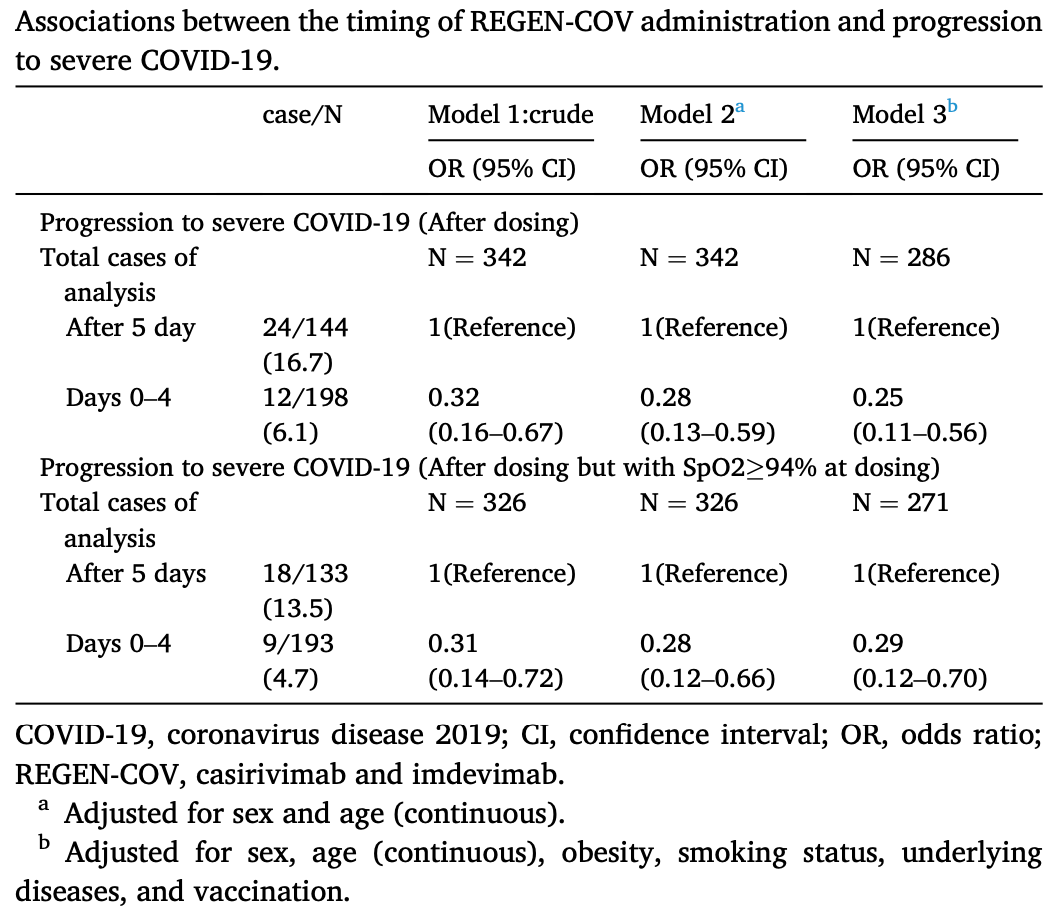
Timing of REGEN-COV administration and progression to severe COVID-19
et al., Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002, Jul 2022
19th treatment shown to reduce risk in
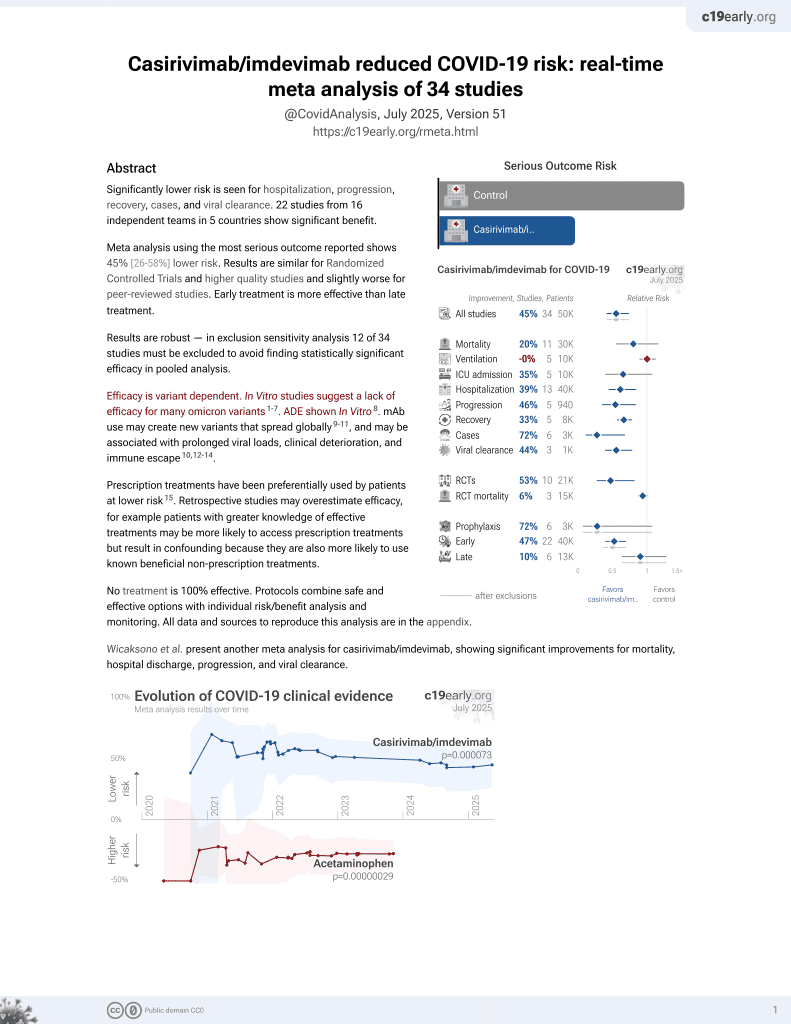
March 2021, now with p = 0.000095 from 34 studies, recognized in 52 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 342 patients in Japan, showing significantly greater efficacy of casirivimab/imdevimab with earlier treatment. The proportion of patients progressing to severe COVID-19 increased daily from symptom onset and increased sharply from day 5.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro research suggests a lack of efficacy for many omicron variants1-7.
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Tatham et al., Lack of Ronapreve (REGN-CoV; casirivimab and imdevimab) virological efficacy against the SARS-CoV 2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) in K18-hACE2 mice, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.01.23.477397.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Kadowaki et al., 11 Jul 2022, retrospective, Japan, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, study period 19 July, 2021 - 30 September, 2021.
Contact: p5j44x0d@s.okayama-u.ac.jp.
Timing of REGEN-COV administration and progression to severe COVID-19
Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, doi:10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002
Introduction: Several clinical trials have demonstrated that REGEN-COV (casirivimab and imdevimab) decreases the risk of hospitalization and death among COVID-19 patients. However, these trials did not evaluate the optimal timing of its administration, and evidence is limited regarding the relationship between the timing of administration and progression to severe COVID-19 among patients who receive REGEN-COV in a real-world setting. We examined the association between the timing of REGEN-COV administration and progression to severe COVID-19 among patients who received REGEN-COV in Japan. Methods: We included a total of 342 COVID-19 patients (37 hospitals) who received REGEN-COV between July 19 and September 30, 2021. We calculated the difference between the date of symptom onset and the date of administration as an indicator of the timing of REGEN-COV administration and determined progression to severe COVID-19 after REGEN-COV administration. We conducted a logistic regression analysis, adjusting for potential confounders. Results: The proportion of cases progressing to severe COVID-19 increased daily from symptom onset and sharply increased from day 5 of onset. The early administration (days 0-4) decreased the risk of progression to severity compared with late administration (after day 5), with an adjusted odds ratio of 0.29 (95% confidence interval: 0.11-0.56). Conclusions: The early administration of REGEN-COV was associated with a decreased risk of progression to severe COVID-19 when the delta variant was dominant. The present epidemiological findings indicate that this monoclonal antibody therapy should be implemented very early in the clinical course probably even for emerging variants such as omicron BA.2.
Authorship statement TK analyzed the data and wrote the first draft. SI, NM, ST, and TY contributed to the design of the study, interpreted the data, and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Declaration of competing interest None.
References
Baum, Fulton, Wloga, Copin, Pascal et al., Antibody cocktail to sars-cov-2 spike protein prevents rapid mutational escape seen with individual antibodies, Science
Berlin, Gulick, Martinez, Severe covid-19, N Engl J Med
Blanco-Melo, Nilsson-Payant, Liu, Uhl, Hoagland et al., Imbalanced host response to sars-cov-2 drives development of covid-19, Cell
Deeks, Casirivimab/imdevimab: first approval, Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40265-021-01620-z
Falcone, Tiseo, Valoriani, Barbieri, Occhineri et al., Efficacy of bamlanivimab/etesevimab and casirivimab/imdevimab in preventing progression to severe covid-19 and role of variants of concern, Infect Dis Ther
Filippo, Crovetto, Bucek, Nahass, Milano et al., Comparative efficacy of early covid-19 monoclonal antibody therapies: a retrospective analysis, Open Forum Infect Dis
Jaworski, Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for covid-19 treatment and prevention, Biomed J
Li, Sempowski, Saunders, Acharya, Haynes, Sars-cov-2 neutralizing antibodies for covid-19 prevention and treatment, Annu Rev Med, doi:10.1146/annurev-med-042420-113838
Matsunaga, Hayakawa, Terada, Ohtsu, Asai et al., Clinical epidemiology of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19) in Japan: report of the covid-19 registry Japan, Clin Infect Dis
O'brien, Forleo-Neto, Musser, Chan, Sarkar, Subcutaneous regen-cov antibody combination to prevent covid-19, N Engl J Med
Siddiqi, Mehra, Covid-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical-therapeutic staging proposal, J Heart Lung Transplant : the official publication of the International Society for Heart Transplantation
Takashita, Kinoshita, Yamayoshi, Sakai-Tagawa, Fujisaki et al., Efficacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against covid-19 omicron variant, N Engl J Med
Takashita, Kinoshita, Yamayoshi, Sakai-Tagawa, Fujisaki et al., Efficacy of antiviral agents against the sars-cov-2 omicron subvariant ba.2, N Engl J Med
Terada, Ohtsu, Saito, Hayakawa, Tsuzuki et al., Risk factors for severity on admission and the disease progression during hospitalisation in a large cohort of patients with covid-19 in Japan, BMJ Open
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in wuhan, China, JAMA
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Ali, Gao et al., Regn-cov2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with covid-19, N Engl J Med
Williamson, Walker, Bhaskaran, Bacon, Bates et al., Factors associated with covid-19-related death using opensafely, Nature
Wu, Chen, Cai, Xia, Zhou et al., Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002",
"ISSN": [
"1341-321X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002",
"alternative-id": [
"S1341321X22001982"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kadowaki",
"given": "Tomoka",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Imajou",
"given": "Sato",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-9980-6092",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Matsumoto",
"given": "Naomi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Takao",
"given": "Soshi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yorifuji",
"given": "Takashi",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-08T16:03:10Z",
"timestamp": 1657296190000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-11T21:34:23Z",
"timestamp": 1657575263000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-11T22:13:25Z",
"timestamp": 1657577605016
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656633600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1341321X22001982?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1341321X22001982?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bj.2020.11.011",
"article-title": "Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies for covid-19 treatment and prevention",
"author": "Jaworski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "Biomed J",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib4",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Casirivimab/imdevimab: first approval",
"author": "Deeks",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib5",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-021-00525-4",
"article-title": "Efficacy of bamlanivimab/etesevimab and casirivimab/imdevimab in preventing progression to severe covid-19 and role of variants of concern",
"author": "Falcone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2479",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib6",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd0831",
"article-title": "Antibody cocktail to sars-cov-2 spike protein prevents rapid mutational escape seen with individual antibodies",
"author": "Baum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1014",
"journal-title": "Science (New York, NY)",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib7",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "Regn-cov2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with covid-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "238",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib8",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2109682",
"article-title": "Subcutaneous regen-cov antibody combination to prevent covid-19",
"author": "O'Brien",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1184",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib9",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"article-title": "Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in wuhan, China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "934",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib13",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2521-4",
"article-title": "Factors associated with covid-19-related death using opensafely",
"author": "Williamson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "430",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib14",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1061",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib15",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009575",
"article-title": "Severe covid-19",
"author": "Berlin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2451",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib16",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1470",
"article-title": "Clinical epidemiology of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19) in Japan: report of the covid-19 registry Japan",
"author": "Matsunaga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e3677",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib17",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Risk factors for severity on admission and the disease progression during hospitalisation in a large cohort of patients with covid-19 in Japan",
"author": "Terada",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.healun.2020.03.012",
"article-title": "Covid-19 illness in native and immunosuppressed states: a clinical-therapeutic staging proposal",
"author": "Siddiqi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "405",
"journal-title": "J Heart Lung Transplant : the official publication of the International Society for Heart Transplantation",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib19",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Sars-cov-2 neutralizing antibodies for covid-19 prevention and treatment",
"author": "Li",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.026",
"article-title": "Imbalanced host response to sars-cov-2 drives development of covid-19",
"author": "Blanco-Melo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1036",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib21",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofac080",
"article-title": "Comparative efficacy of early covid-19 monoclonal antibody therapies: a retrospective analysis",
"author": "San Filippo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib22",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2119407",
"article-title": "Efficacy of antibodies and antiviral drugs against covid-19 omicron variant",
"author": "Takashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "995",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib23",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2201933",
"article-title": "Efficacy of antiviral agents against the sars-cov-2 omicron subvariant ba.2",
"author": "Takashita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1475",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiac.2022.07.002_bib24",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 18,
"references-count": 18,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1341321X22001982"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Timing of REGEN-COV administration and progression to severe COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article"
}