Antiandrogen agents in COVID-19: a meta-analysis of randomized trials
et al., Minerva Medica, doi:10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5, Aug 2022 (preprint)
7th treatment shown to reduce risk in
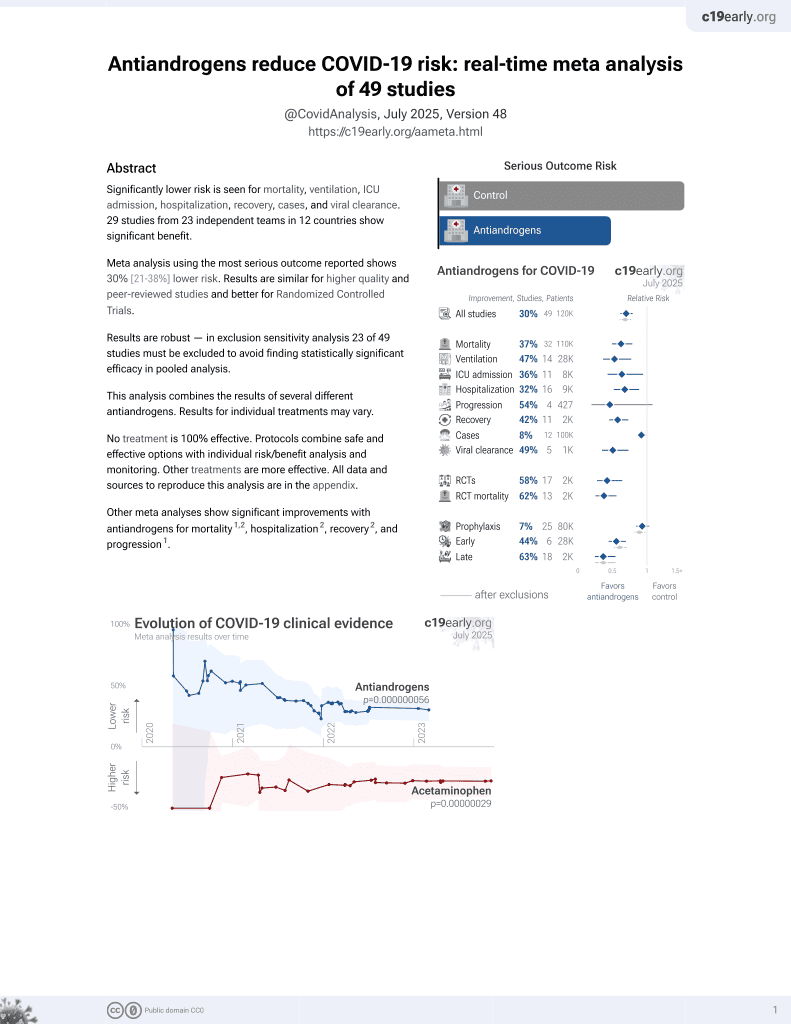
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000056 from 49 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
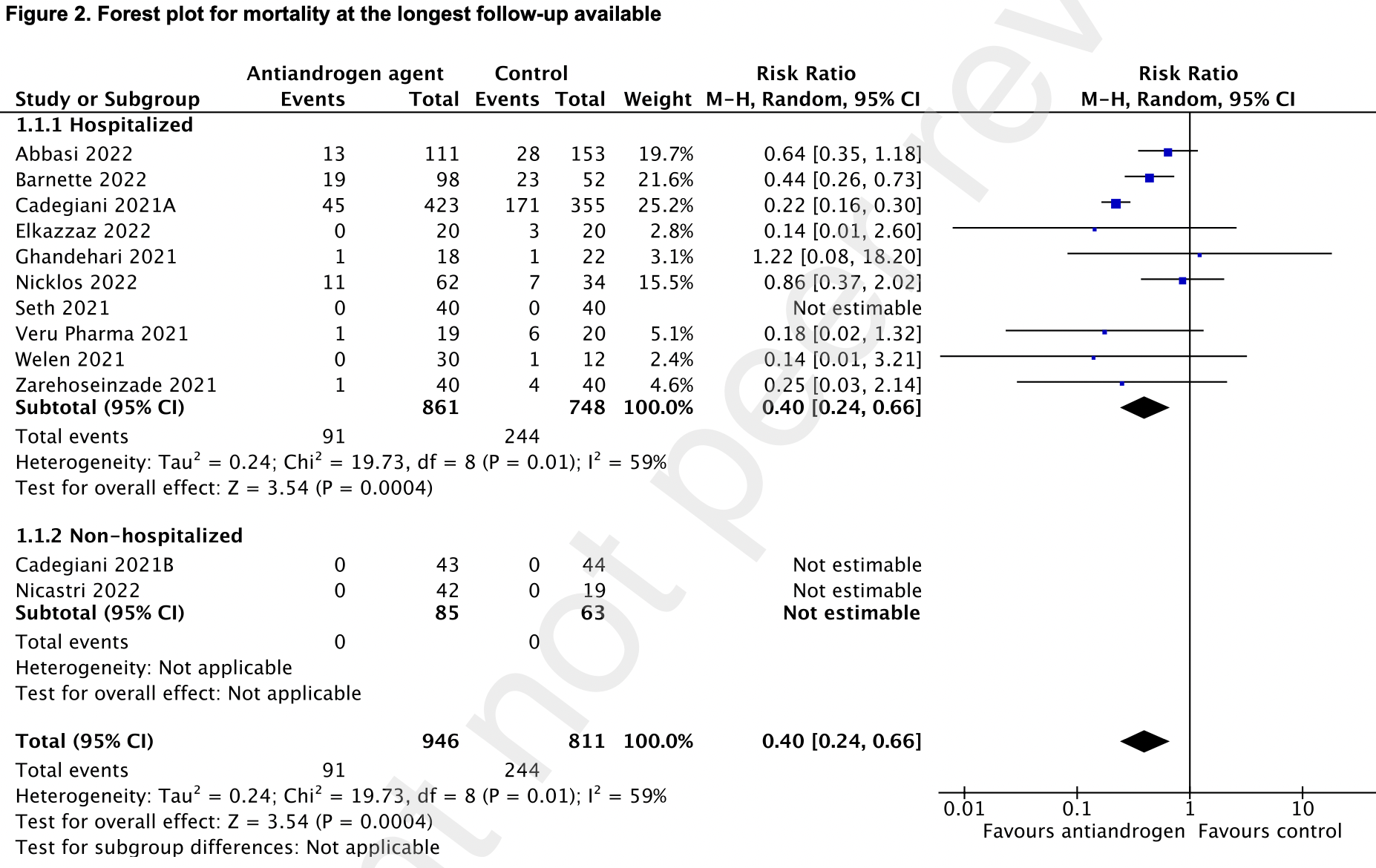
Meta analysis of 12 studies, showing significantly lower mortality with antiandrogen treatment.
2 meta-analyses show significant improvements with antiandrogens for mortality1,2,
hospitalization2,
recovery2, and
progression1.
Currently there are 49 antiandrogens for COVID-19 studies, showing 37% lower mortality [21‑50%], 47% lower ventilation [23‑64%], 36% lower ICU admission [5‑57%], 32% lower hospitalization [11‑48%], and 8% fewer cases [1‑14%].
|
risk of death, 60.0% lower, RR 0.40, p < 0.001.
|
|
risk of progression, 53.0% lower, RR 0.47, p = 0.003.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kotani et al., 4 Aug 2022, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Contact: landoni.giovanni@hsr.it.
antiandrogen agents reduced mortality at the longest follow-up available (91/946 [9•6%] vs 244/811 [30%]; risk ratio (RR) = 0•40; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0•24-0•66; P = 0•0004; low certainty of evidence; I 2 =59%). Antiandrogen therapy also reduced clinical worsening (125/941 [13%] vs 279/809 [35%]; RR = 0•47; 95% CI, 0•29-0•78; P = 0•003; low certainty of evidence; I 2 =72%). There was no significant difference in the need for invasive mechanical ventilation, admission to the intensive care unit, the need for hospitalization, or thrombotic events between the two treatment groups.
Interpretation Antiandrogen therapy reduced mortality and clinical worsening in adult patients with COVID-19.
References
Abbasi, Adatorwovor, Davarpanah, A Randomized Trial of Sitagliptin and Spironolactone With Combination Therapy in Hospitalized Adults With COVID-19, J Endocr Soc
Barnette, Gordon, Rodriguez, Oral Sabizabulin for High-Risk, Hospitalized Adults with Covid-19: Interim Analysis, NEJM Evidence
Cadegiani, Mccoy, Wambier, Goren, Early Antiandrogen Therapy With Dutasteride Reduces Viral Shedding, Inflammatory Responses, and Time-to-Remission in Males With COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Interventional Trial (EAT-DUTA AndroCoV Trial -Biochemical), Cureus
Cadegiani, Zimerman, Fonseca, Final Results of a
Dambha-Miller, Hinton, Wilcox, Joy, Feher et al., Mortality in COVID-19 among women on hormone replacement therapy: a retrospective cohort study, Family Practice
Davey, Grossmann, Androgen Receptor Structure, Function and Biology: From Bench to Bedside, Clin Biochem Rev
Deng, Ru, Russell, Natesan, Asangani, Targeting androgen regulation of TMPRSS2 and ACE2 as a therapeutic strategy to combat COVID-19
Elkazzaz, Abo-Amer, Haydara, 13 cis retinoic acid improved the outcomes of COVID-19 patients. A randomized clinical trial, medRxiv
Ghandehari, Matusov, Pepkowitz, Controlled Pilot Trial
Guyatt, Oxman, Vist, GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations, BMJ
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell
Huang, Li, Gu, Health outcomes in people 2 years after surviving hospitalisation with COVID-19: a longitudinal cohort study, The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Lakbar, Luque-Paz, Mege, Einav, Leone, COVID-19 gender susceptibility and outcomes: A systematic review, PLoS One
Lyon, Li, Cullen, 5α-Reductase Inhibitors Are Associated with Reduced Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Matched-Pair, Registry-Based Analysis, J Urol
Meng, Ge, Li, Protective trend of anti-androgen therapy during the COVID-19 pandemic: A meta-analysis, The Journal of infection
Montopoli, Zumerle, Vettor, Androgen-deprivation therapies for prostate cancer and risk of infection by SARS-CoV-2: a population-based study (N = 4532), Annals of oncology : official journal of the European Society for Medical Oncology
Nguyen, Chinn, De Ferrante, Kirby, Hohmann et al., Male gender is a predictor of higher mortality in hospitalized adults with COVID-19, PLoS One
Nicastri, Marinangeli, Pivetta, A phase 2 randomized, doubleblinded, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of raloxifene for patients with mild to moderate COVID-19, eClinicalMedicine
Nickols, Dematt, Effect of Androgen Suppression on Clinical Outcomes in Hospitalized Men With COVID-19: The HITCH Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Netw Open
Nielsen, Nørgaard, Lanzieri, Vestergaard, Moelbak, Sexdifferences in COVID-19 associated excess mortality is not exceptional for the COVID-19 pandemic, Scientific Reports
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ
Peckham, De Gruijter, Raine, Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission, Nature Communications
Pharma, Veru Announces Oral Late-Breaking Presentation of Phase 2
Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Two-Arm, Parallel Clinical Trial of Proxalutamide for Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients: A Multiregional, Joint Analysis of the Proxa-Rescue AndroCoV Trial, Cureus
Seth, Sharma, Mishra, Solanki, Singh et al., Role of Short-Term Estradiol Supplementation in Symptomatic Postmenopausal COVID-19 Females: A Randomized Controlled Trial, J Midlife Health
Sterne, Savović, Page, RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ
Welén, Rosendal, Gisslén, A Phase 2 Trial of the Effect of Antiandrogen Therapy on COVID-19 Outcome: No Evidence of Benefit, Supported by Epidemiology and In Vitro Data, Eur Urol
Zarehoseinzade, Allami, Ahmadi, Bijani, Mohammadi, Finasteride in hospitalized adult males with COVID-19: A risk factor for severity of the disease or an adjunct treatment: A randomized controlled clinical trial, Med J Islam Repub Iran
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.23736/s0026-4806.23.08538-5",
"ISSN": [
"0026-4806",
"1827-1669"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "KOTANI",
"given": "Yuki",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "LANDONI",
"given": "Giovanni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "SCQUIZZATO",
"given": "Tommaso",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "MOHAMED",
"given": "Nadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "BAIARDO REDAELLI",
"given": "Martina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "SOFIA",
"given": "Rosaria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "FRESILLI",
"given": "Stefano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "ZANGRILLO",
"given": "Alberto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "AZZOLINI",
"given": "Maria L.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Minerva Medica",
"container-title-short": "Minerva Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-19T15:27:35Z",
"timestamp": 1684510055000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-21T09:06:18Z",
"timestamp": 1711011978000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-22T00:39:47Z",
"timestamp": 1711067987202
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1"
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.minervamedica.it/pdf.php?cod=R10Y2024N01A0037",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "17149",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.23736",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Edizioni Minerva Medica",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref001",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard; [Internet]. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/ [cited 2023, Jan 16]."
},
{
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref002",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Living guidance for clinical management of COVID-19; [Internet]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-2019-nCoV-clinical-2021-2 [cited 2022, Jun 8]."
},
{
"key": "#cr-split#-10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref003.1",
"unstructured": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National Institutes of Health"
},
{
"key": "#cr-split#-10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref003.2",
"unstructured": "[Internet]. Available from: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/ [cited 2022, Jun 27]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00126-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref005"
},
{
"article-title": "Androgen Receptor Structure, Function and Biology: From Bench to Bedside",
"author": "Davey RA",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Clin Biochem Rev",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref006",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2021.102254",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.479",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/JU.0000000000002180",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0241827",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n71",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.l4898",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jendso/bvac017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/EVIDoa2200145",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.13047",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7759/cureus.20691",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2022.03.05.22271959",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chest.2021.02.024",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101450",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.7852",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/jmh.JMH_57_21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.17925/USRPD.2022.7.2.32",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref023",
"unstructured": "Pharma V. Veru Announces Oral Late-Breaking Presentation of Phase 2 Data of Sabizabulin for the Treatment of Hospitalized Severe COVID-19 Patients at High Risk for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome at the 32nd European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. 2022."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eururo.2021.12.013",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.47176/mjiri.35.30",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.07.06.21260086",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref026"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref027"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-00213-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref028"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0254066",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref029"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/fampra/cmac041",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref030"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.03.020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref031"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-215383",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref032"
},
{
"article-title": "Antiandrogen activity of drugs for COVID-19. The case of sabizabulin",
"author": "Kotani Y",
"first-page": "ahead of print",
"journal-title": "Signa Vitae",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref033",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2023.2179035",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10.23736/S0026-4806.23.08538-5_ref034"
}
],
"reference-count": 35,
"references-count": 35,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.minervamedica.it/index2.php?show=R10Y2024N01A0037"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Antiandrogen agents in COVID-19: a meta-analysis of randomized trials",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "115"
}