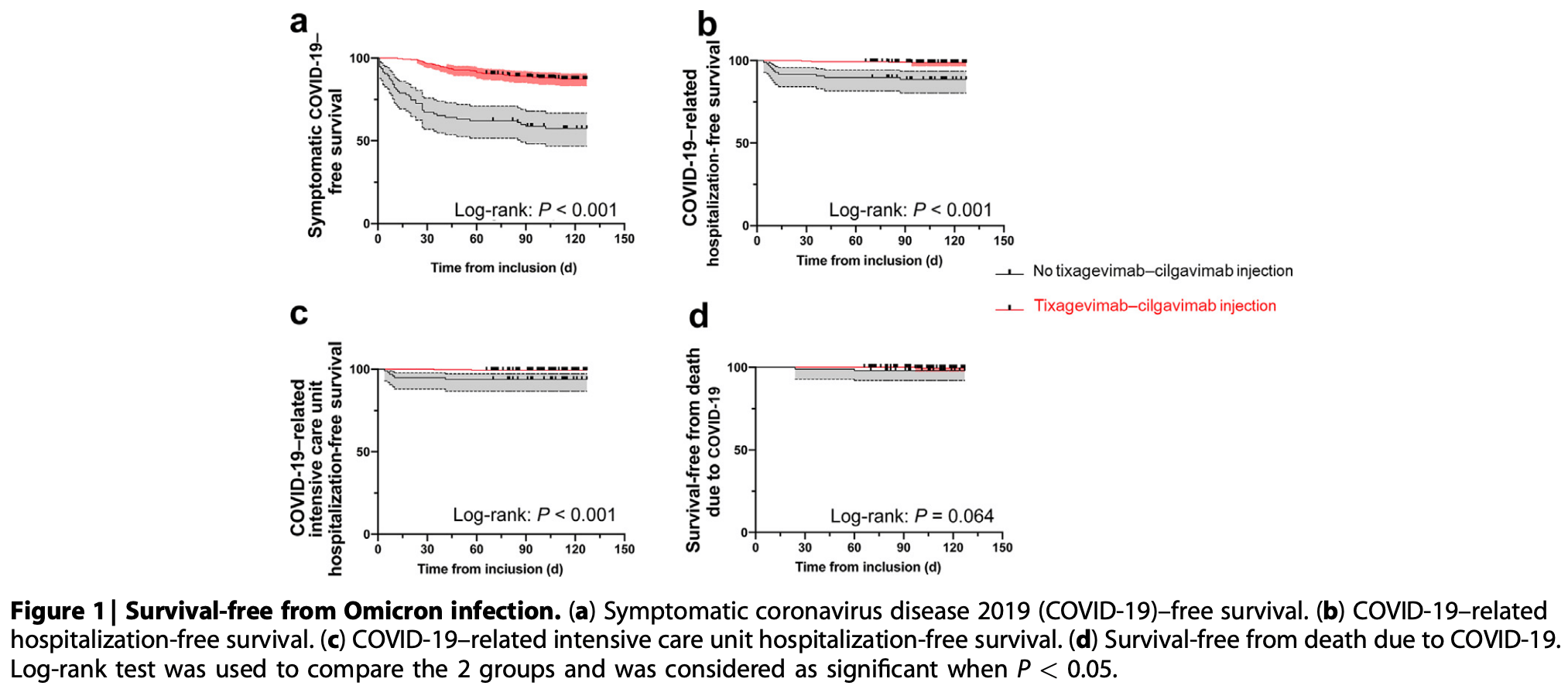
COVID-19 morbidity decreases with tixagevimab–cilgavimab preexposure prophylaxis in kidney transplant recipient nonresponders or low-vaccine responders
et al., Kidney International, doi:10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.008, Oct 2022
42nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
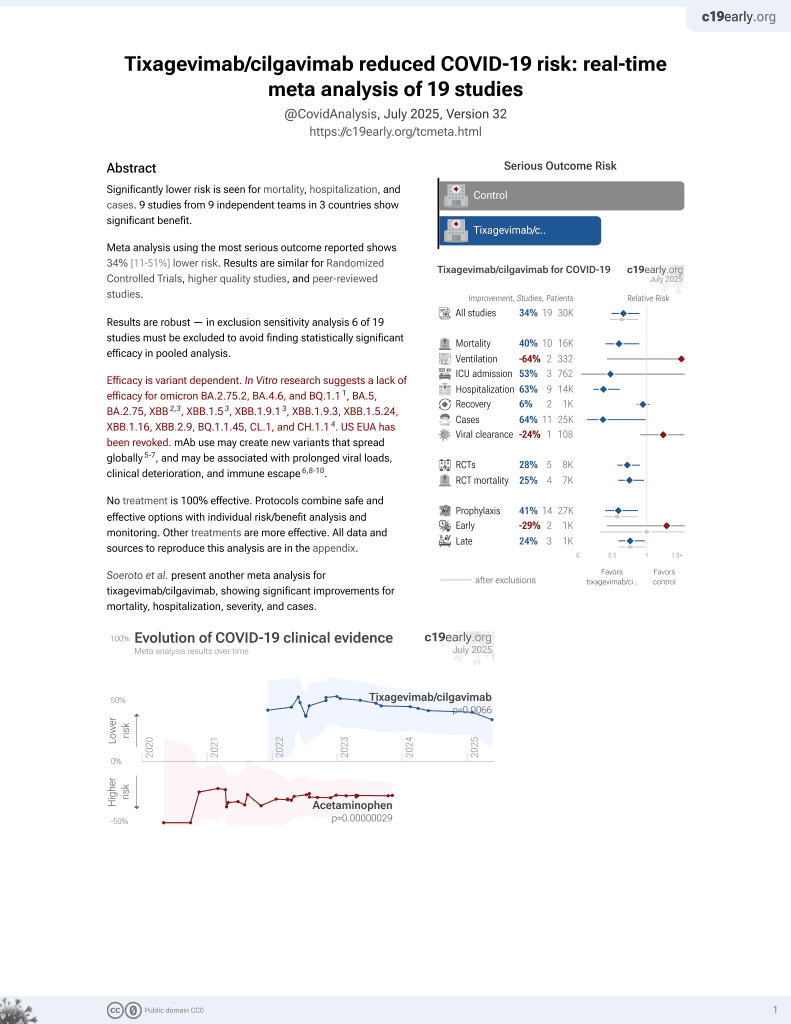
May 2022, now with p = 0.0066 from 19 studies, recognized in 33 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 430 kidney transplant recipients showing significantly lower symptomatic COVID-19 and hospitalization with tixagevimab/cilgavimab preexposure prophylaxis compared to 97 patients who did not receive it, during an omicron wave.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for omicron BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6, BQ.1.11, BA.5, BA.2.75, XBB2,3, XBB.1.53, ХВВ.1.9.13, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.9, BQ.1.1.45, CL.1, and CH.1.14.
|
risk of death, 92.4% lower, HR 0.08, p = 0.07, treatment 1 of 333 (0.3%), control 2 of 97 (2.1%), NNT 57, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 95.5% lower, HR 0.04, p = 0.001, treatment 2 of 333 (0.6%), control 6 of 97 (6.2%), NNT 18, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 95.4% lower, HR 0.05, p = 0.001, treatment 4 of 333 (1.2%), control 11 of 97 (11.3%), NNT 9.9, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of symptomatic case, 98.9% lower, HR 0.01, p = 0.001, treatment 41 of 333 (12.3%), control 42 of 97 (43.3%), NNT 3.2, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
1.
Planas et al., Resistance of Omicron subvariants BA.2.75.2, BA.4.6 and BQ.1.1 to neutralizing antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.11.17.516888.
2.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
Kaminski et al., 31 Oct 2022, retrospective, France, peer-reviewed, 21 authors, study period 28 December, 2021 - 28 February, 2022.
Contact: lionel.couzi@chu-bordeaux.fr.
Abstract: Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with
free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the
company's public news and information website.
Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related
research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre - including this
research content - immediately available in PubMed Central and other
publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights
for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means
with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are
granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre
remains active.
letters to the editor
COVID-19 morbidity
decreases with
tixagevimab–cilgavimab
preexposure prophylaxis in kidney
transplant recipient
nonresponders or low-vaccine
responders
To the editor: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is associated with high mortality in kidney transplant recipients (KTRs).1 Unfortunately,
they display a poor humoral immune response following
coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) mRNA vaccination.2
The use of anti–SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibodies
was therefore proposed for preexposure prophylaxis in individuals who did not exhibit a significant antibody response
following vaccination. Tixagevimab–cilgavimab (Evusheld;
AstraZeneca) was found to be effective in preventing COVID19 during Alpha and Delta waves.3 Because it retained a
neutralizing activity against the Omicron variants BA.1 and
BA.2, it was approved in many countries for preexposure
prophylaxis of KTRs with a low anti–SARS-CoV-2 antibody
response after vaccination.4,5 A recent study of Bertrand et al.
revealed the potential clinical efficiency of tixagevimab–
cilgavimab against Omicron in KTRs with weak or no
response to vaccine.6 At the same time, Benotmane et al.
reported serious Omicron infections despite prophylactic
therapy using tixagevimab–cilgavimab.7 In light of these
conflicting data, we report herein the impact of this preexposure prophylaxis on the incidence of symptomatic
COVID-19; COVID-19–related hospitalizations, including
intensive care unit hospitalizations; and death in a cohort of
KTRs during the Omicron wave.
KTRs from Bordeaux University Hospital (France) were
considered as nonresponders or low responders if they had an
anti-spike antibody level of <7 binding antibody units/ml
(threshold of detection) or between 7 and 264 binding antibody units/ml, respectively, after at least 3 doses of mRNA
vaccines. All patients were to receive i.m. prophylactic injections of tixagevimab–cilgavimab (150 mg tixagevimab and
150 mg cilgavimab) between December 28, 2021, and February
28, 2022 (COVID-19 incidence of 779 of 100,000). This period
corresponded to the peak of the Omicron wave observed on
January 27, 2022 (COVID-19 incidence of 4021 of 100,000) in
our region (https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/). During this
study period, BA.1 was the predominant variant until February
14, 2022, when the BA.2 variant became predominant. The last
follow-up was on May 5, 2022. Diagnosis of COVID-19 was
based on the reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction
of nasopharyngeal swabs, and genome sequencing was
936
www.kidney-international.org
performed when suitable samples were available. All the data
were recovered from our database (Réseau Aquitain..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.008",
"ISSN": [
"0085-2538"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.008",
"alternative-id": [
"S0085253822005506"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "COVID-19 morbidity decreases with tixagevimab–cilgavimab preexposure prophylaxis in kidney transplant recipient nonresponders or low-vaccine responders"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Kidney International"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.008"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kaminski",
"given": "Hannah",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gigan",
"given": "Mickael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vermorel",
"given": "Agathe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Charrier",
"given": "Manon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guirle",
"given": "Laura",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jambon",
"given": "Frederic",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lacapère",
"given": "Arthur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ménard",
"given": "Coline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moreau",
"given": "Karine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Neau-Cransac",
"given": "Martine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Novion",
"given": "Marine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pribat",
"given": "Frederique",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taton",
"given": "Benjamin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Borde",
"given": "Sébastien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Burguet",
"given": "Laure",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Martinez",
"given": "Charlie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jasiek",
"given": "Magali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "D’Halluin",
"given": "Pauline",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lafon",
"given": "Marie-Edith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Merville",
"given": "Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Couzi",
"given": "Lionel",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Kidney International",
"container-title-short": "Kidney International",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"kidney-international.org",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-20T15:31:56Z",
"timestamp": 1658331116000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-20T09:32:22Z",
"timestamp": 1663666342000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-06T22:59:56Z",
"timestamp": 1704581996063
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 24,
"issue": "4",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "4",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1664582400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0085253822005506?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0085253822005506?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "936-938",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.kint.2020.08.005",
"article-title": "An initial report from the French SOT COVID Registry suggests high mortality due to Covid-19 in recipients of kidney transplants",
"author": "Caillard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1549",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.008_bib1",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1681/ASN.2021040480",
"article-title": "Antibody and T cell response to SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA BNT162b2 vaccine in kidney transplant recipients and hemodialysis patients",
"author": "Bertrand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2147",
"journal-title": "J Am Soc Nephrol",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.008_bib2",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116620",
"article-title": "Intramuscular AZD7442 (tixagevimab–cilgavimab) for prevention of Covid-19",
"author": "Levin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2188",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.008_bib3",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04594-4",
"article-title": "Antibody evasion properties of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages",
"author": "Iketani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "553",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.008_bib4",
"volume": "604",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2201933",
"article-title": "Efficacy of antiviral agents against the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariant BA.2",
"author": "Takashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1475",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.008_bib5",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.05.007",
"article-title": "Efficacy of anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody prophylaxis and vaccination on the Omicron variant of COVID-19 in kidney transplant recipients",
"author": "Bertrand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "440",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.008_bib6",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.05.008",
"article-title": "Pre-exposure prophylaxis with 300 mg Evusheld elicits limited neutralizing activity against the Omicron variant",
"author": "Benotmane",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "442",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.kint.2022.07.008_bib7",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 7,
"references-count": 7,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0085253822005506"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nephrology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "COVID-19 morbidity decreases with tixagevimab–cilgavimab preexposure prophylaxis in kidney transplant recipient nonresponders or low-vaccine responders",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "102"
}