Effect of zinc supplementation on symptom reduction and length of hospital stay among pediatric patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
et al., Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011, Mar 2023
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
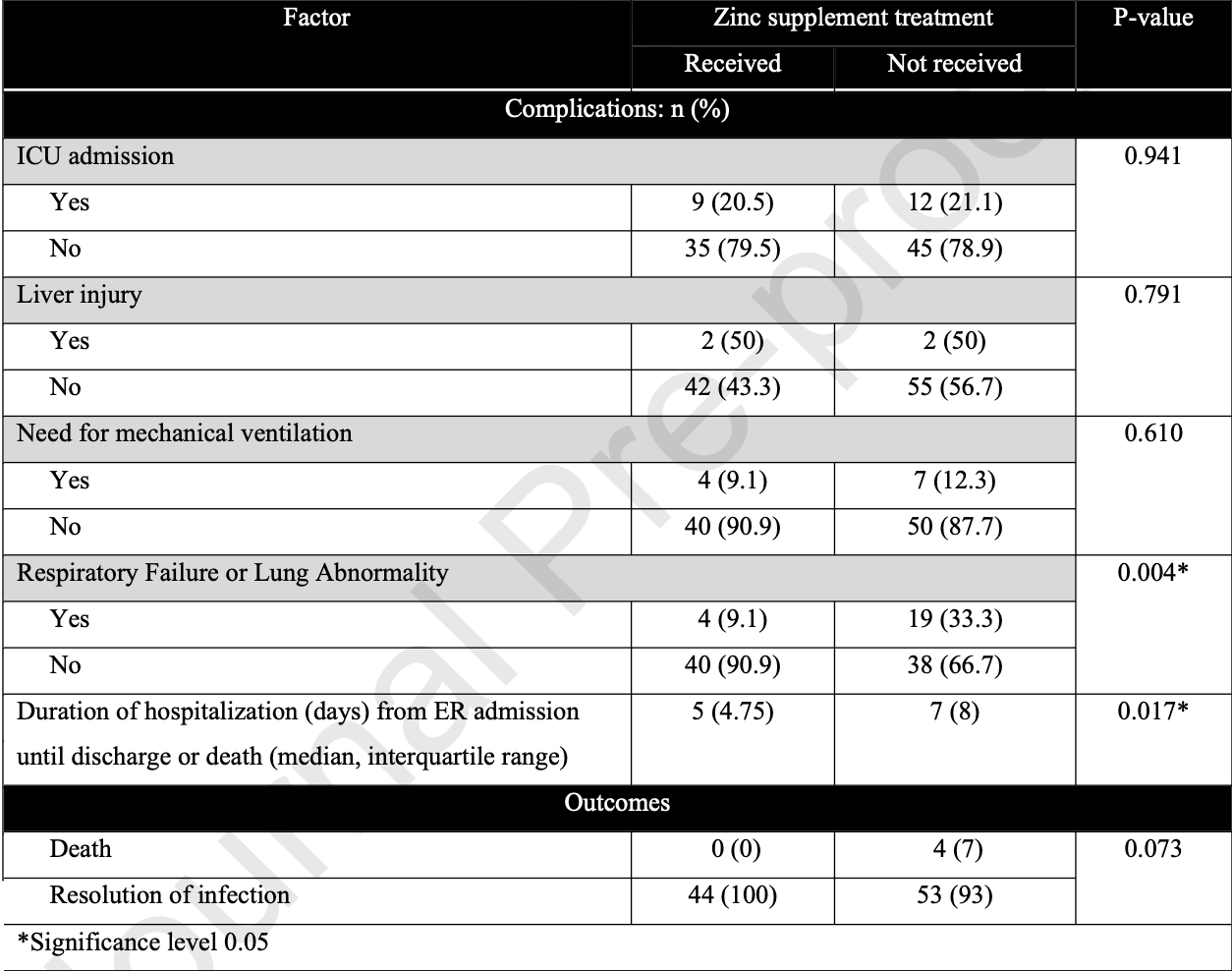
Retrospective 101 hospitalized pediatric patients in Saudi Arabia, showing zinc treatment associated with lower respiratory failure and shorter hospitalization in unadjusted results. Patients receiving zinc were older. Authors note elevated serum creatinine and the possibility of kidney injury.
Authors claim that zinc administration is associated with elevated serum creatinine and potential kidney injury. However, serum creatinine naturally increases with age and muscle mass in children. Given the zinc group was older, this difference is biologically expected and within normal limits.
In Section 3.4, the text states that administering zinc lowered the incidence of 'insomnia' (4.5% vs 26.3%, p=0.004). However, Table 4 reports these percentages for 'anosmia'.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
excessive unadjusted differences between groups.
|
risk of death, 87.6% lower, RR 0.12, p = 0.13, treatment 0 of 44 (0.0%), control 4 of 57 (7.0%), NNT 14, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 26.0% lower, RR 0.74, p = 0.75, treatment 4 of 44 (9.1%), control 7 of 57 (12.3%), NNT 31.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 2.8% lower, RR 0.97, p = 1.00, treatment 9 of 44 (20.5%), control 12 of 57 (21.1%), NNT 167.
|
|
respiratory failure, 72.7% lower, RR 0.27, p = 0.004, treatment 4 of 44 (9.1%), control 19 of 57 (33.3%), NNT 4.1.
|
|
hospitalization time, 28.6% lower, relative time 0.71, p = 0.02, treatment 44, control 57.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ibrahim Alhajjaji et al., 4 Mar 2023, retrospective, Saudi Arabia, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 31 December, 2021.
Contact: ghufran.alhajjaji@gmail.com, nealotaibi@uqu.edu.sa, ph.nada.abutaleb@gmail.com, mmiteb@psmmc.med.sa, ph.alhajjaji@gmail.com, assalotaibi@uqu.edu.sa, bmalshehail@iau.edu.sa, me.alotaibi@psmmc.med.sa.
Effect of zinc supplementation on symptom reduction and length of hospital stay among pediatric patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, doi:10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
Abd-Elsalam, Soliman, Esmail, Zinc supplementation promotes a th1 response and improves clinical symptoms in fewer hours in children with pneumonia younger than 5 years old. A randomized controlled clinical trial, Frontiers in Pediatrics
Alghamdi, Talhi, Najjar, Sobhi, Juaid et al., Epidemiology, clinical characteristics and risk factors of COVID-19 among children in Saudi Arabia: a multicenter chart review study, BMC Pediatr, doi:10.1186/s12887-021-02959-8
Azkur, Akdis, Azkur, Immune response to SARS-COV-2 and mechanisms of immunopathological changes in Covid-19, Allergy
Barnard, Wong, Bailey, Effect of oral Gavage treatment with znal42 and other metallo-ion formulations on influenza A H5N1 and H1N1 virus infections in mice, Antiviral Chemistry and Chemotherapy
Barnett, Hamer, Meydani, Low zinc status: A new risk factor for pneumonia in the elderly?, Nutrition Reviews
Beran, Mhanna, Srour, Ayesh, Stewart et al., Clinical significance of micronutrient supplements in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Nutr ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.12.033
Carlos, Cruz, Cao, Novel wuhan (2019-ncov) coronavirus. American Journal of, Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
Carlucci, Ahuja, Petrilli, Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Journal of Medical Microbiology
Ding, Lu, Fan, The clinical characteristics of pneumonia patients coinfected with 2019 novel coronavirus and influenza virus in Wuhan, China, Journal of Medical Virology
Elalfy, Besheer, El-Mesery, Effect of a combination of nitazoxanide, ribavirin, and ivermectin plus zinc supplement (MANS.NRIZ study) on the clearance of mild COVID-19
Frontera, Rahimian, Yaghi, Treatment with zinc is associated with reduced inhospital mortality among COVID-19 patients: A multi-center cohort study
Gonçalves, Gonçalves, Guarnieri, Association between low zinc levels and severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome by new coronavirus SARS-COV-2, Nutrition in Clinical Practice
Hamer, Kivimäki, Gale, Lifestyle risk factors, inflammatory mechanisms, and covid-19 hospitalization: A community-based cohort study of 387,109 adults in UK, Brain, Behavior, and Immunity
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, The Lancet
Jordan, Adab, Cheng, Covid-19: Risk factors for severe disease and death, BMJ
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Covid-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, International Journal of Infectious Diseases
Kumar, Kubota, Chernov, Potential role of zinc supplementation in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19, Medical Hypotheses
Lee, Critical role of zinc as either an antioxidant or a prooxidant in cellular systems, Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
Lu, Zhang, Du, Zhang, Li et al., Chinese Pediatric Novel Coronavirus Study Team. SARS-COV-2 infection in children, New England Journal Med
Pormohammad, Monych, Turner, Zinc and SARS-COV-2: A molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase and 3c-like proteinase enzymes, International Journal of Molecular Medicine
Qiu, Wu, Hong, Clinical and epidemiological features of 35 children with corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Zhejiang, China. An observational cohort studies, Lancet Infect Dis
Read, Obeid, Ahlenstiel, The role of zinc in antiviral immunity, Advances in Nutrition
Riphagen, Gomez, Gonzalez-Martinez, Hyperinflammatory shock in children during COVID-19 pandemic, The Lancet
Shereen, Khan, Kazmi, Covid-19 infection: Emergence, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses, Journal of Advanced Research
Skalny, Rink, Ajsuvakova, Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for covid-19 (review), International Journal of Molecular Medicine
Su, Wong, Shi, Epidemiology, genetic recombination, and pathogenesis of Coronaviruses, Trends in Microbiology
Sulaiman, Aljuhani, Shaya, Evaluation of zinc sulfate as an adjunctive therapy in COVID-19 critically ill patients: a two-center propensity-score matched study, Critical Care
Tagarro, Epalza, Santos, Screening and severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19) in children in Madrid, Spain, JAMA Pediatrics
Tang, Tou, Wang, Prevention and control strategies for emergency, limited-term, and elective operations in pediatric surgery during the epidemic period of covid-19, World Journal of Pediatric Surgery
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Zn2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathogens
Verdoni, Mazza, Gervasoni, An outbreak of severe kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-COV-2 epidemic: An observational cohort study, The Lancet
Wang, Brar, Covid-19 in children: An epidemiology study from China, The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice
Weiss, Leibowitz, Wessels, Rolles, Rink, Coronavirus pathogenesis
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19) outbreak in China, JAMA
Wu, Wu, Liu, The SARS-COV-2 outbreak: What we know, International Journal of Infectious Diseases
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011",
"ISSN": [
"1319-0164"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011",
"alternative-id": [
"S1319016423000415"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Effect of zinc supplementation on symptom reduction and length of hospital stay among pediatric patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of King Saud University."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ibrahim Alhajjaji",
"given": "Ghufran",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alotaibi",
"given": "Nouf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abutaleb",
"given": "Nada",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alotaibi",
"given": "Mishal M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alhajjaji",
"given": "Abdulrahman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alotaibi",
"given": "Abdulmalik S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alshehail",
"given": "Bashayer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alotaibi",
"given": "Moawad E.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal",
"container-title-short": "Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-04T01:34:01Z",
"timestamp": 1677893641000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-04T01:34:21Z",
"timestamp": 1677893661000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-04T02:11:56Z",
"timestamp": 1677895916726
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677628800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2023-02-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1677456000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1319016423000415?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1319016423000415?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Do Zinc Supplements Enhance the Clinical Efficacy of Hydroxychloroquine?",
"author": "Abd-Elsalam",
"first-page": "3642",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "A Randomized, Multicenter Trial.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0005",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Zinc supplementation promotes a th1 response and improves clinical symptoms in fewer hours in children with pneumonia younger than 5 years old. A randomized controlled clinical trial. Frontiers",
"author": "Acevedo-Murillo",
"first-page": "431",
"journal-title": "Pediatrics.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0010",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12887-021-02959-8",
"article-title": "Epidemiology, clinical characteristics and risk factors of COVID-19 among children in Saudi Arabia: a multicenter chart review study",
"author": "AlGhamdi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "86",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Pediatr.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0015",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Evaluation of zinc sulfate as an adjunctive therapy in COVID-19 critically ill patients: a two-center propensity-score matched study",
"author": "Al Sulaiman",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Critical Care.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0020",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14364",
"article-title": "Immune response to SARS-COV-2 and mechanisms of immunopathological changes in Covid-19",
"author": "Azkur",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1564",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Allergy.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0025",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/095632020701800302",
"article-title": "Effect of oral Gavage treatment with znal42 and other metallo-ion formulations on influenza A H5N1 and H1N1 virus infections in mice",
"author": "Barnard",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Chemistry and Chemotherapy.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0030",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1753-4887.2009.00253.x",
"article-title": "Low zinc status: A new risk factor for pneumonia in the elderly?",
"author": "Barnett",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "30",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrition Reviews.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0035",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.12.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0040",
"unstructured": "Beran A, Mhanna M, Srour O, Ayesh H, Stewart JM, Hjouj M, Khokher W, Mhanna AS, Ghazaleh D, Khader Y, Sayeh W, Assaly R. Clinical significance of micronutrient supplements in patients with coronavirus disease 2019: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2022 Apr;48:167-177. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.12.033. Epub 2022 Jan 13. PMID: 35331487; PMCID: PMC8755558."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.2014P7",
"article-title": "Novel wuhan (2019-ncov) coronavirus",
"author": "Carlos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0045",
"volume": "201",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jmm.0.001250",
"article-title": "Zinc sulfate in combination with a zinc ionophore may improve outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Carlucci",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1228",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Journal of Medical Microbiology.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0050",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0055",
"unstructured": "Coronavirus disease (covid-19), 2020. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/q-a-coronaviruses. [accessed 15th October 2021]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25781",
"article-title": "The clinical characteristics of pneumonia patients coinfected with 2019 novel coronavirus and influenza virus in Wuhan",
"author": "Ding",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1549",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "China. Journal of Medical Virology.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0060",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Elalfy",
"first-page": "3176",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Effect of a combination of nitazoxanide, ribavirin, and ivermectin plus zinc supplement (MANS.NRIZ study) on the clearance of mild COVID-19.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0065",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-94509/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0070",
"unstructured": "Frontera JA, Rahimian JO, Yaghi S, et al. Treatment with zinc is associated with reduced in-hospital mortality among COVID-19 patients: A multi-center cohort study. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ncp.10612",
"article-title": "Association between low zinc levels and severity of acute respiratory distress syndrome by new coronavirus SARS-COV-2",
"author": "Gonçalves",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "186",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrition in Clinical Practice.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0075",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.059",
"article-title": "Lifestyle risk factors, inflammatory mechanisms, and covid-19 hospitalization: A community-based cohort study of 387,109 adults in UK",
"author": "Hamer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "184",
"journal-title": "Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0080",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "China. The Lancet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0085",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"article-title": "Covid-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency",
"author": "Jothimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0090",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Covid-19: Risk factors for severe disease and death",
"author": "Jordan",
"journal-title": "BMJ.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0095",
"volume": "1198",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109848",
"article-title": "Potential role of zinc supplementation in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Medical Hypotheses.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0100",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Critical role of zinc as either an antioxidant or a prooxidant in cellular systems",
"author": "Lee",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0105",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2005073",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0110",
"unstructured": "Lu X, Zhang L, Du H, Zhang J, Li YY, Qu J, et al.; Chinese Pediatric Novel Coronavirus Study Team. SARS-COV-2 infection in children. New England Journal Med 2020; 382: 1663-1665."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790",
"article-title": "Zinc and SARS-COV-2: A molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase and 3c-like proteinase enzymes",
"author": "Pormohammad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "326",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Molecular Medicine.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0115",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30198-5",
"article-title": "Clinical and epidemiological features of 35 children with corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Zhejiang, China. An observational cohort studies",
"author": "Qiu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "689",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0120",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmz013",
"article-title": "The role of zinc in antiviral immunity",
"author": "Read",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "696",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Advances in Nutrition.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0125",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31094-1",
"article-title": "Hyperinflammatory shock in children during COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Riphagen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1607",
"issue": "10237",
"journal-title": "The Lancet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0130",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0135",
"unstructured": "Saudi MoH Protocol for Patients Suspected of/Confirmed with COVID-19, 2022. Ministry of health (MOH). https://www.moh.gov.sa/en/Ministry/MediaCenter/Publications/Pages/covid19.aspx[accessed 18th January 2023]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jare.2020.03.005",
"article-title": "Covid-19 infection: Emergence, transmission, and characteristics of human coronaviruses",
"author": "Shereen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Journal of Advanced Research.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0140",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for covid-19 (review)",
"author": "Skalny",
"first-page": "17",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Molecular Medicine.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0145",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tim.2016.03.003",
"article-title": "Epidemiology, genetic recombination, and pathogenesis of Coronaviruses",
"author": "Su",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "490",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Trends in Microbiology.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0150",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1346",
"article-title": "Screening and severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (covid- 19) in children in Madrid",
"author": "Tagarro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "316",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Spain. JAMA Pediatrics.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0155",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Prevention and control strategies for emergency, limited-term, and elective operations in pediatric surgery during the epidemic period of covid-19. World",
"author": "Tang",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Journal of Pediatric Surgery.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0160",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1001176",
"article-title": "Zn2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture",
"author": "Te Velthuis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathogens.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0165",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31103-X",
"article-title": "An outbreak of severe kawasaki-like disease at the Italian epicentre of the SARS-COV-2 epidemic: An observational cohort study",
"author": "Verdoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1771",
"issue": "10239",
"journal-title": "The Lancet.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0170",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Covid-19 in children: An epidemiology study from China. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology",
"author": "Wang",
"first-page": "2118",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "In Practice.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0175",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/B978-0-12-385885-6.00009-2",
"article-title": "Coronavirus pathogenesis",
"author": "Weiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Advances in Virus Research.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0180",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01712",
"article-title": "The Potential Impact of Zinc Supplementation on COVID-19 Pathogenesis",
"author": "Wessels",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Immunology.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0185",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.004",
"article-title": "The SARS-COV-2 outbreak: What we know",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0190",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"article-title": "Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19) outbreak in China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1239",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "10.1016/j.jsps.2023.02.011_b0195",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 39,
"references-count": 39,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1319016423000415"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmaceutical Science",
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of zinc supplementation on symptom reduction and length of hospital stay among pediatric patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
