) Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: the current evidence and treatment strategies. Front Immunol 10(11):1708. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.01708",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10091132",
"author": "J Timoneda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1132",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "210_CR3",
"unstructured": "Timoneda J, Rodriguez-Fernandez L, Zaragoza R, Marin MP, Cabezuelo MT, Torres L et al (2018) Vitamin A Deficiency and the Lung. Nutrients 10:1132",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/134.1.257S",
"author": "BP Chew",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "257S",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "210_CR4",
"unstructured": "Chew BP, Park JS (2004) Carotenoid action on the immune response. J Nutr 134:257S–261S",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm7090258",
"author": "Z Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "258",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "210_CR5",
"unstructured": "Huang Z, Liu Y, Qi G, Brand D, Zheng SG (2018) Role of Vitamin A in the Immune System. J Clin Med 7:258",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.1S3.1895",
"author": "S DE Flora",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "E34",
"issue": "1 Suppl 3",
"journal-title": "J Prev Med Hyg",
"key": "210_CR6",
"unstructured": "DE Flora S, Balansky R, LA Maestra S (2021) Antioxidants and COVID-19. J Prev Med Hyg 62(1 Suppl 3):E34–E45. https://doi.org/10.15167/2421-4248/jpmh2021.62.1S3.1895. PMID: 34622082; PMCID: PMC8452284. Italian",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"author": "C Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "934",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "China JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "210_CR7",
"unstructured": "Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Xia J, Zhou X, Xu S et al (2020) Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan. China JAMA Intern Med 180(7):934–943. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994. Erratum.In:JAMAInternMed.2020Jul1;180(7):1031.PMID:32167524;PMCID:PMC7070509",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13072173",
"author": "PR Tepasse",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2173",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "210_CR8",
"unstructured": "Tepasse PR, Vollenberg R, Fobker M, Kabar I, Schmidt H, Meier JA et al (2021) Vitamin A Plasma Levels in COVID-19 Patients: a prospective multicenter study and hypothesis. Nutrients 13(7):2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13072173. PMID:34202697;PMCID:PMC8308355",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104370",
"author": "F Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104370",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "210_CR9",
"unstructured": "Liu F, Li L, Xu M, Wu J, Luo D, Zhu Y et al (2020) Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with COVID-19. J Clin Virol 127:104370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104370. PMID: 32344321; PMCID: PMC7194648",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014",
"author": "H Ejaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1833",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "210_CR10",
"unstructured": "Ejaz H, Alsrhani A, Zafar A, Javed H, Junaid K, Abdalla AE et al (2020) COVID-19 and comorbidities: Deleterious impact on infected patients. J Infect Public Health 13(12):1833–1839. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014. Epub 2020 Aug 4. PMID: 32788073; PMCID: PMC7402107",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa601",
"author": "R Fadel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2114",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "210_CR11",
"unstructured": "Fadel R, Morrison AR, Vahia A, Smith ZR, Chaudhry Z, Bhargava P et al (2020) Early short-course corticosteroids in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. Clin Infect Dis 71(16):2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa601. PMID:32427279;PMCID:PMC7314133",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13145",
"author": "F Sanz Herrero",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "259",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "210_CR12",
"unstructured": "Sanz Herrero F, PuchadesGimeno F, Ortega García P, Ferrer Gómez C, OceteMochón MD, García Deltoro M (2021) Methylprednisolone added to tocilizumab reduces mortality in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: An observational study. J Intern Med 289(2):259–263. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.13145. PMID: 32603493; PMCID: PMC7361229",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/eci.13319",
"author": "DR Giacobbe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e13319",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Invest",
"key": "210_CR13",
"unstructured": "Giacobbe DR, Battaglini D, Ball L, Brunetti I, Bruzzone B, Codda G et al (2020) Bloodstream infections in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Eur J Clin Invest 50(10):e13319. https://doi.org/10.1111/eci.13319. PMID: 32535894; PMCID: PMC7323143",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/metabo11090565",
"author": "TM Tomasa-Irriguible",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "565",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Metabolites",
"key": "210_CR14",
"unstructured": "Tomasa-Irriguible TM, Bielsa-Berrocal L, Bordejé-Laguna L, Tural-Llàcher C, Barallat J, Manresa-Domínguez JM et al (2021) Low Levels of Few Micronutrients May Impact COVID-19 Disease Progression: an observational study on the first wave. Metabolites 11(9):565. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11090565. PMID:34564381;PMCID:PMC8467487",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "LB Berrocal",
"first-page": "26",
"key": "210_CR15",
"unstructured": "Berrocal LB, Irriguible TT, Philibert V, Llàcher CT, de Osaba JB, Domínguez JM et al (2020) Zinc and vitamin a deficiency predisposes to the need for intubation and icu admission in patients with COVID-19. An observational study. Research Square. p 26",
"volume-title": "Zinc and vitamin a deficiency predisposes to the need for intubation and icu admission in patients with COVID-19. An observational study. Research Square",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.nutr.21.1.167",
"author": "CB Stephensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "167",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Nutr",
"key": "210_CR16",
"unstructured": "Stephensen CB (2001) Vitamin A, infection, and immune function. Annu Rev Nutr 21:167–192",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1194/jlr.M600528-JLR200",
"author": "SH Gieng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "904",
"journal-title": "J Lipid Res",
"key": "210_CR17",
"unstructured": "Gieng SH, Green MH, Green JB, Rosales FJ (2007) Model-based compartmental analysis indicates a reduced mobilization of hepatic vitamin A during inflammation in rats. J Lipid Res 48:904–913",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.110.125500",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "210_CR18",
"unstructured": "Aklamati EK, Mulenga M, Dueker SR, Buchholz BA, Peerson JM, Kafwembe, et al. Accelerator mass spectrometry can be used to assess vitamin A metabolism quantitatively in boys in a community setting. J Nutr. 2010;140:1588–1594"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110250",
"author": "AR Sarohan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110250",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses",
"key": "210_CR19",
"unstructured": "Sarohan AR (2020) COVID-19: endogenous retinoic acid theory and retinoic acid depletion syndrome. Med Hypotheses 144:110250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110250",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0098-2997(03)00039-6",
"author": "HK Biesalski",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "431",
"journal-title": "Mol Aspects Med",
"key": "210_CR20",
"unstructured": "Biesalski HK, Nohr D (2003) Importance of vitamin-A for lung function and development. Mol Aspects Med 24:431–440",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/tropej/48.2.72.84",
"author": "RM D’Souza",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "72",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Trop Pediatr",
"key": "210_CR21",
"unstructured": "D’Souza RM, D’Souza R (2002) Vitamin A for preventing secondary infections in children with measles–a systematic review. J Trop Pediatr 48(2):72–77. https://doi.org/10.1093/tropej/48.2.72.84",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-51684-x",
"author": "JL McGill",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "15157",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "210_CR22",
"unstructured": "McGill JL, Kelly SM, Guerra-Maupome M, Winkley E, Henningson J, Narasimhan B et al (2019) Vitamin A deficiency impairs the immune response to intranasal vaccination and RSV infection in neonatal calves. Sci Rep 9(1):15157. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51684-x",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114521000246",
"author": "CB Stephensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1663",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr",
"key": "210_CR23",
"unstructured": "Stephensen CB, Lietz G (2021) Vitamin A in resistance to and recovery from infection: relevance to SARS-CoV2. Br J Nutr 126(11):1663–1672. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114521000246. Epub 2021 Jan 20. PMID: 33468263; PMCID: PMC7884725",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092550",
"author": "TH Jovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2550",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "210_CR24",
"unstructured": "Jovic TH, Ali SR, Ibrahim N, Jessop ZM, Tarassoli SP, Dobbs TD et al (2020) Could Vitamins Help in the Fight Against COVID-19? Nutrients 12(9):2550. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12092550",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31838/SRP.2021.1.33",
"author": "MM Al-Sumiadai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7347",
"journal-title": "Eurasia J Biosci",
"key": "210_CR25",
"unstructured": "Al-Sumiadai MM, Ghazzay H, Al-Dulaimy WZS (2020) Therapeutic effect of Vitamin A on severe COVID-19 patients. Eurasia J Biosci 14:7347–7350. https://doi.org/10.31838/SRP.2021.1.33",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01669-y",
"author": "S Fiorino",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2115",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Aging Clin Exp Res",
"key": "210_CR26",
"unstructured": "Fiorino S, Gallo C, Zippi M, Sabbatani S, Manfredi R, Moretti R et al (2020) Cytokine storm in aged people with CoV-2: possible role of vitamins as therapy or preventive strategy. Aging Clin Exp Res 32(10):2115–2131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-020-01669-y",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.306.6874.366",
"author": "PP Glasziou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "366",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "210_CR27",
"unstructured": "Glasziou PP, Mackerras DE (1993) Vitamin A supplementation in infectious diseases: A meta-analysis. BMJ 306:366–370",
"volume": "306",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/138.10.1835",
"author": "A Sommer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1835",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "210_CR28",
"unstructured": "Sommer A (2008) Vitamin a deficiency and clinical disease: An historical overview. J Nutr 138:1835–1839",
"volume": "138",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v11100907",
"author": "N Patel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "907",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "210_CR29",
"unstructured": "Patel N, Penkert RR, Jones BG, Sealy RE, Surman SL, Sun Y et al (2019) Baseline serum vitamin A and D levels determine benefit of oral vitamin A&D supplements to humoral immune responses following pediatric influenza vaccination. Viruses 11(10):907. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11100907",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.34172/ipp.2022.08",
"author": "A Hakamifard",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e08",
"journal-title": "Immunopathol Persa",
"key": "210_CR30",
"unstructured": "Hakamifard A, Soltani R, Maghsoudi A, Rismanbaf A, Aalinezhad M, Tarrahi MJ et al (2021) The effect of vitamin E and vitamin C in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia; a randomized controlled clinical trial. Immunopathol Persa 8:e08. https://doi.org/10.34172/ipp.2022.08",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111047",
"author": "A Gorji",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "111047",
"journal-title": "Nutrition",
"key": "210_CR31",
"unstructured": "Gorji A, Ghadiri MK (2021) Potential roles of micronutrient deficiency and immune system dysfunction in the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic. Nutrition 82:111047",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015",
"author": "R Jayawardena",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "367",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "210_CR32",
"unstructured": "Jayawardena R, Sooriyaarachchi P, Chourdakis M, Jeewandara C, Ranasinghe P (2020) Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: a review. Diabetes Metab Syndr 14(4):367–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "J Tanaka",
"first-page": "727",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "210_CR33",
"unstructured": "Tanaka J, Fujiwara H, Torisu M (1979) Vitamin E and immune response I Enhancement of Helper T-Cell Activity by Dietary Supplementation of Vitamin E in Mice. Immunology 38(4):727–734.146",
"volume": "38",
"year": "1979"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/iub.1976",
"author": "ED Lewis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "487",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "IUBMB Life",
"key": "210_CR34",
"unstructured": "Lewis ED, Meydani SN, Wu D (2019) Regulatory role of vitamin E in the immune system and inflammation. IUBMB Life 71(4):487–494. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1976",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JIR.S307333",
"author": "N Samad",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2091",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "J Inflamm Res",
"key": "210_CR35",
"unstructured": "Samad N, Dutta S, Sodunke TE, Fairuz A, Sapkota A, Miftah ZF et al (2021) Fat-Soluble Vitamins and the Current Global Pandemic of COVID-19: Evidence-Based Efficacy from Literature Review. J Inflamm Res 21(14):2091–2110. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S307333. PMID:34045883;PMCID:PMC8149275",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.111.023812",
"author": "A Duncan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "64",
"journal-title": "Am J Clin Nutr",
"key": "210_CR36",
"unstructured": "Duncan A, Talwar D, McMillan D, Stefanowicz F, O’Reilly DSJ (2011) Quantitative data on the magnitude of the systemic inflammatory response and its effect on micronutrient status based on plasma measurements. Am J Clin Nutr 95:64–71",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fped.2021.756217",
"author": "X Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "756217",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Front Pediatr.",
"key": "210_CR37",
"unstructured": "Wang X, Li X, Jin C, Bai X, Qi X, Wang J et al (2021) Association Between Serum Vitamin A Levels and Recurrent Respiratory Tract Infections in Children. Front Pediatr. 24(9):756217. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2021.756217. PMID: 35004539; PMCID: PMC8740126",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://ejb.springeropen.com/articles/10.1186/s43168-023-00210-9"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Earth and Planetary Sciences",
"General Environmental Science",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Evaluation of vitamin A and E deficiency with severity of SARS-COV-2 disease: a case–control study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "17"
}