The Effect of Vitamin C on Pathological Parameters and Survival Duration of Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.717816, IRCT20151226025699N5, Dec 2021
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000076 from 73 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 100 ICU patients in Iran, 31 treated with vitamin C, showing lower mortality with treatment.
This is the 9th of 20 COVID-19 RCTs for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0016.
This is the 36th of 73 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000076.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
very late stage, ICU patients.
|
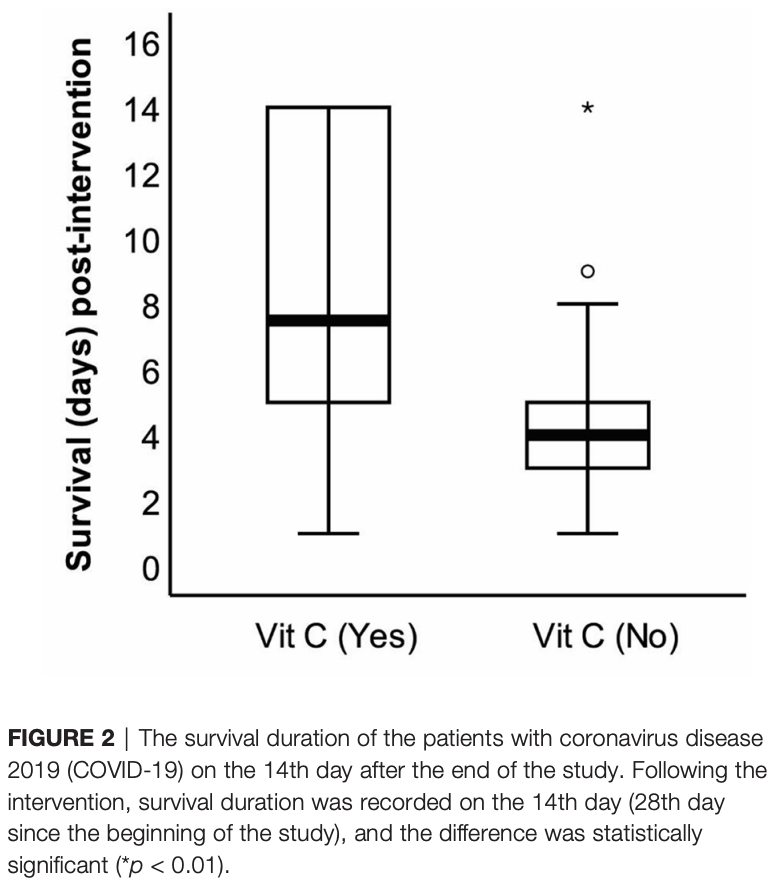
risk of death, 13.6% lower, RR 0.86, p = 0.03, treatment 26 of 31 (83.9%), control 67 of 69 (97.1%), NNT 7.6, day 28.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Majidi et al., 15 Dec 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 16 authors, study period May 2020 - July 2020, dosage 500mg days 1-14, trial IRCT20151226025699N5.
The Effect of Vitamin C on Pathological Parameters and Survival Duration of Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.717816
Conclusion: The present study demonstrated the potential of vitamin C supplementation in enhancing the survival duration of critically ill patients with COVID-19.
ETHICS STATEMENT The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Ethical code: IR.MEDSAB.REC.1399.195. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS NM, AH, SD, SG, SR, MG, FB, and NA designed the study and were involved in the data collection, analysis, and drafting of the manuscript. MA, BB, NA, AA, MSh, FS, AM, and KS were involved in the design of the study and analysis of the data and critically reviewed the manuscript. BB contributed to the data analysis and review of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
FUNDING The funding for this study was provided by Sabzevar University of Medical Sciences, Sabzevar, Iran (code 99213).
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Publisher's Note: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abobaker, Alzwi, Alraied, Overview of the Possible Role of Vitamin C in Management of COVID-19, Pharmacol Rep, doi:10.1007/s43440-020-00176-1
Abu-Raya, Predictors of Refractory Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pneumonia, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa409
Ahnach, Zbiri, Nejjari, Ousti, Elkettani, C-Reactive Protein as an Early Predictor of COVID-19 Severity, J Med Biochem, doi:10.5937/jomb0-27554
Biancatelli, Berrill, Catravas, Marik, Quercetin and Vitamin C: An Experimental, Synergistic Therapy for the Prevention and Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Related Disease (COVID-19), Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01451
Bourbour, Dahka, Gholamalizadeh, Akbari, Shadnoush et al., Nutrients in Prevention, Treatment, and Management of Viral Infections; Special Focus on Coronavirus, Arch Physiol Biochem, doi:10.1080/13813455.2020.1791188
Carr, A New Clinical Trial to Test High-Dose Vitamin C in Patients With COVID-19, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/s13054-020-02851-4
Cheng, Can Early and High Intravenous Dose of Vitamin C Prevent and Treat Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)?, Med Drug Discov, doi:10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100028
Cosler, Tal, Strategy and Statistics in Clinical Trials: A non-Statisticians Guide to Thinking, Designing and Executing
Covid Cd, Team, Covid, Team, Zhang, Geographic Differences in COVID-19 Cases, Deaths, and Incidence-United States, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report
Earar, Arbune, Dorobat, Rusu-Negraia, Stefanescu et al., Biochemical Effects and Therapeutic Application of Vitamin C (C6H8O6) on COVID-19 Infection, Rev Chim, doi:10.37358/RC.20.5.8159
Fowler Aa3rd, Truwit, Hite, Morris, Dewilde et al., Effect of Vitamin C Infusion on Organ Failure and Biomarkers of Inflammation and Vascular Injury in Patients With Sepsis and Severe Acute Respiratory Failure: The CITRIS-ALI Randomized Clinical Trial, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2019.11825
Fujii, Luethi, Young, Frei, Eastwood et al., Effect of Vitamin C, Hydrocortisone, and Thiamine vs Hydrocortisone Alone on Time Alive and Free of Vasopressor Support Among Patients With Septic Shock: The VITAMINS Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2019.22176
Hemilä, Chalker, Vitamin C can Shorten the Length of Stay in the ICU: A Meta-Analysis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11040708
Levine, Conry-Cantilena, Wang, Welch, Washko et al., Vitamin C Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Volunteers: Evidence for a Recommended Dietary Allowance, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.93.8.3704
Liu, Zhang, Weng, Yang, Fan, Association Between Average Plasma Potassium Levels and 30-Day Mortality During Hospitalization in Patients With COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, Int J Med Sci, doi:10.7150/ijms.50965
Liu, Zhu, Zhang, Li, Peng, Intravenous High-Dose Vitamin C for the Treatment of Severe COVID-19: Study Protocol for a Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039519
Lmasi-Hashiani, Doosti-Irani, Mansournia, Case Fatality Rate of COVID-19: Meta-Analysis Approach, Arch Iranian Med
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: Consider Cytokine Storm Syndromes and Immuno suppression, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0
Padayatty, Sun, Chen, Espey, Drisko et al., Vitamin C: Intravenous Use by Complementary and Alternative Medicine Practitioners and Adverse Effects, PloS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011414
Patterson, Cm, Fulzele, Low Level of Vitamin C and Dysregulation of Vitamin C Transporter Might be Involved in the Severity of COVID-19
Zhang, Rao, Li, Zhu, Liu et al., High-Dose Vitamin C Infusion for the Treatment of Critically Ill COVID-19, Ann Intensive Care, doi:10.1186/s13613-020-00792-3
Zou, Dai, Zhang, Zhang, Zhang, Hydroxychloroquine and Chloroquine: A Potential and Controversial Treatment for COVID-19, Arch Pharm Res, doi:10.1007/s12272-020-01258-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.717816",
"ISSN": [
"1664-3224"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.717816",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Introduction</jats:title><jats:p>Vitamin C has been reported to have beneficial effects on patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This study aimed to investigate the effect of vitamin C supplementation on pathological parameters and survival duration of critically ill patients with COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>This clinical trial was conducted on 120 hospitalized critically ill patients infected with COVID-19. The intervention group (n = 31) received one capsule of 500 mg of vitamin C daily for 14 days. The control group (n = 69) received the same nutrition except for vitamin C supplements. Measurement of pathological and biochemical parameters was performed at baseline and after 2 weeks of the intervention.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Following 2 weeks of vitamin C supplementation, the level of serum K was significantly lower in the patients compared with the control group (3.93 vs. 4.21 mEq/L, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> &lt; 0.01). Vitamin C supplementation resulted in a higher mean survival duration compared with that of the control group (8 vs. 4 days, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> &lt; 0.01). There was a linear association between the number of days of vitamin C intake and survival duration (B = 1.66, <jats:italic>p</jats:italic> &lt; 0.001). The vitamin C supplementation had no effect on blood glucose, mean arterial pressure, arterial blood gas (ABG) parameters, Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS), kidney function, cell blood count (CBC), hemoglobin (Hb), platelet (Plt), partial thromboplastin time (PTT), albumin, hematocrit (Hct), and other serum electrolytes including sodium (Na), calcium, and phosphorus (P).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>The present study demonstrated the potential of vitamin C supplementation in enhancing the survival duration of critically ill patients with COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Clinical Trial Registration</jats:title><jats:p><jats:uri>https://www.irct.ir/trial/55074</jats:uri>, identifier IRCT20151226025699N5</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fimmu.2021.717816"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Majidi",
"given": "Nazanin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rabbani",
"given": "Faezeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gholami",
"given": "Somayeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gholamalizadeh",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "BourBour",
"given": "Fatemeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rastgoo",
"given": "Samira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hajipour",
"given": "Azadeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shadnoosh",
"given": "Mahdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akbari",
"given": "Mohammad Esmail",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bahar",
"given": "Bojlul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ashoori",
"given": "Narjes",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alizadeh",
"given": "Atiyeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Samipoor",
"given": "Forough",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moslem",
"given": "Alireza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Doaei",
"given": "Saeid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suzuki",
"given": "Katsuhiko",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Frontiers in Immunology"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-15T04:58:25Z",
"timestamp": 1639544305000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-15T04:58:29Z",
"timestamp": 1639544309000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-16T06:44:05Z",
"timestamp": 1639637045910
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1664-3224"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-15T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1639526400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2021.717816/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.5937/jomb0-27554",
"article-title": "C-Reactive Protein as an Early Predictor of COVID-19 Severity",
"author": "Ahnach",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Biochem",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Geographic Differences in COVID-19 Cases, Deaths, and Incidence—United States, February 12–April 7, 2020. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report",
"author": "COVID",
"key": "B2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Case Fatality Rate of COVID-19: Meta-Analysis Approach",
"author": "lmasi-Hashiani",
"key": "B3",
"volume-title": "Arch Iranian Med",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12272-020-01258-7",
"article-title": "Hydroxychloroquine and Chloroquine: A Potential and Controversial Treatment for COVID-19",
"author": "Zou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Arch Pharm Res",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa409",
"article-title": "Predictors of Refractory Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pneumonia",
"author": "Abu-Raya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13813455.2020.1791188",
"article-title": "Nutrients in Prevention, Treatment, and Management of Viral Infections; Special Focus on Coronavirus",
"author": "BourBour",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Arch Physiol Biochem",
"key": "B6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.37358/RC.20.5.8159",
"article-title": "Biochemical Effects and Therapeutic Application of Vitamin C (C6H8O6) on COVID-19 Infection",
"author": "Earar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Rev Chim",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s43440-020-00176-1",
"article-title": "Overview of the Possible Role of Vitamin C in Management of COVID-19",
"author": "Abobaker",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-02851-4",
"article-title": "A New Clinical Trial to Test High-Dose Vitamin C in Patients With COVID-19",
"author": "Carr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "133",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medidd.2020.100028",
"article-title": "Can Early and High Intravenous Dose of Vitamin C Prevent and Treat Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100028",
"journal-title": "Med Drug Discov",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01451",
"article-title": "Quercetin and Vitamin C: An Experimental, Synergistic Therapy for the Prevention and Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Related Disease (COVID-19)",
"author": "Colunga Biancatelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0011414",
"article-title": "Vitamin C: Intravenous Use by Complementary and Alternative Medicine Practitioners and Adverse Effects",
"author": "Padayatty",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e11414",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"article-title": "Strategy and Statistics in Clinical Trials: A non-Statisticians Guide to Thinking, Designing and Executing",
"author": "Cosler",
"first-page": "267",
"key": "B13",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "High-Dose Vitamin C Infusion for the Treatment of Critically Ill COVID-19",
"author": "Zhang",
"first-page": "5",
"key": "B14",
"volume-title": "Ann Intensive Care",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11040708",
"article-title": "Vitamin C can Shorten the Length of Stay in the ICU: A Meta-Analysis",
"author": "Hemilä",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "708",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.93.8.3704",
"article-title": "Vitamin C Pharmacokinetics in Healthy Volunteers: Evidence for a Recommended Dietary Allowance",
"author": "Levine",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "93",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2019.11825",
"article-title": "Effect of Vitamin C Infusion on Organ Failure and Biomarkers of Inflammation and Vascular Injury in Patients With Sepsis and Severe Acute Respiratory Failure: The CITRIS-ALI Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Fowler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "322",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2019.22176",
"article-title": "Effect of Vitamin C, Hydrocortisone, and Thiamine vs Hydrocortisone Alone on Time Alive and Free of Vasopressor Support Among Patients With Septic Shock: The VITAMINS Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Fujii",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijms.50965",
"article-title": "Association Between Average Plasma Potassium Levels and 30-Day Mortality During Hospitalization in Patients With COVID-19 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "736",
"journal-title": "Int J Med Sci",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30628-0",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Consider Cytokine Storm Syndromes and Immunosuppression",
"author": "Mehta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039519",
"article-title": "Intravenous High-Dose Vitamin C for the Treatment of Severe COVID-19: Study Protocol for a Multicentre Randomised Controlled Trial",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14336/AD.2020.0918",
"article-title": "Low Level of Vitamin C and Dysregulation of Vitamin C Transporter Might be Involved in the Severity of COVID-19 Infection",
"author": "Patterson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Aging Dis",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "12",
"year": ""
}
],
"reference-count": 22,
"references-count": 22,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Front. Immunol."
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Immunology",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"The Effect of Vitamin C on Pathological Parameters and Survival Duration of Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "12"
}
