Deep Learning-Based Comparative Prediction and Functional Analysis of Intrinsically Disordered Regions in SARS-CoV-2
et al., International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26073411, Apr 2025
In silico study showing that intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) in SARS-CoV-2 proteins are promising targets for small-molecule drug discovery.
Ilyas et al., 5 Apr 2025, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: sidrailyas6@gachon.ac.kr (corresponding author), mananriaz012@gmail.com, dlee@gachon.ac.kr.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Deep Learning-Based Comparative Prediction and Functional Analysis of Intrinsically Disordered Regions in SARS-CoV-2
International Journal of Molecular Sciences, doi:10.3390/ijms26073411
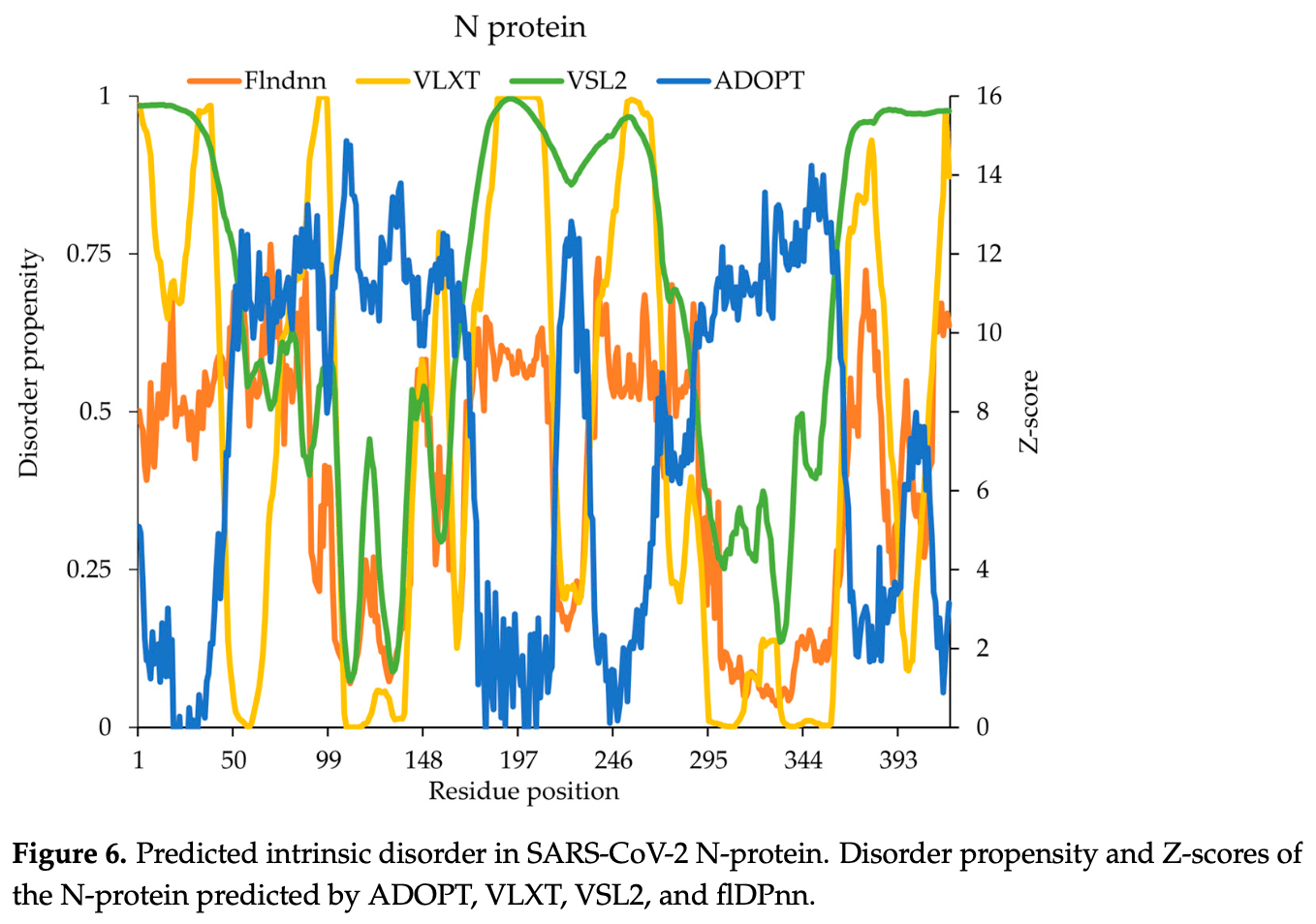
This study explores the role of intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) in the SARS-CoV-2 proteome and their potential as targets for small-molecule drug discovery. Experimentally validated intrinsic disordered regions from the literature were utilized to assess the prediction of intrinsic disorder across a selection of SARS-CoV-2 proteins. The disorder propensities of proteins using four deep learning-based disorder prediction models: ADOPT, PONDR ® VLXT, PONDR ® VSL2, and flDPnn, were analyzed. ADOPT, VSL2, and VLXT identified a flexible linker (129-147), while VSL2 and VLXT predicted disorder in the Cu(II) binding region (163-167) of NSP1. ADOPT did not predict disordered regions in NSP11; however, VSL2 and VLXT identified disorder in the experimentally validated regions. The IDR in ORF3a is crucial for protein localization and immune modulation, affecting inflammatory pathways. VSL2 predicted significant disorder in the N-terminal domain (18-23), which aligns with experimental data (1-41), overlapping with the TRAF-binding motif, while ADOPT indicated high disorder in the C-terminal domain (255-275), consistent with VSL2 and flDPnn. All tools identified disorder in the N-terminal (1-68), central linker (181-248), and C-terminal (370-419) regions of the nucleocapsid (N) protein, suggesting flexibility and accuracy. The S2 subunit of the spike protein displayed more predicted disorder than the S1 subunit across ADOPT, VSL2, and flDPnn. These IDRs are essential for viral functions, like protein localization, immune modulation, receptor binding, and membrane fusion. This study highlights the importance of IDR in modulating key inflammatory pathways, suggesting that they could serve as promising targets for small-molecule drug development to combat COVID-19.
Statistical Analysis The statistical analysis was conducted using Python 3.6, employing the SciPy statistics library. A Chi-squared test was conducted to evaluate the relationship between experimentally validated and predicted disorder data from the ADOPT, VLXT, VSL2, and flDPnn models. This statistical test was employed to determine whether there was a significant association between the observed frequencies of disorder classifications and the expected frequencies under the assumption of independence. By comparing the distribution of predicted and experimentally validated data, the Chi-squared test allowed us to evaluate the degree of agreement between computational predictions and experimental data, thereby providing a quantitative measure of the models' predictive reliability.
Conclusions The analysis of intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) in various SARS-CoV-2 proteins highlights their essential roles in viral replication, host interactions, and immune modulation. Due to their structural plasticity, IDRs enable dynamic protein conformations that facilitate crucial interactions with viral RNA, host cell membranes, and immune pathways. In the SARS-CoV-2 replicase polyprotein 1ab, multiple IDRs, including the flexible linker/spacer in NSP1, the Cu(II)-binding domain in NSP1, the RNA-binding domain in the polymerase, and the lipid-binding region in NSP6, are integral to viral replication and protein synthesis. Their structural flexibility and dynamic interactions with..
References
Anjum, Mohammad, Asrani, Shafie, Singh et al., Identification of Intrinsically Disorder Regions in Non-Structural Proteins of SARS-CoV-2: New Insights into Drug and Vaccine Resistance, Mol. Cell Biochem, doi:10.1007/s11010-022-04393-5
Bah, Vernon, Siddiqui, Krzeminski, Muhandiram et al., Folding of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein by Phosphorylation as a Regulatory Switch, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature13999
Bai, Cao, Liu, Li, The SARS-Cov-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Role in Viral Structure, Biological Functions, and a Potential Target for Drug or Vaccine Mitigation, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13061115
Cheng, Legall, Oldfield, Mueller, Van et al., Rational Drug Design via Intrinsically Disordered Protein, Trends Biotechnol, doi:10.1016/j.tibtech.2006.07.005
Coutard, Valle, De Lamballerie, Canard, Seidah et al., The Spike Glycoprotein of the New Coronavirus 2019-NCoV Contains a Furin-like Cleavage Site Absent in CoV of the Same Clade, Antiviral Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104742
Cubuk, Alston, Incicco, Holehouse, Hall et al., The Disordered N-Terminal Tail of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Forms a Dynamic Complex with RNA, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkad1215
Deng, Jia, Zhang, Protein Structure Prediction, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B, doi:10.1142/S021797921840009X
Dunker, Bondos, Huang, Oldfield, Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Multicellular Organisms, Semin. Cell Dev. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.09.025
Erkizan, Kong, Merchant, Schlottmann, Barber-Rotenberg et al., A Small Molecule Blocking Oncogenic Protein EWS-FLI1 Interaction with RNA Helicase A Inhibits Growth of Ewing's Sarcoma, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/nm.1983
Gadhave, Kumar, Kumar, Bhardwaj, Garg et al., Conformational Dynamics of 13 Amino Acids Long NSP11 of SARS-CoV-2 under Membrane Mimetics and Different Solvent Conditions, Microb. Pathog, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105041
Hattori, Koide, Noval, Panchenko, Romero et al., The ACE2-Binding Interface of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Inherently Deflects Immune Recognition, J. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2020.166748
Hillen, Kokic, Farnung, Dienemann, Tegunov et al., Structure of Replicating SARS-CoV-2 Polymerase, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2368-8
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052
Hu, Katuwawala, Wang, Wu, Ghadermarzi et al., Accurate Intrinsic Disorder Prediction with Putative Propensities of Disorder Functions, Nat. Commun
Huang, Yang, Xu, Xu, Liu, Structural and Functional Properties of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein: Potential Antivirus Drug Development for COVID-19, Acta Pharmacol. Sin, doi:10.1038/s41401-020-0485-4
Iconaru, Das, Nourse, Shelat, Zuo et al., Small Molecule Sequestration of the Intrinsically Disordered Protein, P27Kip1, Within Soluble Oligomers, J. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167120
Kern, Sorum, Mali, Hoel, Sridharan et al., Cryo-EM Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 3a Ion Channel in Lipid Nanodiscs, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.06.17.156554
Khan, Zeb, Ahsan, Ahmed, Ali et al., SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and Nsp3 Binding: An in Silico Study, Arch. Microbiol, doi:10.1007/s00203-020-01998-6
Krishnan, Koveal, Miller, Xue, Akshinthala et al., Targeting the Disordered C Terminus of PTP1B with an Allosteric Inhibitor, Nat. Chem. Biol, doi:10.1038/nchembio.1528
Kumar, Kumar, Saumya, Giri, Investigating the Conformational Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 NSP6 Protein with Emphasis on Non-Transmembrane 91-112 & 231-290 Regions, Microb. Pathog, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105236
Leach, Kuntimaddi, Schmidt, Cierpicki, Johnson et al., Leukemia Fusion Target AF9 Is an Intrinsically Disordered Transcriptional Regulator That Recruits Multiple Partners via Coupled Folding and Binding, Structure, doi:10.1016/j.str.2012.11.011
Li, Romero, Rani, Dunker, Obradovic, Predicting Protein Disorder for N-, C-, and Internal Regions, Genome Inform. Ser. Workshop Genome Inform
Lu, Ye, Singh, Cao, Diedrich et al., The SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Phosphoprotein Forms Mutually Exclusive Condensates with RNA and the Membrane-Associated M Protein, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-20768-y
Mishra, Verma, Rao, Uversky, Nandi, Intrinsically Disordered Proteins of Viruses: Involvement in the Mechanism of Cell Regulation and Pathogenesis, Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci
Morales, Ravanfar, Oyala, Gray, Winkler, Copper(II) Binding to the Intrinsically Disordered C-Terminal Peptide of SARS-CoV-2 Virulence Factor Nsp1, Inorg. Chem, doi:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c01329
Peng, Radivojac, Vucetic, Dunker, Obradovic, Length-Dependent Prediction of Protein in Intrinsic Disorder, BMC Bioinform, doi:10.1186/1471-2105-7-208
Perdikari, Murthy, Ryan, Watters, Naik et al., SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Phase-separates with RNA and with Human HnRNPs, EMBO J, doi:10.15252/embj.2020106478
Pontoriero, Schiavina, Korn, Schlundt, Pierattelli et al., NMR Reveals Specific Tracts within the Intrinsically Disordered Regions of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Involved in RNA Encountering, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom12070929
Quaglia, Salladini, Carraro, Minervini, Tosatto et al., SARS-CoV-2 Variants Preferentially Emerge at Intrinsically Disordered Protein Sites Helping Immune Evasion, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.16379
Redl, Fisicaro, Dutton, Hoffmann, Henderson et al., Intrinsic Protein Disorder Prediction through Deep Bidirectional Transformers, NAR Genom. Bioinform, doi:10.1093/nargab/lqad041
Rizzuti, Lan, Santofimia-Castaño, Zhou, Velázquez-Campoy et al., Design of Inhibitors of the Intrinsically Disordered Protein Nupr1: Balance between Drug Affinity and Target Function, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom11101453
Romero, Obradovic, Li, Garner, Brown et al., Sequence Complexity of Disordered Protein, Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet, doi:10.1002/1097-0134(20010101)42:1%3C38::AID-PROT50%3E3.0.CO;2-3
Salma, Chhatbar, Seshadri, Intrinsically Unstructured Proteins: Potential Targets for Drug Discovery, Am. J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.3844/ajidsp.2009.126.134
Santofimia-Castaño, Rizzuti, Xia, Abian, Peng et al., Targeting Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Involved in Cancer, Cell. Mol. Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s00018-019-03347-3
Schiavina, Pontoriero, Uversky, Felli, Pierattelli, The Highly Flexible Disordered Regions of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid N Protein within the 1-248 Residue Construct: Sequence-Specific Resonance Assignments through NMR, Biomol. NMR Assign, doi:10.1007/s12104-021-10009-8
Schubert, Karousis, Jomaa, Scaiola, Echeverria et al., SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 Binds the Ribosomal MRNA Channel to Inhibit Translation, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol, doi:10.1038/s41594-020-0511-8
Shangary, Wang, Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the MDM2-P53 Protein-Protein Interaction to Reactivate P53 Function: A Novel Approach for Cancer Therapy, Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol
Siu, Yuen, Castano-Rodriguez, Ye, Yeung et al., Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus ORF3a Protein Activates the NLRP3 Inflammasome by Promoting TRAF3-Dependent Ubiquitination of ASC, FASEB J, doi:10.1096/fj.201802418R
Thoms, Buschauer, Ameismeier, Koepke, Denk et al., Structural Basis for Translational Shutdown and Immune Evasion by the Nsp1 Protein of SARS-CoV-2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abc8665
Todorov, Uversky, A Possible Path towards Rapid Development of Live-Attenuated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: Plunging into the Natural Pool, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom10101438
Tompa, Intrinsically Disordered Proteins: A 10-Year Recap, Trends Biochem. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2012.08.004
Uversky, New Technologies to Analyse Protein Function: An Intrinsic Disorder Perspective, doi:10.12688/f1000research.20867.1
Van Roey, Gibson, Davey, Motif Switches: Decision-Making in Cell Regulation, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol, doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2012.03.004
Vasović, Pavlović-Lažetić, Kovačević, Beljanski, Uversky, Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation in SARS-CoV-2 Interactomes, J. Cell Biochem, doi:10.1002/jcb.30502
Wang, Cao, Zhao, Li, Novel Strategies for Drug Discovery Based on Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDPs), Int. J. Mol. Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms12053205
Watanabe, Allen, Wrapp, Mclellan, Crispin, Site-Specific Glycan Analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abb9983
Xie, Vucetic, Iakoucheva, Oldfield, Dunker et al., Functional Anthology of Intrinsic Disorder. 1. Biological Processes and Functions of Proteins with Long Disordered Regions, J. Proteome Res, doi:10.1021/pr060392u
Yang, Rao, Structural Biology of SARS-CoV-2 and Implications for Therapeutic Development, Nat. Rev. Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-021-00630-8
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms26073411",
"ISSN": [
"1422-0067"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073411",
"abstract": "<jats:p>This study explores the role of intrinsically disordered regions (IDRs) in the SARS-CoV-2 proteome and their potential as targets for small-molecule drug discovery. Experimentally validated intrinsic disordered regions from the literature were utilized to assess the prediction of intrinsic disorder across a selection of SARS-CoV-2 proteins. The disorder propensities of proteins using four deep learning-based disorder prediction models: ADOPT, PONDR®VLXT, PONDR®VSL2, and flDPnn, were analyzed. ADOPT, VSL2, and VLXT identified a flexible linker (129–147), while VSL2 and VLXT predicted disorder in the Cu(II) binding region (163–167) of NSP1. ADOPT did not predict disordered regions in NSP11; however, VSL2 and VLXT identified disorder in the experimentally validated regions. The IDR in ORF3a is crucial for protein localization and immune modulation, affecting inflammatory pathways. VSL2 predicted significant disorder in the N-terminal domain (18–23), which aligns with experimental data (1–41), overlapping with the TRAF-binding motif, while ADOPT indicated high disorder in the C-terminal domain (255–275), consistent with VSL2 and flDPnn. All tools identified disorder in the N-terminal (1–68), central linker (181–248), and C-terminal (370–419) regions of the nucleocapsid (N) protein, suggesting flexibility and accuracy. The S2 subunit of the spike protein displayed more predicted disorder than the S1 subunit across ADOPT, VSL2, and flDPnn. These IDRs are essential for viral functions, like protein localization, immune modulation, receptor binding, and membrane fusion. This study highlights the importance of IDR in modulating key inflammatory pathways, suggesting that they could serve as promising targets for small-molecule drug development to combat COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"ijms26073411"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5339-6561",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Herbal Pharmacology, College of Korean Medicine, Gachon University, 1342 Seongnamdae-ro, Sujeong-gu, Seongnam-si 13120, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ilyas",
"given": "Sidra",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0000-8428-9179",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Molecular Science and Technology, Ajou University, Suwon 16499, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Manan",
"given": "Abdul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1075-0713",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Herbal Pharmacology, College of Korean Medicine, Gachon University, 1342 Seongnamdae-ro, Sujeong-gu, Seongnam-si 13120, Republic of Korea"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Donghun",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Molecular Sciences",
"container-title-short": "IJMS",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-08T09:59:00Z",
"timestamp": 1744106340000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-08T10:16:59Z",
"timestamp": 1744107419000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003725",
"award": [
"RS-2024-00354414"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "crossref",
"id": "10.13039/501100003725",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Research Foundation of Korea"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-09T04:17:09Z",
"timestamp": 1744172229038,
"version": "3.40.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1743811200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/26/7/3411/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "3411",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom10101438",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "Todorov, G., and Uversky, V.N. (2020). A Possible Path towards Rapid Development of Live-Attenuated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines: Plunging into the Natural Pool. Biomolecules, 10."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11010-022-04393-5",
"article-title": "Identification of Intrinsically Disorder Regions in Non-Structural Proteins of SARS-CoV-2: New Insights into Drug and Vaccine Resistance",
"author": "Anjum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1607",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell Biochem.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "477",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.09.025",
"article-title": "Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Multicellular Organisms",
"author": "Dunker",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "Semin. Cell Dev. Biol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/pr060392u",
"article-title": "Functional Anthology of Intrinsic Disorder. 1. Biological Processes and Functions of Proteins with Long Disordered Regions",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1882",
"journal-title": "J. Proteome Res.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12688/f1000research.20867.1",
"article-title": "New Technologies to Analyse Protein Function: An Intrinsic Disorder Perspective",
"author": "Uversky",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "F1000 Faculty Rev-101",
"journal-title": "F1000Res.",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.16379",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Variants Preferentially Emerge at Intrinsically Disordered Protein Sites Helping Immune Evasion",
"author": "Quaglia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4240",
"journal-title": "FEBS J.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "289",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc8665",
"article-title": "Structural Basis for Translational Shutdown and Immune Evasion by the Nsp1 Protein of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Thoms",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1249",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.pmbts.2020.03.001",
"article-title": "Intrinsically Disordered Proteins of Viruses: Involvement in the Mechanism of Cell Regulation and Pathogenesis",
"author": "Mishra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tibs.2012.08.004",
"article-title": "Intrinsically Disordered Proteins: A 10-Year Recap",
"author": "Tompa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "Trends Biochem. Sci.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sbi.2012.03.004",
"article-title": "Motif Switches: Decision-Making in Cell Regulation",
"author": "Gibson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "378",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol.",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature13999",
"article-title": "Folding of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein by Phosphorylation as a Regulatory Switch",
"author": "Bah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "106",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "519",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2020.166748",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Hattori, T., Koide, A., Noval, M.G., Panchenko, T., Romero, L.A., Teng, K.W., Tada, T., Landau, N.R., Stapleford, K.A., and Koide, S. (2021). The ACE2-Binding Interface of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Inherently Deflects Immune Recognition. J. Mol. Biol., 433."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41401-020-0485-4",
"article-title": "Structural and Functional Properties of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein: Potential Antivirus Drug Development for COVID-19",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1141",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharmacol. Sin.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00203-020-01998-6",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and Nsp3 Binding: An in Silico Study",
"author": "Khan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "Arch. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13061115",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_15",
"unstructured": "Bai, Z., Cao, Y., Liu, W., and Li, J. (2021). The SARS-Cov-2 Nucleocapsid Protein and Its Role in Viral Structure, Biological Functions, and a Potential Target for Drug or Vaccine Mitigation. Viruses, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12104-021-10009-8",
"article-title": "The Highly Flexible Disordered Regions of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid N Protein within the 1–248 Residue Construct: Sequence-Specific Resonance Assignments through NMR",
"author": "Schiavina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "219",
"journal-title": "Biomol. NMR Assign.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms12053205",
"article-title": "Novel Strategies for Drug Discovery Based on Intrinsically Disordered Proteins (IDPs)",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3205",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Sci.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00630-8",
"article-title": "Structural Biology of SARS-CoV-2 and Implications for Therapeutic Development",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "685",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-020-0511-8",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 Binds the Ribosomal MRNA Channel to Inhibit Translation",
"author": "Schubert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "959",
"journal-title": "Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c01329",
"article-title": "Copper(II) Binding to the Intrinsically Disordered C-Terminal Peptide of SARS-CoV-2 Virulence Factor Nsp1",
"author": "Morales",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8992",
"journal-title": "Inorg. Chem.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2368-8",
"article-title": "Structure of Replicating SARS-CoV-2 Polymerase",
"author": "Hillen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105236",
"article-title": "Investigating the Conformational Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 NSP6 Protein with Emphasis on Non-Transmembrane 91–112 & 231–290 Regions",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105236",
"journal-title": "Microb. Pathog.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "161",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105041",
"article-title": "Conformational Dynamics of 13 Amino Acids Long NSP11 of SARS-CoV-2 under Membrane Mimetics and Different Solvent Conditions",
"author": "Gadhave",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105041",
"journal-title": "Microb. Pathog.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104742",
"article-title": "The Spike Glycoprotein of the New Coronavirus 2019-NCoV Contains a Furin-like Cleavage Site Absent in CoV of the Same Clade",
"author": "Coutard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "104742",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb9983",
"article-title": "Site-Specific Glycan Analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike",
"author": "Watanabe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "330",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.06.17.156554",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Kern, D.M., Sorum, B., Mali, S.S., Hoel, C.M., Sridharan, S., Remis, J.P., Toso, D.B., Kotecha, A., Bautista, D.M., and Brohawn, S.G. (2021). Cryo-EM Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 3a Ion Channel in Lipid Nanodiscs. bioRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fj.201802418R",
"article-title": "Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus ORF3a Protein Activates the NLRP3 Inflammasome by Promoting TRAF3-Dependent Ubiquitination of ASC",
"author": "Siu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8865",
"journal-title": "FASEB J.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom12070929",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_29",
"unstructured": "Pontoriero, L., Schiavina, M., Korn, S.M., Schlundt, A., Pierattelli, R., and Felli, I.C. (2022). NMR Reveals Specific Tracts within the Intrinsically Disordered Regions of the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Involved in RNA Encountering. Biomolecules, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkad1215",
"article-title": "The Disordered N-Terminal Tail of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Forms a Dynamic Complex with RNA",
"author": "Cubuk",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2609",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcb.30502",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_31",
"unstructured": "Vasović, L.M., Pavlović-Lažetić, G.M., Kovačević, J.J., Beljanski, M.V., and Uversky, V.N. (2023). Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation in SARS-CoV-2 Interactomes. J. Cell Biochem., 125."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-20768-y",
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Phosphoprotein Forms Mutually Exclusive Condensates with RNA and the Membrane-Associated M Protein",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "502",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2020106478",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Phase-separates with RNA and with Human HnRNPs",
"author": "Perdikari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e106478",
"journal-title": "EMBO J.",
"key": "ref_33",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3844/ajidsp.2009.126.134",
"article-title": "Intrinsically Unstructured Proteins: Potential Targets for Drug Discovery",
"author": "Salma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "126",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tibtech.2006.07.005",
"article-title": "Rational Drug Design via Intrinsically Disordered Protein",
"author": "Cheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "435",
"journal-title": "Trends Biotechnol.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-019-03347-3",
"article-title": "Targeting Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Involved in Cancer",
"author": "Rizzuti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1695",
"journal-title": "Cell. Mol. Life Sci.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.48.113006.094723",
"article-title": "Small-Molecule Inhibitors of the MDM2-P53 Protein-Protein Interaction to Reactivate P53 Function: A Novel Approach for Cancer Therapy",
"author": "Shangary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nchembio.1528",
"article-title": "Targeting the Disordered C Terminus of PTP1B with an Allosteric Inhibitor",
"author": "Krishnan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "558",
"journal-title": "Nat. Chem. Biol.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.1983",
"article-title": "A Small Molecule Blocking Oncogenic Protein EWS-FLI1 Interaction with RNA Helicase A Inhibits Growth of Ewing’s Sarcoma",
"author": "Erkizan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "750",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167120",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_40",
"unstructured": "Iconaru, L.I., Das, S., Nourse, A., Shelat, A.A., Zuo, J., and Kriwacki, R.W. (2021). Small Molecule Sequestration of the Intrinsically Disordered Protein, P27Kip1, Within Soluble Oligomers. J. Mol. Biol., 433."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.str.2012.11.011",
"article-title": "Leukemia Fusion Target AF9 Is an Intrinsically Disordered Transcriptional Regulator That Recruits Multiple Partners via Coupled Folding and Binding",
"author": "Leach",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "176",
"journal-title": "Structure",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biom11101453",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_42",
"unstructured": "Rizzuti, B., Lan, W., Santofimia-Castaño, P., Zhou, Z., Velázquez-Campoy, A., Abián, O., Peng, L., Neira, J.L., Xia, Y., and Iovanna, J.L. (2021). Design of Inhibitors of the Intrinsically Disordered Protein Nupr1: Balance between Drug Affinity and Target Function. Biomolecules, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1142/S021797921840009X",
"article-title": "Protein Structure Prediction",
"author": "Deng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1840009",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mod. Phys. B",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/1097-0134(20010101)42:1<38::AID-PROT50>3.0.CO;2-3",
"article-title": "Sequence Complexity of Disordered Protein",
"author": "Romero",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "38",
"journal-title": "Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"article-title": "Predicting Protein Disorder for N-, C-, and Internal Regions",
"author": "Li",
"first-page": "30",
"journal-title": "Genome Inform. Ser. Workshop Genome Inform.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "10",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-7-208",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_46",
"unstructured": "Peng, K., Radivojac, P., Vucetic, S., Dunker, A.K., and Obradovic, Z. (2006). Length-Dependent Prediction of Protein in Intrinsic Disorder. BMC Bioinform., 7."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nargab/lqad041",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_47",
"unstructured": "Redl, I., Fisicaro, C., Dutton, O., Hoffmann, F., Henderson, L., Owens, B.M.J., Heberling, M., Paci, E., and Tamiola, K. (2023). ADOPT: Intrinsic Protein Disorder Prediction through Deep Bidirectional Transformers. NAR Genom. Bioinform., 5."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-24773-7",
"article-title": "FlDPnn: Accurate Intrinsic Disorder Prediction with Putative Propensities of Disorder Functions",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4438",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 48,
"references-count": 48,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/26/7/3411"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Deep Learning-Based Comparative Prediction and Functional Analysis of Intrinsically Disordered Regions in SARS-CoV-2",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "26"
}