Post-COVID-19 complications in home and hospital-based care: A study from Dhaka city, Bangladesh
et al., Frontiers in Rehabilitation Sciences, doi:10.3389/fresc.2022.1037649, Nov 2022
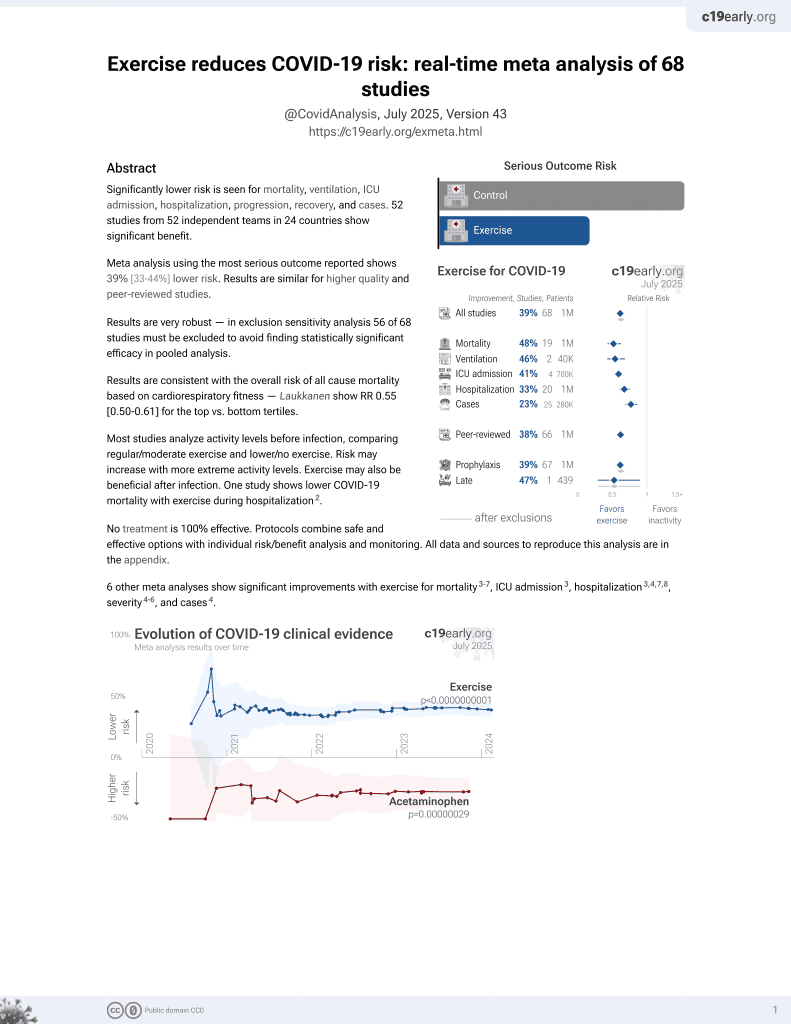
Exercise for COVID-19
9th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 68 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 925 COVID-19 patients in Bangladesh reporting that "physical activity and exposure to sunlight was positively associated with earlier recovery from COVID-19 both in home and hospital care". Details are not provided.
Study covers sunlight and exercise.
Khandker et al., 24 Nov 2022, retrospective, Bangladesh, peer-reviewed, survey, mean age 38.4, 7 authors.
Contact: rsalamat@daffodilvarsity.edu.bd.
Post-COVID-19 complications in home and hospital-based care: A study from Dhaka city, Bangladesh
Frontiers in Rehabilitation Sciences, doi:10.3389/fresc.2022.1037649
A cross-sectional survey was undertaken to understand the management patterns and post-COVID-19 complications among hospital and hometreated participants. Retrospective information was collected from four COVID-19 dedicated hospitals and four selected community settings. Using probability proportional sampling, 925 participants were selected. Data were collected using a semi-structured questionnaire. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis and the exact chi-square tests were utilized to analyze the association between the studied variables. A total of 659 participants responded (response rate 70.93%); 375 from hospitals and 284 from communities. About 80% of participants were mild cases, 75% were treated at home, and 65% of hospital-treated participants were referred after home treatment. Participants treated at home-to hospital and directly in the hospital had 1.64 and 3.38 times longer recovery time respectively than what home-based participants had. A significant increasing trend ( p < 0.001) of co-morbidities was found among referred and hospital treated participants. Age, level of education, physical exercise, practicing preventive measures, exposure to sunlight, and intake of carbohydrate, additional liquid, food supplements, and avoidance of junk foods were significantly associated with place of treatment. Post-COVID-19 difficulties of all factors were statistically significant for home treatment participants, whilst only depression ( p = 0.026), chest pain ( p = 0.017), and digestive disorders ( p = 0.047) were significant ( p < 0.05) for hospital treated participants. The outcomes from this study provide insight into a range of post-COVID-19 difficulties relating to at home and in hospital treatment participants. There are clear differences in the complications experienced, many of which are statistically significant. The health care professionals, the community people and COVID-19 survivors will be benefitted from the study findings, and the policy level people may use the information for designing health education program on post COVID-19 complications.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Anwar, Tuhin, Health system in Bangladesh: challenges and opportunities
Asyary, Veruswati, Sunlight exposure increased COVID-19 recovery rates: a study in the central pandemic area of Indonesia, Sci Total Environ, doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139016
Ayoubkhani, Khunti, Nafilyan, Maddox, Humberstone et al., Post-covid syndrome in individuals admitted to hospital with covid-19: retrospective cohort study, J Endocrinol Investig, doi:10.1007/s40618-020-01236-2
Bergman, Usher, Olson, Chipman, Brunsvold et al., Comparison of outcomes and process of care for patients treated at hospitals dedicated for COVID-19 care vs other hospital, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.0873
Bhuiyan, Sakib, Pakpour, Griffiths, Mamun, COVID-19-related suicides in Bangladesh due to lockdown and economic factors: case study evidence from media reports, Int J Ment Health Addict
Bhuyan, Mahtab, Ashab, Haque, Hoque et al., Treatment of COVID-19 patients at a medical college hospital in Bangladesh, Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol
Chen, Klaus, Michael, Pascal, Till, COVID-19 and sunlight: impact on SARS-CoV-2 transmissibility, morbidity, and mortality, Nature. Sci Rep, doi:10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102419
Chippa, Aleem, Anjum, Post Acute Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Doerre, Doblhammer, Peckham, De Gruijter, Raine et al., The influence of gender on COVID-19 infection and mortality in Germany: insights from age-and gender-specific modeling of contact rates, infections, and deaths in the early phase of the pandemic, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6
Grag, Kim, Whitaker, 'halloran, Cummings et al., Hospitalization rates and characteristics of patients hospitalized with laboratoryconfirmed coronavirus disease 2019 -COVID-NET, 14 states, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1601896
Halabchi, Mazaheri, Sabeti, Yunesian, Alizadeh et al., Regular sports participation as a potential predictor of better clinical outcome in adult patients with COVID-19: a large cross-sectional study, J Phys Act Health
Hossain, Das, Raza, Ahmed, Eva et al., Immediate and post-COVID complications of symptomatic and asymptomatic COVID-19 patients in Bangladesh: a cross-sectional retrospective study, Asian J Med Biol Res, doi:10.3329/ajmbr.v7i2.54999
Karmakar, Lantz, Tipirneni, Sohrabi, Amin et al., Sociodemographic determinants and clinical risk factors associated with COVID-19 severity: a cross-sectional analysis of over 200,000 patients in Tehran, Iran, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1186/s12879-021-06179-4
Khandker, None
Li, Haung, Zou, Yang, Zi et al., Epidemiology of COVID -19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical characteristics, risk factors, and outcomes, J Med Virol, doi:10.1101/2020.08.18.20177089
Lin, Hsu, Lin, Antiviral natural products and herbal medicines
Mark, Catharine, Batty, Lifestyle risk factors, inflammatory mechanisms, and COVID-19 hospitalization: a community-based cohort study of 387,109 adults in the UK, Brain Behav Immun, doi:10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.059
Nasserie, Hittle, Goodman, Carfì, Bernabei et al., Assessment of the frequency and variety of persistent symptoms among patients with COVID-19: a systematic review, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z
Nicastro, Sironi, Antonello, Bianco, Biasin et al., Solar UV-B/A radiation is highly effective in inactivating SARS-CoV-2, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-94417-9
Perego, Callard, Stras, Melville-Johannesson, Pope et al., Why the patient-made term "long COVID" is needed, Wellcome Open Res, doi:10.12688/wellcomeopenres.16307.1
Pereira, Dantas, Galvao, Oliver De, Da et al., Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, doi:10.1016/j.jns.2020.116832
Roessler, Tesch, Batram, Jacob, Loser et al., Post COVID-19 in children, adolescents, and adults: Results of a matched cohort study including more than 150,000 individuals with COVID-19, doi:10.1101/2021.10.21.21265133
Senjam, Balhara, Kumar, Nichal, Manna et al., Assessment of post COVID-19 health problems and its determinants in north India: A descriptive cross sectional study, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, doi:10.1101/2021.10.03.21264490
Silveira, Da, Fagundes, Bizuti, Starck et al., Physical exercise as a tool to help the immune system against COVID-19: an integrative review of the current literature, Clin Exp Med, doi:10.1007/s10238-020-00650-3
Sultana, Clinical manifestations and socio-demographic status of COVID-19 patients during the second wave of pandemic: a Bangladeshi experience, J Infect Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2021.06.011
Syed, Bushra, Iqbal, Tahmina, Rumana et al., Bangladesh Health system review, Health Syst Transit
Weyh, Krüger, Strasser, Physical activity and diet shape the immune system during aging, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12030622
Who, A clinical case definition of post COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fresc.2022.1037649",
"ISSN": [
"2673-6861"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fresc.2022.1037649",
"abstract": "<jats:p>A cross-sectional survey was undertaken to understand the management patterns and post-COVID-19 complications among hospital and home-treated participants. Retrospective information was collected from four COVID-19 dedicated hospitals and four selected community settings. Using probability proportional sampling, 925 participants were selected. Data were collected using a semi-structured questionnaire. Bivariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis and the exact chi-square tests were utilized to analyze the association between the studied variables. A total of 659 participants responded (response rate 70.93%); 375 from hospitals and 284 from communities. About 80% of participants were mild cases, 75% were treated at home, and 65% of hospital-treated participants were referred after home treatment. Participants treated at home-to hospital and directly in the hospital had 1.64 and 3.38 times longer recovery time respectively than what home-based participants had. A significant increasing trend (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> &lt; 0.001) of co-morbidities was found among referred and hospital treated participants. Age, level of education, physical exercise, practicing preventive measures, exposure to sunlight, and intake of carbohydrate, additional liquid, food supplements, and avoidance of junk foods were significantly associated with place of treatment. Post-COVID-19 difficulties of all factors were statistically significant for home treatment participants, whilst only depression (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.026), chest pain (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.017), and digestive disorders (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> = 0.047) were significant (<jats:italic>p</jats:italic> &lt; 0.05) for hospital treated participants. The outcomes from this study provide insight into a range of post-COVID-19 difficulties relating to at home and in hospital treatment participants. There are clear differences in the complications experienced, many of which are statistically significant. The health care professionals, the community people and COVID-19 survivors will be benefitted from the study findings, and the policy level people may use the information for designing health education program on post COVID-19 complications.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fresc.2022.1037649"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khandker",
"given": "Salamat",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Akther",
"given": "Aivee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Syed",
"given": "Billal H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shafiullah",
"given": "Rezoun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "Kawsar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chowdhury",
"given": "Alauddin A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khan",
"given": "Salim",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Rehabilitation Sciences",
"container-title-short": "Front. Rehabilit. Sci.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-24T14:11:48Z",
"timestamp": 1669299108000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-24T14:11:53Z",
"timestamp": 1669299113000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-25T06:12:58Z",
"timestamp": 1669356778963
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
24
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1669248000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fresc.2022.1037649/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"key": "B1",
"year": ""
},
{
"key": "B2",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.11648/j.ajhr.20140206.18",
"article-title": "Health system in Bangladesh: challenges and opportunities",
"author": "Anwar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "366",
"journal-title": "Am J Health Res",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "B4",
"year": ""
},
{
"key": "B5",
"year": ""
},
{
"key": "B6",
"year": ""
},
{
"article-title": "Bangladesh Health system review",
"author": "Syed",
"first-page": "24",
"journal-title": "Health Syst Transit",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"key": "B8",
"year": ""
},
{
"key": "B9",
"year": ""
},
{
"key": "B10",
"year": ""
},
{
"key": "B11",
"year": ""
},
{
"author": "Chippa",
"key": "B12",
"year": ""
},
{
"author": "Roessler",
"key": "B13",
"volume-title": "Post COVID-19 in children, adolescents, and adults: Results of a matched cohort study including more than 150,000 individuals with COVID-19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "B14",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.12688/wellcomeopenres.16307.1",
"article-title": "Why the patient-made term “long COVID” is needed",
"author": "Perego",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "224",
"journal-title": "Wellcome Open Res",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B16",
"year": ""
},
{
"key": "B17",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11417",
"article-title": "Assessment of the frequency and variety of persistent symptoms among patients with COVID-19: a systematic review",
"author": "Nasserie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2111417",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12603",
"article-title": "Persistent symptoms in patients after acute COVID-19",
"author": "Carfì",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "603",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01283-z",
"article-title": "Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome",
"author": "Nalbandian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "601",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Senjam",
"key": "B21",
"volume-title": "Assessment of post COVID-19 health problems and its determinants in north India: A descriptive cross sectional study",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "B22",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11469-020-00307-y",
"article-title": "COVID-19-related suicides in Bangladesh due to lockdown and economic factors: case study evidence from media reports",
"author": "Bhuiyan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2110",
"journal-title": "Int J Ment Health Addict",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm6915e3",
"article-title": "Hospitalization rates and characteristics of patients hospitalized with laboratory-confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 — COVID-NET, 14 states, March 1–30, 2020",
"author": "Grag",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "458",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2016.06.015",
"article-title": "Prevalence of comorbidities in the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV): a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Badawi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "129",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1601896",
"article-title": "Sex-based differences in susceptibility to severe acute respiratory synndrome coronavirus infection",
"author": "Channappanavar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4046",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "198",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26424",
"article-title": "Epidemiology of COVID - 19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical characteristics, risk factors, and outcomes",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1449",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "93",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.18.20177089",
"article-title": "Clinico-epidemiological characteristics of asymptomatic and symptomatic COVID-19-positive patients in Bangladesh",
"author": "Jahid Hasan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "MedRxiv",
"key": "B28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2021.06.011",
"article-title": "Clinical manifestations and socio-demographic status of COVID-19 patients during the second wave of pandemic: a Bangladeshi experience",
"author": "Md Roushan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1367",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Shaha",
"key": "B30",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.36462",
"article-title": "Association of social and demographic factors with COVID-19 incidence and death rates in the US",
"author": "Karmakar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2036462",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-021-06179-4",
"article-title": "Sociodemographic determinants and clinical risk factors associated with COVID-19 severity: a cross-sectional analysis of over 200,000 patients in Tehran, Iran",
"author": "Sohrabi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "474",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "2021",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0268119",
"article-title": "The influence of gender on COVID-19 infection and mortality in Germany: insights from age- and gender-specific modeling of contact rates, infections, and deaths in the early phase of the pandemic",
"author": "Doerre",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0268119",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6",
"article-title": "Male Sex identified by global COVID -19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission",
"author": "Peckham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6317",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Treatment of COVID-19 patients at a medical college hospital in Bangladesh",
"author": "Bhuyan",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10238-020-00650-3",
"article-title": "Physical exercise as a tool to help the immune system against COVID-19: an integrative review of the current literature",
"author": "Da Silveira",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Med",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.059",
"article-title": "Lifestyle risk factors, inflammatory mechanisms, and COVID-19 hospitalization: a community-based cohort study of 387,109 adults in the UK",
"author": "Mark",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "184",
"journal-title": "Brain Behav Immun",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1123/jpah.2020-0392",
"article-title": "Regular sports participation as a potential predictor of better clinical outcome in adult patients with COVID-19: a large cross-sectional study",
"author": "Halabchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "8",
"journal-title": "J Phys Act Health",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139016",
"article-title": "Sunlight exposure increased COVID-19 recovery rates: a study in the central pandemic area of Indonesia",
"author": "Asyary",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "139016",
"journal-title": "Sci Total Environ",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "729",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B40",
"year": ""
},
{
"key": "B41",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-87692-z",
"article-title": "Climate and the spread of COVID-19. Nature",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9042",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102419",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and sunlight: impact on SARS-CoV-2 transmissibility, morbidity, and mortality",
"author": "Sharun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102419",
"journal-title": "Ann Med Surg",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-94417-9",
"article-title": "Solar UV-B/A radiation is highly effective in inactivating SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Nicastro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14805",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Pereira",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1311",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2020.561264",
"article-title": "Clinical symptom differences between mild and severe COVID-19 patients in China: A meta-analysis",
"author": "He",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front. Public Health",
"key": "B46",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jns.2020.116832",
"article-title": "Central nervous system manifestations of COVID-19: a systematic review",
"author": "Asadi-Pooya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "116832",
"journal-title": "J Neurol Sci",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3329/ajmbr.v7i2.54999",
"article-title": "Immediate and post-COVID complications of symptomatic and asymptomatic COVID-19 patients in Bangladesh: a cross-sectional retrospective study",
"author": "Hossain",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "191",
"journal-title": "Asian J Med Biol Res",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/2225-4110.124335",
"article-title": "Antiviral natural products and herbal medicines",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "24",
"journal-title": "J Tradit Complement Med",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "B50",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12030622",
"article-title": "Physical activity and diet shape the immune system during aging",
"author": "Weyh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "622",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B52",
"year": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.0873",
"article-title": "Comparison of outcomes and process of care for patients treated at hospitals dedicated for COVID-19 care vs other hospital",
"author": "Bergman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e220873",
"journal-title": "JAMA Network Open",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "B54",
"year": ""
},
{
"article-title": "Post-covid syndrome in individuals admitted to hospital with covid-19: retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Ayoubkhani",
"first-page": "372",
"key": "B55",
"volume-title": "BMJ",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpsychores.2021.110525",
"article-title": "Physical and mental health complications post-COVID-19: scoping review",
"author": "Shanbehzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "110525",
"journal-title": "J Psychosom Res",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-020-01236-2",
"article-title": "Prevalence and impact of diabetes among people infected with SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Fadini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "867",
"journal-title": "J Endocrinol Investig",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 57,
"references-count": 57,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fresc.2022.1037649/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Materials Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Post-COVID-19 complications in home and hospital-based care: A study from Dhaka city, Bangladesh",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "3"
}
khandker