Safety, Tolerability and Efficacy and Dose Response of GLS-1027 in the Prevention of Severe Pneumonitis Caused by SARS-CoV-2 Infection
et al., NCT04590547, NCT04590547, Apr 2025
RCT 132 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in outcomes with zenuzolac (GLS-1027) treatment.
|
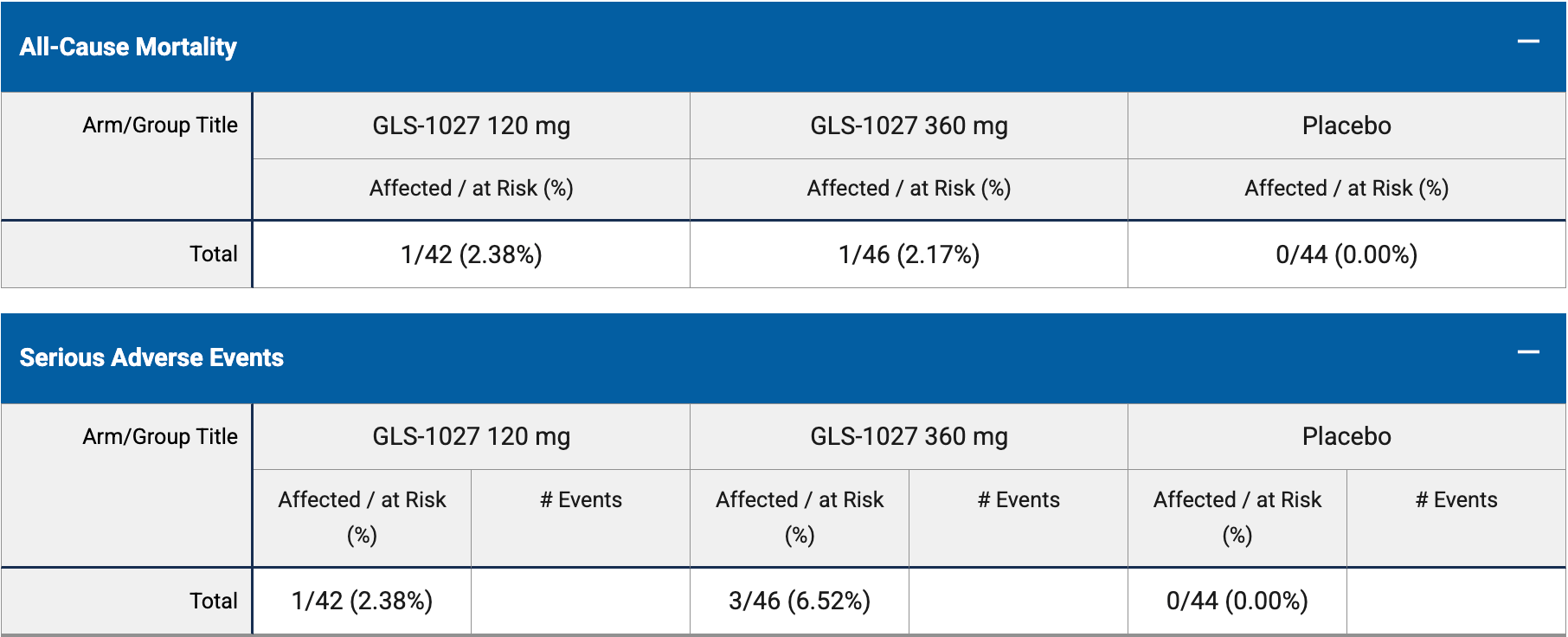
risk of death, 200.2% higher, RR 3.00, p = 0.34, treatment 46, control 44.
|
|
risk of death, 195.7% higher, RR 2.96, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 46 (2.2%), control 0 of 44 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), 360mg.
|
|
risk of death, 204.8% higher, RR 3.05, p = 0.49, treatment 1 of 42 (2.4%), control 0 of 44 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), 120mg.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 0.7% higher, RR 1.01, p = 0.99, treatment 46, control 44.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 43.5% higher, RR 1.43, p = 1.00, treatment 3 of 46 (6.5%), control 2 of 44 (4.5%), 360mg.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 47.6% lower, RR 0.52, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 42 (2.4%), control 2 of 44 (4.5%), NNT 46, 120mg.
|
|
hospitalization time, 1.1% lower, relative time 0.99, p = 0.87, treatment 46, control 44.
|
|
hospitalization time, 1.1% lower, relative time 0.99, p = 0.90, treatment mean 9.3 (±3.65) n=46, control mean 9.4 (±4.1) n=44, 360mg.
|
|
hospitalization time, 1.1% lower, relative time 0.99, p = 0.91, treatment mean 9.3 (±4.2) n=42, control mean 9.4 (±4.1) n=44, 120mg.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kane et al., 11 Apr 2025, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, multiple countries, preprint, 1 author, trial NCT04590547 (history).
Contact: dkane@genels.us.
Zenuzolac (GLS-1027) is an oral, small molecule isoxazole immunomodulator that down-regulates NF-κB/p38-mediated pro-inflammatory cytokine production and Th17 responses.