COVID-19 Disease as an Acute Angiotensin 1-7 Deficiency: A Preliminary Phase 2 Study with Angiotensin 1-7 in Association with Melatonin and Cannabidiol in Symptomatic COVID19 -Infected Subjects
et al., Journal of Infectiology, doi:10.29245/2689-9981/2018/2.1162, Dec 2020
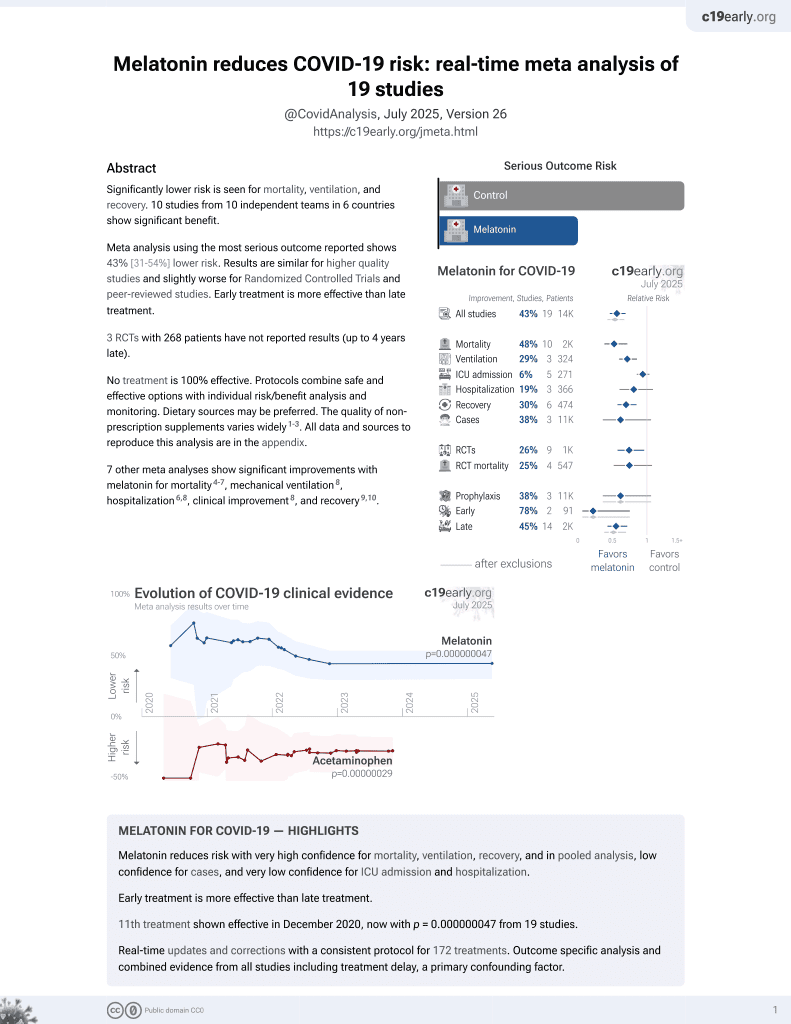
Melatonin for COVID-19
12th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.000000015 from 18 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
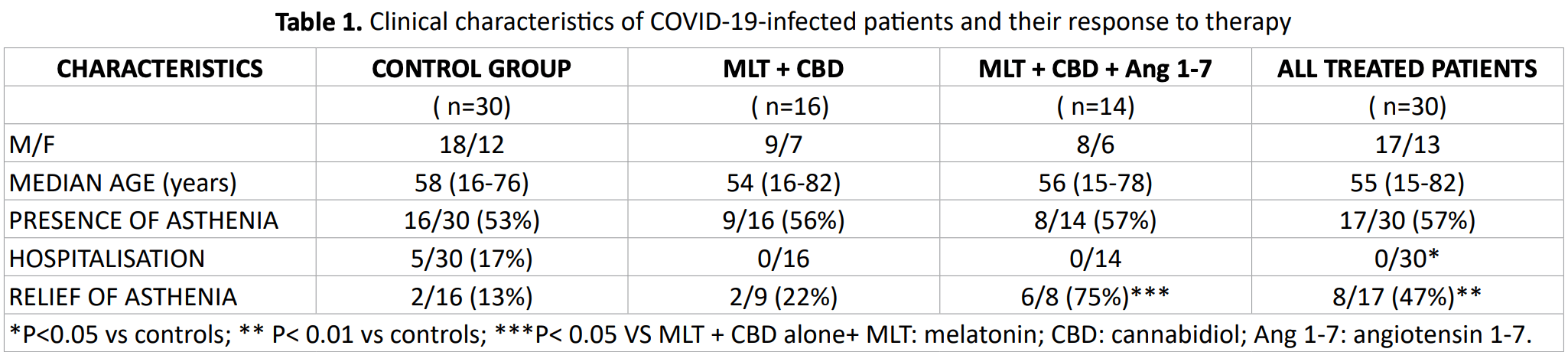
Small study with 30 patients treated with melatonin, cannabidiol, and for 14 patients angiotensin 1-7, compared with an age/sex matched control group during the same period, showing lower hospitalization with treatment.
|
risk of hospitalization, 90.9% lower, RR 0.09, p = 0.05, treatment 0 of 30 (0.0%), control 5 of 30 (16.7%), NNT 6.0, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Lissoni et al., 30 Dec 2020, prospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 14 authors, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with cannabidiol and angiotensin 1-7) - results of individual treatments may vary.
COVID-19 Disease as an Acute Angiotensin 1-7 Deficiency: A Preliminary Phase 2 Study with Angiotensin 1-7 in Association with Melatonin and Cannabidiol in Symptomatic COVID19 -Infected Subjects
COVID-19 disease is characterized by severe and acute immune alterations, consisting of an abnormal secretion of inflammatory cytokines, mainly IL-17, IL-6 and TNF-alpha, in association with decline in lymphocyte and increase in monocyte counts. ACE2 is the key for COVID19 entry into the cells. However, the link of viral spike protein to ACE2 receptor on cell surface would also block the ACE2 enzymatic activity itself, with a consequent diminished production of angiotensin 1-7 (Ang 1-7), which is provided by fundamental anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulant properties. Then, the severe and acute Ang 1-7 deficiency would allow an exaggerated cytokine-induced inflammatory response, endothelial damage, leak capillary syndrome and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Moreover, because of the documented connections occurring among ACE2, cannabinoid system and melatonin (MLT) secretion from the pineal gland, the block of ACE2 activity would also allow a concomitant deficiency of pineal-cannabinoid system axis, which plays a fundamental antiinflammatory role by inhibiting IL-17 secretion, one of the main cytokine involved in COVID19 infection. Therefore, COVID19-induced exaggerated inflammatory response could be controlled at least in part by correcting Ang 1-7, MLT and cannabinoid deficiency through their exogenous administration. On these bases, a study was planned in 30 COVID19-infected patients with initial or important symptomatology, 16 of whom orally treated by MLT (20 mg/day in the evening) plus cannabidiol (CBD) (10 mg x 2/day) only, while the other 14 patients received also Ang 1-7 (0.5 mg 2/day orally). The results were compared to those observed in a control group of 30 COVID-19 infected patient, who received the only supportive therapy. No hospitalisation for initial respiratory failure was required in the group of patients treated by the neuroimmune regimen. In addition, most patients referred a rapid disappearance of fever and myalgia, as well as a relief of asthenia, particularly in those concomitantly treated with Ang 1-7. On the contrary, 5/30 (17%) control patients required hospitalisation. The difference was statistically significant (0/30 vs 5/30, P< 0.05). This preliminary study would suggest that a neuroimmune approach consisting of MLT and CBD in association with Ang 1-7 is an effective and nontoxic regimen in the therapy of COVID19-related symptoms, which could also control the clinical evolution of disease and reduce the need of hospitalisation.
References
Capettini, Montecucco, Mach, Role of renin-angiotensin system in inflammation, immunity and aging, CurrPharmDes
Casillo, Mansour, Raucci, Could IL-17 represent a new therapeutic target for the treatment and/or management of COVID-19-related respiratory syndrome?, Pharmacol Res, doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104791
Fraga-Silva, Fp, Sousa, An orally active formulation of angiotensin-(1-7) produces an antithrombotic effects, Clinics
Grotenhermen, Pharmacology of cannabinoids, Neuroendocrinol Lett
Kryczek, Wei, Vatan, Cutting edge: opposite effects of IL-1 and IL-2 on the regulation of IL-17+ T cell pool IL-1 subverts IL-2-mediated suppression, J Immunol
Kuklina, Glebezdina, Nekrasovaiv, Role of melatonin in the regulation of differentiation of T cells producing interleukin-17 (Th17), Bull Exp Biol Med
Lanza, Perez, Costa, Covid-19: the renin-angiotensin system imbalance hypothesis, Clin Sci (Lond)
Li, Gu, Tu, Blockadeof interleukin-17 restrains the development of acute lung injury, Scand J Immunol, doi:10.1111/sji.12408
Lissoni, Rovelli, Messina, A review on the neuroendocrine regulation of cytokine secretion: possible modulation of the cytokine network by the pineal hormone melatonin and cannabidiol, Oncol Res Rev
Lissoni, Rovelli, Monzon, Evidence of abnormally low lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio in Covid-19-induced severe acute respiratory syndrome, J ImmunoAllerg
Lissoni, Rovelli, Pelizzoni, Coronavirus-induced severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) as a possible expression of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) hyper-function and possible therapeutic role of FAAH inhibitors in Covid 19-induced SARS, J Clin Res Rep, doi:10.31579/2690-1919/108
Madhur, Lob, Mccann, Interleukin17 promotes angiotensin II-induced hypertension and vascular dysfunction, Hypertension
Megna, Napolitano, Fabbrocini, May IL-17 have a role in COVID-19 infection?, Med Hypotheses
Nagarkatti, Pandey, Rieder, Cannabinoids as novel antiinflammatory drugs, Future Med Chem
Patel, Takawale, Ramprasath, Antagonism of angiotensin 1-7 prevents the therapeutic effects of recombinant human ACE2, J Mol Med
Peirò, Moncada, Substituting angiotensin-(1-7) to prevent lung damage in SARS-CoV-2 infection? Ciirculation
Ramlall, Zucker, Tatonetti, Melatonin is significantly associated with survival of intubated COVID-19 patients, Version, doi:10.1101/2020.10.15.20213546
Robert, Miossec, Effects of interleukin-17 on the cardiovascular system, Autoimmun Rev
Rodriguez-Prestes, Rocha, Miranda, The antiinflammatory potential of ACE2/Angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas receptor axis: evidence from basic and clinical research, Curr Drug Targets
Russo, Clinical endocannabinoid deficiency (CECD)
Santos, Sampaio, Alzamora, The ACE2/ Angiotensin-(1-7)/Mas axis of the renin-angiotensin system: focus on Angiotensin-(1-7), Physiol Res
Shete, Urgent need for evaluating agonists of angiotensin-(1-7)/ Mas receptor axis for treating patients with COVID-19, Int J Infect Dis
Verdecchia, Cavallini, Spanevello, The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur J Int Med