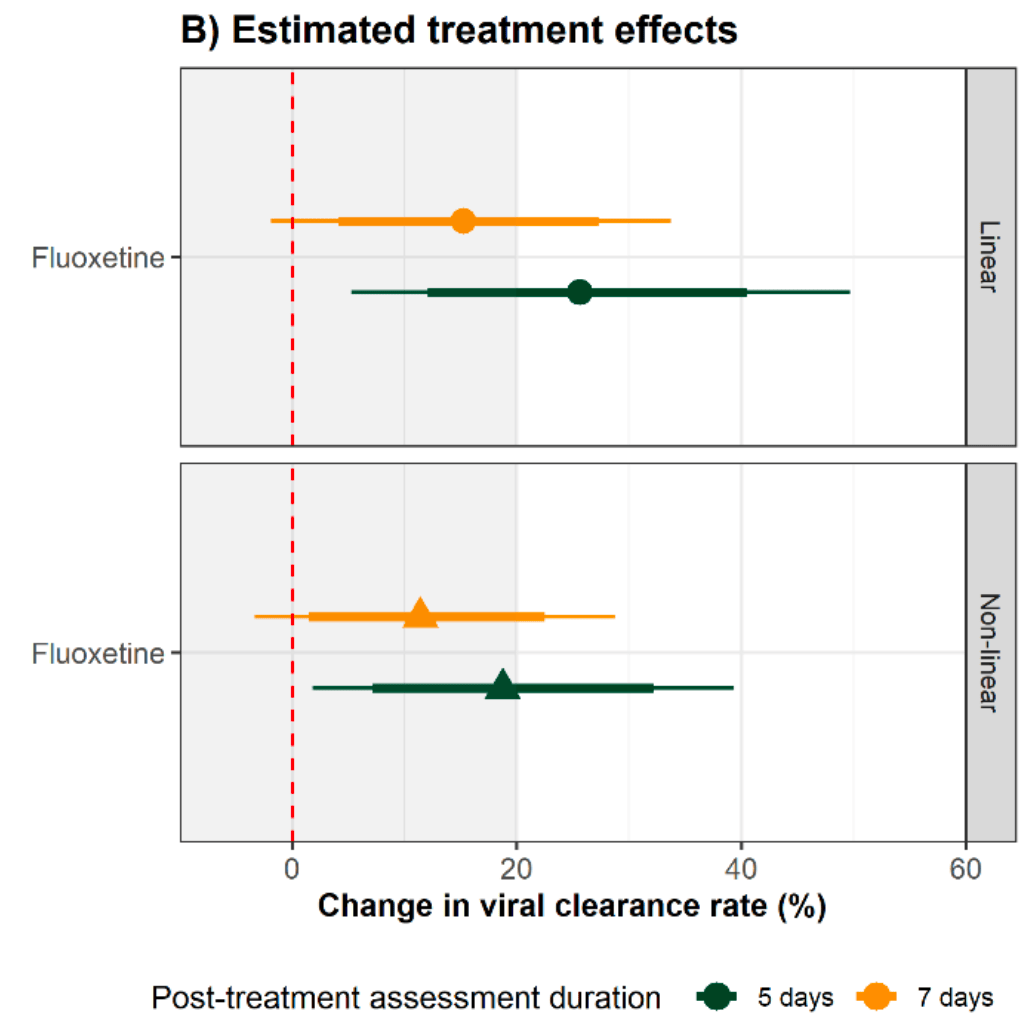
Antiviral efficacy of fluoxetine in early symptomatic COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial (PLATCOV)
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036, PLATCOV, NCT05041907, Jan 2024 (preprint)
31st treatment shown to reduce risk in
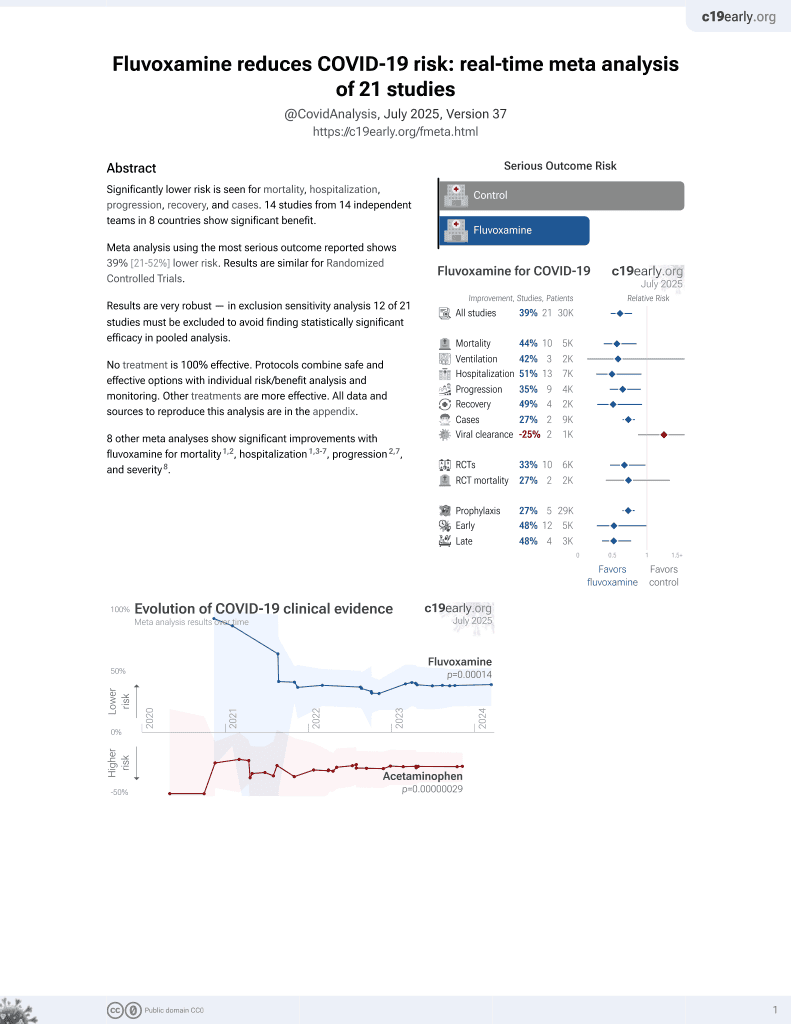
November 2021, now with p = 0.00014 from 21 studies, recognized in 2 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 271 low-risk outpatients, showing improved viral clearance with fluoxetine in low-risk adult outpatients.
Jittamala et al., 18 Jan 2024, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 43 authors, study period 5 April, 2022 - 8 May, 2023, trial NCT05041907 (history) (PLATCOV).
Contact: william@tropmedres.ac, nickw@tropmedres.ac.
Antiviral efficacy of fluoxetine in early symptomatic COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial (PLATCOV)
eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036
Background The selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) fluoxetine and fluvoxamine were repurposed for the treatment of early COVID-19 based on their antiviral activity in vitro, and observational and clinical trial evidence suggesting they prevented progression to severe disease. However, these SSRIs have not been recommended in therapeutic guidelines and their antiviral activity in vivo has not been characterised.
Methods PLATCOV is an open-label, multicentre, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive pharmacometric platform trial running in Thailand, Brazil, Pakistan, and Laos. We recruited low-risk adult outpatients aged 18-50 with early symptomatic COVID-19 (symptoms <4 days) between 5 April 2022 and 8 May 2023. Patients were assigned using block randomisation to one of eleven treatment arms including oral fluoxetine (40 mg/day for 7 days), or no study drug. Uniform randomisation ratios were applied across the active treatment groups while the no study drug group comprised ≥20% of patients at all times. The primary endpoint was the rate of oropharyngeal viral clearance assessed until day 7. Measurements were taken daily between days 0 and 7 and analysed in a modified intention-to-treat population (>2 days follow-up). The viral clearance rate was estimated under a Bayesian hierarchical linear model fitted to the log 10 viral densities measured in standardised duplicate oropharyngeal swab eluates taken daily over one week (18 measurements per patient). Secondary endpoints were all-cause hospital admission at 28 days, and time to resolution of fever and symptoms. This ongoing trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT05041907).
Ethics The trial was approved in Thailand by the Faculty of Tropical Medicine Ethics Committee (Mahidol University, FTMEC Ref: TMEC 21-058) and the Central Research Ethics Committee (CREC, Bangkok, Thailand, CREC Ref: CREC048/64BP-MED34), in Brazil by the Research Ethics Committee of the Universidade Federal de Minas Gerais (COEP-UFMG, Minas Gerais, Brazil, COEP-UFMG) and National Research Ethics Contributors PJ-investigation, methodology, project administration, supervision, validation, and writing-original draft. SB-investigation, methodology, project administration, writing-original draft. PJ and SB contributed equally. WHKS-funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project administration, supervision, validation, and writing-original draft. JAWconceptualisation, data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, methodology, visualisation, and writing-original draft. TN, TS, and VL-Investigation, methodology, supervision. EMB-data curation, formal analysis, visualisation. PW-data curation, formal analysis, visualisation, and writing-original draft. RSA, FRA, and NKG-formal analysis, investigation. LME, PJA, CC, JJC, SS, VK, TN, JT, FQ, and AMK-methodology, investigation, project administration. WM, KS, and AP-investigation, methodology. BH and KP-methodology, investigation, supervision. MP, AS, and BL-resources. WRJT-methodology, supervision. KC and MI-formal analysis, investigation, resources, supervision. SP, AMD, MAB, MMT, WaP, WeP, DC, and SV-methodology,..
References
Bramante, Huling, Tignanelli, Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Butler, Hobbs, Gbinigie, Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial, Lancet
Clelland, Ramiah, Steinberg, Clelland, Analysis of the impact of antidepressants and other medications on COVID-19 infection risk in a chronic psychiatric in-patient cohort, BJPsych Open
De Grooth, Parienti, Surrogate endpoints in pandemic preparedness, J Infect Dis
Development, RStan: the R interface to Stan
Dorji, Tshering, Bangchang, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A5 polymorphisms in South-East and East Asian populations: a systematic review, J Clin Pharm Therapeut
Elias, Khan, Stadler, Viral clearance as a surrogate of clinical efficacy for COVID-19 therapies in outpatients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet Microbe
Eugene, Fluoxetine pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution suggest a possible role in reducing SARS-CoV-2 titers, Research
Fred, Kuivanen, Ugurlu, Antidepressant and antipsychotic drugs reduce viral infection by SARS-CoV-2 and fluoxetine shows antiviral activity against the novel variants in vitro, Front Pharmacol
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Hoertel, Do the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants fluoxetine and fluvoxamine reduce mortality among patients with COVID-19?, JAMA Netw Open
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Gulbins, Association between FIASMA psychotropic medications and reduced risk of intubation or death in individuals with psychiatric disorders hospitalized for severe COVID-19: an observational multicenter study, Transl Psychiatry
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Kornhuber, Antidepressant use and its association with 28-day mortality in inpatients with SARS-CoV-2: support for the FIASMA model against COVID-19, J Clin Med
Hoertel, Sánchez-Rico, Vernet, Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: results from an observational study, Mol Psychiatry
Jittamala, Schilling, Watson, Clinical antiviral efficacy of remdesivir and casirivimab/imdevimab against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.10.17.22281161
Jittamala, Schilling, Watson, Clinical antiviral efficacy of remdesivir in coronavirus disease 2019: an open-label, randomized controlled adaptive platform trial (PLATCOV), J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiad275
Kornhuber, Hoertel, Gulbins, The acid sphingomyelinase/ceramide system in COVID-19, Mol Psychiatry
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Luvira, Schilling, Jittamala, Clinical antiviral efficacy of favipiravir in early COVID-19 (PLATCOV): an open-label, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial, BMC Infect Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-023-08835-3
Mccarthy, Naggie, Boulware, Effect of fluvoxamine vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Oskotsky, Marić, Tang, Mortality risk among patients with COVID-19 prescribed selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants, JAMA Netw Open
Pauletto, Delgado, Da Rocha, Acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) and COVID-19: a review of the potential use of ASM inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2, Cell Biochem Funct
Reiersen, Mattar, Ignacio, The STOP COVID 2 study: fluvoxamine vs placebo for outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19, a fully remote randomized controlled trial, Open Forum Infect Dis
Reis, Moreira-Silva, Silva, Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Glob Health
Reis, Silva, Silva, Oral fluvoxamine with inhaled budesonide for treatment of early-onset COVID-19: a randomized platform trial, Ann Intern Med
Sanderson, Hisner, Ia, A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes, Nature
Schilling, Jittamala, Watson, Antiviral efficacy of molnupiravir versus ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir in patients with early symptomatic COVID-19 (PLATCOV): an open-label, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive trial, Lancet Infect Dis
Schilling, Jittamala, Watson, Pharmacometric assessment of the in vivo antiviral activity of ivermectin in early symptomatic COVID-19, Elife
Singh, Boyd, Schilling, The relationship between viral clearance rates and disease progression in early symptomatic COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis, J Antimicrob Chemother
Siripongboonsitti, Ungtrakul, Tawinprai, Efficacy of combination therapy of fluvoxamine and favipiravir vs favipiravir monotherapy to prevent severe COVID-19 among mild to moderate COVID-19 patients: open-label randomized controlled trial (EFFaCo study), Int J Infect Dis
Standing, Buggiotti, Guerra-Assuncao, Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients, Nat Commun
Stewart, Rebolledo, Mourad, Higher-dose fluvoxamine and time to sustained recovery in outpatients with COVID-19: the ACTIV-6 randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Usher, The global COVID-19 treatment divide, Lancet
Vehtari, Gelman, Gabry, Practical Bayesian model evaluation using leave-one-out cross-validation and WAIC, Stat Comput
Vehtari, Gelman, Simpson, Carpenter, Bürkner, Ranknormalization, folding, and localization: an improved rhat for assessing convergence of MCMC (with discussion), Bayesian Anal
Visser, Identifying efficacious SARS-CoV-2 antivirals in a changing immune landscape, Lancet Infect Dis
Watson, Kissler, Day, Characterizing SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance kinetics to improve the design of antiviral pharmacometric studies, Antimicrob Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/aac.00192-22
Wongnak, Schilling, Jittamala, Temporal changes in SARS-CoV-2 clearance kinetics and the optimal design of antiviral pharmacodynamic studies: an individual patient data metaanalysis of a randomised, controlled, adaptive platform study (PLATCOV), Lancet Infect Dis
Zhuang, Xu, Wu, Post-marketing safety concerns with nirmatrelvir: a disproportionality analysis of spontaneous reports submitted to the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System, Br J Clin Pharmacol
Zimniak, Kirschner, Hilpert, The serotonin reuptake inhibitor Fluoxetine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung tissue, Sci Rep
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036",
"ISSN": [
"2589-5370"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036",
"alternative-id": [
"S2589537024006151"
],
"article-number": "103036",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Antiviral efficacy of fluoxetine in early symptomatic COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial (PLATCOV)"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "eClinicalMedicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jittamala",
"given": "Podjanee",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Boyd",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6328-8748",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Schilling",
"given": "William H.K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Watson",
"given": "James A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ngamprasertchai",
"given": "Thundon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siripoon",
"given": "Tanaya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luvira",
"given": "Viravarn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Batty",
"given": "Elizabeth M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wongnak",
"given": "Phrutsamon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Esper",
"given": "Lisia M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Almeida",
"given": "Pedro J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cruz",
"given": "Cintia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ascencao",
"given": "Fernando R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aguiar",
"given": "Renato S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghanchi",
"given": "Najia K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Callery",
"given": "James J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Singh",
"given": "Shivani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kruabkontho",
"given": "Varaporn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ngernseng",
"given": "Thatsanun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tubprasert",
"given": "Jaruwan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madmanee",
"given": "Wanassanan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Suwannasin",
"given": "Kanokon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Promsongsil",
"given": "Amornrat",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hanboonkunupakarn",
"given": "Borimas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Poovorawan",
"given": "Kittiyod",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Potaporn",
"given": "Manus",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Srisubat",
"given": "Attasit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Loharjun",
"given": "Bootsakorn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Taylor",
"given": "Walter R.J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Qamar",
"given": "Farah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kazi",
"given": "Abdul Momin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Beg",
"given": "M. Asim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chommanam",
"given": "Danoy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vidhamaly",
"given": "Sisouphanh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chotivanich",
"given": "Kesinee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Imwong",
"given": "Mallika",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pukrittayakamee",
"given": "Sasithon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dondorp",
"given": "Arjen M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Day",
"given": "Nicholas P.J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6944-3008",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Teixeira",
"given": "Mauro M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Piyaphanee",
"given": "Watcharapong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Phumratanaprapin",
"given": "Weerapong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "White",
"given": "Nicholas J.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "eClinicalMedicine",
"container-title-short": "eClinicalMedicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-18T18:54:25Z",
"timestamp": 1737226465000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-04T17:54:24Z",
"timestamp": 1738691664000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100010269",
"award": [
"223195/Z/21/Z"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100010269",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Wellcome Trust"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-04T18:10:23Z",
"timestamp": 1738692623662,
"version": "3.37.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1738368000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1738368000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1734307200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2589537024006151?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2589537024006151?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "103036",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib1",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00372-5",
"article-title": "The global COVID-19 treatment divide",
"author": "Usher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "779",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib2",
"volume": "10327",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bcp.15783",
"article-title": "Post-marketing safety concerns with nirmatrelvir: a disproportionality analysis of spontaneous reports submitted to the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System",
"author": "Zhuang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2830",
"journal-title": "Br J Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib3",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00493-0",
"article-title": "Antiviral efficacy of molnupiravir versus ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir in patients with early symptomatic COVID-19 (PLATCOV): an open-label, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive trial",
"author": "Schilling",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib4",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06649-6",
"article-title": "A molnupiravir-associated mutational signature in global SARS-CoV-2 genomes",
"author": "Sanderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "594",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib5",
"volume": "623",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01021-4",
"article-title": "Association between antidepressant use and reduced risk of intubation or death in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: results from an observational study",
"author": "Hoertel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5199",
"journal-title": "Mol Psychiatry",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib6",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.33090",
"article-title": "Mortality risk among patients with COVID-19 prescribed selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants",
"author": "Oskotsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib7",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Antidepressant use and its association with 28-day mortality in inpatients with SARS-CoV-2: support for the FIASMA model against COVID-19",
"author": "Hoertel",
"first-page": "5882",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib8",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41398-022-01804-5",
"article-title": "Association between FIASMA psychotropic medications and reduced risk of intubation or death in individuals with psychiatric disorders hospitalized for severe COVID-19: an observational multicenter study",
"author": "Hoertel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "90",
"journal-title": "Transl Psychiatry",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib9",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1192/bjo.2021.1053",
"article-title": "Analysis of the impact of antidepressants and other medications on COVID-19 infection risk in a chronic psychiatric in-patient cohort",
"author": "Clelland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e6",
"journal-title": "BJPsych Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib10",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Lenze",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2292",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib11",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4",
"article-title": "Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial",
"author": "Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e42",
"journal-title": "Lancet Glob Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib12",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-3305",
"article-title": "Oral fluvoxamine with inhaled budesonide for treatment of early-onset COVID-19: a randomized platform trial",
"author": "Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "667",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib13",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofad419",
"article-title": "The STOP COVID 2 study: fluvoxamine vs placebo for outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19, a fully remote randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Reiersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib14",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2023.23363",
"article-title": "Higher-dose fluvoxamine and time to sustained recovery in outpatients with COVID-19: the ACTIV-6 randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Stewart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2354",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib15",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2201662",
"article-title": "Randomized trial of metformin, ivermectin, and fluvoxamine for Covid-19",
"author": "Bramante",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "599",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib16",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.24100",
"article-title": "Effect of fluvoxamine vs placebo on time to sustained recovery in outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "McCarthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "296",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib17",
"volume": "329",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2023.06.018",
"article-title": "Efficacy of combination therapy of fluvoxamine and favipiravir vs favipiravir monotherapy to prevent severe COVID-19 among mild to moderate COVID-19 patients: open-label randomized controlled trial (EFFaCo study)",
"author": "Siripongboonsitti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "211",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib18",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41380-021-01309-5",
"article-title": "The acid sphingomyelinase/ceramide system in COVID-19",
"author": "Kornhuber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "307",
"journal-title": "Mol Psychiatry",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib19",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cbf.3789",
"article-title": "Acid sphingomyelinase (ASM) and COVID-19: a review of the potential use of ASM inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Pauletto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "284",
"journal-title": "Cell Biochem Funct",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib20",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.755600",
"article-title": "Antidepressant and antipsychotic drugs reduce viral infection by SARS-CoV-2 and fluoxetine shows antiviral activity against the novel variants in vitro",
"author": "Fred",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib21",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib22",
"series-title": "WHO Model List of Essential Medicines - 23rd List",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-85049-0",
"article-title": "The serotonin reuptake inhibitor Fluoxetine inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human lung tissue",
"author": "Zimniak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5890",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib23",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12688/f1000research.53275.1",
"article-title": "Fluoxetine pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution suggest a possible role in reducing SARS-CoV-2 titers",
"author": "Eugene",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "477",
"journal-title": "F1000 Research",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib24",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Butler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib25",
"volume": "401",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiae052",
"article-title": "Surrogate endpoints in pandemic preparedness",
"author": "de Grooth",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1244",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib26",
"volume": "229",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00398-1",
"article-title": "Viral clearance as a surrogate of clinical efficacy for COVID-19 therapies in outpatients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Elias",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e459",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib27",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkae045",
"article-title": "The relationship between viral clearance rates and disease progression in early symptomatic COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-regression analysis",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "935",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib28",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "Pharmacometric assessment of the in vivo antiviral activity of ivermectin in early symptomatic COVID-19",
"author": "Schilling",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib29",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical antiviral efficacy of remdesivir and casirivimab/imdevimab against the SARS-CoV-2 Delta and Omicron variants",
"author": "Jittamala",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiad275",
"article-title": "Clinical antiviral efficacy of remdesivir in coronavirus disease 2019: an open-label, randomized controlled adaptive platform trial (PLATCOV)",
"author": "Jittamala",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1318",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib31",
"volume": "228",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-023-08835-3",
"article-title": "Clinical antiviral efficacy of favipiravir in early COVID-19 (PLATCOV): an open-label, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial",
"author": "Luvira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "89",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib32",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00183-X",
"article-title": "Temporal changes in SARS-CoV-2 clearance kinetics and the optimal design of antiviral pharmacodynamic studies: an individual patient data meta-analysis of a randomised, controlled, adaptive platform study (PLATCOV)",
"author": "Wongnak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "953",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib34",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.00192-22",
"article-title": "Characterizing SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance kinetics to improve the design of antiviral pharmacometric studies",
"author": "Watson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib35",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00254-8",
"article-title": "Identifying efficacious SARS-CoV-2 antivirals in a changing immune landscape",
"author": "Visser",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "936",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib36",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1214/20-BA1221",
"article-title": "Rank-normalization, folding, and localization: an improved rhat for assessing convergence of MCMC (with discussion)",
"author": "Vehtari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "667",
"journal-title": "Bayesian Anal",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib38",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11222-016-9696-4",
"article-title": "Practical Bayesian model evaluation using leave-one-out cross-validation and WAIC",
"author": "Vehtari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1413",
"journal-title": "Stat Comput",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib39",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Do the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor antidepressants fluoxetine and fluvoxamine reduce mortality among patients with COVID-19?",
"author": "Hoertel",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib40",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib42",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 and CYP3A5 polymorphisms in South-East and East Asian populations: a systematic review",
"author": "Dorji",
"first-page": "508",
"journal-title": "J Clin Pharm Therapeut",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib43",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-024-45641-0",
"article-title": "Randomized controlled trial of molnupiravir SARS-CoV-2 viral and antibody response in at-risk adult outpatients",
"author": "Standing",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1652",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2024.103036_bib44",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
}
],
"reference-count": 41,
"references-count": 41,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2589537024006151"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"special_numbering": "C",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Antiviral efficacy of fluoxetine in early symptomatic COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, controlled, adaptive platform trial (PLATCOV)",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "80"
}