Structural basis for small molecule binding to the SARS-CoV-2 nsp10–nsp14 ExoN complex
et al., Nucleic Acids Research, doi:10.1093/nar/gkaf753, Aug 2025
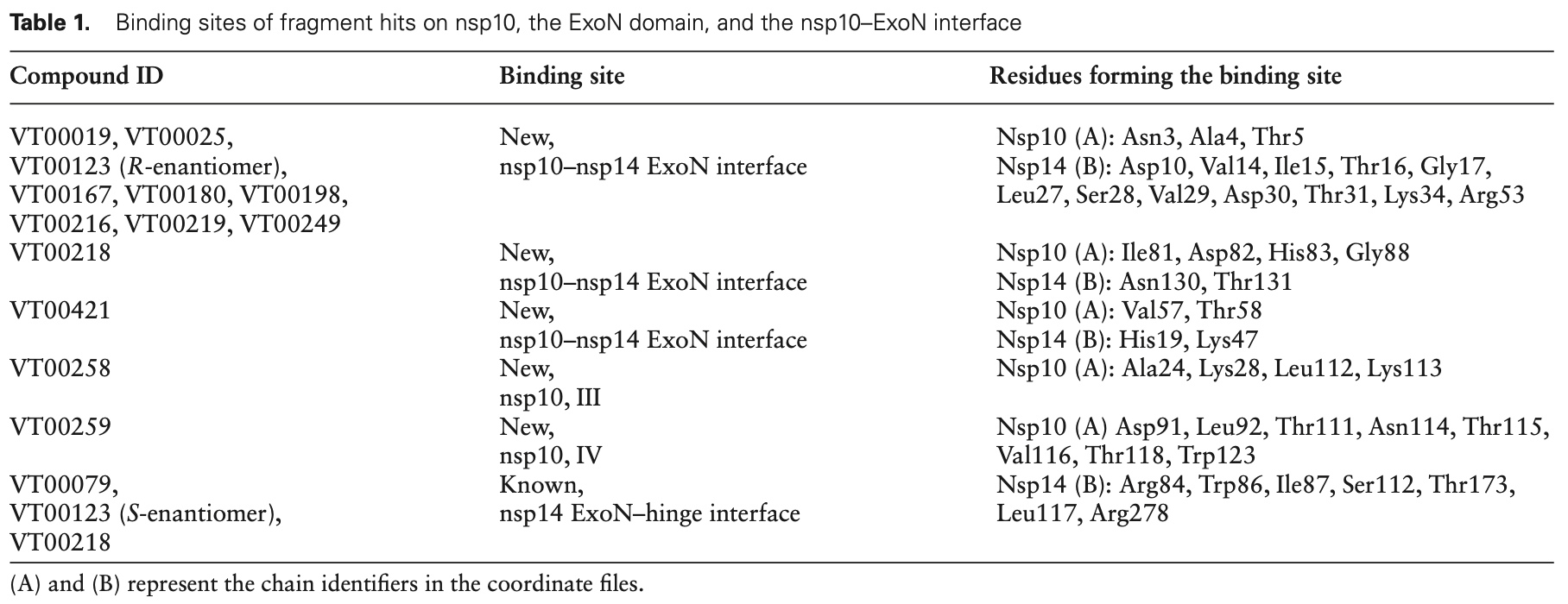
In vitro and crystallographic study identifying 14 small molecule fragments that bind to novel sites in the SARS-CoV-2 nsp10-nsp14 ExoN complex, potentially inhibiting viral proofreading activity that causes resistance to nucleoside analogue drugs.
Kozielski et al., 5 Aug 2025, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Structural basis for small molecule binding to the SARS-CoV-2 nsp10-nsp14 ExoN complex
doi:10.1093/nar/gkaf753
Coronavirus outbreaks have occurred over the past 25 years with SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2) causing a global pandemic. T he SAR S-CoV-2 non-str uct ural proteins 10 (nsp10) and 1 4 (nsp1 4) are considered as potential drug targets. Nsp10 stimulates the 3to-5 e x oribonuclease (Ex oN) activity of nsp14. The ExoN domain excises mis-incorporated nucleotides from the nascent RNA chain and therefore causes resistance to nucleoside analogue drugs. We cry stalliz ed the nsp10-nsp14 Ex oN comple x in distinct space groups, allowing us to describe conformational changes. In particular, the general base, His268, classifying the ExoN domain as a member of the DEDDh family, is trapped in the inactive and active orientations. By X-ray fragment screening, we identified five novel fragment binding sites in the nsp10-nsp14 interface, the hinge region connecting ExoN and N7 -methyltransf erase domains, and on nsp10. One new site in the nsp10-nsp14 interface accommodates nine str uct urally and chemically related hits, providing an initial str uct ure-activity relationship st udy. We could also identify enantiomers of one fragment selectively bound to two different binding sites. The binding affinities of fragment hits were estimated using microscale thermophoresis and the new sites were investigated for their potential to inhibit protein-protein interactions between nsp10 and nsp14. Our fragments represent no v el starting points for hit development by str uct ure-based design.
Supplementary data Supplementary data is available at NAR online.
Conflict of interest None declared.
References
Abbasian, Mahmanzar, Rahimian, Global landscape of S AR S-CoV-2 mutations and conserved regions, J Transl Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-023-03996-w
Afonine, Grosse-Kunstleve, Echols, Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.Refine, Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, doi:10.1107/S0907444912001308
Agirre, Atanasova, Bagdonas, The CCP 4 suite: integrative software for macromolecular crystallography, Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol, doi:10.1107/S2059798323003595
Agostini, Andres, Sims, Coronavirus susceptibility to the antiviral remdesivir (GS-5734) is mediated by the viral polymerase and the proofreading exoribonuclease, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.00221-00218
Bancet, Raingeval, Lomberget, Fragment linking strategies for structure-based drug design, J Med Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.0c00242
Bouvet, Imbert, Subissi, RNA 3 -end mismatch excision by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus nonstructural protein nsp10 / nsp14 exoribonuclease complex, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1201130109
Chen, Cai, Pan, Functional screen reveals S AR S coronavirus nonstructural protein nsp14 as a novel cap N7 methyltransferase, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.0808790106
Chen, Guo, Molecular mechanisms of coronavirus RNA capping and methylation, Virol Sin, doi:10.1007/s12250-016-3726-4
Chen, Zhou, Wei, Development of pan-anti-S AR S-CoV-2 agents through allosteric inhibition of nsp14 / nsp10 complex, ACS Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1021/acsinfecdis.3c00356
Chinthapatla, Sotoudegan, Srivastava, Interfering with nucleotide excision by the coronavirus 3 -to-5 exoribonuclease, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkac1177
Czarna, Plewka, Kresik, Refolding of lid subdomain of S AR S-CoV-2 nsp14 upon nsp10 interaction releases exonuclease activity, Structure, doi:10.1016/j.str.2022.04.014
De Silva, Choudhury, Bailey, The crystal structure of TREX1 explains the 3 nucleotide specificity and reveals a polyproline II helix for protein partnering, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M700039200
De Zitter, Coquelle, Oeser, Xtrapol8 enables automatic elucidation of low-occupancy intermediate-states in crystallographic studies, Commun Biol, doi:10.1038/s42003-022-03575-7
Emsley, Lohkamp, Scott, Features and development of Coot, Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, doi:10.1107/S0907444910007493
Evans, Murshudov, How good are my data and what is the resolution?, Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, doi:10.1107/S0907444913000061
Ferron, Subissi, Morais, Structural and molecular basis of mismatch correction and ribavirin excision from coronavirus RNA, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1718806115
Hsiao, Yang, Lin, Structural basis for RNA trimming by RNase T in stable RNA 3 -end maturation, Nat Chem Biol, doi:10.1038/nchembio.524
Hsu, Laurent-Rolle, Pawlak, Translational shutdown and evasion of the innate immune response by S AR S-CoV-2 NSP14 protein, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2101161118
Huang, Hsu, Chu, Identification of inhibitors for the DEDDh family of exonucleases and a unique inhibition mechanism by crystal structure analysis of CRN-4 bound with 2-morpholin-4-ylethanesulfonate (MES), J Med Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00794
Imprachim, Yosaatmadja, Newman, Crystal structures and fragment screening of S AR S-CoV-2 NSP14 reveal details of exoribonuclease activation and mRNA capping and provide starting points for antiviral drug development, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkac1207
Jiang, Tong, Yao, Genome-wide analysis of protein-protein interactions and involvement of viral proteins in S AR S-CoV-2 replication, Cell Biosci, doi:10.1186/s13578-021-00644-y
Kabinger, Stiller, Schmitzová, Mechanism of molnupiravir-induced S AR S-CoV-2 mutagenesis, Nat Struct Mol Biol
Kabsch, Xds, None, Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, doi:10.1107/S0907444909047337
Knecht, Fisher, Lou, Oligomeric State of β-coronavirus non-structural protein 10 stimulators studied by small angle X-ray scattering, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms241713649
Kozielski, Sele, Vo, Identification of fragments binding to S AR S-CoV-2 nsp10 reveals ligand-binding sites in conserved interfaces between nsp10 and nsp14 / nsp16, RSC Chem Biol, doi:10.1039/D1CB00135C
Krafcikova, Silhan, Nencka, Structural analysis of the S AR S-CoV-2 methyltransferase complex involved in RNA cap creation bound to sinefungin, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17495-9
Li, Coupling of N7-methyltransferase and 3 -5 exoribonuclease with S AR S-CoV-2 polymerase reveals mechanisms for capping and proofreading, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.033
Li, Hilgenfeld, Whitley, Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: progress and lessons learned, Nat Rev Drug Discov, doi:10.1038/s41573-023-00672-y
Lima, Talibov, Jagudin, FragMAX: the fragment-screening platform at the MAX IV Laboratory, Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol, doi:10.1107/S205979832000889X
Lin, Chen, Chen, Crystal structure of S AR S-CoV-2 nsp10 bound to nsp14-ExoN domain reveals an exoribonuclease with both structural and functional integrity, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkab320
Liu, Shi, Becker, Structural basis of mismatch recognition by a S AR S-CoV-2 proofreading enzyme, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abi9310
Long, Nicholls, Emsley, AceDRG: a stereochemical description generator for ligands, Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol, doi:10.1107/S2059798317000067
Ma, Wu, Shaw, Structural basis and functional analysis of the S AR S coronavirus nsp14-nsp10 complex, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1508686112
Mccoy, Grosse-Kunstleve, Adams, Phaser crystallographic software, J Appl Crystallogr, doi:10.1107/S0021889807021206
Moeller, Shi, Demir, Structure and dynamics of S AR S-CoV-2 proofreading exoribonuclease ExoN, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2106379119
Moghadasi, Heilmann, Khalil, Transmissible S AR S-CoV-2 variants with resistance to clinical protease inhibitors, Sci Adv, doi:10.1126/sciadv.ade8778
Murshudov, Skubák, Lebedev, REFMAC5 for the refinement of macromolecular crystal structures, Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, doi:10.1107/S0907444911001314
Ogando, Zevenhoven-Dobbe, Der Meer, The enzymatic activity of the nsp14 exoribonuclease is critical for replication of MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01246-20
Pearce, Krojer, Bradley, A multi-crystal method for extracting obscured crystallographic states from conventionally uninterpretable electron density, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/ncomms15123
Pruijssers, Denison, Nucleoside analogues for the treatment of coronavirus infections, Curr Opin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2019.04.002
Rogstam, Nyblom, Christensen, Crystal structure of non-structural protein 10 from severe acute Respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms21197375
Saramago, Bárria, Costa, New targets for drug design: importance of nsp14 / nsp10 complex formation for the 3 -5 exoribonucleolytic activity on S AR S-CoV-2, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15815
Sele, Krupinska, Rasmussen, New insights into complex formation by S AR S-CoV-2 nsp10 and nsp14, Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids
Shannon, Canard, Kill or corrupt: mechanisms of action and drug-resistance of nucleotide analogues against S AR S-CoV-2, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105501
Subissi, Imbert, Ferron, S AR S-CoV ORF1b-encoded nonstructural proteins 12-16: replicative enzymes as antiviral targets, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.11.006
Tompa, Immanuel, Srikanth, Trends and strategies to combat viral infections: a review on FDA approved antiviral drugs, Int J Biol Macromol, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.076
Ursby, Åhnberg, Appio, BioMAX-the first macromolecular crystallography beamline at MAX IV Laboratory, J Synchrotron Radiat, doi:10.1107/S1600577520008723
Viswanathan, Arya, Chan, Structural basis of RNA cap modification by S AR S-CoV-2, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17496-8
Vonrhein, Flensburg, Keller, Data processing and analysis with the autoPROC toolbox, Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr, doi:10.1107/S0907444911007773
Wang, Rizvi, Dong, Emerging variants of S AR S-CoV-2 NSP10 highlight strong functional conservation of its binding to two non-structural proteins, NSP14 and NSP16, eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.87884.3
Wu, Peng, Huang, Genome composition and divergence of the novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) originating in China, Cell Host Microbe, doi:10.1016/j.chom.2020.02.001
Yu, Modugula, Ichihara, General theory of fragment linking in molecular design: why fragment linking rarely succeeds and how to improve outcomes, J Chem Theory Comput, doi:10.1021/acs.jctc.0c01004
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkaf753",
"ISSN": [
"1362-4962"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf753",
"container-title": "Nucleic Acids Research",
"container-title-short": "nar",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-27T12:44:10Z",
"timestamp": 1756298650000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-27T12:44:10Z",
"timestamp": 1756298650000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-27T13:10:01Z",
"timestamp": 1756300201312,
"version": "3.44.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
8
]
]
},
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/53/14/gkaf753/8222438"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Structural basis for small molecule binding to the SARS-CoV-2 nsp10–nsp14 ExoN complex",
"type": "journal-article"
}