Inhaled hydroxychloroquine to improve efficacy and reduce harm in the treatment of COVID-19
et al., Med. Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110, Jul 2020
HCQ for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 424 studies, used in 59 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
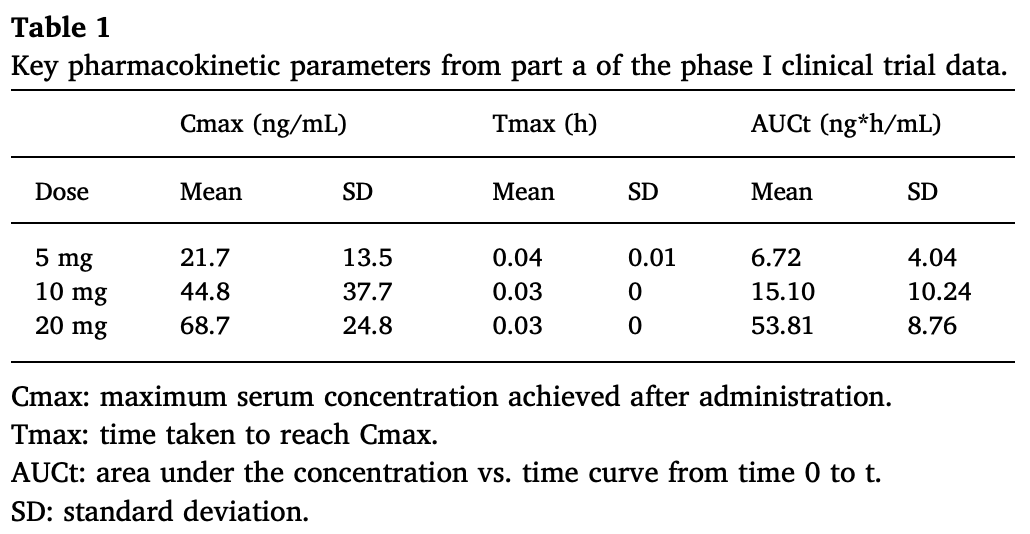
Proposal to use an inhaled formulation of HCQ which has passed safety studies in clinical trials for the treatment of asthma. Authors advocate for early treatment or prophylaxis of COVID-19, using HCQ as an inhaled aerosol, to deliver the drug directly to the lungs at a lower dose than that required for oral systemic delivery.
1.
Alsmadi et al., The In Vitro, In Vivo, and PBPK Evaluation of a Novel Lung-Targeted Cardiac-Safe Hydroxychloroquine Inhalation Aerogel, AAPS PharmSciTech, doi:10.1208/s12249-023-02627-3.
2.
Faísca et al., Enhanced In Vitro Antiviral Activity of Hydroxychloroquine Ionic Liquids against SARS-CoV-2, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics14040877.
3.
Zelenko, Z., Nebulized Hydroxychloroquine for COVID-19 Treatment: 80x Improvement in Breathing, Preprint, faculty.utrgv.edu/eleftherios.gkioulekas/zelenko/Zelenko-nebulized-hcq.pdf.
Kavanagh et al., 15 Jul 2020, peer-reviewed, 9 authors.
Inhaled hydroxychloroquine to improve efficacy and reduce harm in the treatment of COVID-19
Medical Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110
Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information website. Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre -including this research content -immediately available in PubMed Central and other publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre remains active.
PeakProsperity for simulating their first discussions on this topic.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no competing financial interest. The HCQ formulation was developed and IP filed by APT Corporation. The clinical and regulatory work was done by Aradigm under contract to, and paid for by APT. While both corporations no longer exist, the rights to the data have since been licensed to Pulmoquine and development is progressing for COVID-19. Appropriate intellectual property has been filed.
Authorship statement JF conceptualised this project. OK and AMH drafted the manuscript and OK preformed the analysis of the ClinicalTrials.gov data. FD provided the phase I and II clinical data and described the formulation. Discussions with SR, JF, NO'R and BM helped develop the idea. GW and AMH acquired funding to support the project. AA was responsible for logistical arrangements. All authors reviewed and agreed to the final manuscript.
Appendix A. Supplementary data Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https:// doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110.
References
Arnold, Buckner, Hydroxychloroquine for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection? Improving our confidence in a model-based approach to dose selection, Clin Transl Sci, doi:10.1111/cts.12797
Belitz, Wieser, Food Reviews International Bitter compounds: Occurrence and structure-activity relationships BITTER COMPOUNDS: OCCURRENCE AND STRUCTURE-ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIPS, Food Rev Int
Bonow, Hernandez, Turakhia, Hydroxychloroquine, Coronavirus Disease 2019, and QT Prolongation, JAMA Cardiol
Dayton, Communication, Clinical Study Report: A two-part, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, ascending-dose study to evaluate the safety, tolerance and pharmacokinetics of orally inhaled hydroxychloroquine sulfate via the AERx System in healthy adult volunteers, Sponsor Protocol No
Dayton, Communication, Clinical study Report: A randomised, doubleblind, placebo-controlled, multiple-dose study to evaluate the safety, tolerance and efficacy of orally inhaled hydroxychloroquine sulfate (HCQ) via the AERx® System in asthmatic subjects, Sponsor Protocol No
Dayton, None
Dayton, Owen, Cipolla, Development of an inhaled hydroxychloroquine sulfate product using the AERx ® system to treat asthma, Respir Drug Deliv
Dörner, Therapy: hydroxychloroquine in SLE: old drug, new perspectives, Nat Rev Rheumatol
Garcia-Cremades, Solans, Hughes, Optimizing hydroxychloroquine dosing for patients with COVID-19: An integrative modeling approach for effective drug repurposing, Clin Pharmacol Ther
Gorbalenya, Baker, Baric, The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2, Nat Microbiol
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Krueger, Mueller, Drosten et al., The novel coronavirus 2019 (2019-nCoV) uses the SARS-coronavirus receptor ACE2 and the cellular protease TMPRSS2 for entry into target cells, Internet
Klimke, Hefner, Will, Voss, Hydroxychloroquine as an aerosol might markedly reduce and even prevent severe clinical symptoms after SARS-CoV-2 infection, Med Hypotheses
Morice, Kardos, Comprehensive evidence-based review on European antitussives, BMJ Open Respir Res
Morris, Tisi, Tan, Worthington, Development and palatability assessment of norvir® (Ritonavir) 100 mg powder for pediatric population, Int J Mol Sci
Pauli, Joshi, Vasavada, Brackett, Towa, Evaluation of an immediaterelease formulation of hydroxychloroquine sulfate with an interwoven pediatric taste-masking system, J Pharm Sci
Rabkin, Aging effects on QT interval: implications for cardiac safety of antipsychotic drugs, J Geriatr Cardiol
Rabkin, Cheng, Thompson, Detailed analysis of the impact of age on the QT interval, J Geriatr Cardiol
Sanders, Monogue, Jodlowski, Cutrell, Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review, JAMA -J Am Med Assoc
Savarino, Boelaert, Cassone, Majori, Cauda, Effects of chloroquine on viral infections: an old drug against today's diseases?, Lancet Infect Dis
Savarino, Trani, Donatelli, Cauda, Cassone, New insights into the antiviral effects of chloroquine, Lancet Infect Dis
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res
Weinstein, Anderson, The aging kidney: physiological changes, Adv Chronic Kidney Dis
Williamson, OpenSAFELY: factors associated with COVID-19 death in 17 million patients, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2521-2524
Wise, Breslin, Dalton, Effect of taste sensation on cough reflex sensitivity, Lung
Wise, Breslin, Dalton, Sweet taste and menthol increase cough reflex thresholds, Pulm Pharmacol Ther
Yao, Ye, Zhang, In vitro antiviral activity and projection of optimized dosing design of hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Clin Infect Dis
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110",
"ISSN": [
"0306-9877"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110",
"alternative-id": [
"S0306987720315176"
],
"article-number": "110110",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Inhaled hydroxychloroquine to improve efficacy and reduce harm in the treatment of COVID-19"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Medical Hypotheses"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kavanagh",
"given": "Oisín",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Marie Healy",
"given": "Anne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dayton",
"given": "Francis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Shane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "O'Reilly",
"given": "Niall J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahoney",
"given": "Brian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arthur",
"given": "Aisling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Walker",
"given": "Gavin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farragher",
"given": "John P.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Medical Hypotheses",
"container-title-short": "Medical Hypotheses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-15T06:02:52Z",
"timestamp": 1594792972000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-01-23T15:32:45Z",
"timestamp": 1611415965000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001602",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Science Foundation Ireland"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-01T18:59:15Z",
"timestamp": 1709319555028
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 26,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2020-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1601510400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0306987720315176?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0306987720315176?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "110110",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0005",
"unstructured": "European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. COVID-19 situation update worldwide, as of 9 May 2020 [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 May 9]; Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/geographical-distribution-2019-ncov-cases."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6019",
"article-title": "Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): a review",
"author": "Sanders",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA - J Am Med Assoc",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0010",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0015",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(03)00806-5",
"article-title": "Effects of chloroquine on viral infections: an old drug against today’s diseases?",
"author": "Savarino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "722",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0020",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70361-9",
"article-title": "New insights into the antiviral effects of chloroquine",
"author": "Savarino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "67",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0025",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrrheum.2009.235",
"article-title": "Therapy: hydroxychloroquine in SLE: old drug, new perspectives",
"author": "Dörner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Rheumatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0030",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1782",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0035",
"unstructured": "Bonow RO, Hernandez AF, Turakhia M. Hydroxychloroquine, Coronavirus Disease 2019, and QT Prolongation. JAMA Cardiol [Internet] 2020 [cited 2020 May 7]; Available from: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamacardiology/fullarticle/2765632."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"article-title": "OpenSAFELY: factors associated with COVID-19 death in 17 million patients",
"author": "Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0040",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Detailed analysis of the impact of age on the QT interval",
"author": "Rabkin",
"first-page": "740",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Geriatr Cardiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0045",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Aging effects on QT interval: implications for cardiac safety of antipsychotic drugs",
"author": "Rabkin",
"first-page": "20",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Geriatr Cardiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0050",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0055",
"unstructured": "European Medicines Agency. COVID-19: reminder of risk of serious side effects with chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine [Internet]. Amsterdam: 2020 [cited 2020 May 9]. Available from: www.ema.europa.eu/contact."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0060",
"unstructured": "Food and Drug Administration. FDA Drug Safety Communication: FDA cautions against use of hydroxychloroquine or chloroquine for COVID-19 outside of the hospital setting or a clinical trial due to risk of heart rhythm problems [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 May 9]. Available from: www.clinicaltrials.gov."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa237",
"article-title": "In vitro antiviral activity and projection of optimized dosing design of hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)",
"author": "Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0065",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12797",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0070",
"unstructured": "Arnold SL, Buckner F. Hydroxychloroquine for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection? Improving our confidence in a model-based approach to dose selection. Clin Transl Sci [Internet] 2020 [cited 2020 May 9]; DOI:10.1111/cts.12797."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpt.1856",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0075",
"unstructured": "Garcia-Cremades M, Solans BP, Hughes E, et al. Optimizing hydroxychloroquine dosing for patients with COVID-19: An integrative modeling approach for effective drug repurposing. Clin Pharmacol Ther [Internet] 2020 [cited 2020 May 9]; Available from: DOI:10.1002/cpt.1856."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.ackd.2010.05.002",
"article-title": "The aging kidney: physiological changes",
"author": "Weinstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "302",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Adv Chronic Kidney Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0080",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z",
"article-title": "The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Gorbalenya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "536",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0085",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.01.31.929042",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0090",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Krueger N, Mueller MA, Drosten C, Poehlmann S. The novel coronavirus 2019 (2019-nCoV) uses the SARS-coronavirus receptor ACE2 and the cellular protease TMPRSS2 for entry into target cells [Internet]. bioRxiv. 2020 [cited 2020 May 11];2020.01.31.929042. Available from: http://biorxiv.org/content/early/2020/01/31/2020.01.31.929042.abstract."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109783",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0095",
"unstructured": "Klimke A, Hefner G, Will B, Voss U. Hydroxychloroquine as an aerosol might markedly reduce and even prevent severe clinical symptoms after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Med Hypotheses [Internet] 2020 [cited 2020 May 11];142:109783. Available from: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0306987720307076."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0100",
"unstructured": "Dayton F. Personal communication (May 11 2020)."
},
{
"article-title": "Development of an inhaled hydroxychloroquine sulfate product using the AERx ® system to treat asthma",
"author": "Dayton",
"journal-title": "Respir Drug Deliv",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0105",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0110",
"unstructured": "Dayton F, Personal Communication, Clinical Study Report: A two- part, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, ascending-dose study to evaluate the safety, tolerance and pharmacokinetics of orally inhaled hydroxychloroquine sulfate via the AERx System in healthy adult volunteers. Sponsor Protocol No. PYX-04-01 (2005)."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0115",
"unstructured": "Dayton F, Personal Communication, Clinical study Report: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple-dose study to evaluate the safety, tolerance and efficacy of orally inhaled hydroxychloroquine sulfate (HCQ) via the AERx® System in asthmatic subjects. Sponsor Protocol No. ARD-1300-0501 (2007)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/87559128509540773",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0120",
"unstructured": "Belitz H-D, Wieser H. Food Reviews International Bitter compounds: Occurrence and structure-activity relationships BITTER COMPOUNDS: OCCURRENCE AND STRUCTURE-ACTIVITY RELATIONSHIPS. Food Rev Int [Internet] 1985 [cited 2020 May 12];1(2):271–354. Available from: https://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?journalCode=lfri20."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xphs.2019.12.014",
"article-title": "Evaluation of an immediate-release formulation of hydroxychloroquine sulfate with an interwoven pediatric taste-masking system",
"author": "Pauli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1493",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Pharm Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0125",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjresp-2016-000137",
"article-title": "Comprehensive evidence-based review on European antitussives",
"author": "Morice",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open Respir Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0130",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00408-013-9515-z",
"article-title": "Effect of taste sensation on cough reflex sensitivity",
"author": "Wise",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Lung",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0135",
"volume": "192",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pupt.2012.03.005",
"article-title": "Sweet taste and menthol increase cough reflex thresholds",
"author": "Wise",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "236",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Pulm Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0140",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms20071718",
"article-title": "Development and palatability assessment of norvir® (Ritonavir) 100 mg powder for pediatric population",
"author": "Morris",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110110_b0145",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0306987720315176"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Inhaled hydroxychloroquine to improve efficacy and reduce harm in the treatment of COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "143"
}
