Efficacy and Safety of Aspirin, Promethazine, and Micronutrients for Rapid Clinical Recovery in Mild to Moderate COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
et al., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.25467, CTRI/2021/06/034254, May 2022
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
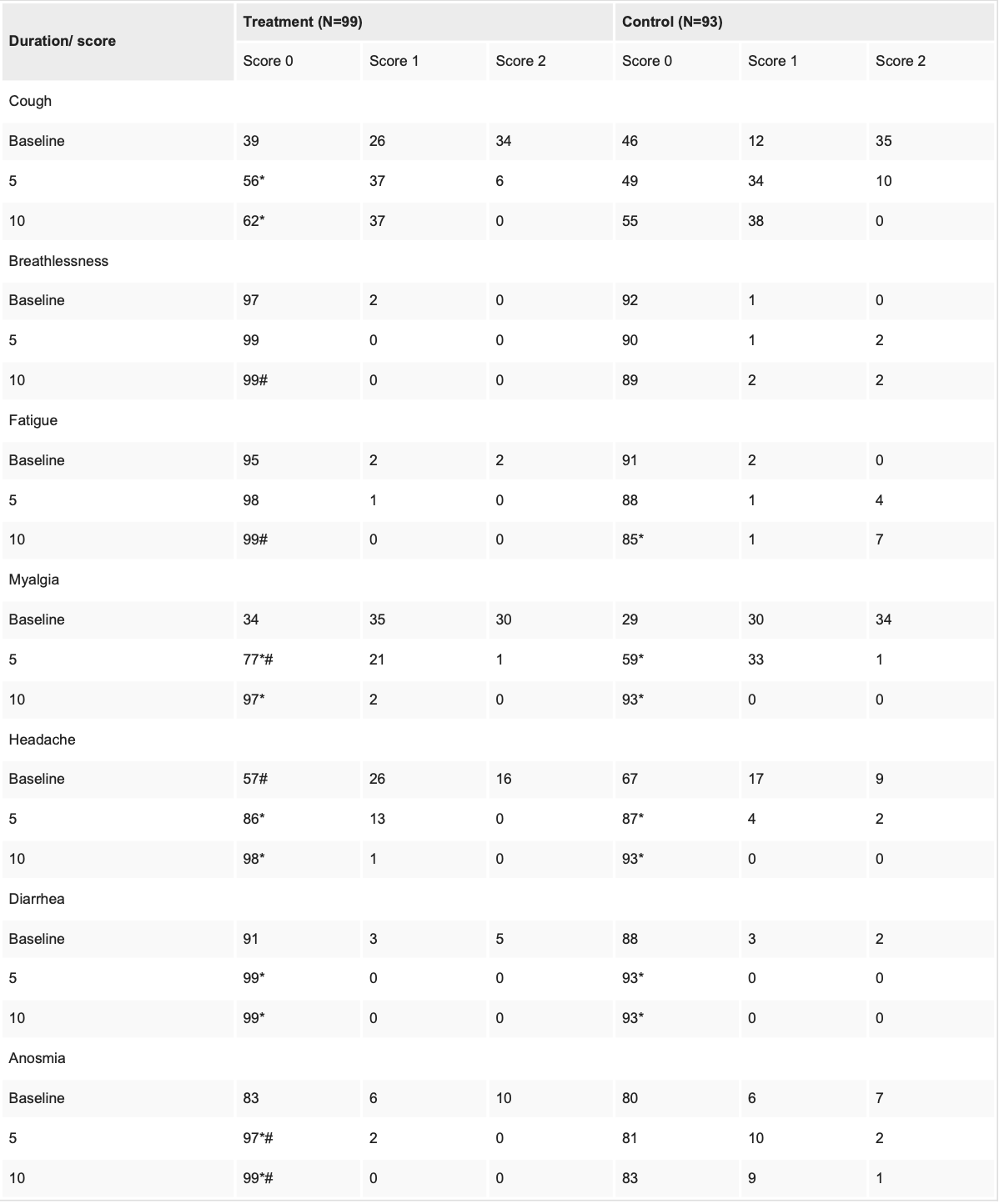
RCT 260 patients in India, 130 treated with aspirin, promethazine, vitamin C, D, B3, zinc, and selenium, showing faster recovery with treatment. There was no hospitalization, ICU admission, or supplemental oxygen requirements in either group.
|
risk of no recovery, 89.2% lower, RR 0.11, p = 0.05, treatment 0 of 99 (0.0%), control 4 of 93 (4.3%), NNT 23, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 10, dyspnea.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 95.4% lower, RR 0.05, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 99 (0.0%), control 10 of 93 (10.8%), NNT 9.3, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 10, anosmia.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 94.3% lower, RR 0.06, p = 0.003, treatment 0 of 99 (0.0%), control 8 of 93 (8.6%), NNT 12, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 10, fatigue.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 387.9% higher, RR 4.88, p = 0.50, treatment 2 of 99 (2.0%), control 0 of 93 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 10, myalgia.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 193.9% higher, RR 2.94, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 99 (1.0%), control 0 of 93 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 10, headache.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 8.5% lower, RR 0.91, p = 0.66, treatment 37 of 99 (37.4%), control 38 of 93 (40.9%), NNT 29, day 10, cough.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kumar et al., 30 May 2022, Randomized Controlled Trial, India, peer-reviewed, mean age 36.0, 8 authors, study period December 2021 - February 2022, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with aspirin, promethazine, vitamin C, D, B3, and selenium) - results of individual treatments may vary, trial CTRI/2021/06/034254.
Contact: vgvclinical@gmail.com.
Efficacy and Safety of Aspirin, Promethazine, and Micronutrients for Rapid Clinical Recovery in Mild to Moderate COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.25467
Introduction In the present study, the combination of two tablets, one with Aspirin and Promethazine and the other with vitamin D3, C, and B3 along with zinc and selenium supplementation was proposed as an intervention (APMV2020). The ingredients in the formulation represent a precise, tailored therapy for the symptoms of COVID-19, combined with natural constituents to help the body itself build immunity to recover from infection. The present study was conducted to clinically validate the safety and efficacy of the APMV2020 tablets.
Trial design The present trial is a randomized, multicentric, controlled clinical trial involving 260 mild to moderate COVID-19 patients. The treatment duration was of 10 days.
Methodology The subjects were randomized to receive either the control intervention (clinical management protocol for COVID-19 advocated by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) or the test intervention (treatment with APMV2020 tablets along with the standard control treatment. The assessment days were baseline, days five and 10.
Results APMV2020 significantly (<0.05) improved symptoms of COVID-19 like cough, myalgia, headache, and anosmia as compared to the control group. APMV2020 treatment also reduced inflammatory markers like lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), ferritin, and C-reactive protein (CRP).
Conclusion APMV2020 can prove as a good candidate to be integrated into the COVID-19 management protocol. As it can offer speedy clinical recovery to reduce the burden on healthcare infrastructure, second, the combination shows significant anti-inflammatory potential to improve prognosis, and lastly, the immunomodulatory properties offer long-term protection that can help in combating long COVID symptoms and complications.
Additional Information Disclosures Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Royal Pune Independent Ethics Committee, Pune, Maharashtra. issued approval CTRI/2021/06/034254. The study was approved by the Institutional ethics committee, Lokmanya Medical Research Centre, and Royal Pune Independent Ethics Committee and was registered with the Clinical Trial Registry of India (CTRI/2021/06/034254). Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of
References
Alam, Bhuiyan, Emon, Hasan, Prospects of nutritional interventions in the care of COVID-19 patients, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06285
Banoun, Evolution of SARS-CoV-2: review of mutations, role of the host immune system, Nephron, doi:10.1159/000515417
Becerra-Flores, Cardozo, SARS-CoV-2 viral spike G614 mutation exhibits higher case fatality rate, Int J Clin Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.13525
Calder, Nutrition and immunity: lessons for COVID-19, Nutr Diabetes, doi:10.1038/s41387-021-00165-0
Cantisani, Ricci, Grieco, Paolino, Faina et al., Topical promethazine side effects: our experience and review of the literature, Biomed Res Int, doi:10.1155/2013/151509
Carr, Rowe, The emerging role of vitamin C in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12113286
Chinni, El-Khoury, Perera, Zinc supplementation as an adjunct therapy for COVID-19: challenges and opportunities, Br J Clin Pharmacol, doi:10.1111/bcp.14826
Chow, Khanna, Kethireddy, Aspirin use is associated with decreased mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit admission, and in-hospital mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019, Anesth Analg, doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000005292
Khatiwada, Subedi, A mechanistic link between selenium and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Curr Nutr Rep, doi:10.1007/s13668-021-00354-4
Kumar, None, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.2546710of10
Lotfi, Akbarzadeh-Khiavi, Lotfi, Micronutrient therapy and effective immune response: a promising approach for management of COVID-19, Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-021-01644-3
Mahmud, Rahman, Rassel, Monayem, Sayeed et al., Post-COVID-19 syndrome among symptomatic COVID-19 patients: a prospective cohort study in a tertiary care center of Bangladesh, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0249644
Name, Souza, Vasconcelos, Prado, Pereira et al., perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2020.606398
Osuchowski, Winkler, Skirecki, It can be concluded that APMV2020 treatment for COVID-19 patients provides advantages over the standard of care treatment alone. There was a faster recovery of subjects from COVID-19 symptoms, along with a significant reduction in inflammatory markers like LDH ferritin, and CRP. This study serves as preliminary evidence for further research using aspirin, promethazine, vitamin D, C, and micronutrient therapy as an intervention in the management of long COVID symptoms, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00218-6
Shakoor, Feehan, Mikkelsen, Be well: a potential role for vitamin B in COVID-19, Maturitas, doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.08.007
Tay, Poh, Rénia, Macary, Ng, The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8
Wijaya, Andhika, Huang, Purwiga, Budiman, The effects of aspirin on the outcome of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Epidemiol Glob Health, doi:10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100883
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.25467",
"ISSN": [
"2168-8184"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.7759/cureus.25467",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Dr. G. Sunil",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vadgaonkar",
"given": "Dr.Atul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Purunaik",
"given": "Dr. Srilata",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shelatkar",
"given": "Rohit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vaidya",
"given": "Vidyadhar G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ganu",
"given": "Dr. Gayatri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vadgaonkar",
"given": "Dr. Aditya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Joshi",
"given": "Shashank",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Cureus",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-30T07:16:46Z",
"timestamp": 1653895006000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-30T07:16:48Z",
"timestamp": 1653895008000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2022-05-30T07:41:06Z",
"timestamp": 1653896466960
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
30
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/96829-efficacy-and-safety-of-aspirin-promethazine-and-micronutrients-for-rapid-clinical-recovery-in-mild-to-moderate-covid-19-patients-a-randomized-controlled-clinical-trial",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "4492",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.7759",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
5,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cureus, Inc.",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00218-6",
"article-title": "The COVID-19 puzzle: deciphering pathophysiology and phenotypes of a new disease entity",
"author": "Osuchowski MF",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Osuchowski MF, Winkler MS, Skirecki T, et al.. The COVID-19 puzzle: deciphering pathophysiology and phenotypes of a new disease entity. Lancet Respir Med. 2021, 9:622-42. 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00218-6",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.13525",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral spike G614 mutation exhibits higher case fatality rate",
"author": "Becerra-Flores M",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Clin Pract",
"key": "ref2",
"unstructured": "Becerra-Flores M, Cardozo T. SARS-CoV-2 viral spike G614 mutation exhibits higher case fatality rate. Int J Clin Pract. 2020, 74:e13525. 10.1111/ijcp.13525",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12113286",
"article-title": "The emerging role of vitamin C in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Carr AC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref3",
"unstructured": "Carr AC, Rowe S. The emerging role of vitamin C in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Nutrients. 2020, 12:10.3390/nu12113286",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000515417",
"article-title": "Evolution of SARS-CoV-2: review of mutations, role of the host immune system",
"author": "Banoun H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nephron",
"key": "ref4",
"unstructured": "Banoun H. Evolution of SARS-CoV-2: review of mutations, role of the host immune system. Nephron. 2021, 145:392-403. 10.1159/000515417",
"volume": "145",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100883",
"article-title": "The effects of aspirin on the outcome of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Wijaya I",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Epidemiol Glob Health",
"key": "ref5",
"unstructured": "Wijaya I, Andhika R, Huang I, Purwiga A, Budiman KY. The effects of aspirin on the outcome of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Epidemiol Glob Health. 2021, 12:100883. 10.1016/j.cegh.2021.100883",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1213/ANE.0000000000005292",
"article-title": "Aspirin use is associated with decreased mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit admission, and in-hospital mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Chow JH",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Anesth Analg",
"key": "ref6",
"unstructured": "Chow JH, Khanna AK, Kethireddy S, et al.. Aspirin use is associated with decreased mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit admission, and in-hospital mortality in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Anesth Analg. 2021, 132:930-41. 10.1213/ANE.0000000000005292",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2013/151509",
"article-title": "Topical promethazine side effects: our experience and review of the literature",
"author": "Cantisani C",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biomed Res Int",
"key": "ref7",
"unstructured": "Cantisani C, Ricci S, Grieco T, Paolino G, Faina V, Silvestri E, Calvieri S. Topical promethazine side effects: our experience and review of the literature. Biomed Res Int. 2013, 2013:151509. 10.1155/2013/151509",
"volume": "2013",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.14826",
"article-title": "Zinc supplementation as an adjunct therapy for COVID-19: challenges and opportunities",
"author": "Chinni V",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Br J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "ref8",
"unstructured": "Chinni V, El-Khoury J, Perera M, et al.. Zinc supplementation as an adjunct therapy for COVID-19: challenges and opportunities. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2021, 87:3737-46. 10.1111/bcp.14826",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0249644",
"article-title": "Post-COVID-19 syndrome among symptomatic COVID-19 patients: a prospective cohort study in a tertiary care center of Bangladesh",
"author": "Mahmud R",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "ref9",
"unstructured": "Mahmud R, Rahman MM, Rassel MA, Monayem FB, Sayeed SK, Islam MS, Islam MM. Post-COVID-19 syndrome among symptomatic COVID-19 patients: a prospective cohort study in a tertiary care center of Bangladesh. PLoS One. 2021, 16:e0249644. 10.1371/journal.pone.0249644",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8",
"article-title": "The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention",
"author": "Tay MZ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "ref10",
"unstructured": "Tay MZ, Poh CM, Rénia L, MacAry PA, Ng LF. The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020, 20:363-74. 10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2020.606398",
"article-title": "Zinc, vitamin D and vitamin C: perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity",
"author": "Name JJ",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "ref11",
"unstructured": "Name JJ, Souza AC, Vasconcelos AR, Prado PS, Pereira CP. Zinc, vitamin D and vitamin C: perspectives for COVID-19 with a focus on physical tissue barrier integrity. Front Nutr. 2020, 7:606398. 10.3389/fnut.2020.606398",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.08.007",
"article-title": "Be well: a potential role for vitamin B in COVID-19",
"author": "Shakoor H",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Maturitas",
"key": "ref12",
"unstructured": "Shakoor H, Feehan J, Mikkelsen K, et al.. Be well: a potential role for vitamin B in COVID-19. Maturitas. 2021, 144:108-11. 10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.08.007",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13668-021-00354-4",
"article-title": "A mechanistic link between selenium and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Khatiwada S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Curr Nutr Rep",
"key": "ref13",
"unstructured": "Khatiwada S, Subedi A. A mechanistic link between selenium and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Curr Nutr Rep. 2021, 10:125-36. 10.1007/s13668-021-00354-4",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s15010-021-01644-3",
"article-title": "Micronutrient therapy and effective immune response: a promising approach for management of COVID-19",
"author": "Lotfi F",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Infection",
"key": "ref14",
"unstructured": "Lotfi F, Akbarzadeh-Khiavi M, Lotfi Z, et al.. Micronutrient therapy and effective immune response: a promising approach for management of COVID-19. Infection. 2021, 49:1133-47. 10.1007/s15010-021-01644-3",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41387-021-00165-0",
"article-title": "Nutrition and immunity: lessons for COVID-19",
"author": "Calder PC",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutr Diabetes",
"key": "ref15",
"unstructured": "Calder PC. Nutrition and immunity: lessons for COVID-19. Nutr Diabetes. 2021, 11:19. 10.1038/s41387-021-00165-0",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06285",
"article-title": "Prospects of nutritional interventions in the care of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Alam S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "ref16",
"unstructured": "Alam S, Bhuiyan FR, Emon TH, Hasan M. Prospects of nutritional interventions in the care of COVID-19 patients. Heliyon. 2021, 7:e06285. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06285",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 16,
"references-count": 16,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cureus.com/articles/96829-efficacy-and-safety-of-aspirin-promethazine-and-micronutrients-for-rapid-clinical-recovery-in-mild-to-moderate-covid-19-patients-a-randomized-controlled-clinical-trial"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Aerospace Engineering"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy and Safety of Aspirin, Promethazine, and Micronutrients for Rapid Clinical Recovery in Mild to Moderate COVID-19 Patients: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article"
}
kumar3
