Safety and Intranasal Retention of a Broad-Spectrum Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibody SA55 Nasal Spray in Healthy Volunteers: A Phase I Clinical Trial
et al., Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics17010043, NCT06048393, Dec 2024
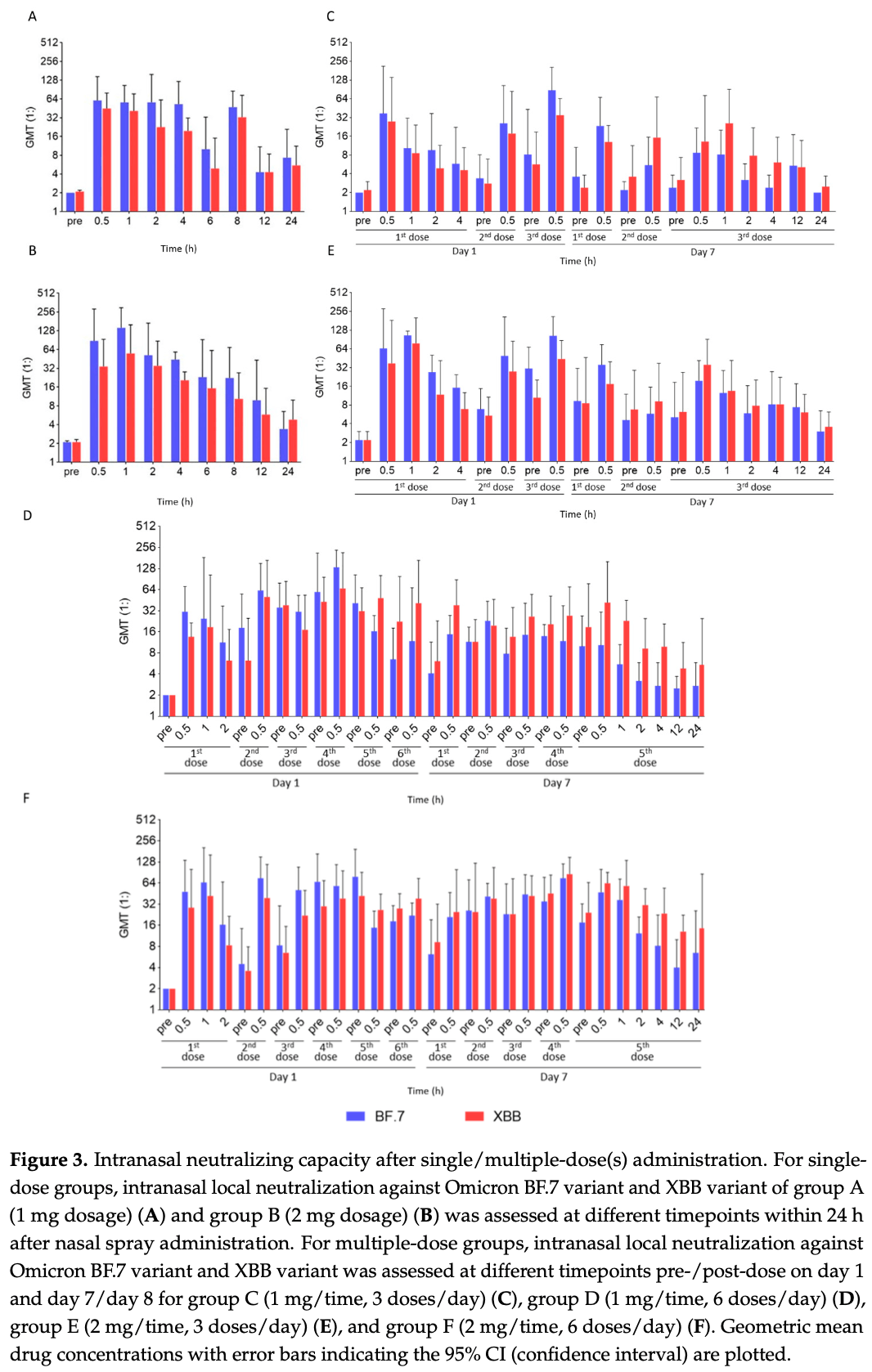
Phase 1 dose-escalation trial of 80 healthy volunteers showing favorable safety, tolerability, nasal retention, and neutralizing activity with a single dose or 7 days of an intranasal broad-spectrum anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody SA55 nasal spray. Nasal local drug concentration and neutralizing activity were generally stable within 4-8 hours after administration, with favorable neutralization activity against Omicron BF.7 and XBB strains. No serious adverse events were reported.
Hu et al., 31 Dec 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, China, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, study period 2 June, 2023 - 11 August, 2023, trial NCT06048393 (history).
Contact: yunlongcao@pku.edu.cn (corresponding author), huchaoying@mail.ccmu.edu.cn, zhouyibo@mail.ccmu.edu.cn, mengx@sinovac.com, jhli@cdc.zj.cn, chenjx0369@sinovac.com, huyl@sinovac.com, yzf_0812@nifdc.org.cn, sunneyxie@pku.edu.cn, ronghuajin@ccmu.edu.cn.
Safety and Intranasal Retention of a Broad-Spectrum Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibody SA55 Nasal Spray in Healthy Volunteers: A Phase I Clinical Trial
Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics17010043
Background: A broad-spectrum anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody (mAb), SA55, is highly effective against SARS-CoV-2 variants. This trial aimed at demonstrating the safety, tolerability, local drug retention and neutralizing activity, systemic exposure level, and immunogenicity of the SA55 nasal spray in healthy individuals. Methods: This phase I, dose-escalation clinical trial combined an open-label design with a randomized, controlled, double-blind design. Healthy participants aged 18-65 years were enrolled and received a single dose of the SA55 nasal spray (1 mg or 2 mg) or multiple doses of SA55 nasal spray/placebo for 7 days (1 or 2 mg/dose, 3 or 6 doses/day). Safety monitoring was conducted throughout the study. Nasal swabs and venous blood samples were collected to analyze local drug concentration/neutralization, systemic exposure, and immunogenicity. Results: From 2 June to 11 August 2023, 80 participants were enrolled and received study intervention. The severity of adverse reactions (ADRs) reported during the study was mild in all cases, and all ADRs were laboratory test abnormalities without corresponding symptoms or vital signs. A total of 9 ADRs were reported, of which all were mild in severity. Overall ADR incidence rate was 16.67% (8/48) in single-dose groups and 4.17% (1/24) in multiple-dose groups. The nasal local drug concentration and neutralizing activity were generally stable within 4-8 h, with favorable neutralization activity against Omicron BF.7 and XBB strains. Conclusions: This study demonstrated favorable safety and tolerability of the SA55 nasal spray in healthy volunteers, exhibited satisfactory neutralizing activity against Omicron variants intranasally, and indicated low systemic toxicity risk.
pharmacokinetics after a single dose and to eliminate the underestimation of local drug residue caused by multiple sampling after a single dose in the same place, participants in the single-dose group were only sampled once from each nasal cavity after administration. Therefore, the drug concentration-time curve was plotted based on data from different participants, making it impossible to calculate pharmacokinetic parameters. In conclusion, this study demonstrated the favorable safety and tolerability of the SA55 nasal spray in healthy volunteers and satisfactory intranasal neutralizing activity against Omicron variants after administration. Furthermore, minimal systemic exposure was observed in the highest-dosage group, and no drug-related anti-drug antibodies were detected, indicating a low risk of systemic toxicity.
Supplementary Materials: The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www. mdpi.com/article/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010043/s1 , Figure S1 : Blood concentration of SA55 in Group F at different timepoints after administration; Table S1 : Study design of dosing regimen and sample collection timepoints. Author Contributions: C.H., X.M., J.C. and R.J. designed/generated the study protocol. X.S.X., Y.H. and Y.C. provided oversight and supervision and contributed to the conception of this work. Y.Z., C.H. and R.J. coordinated the trial and were responsible for the field work. J.C. conducted project management. J.L. and Z.Y. contributed to..
References
Aleem, Vaqar, Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for High-Risk Coronavirus (COVID 19) Patients With Mild To Moderate Disease Presentations
Cameroni, Bowen, Rosen, Saliba, Zepeda et al., Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron antigenic shift, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04386-2
Cao, Jian, Zhang, Yisimayi, Hao et al., Rational identification of potent and broad sarbecovirus-neutralizing antibody cocktails from SARS convalescents, Cell Reports, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111845
Cao, Wang, Jian, Xiao, Song et al., Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3
Cele, Jackson, Khoury, Khan, Moyo-Gwete et al., Omicron extensively but incompletely escapes Pfizer BNT162b2 neutralization, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-021-04387-1
Chen, Nadeau, Yared, Voinov, Xie et al., CoV-Spectrum: Analysis of globally shared SARS-CoV-2 data to identify and characterize new variants, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btab856
Cohen, Nirula, Mulligan, Novak, Marovich et al., Effect of Bamlanivimab vs. Placebo on Incidence of COVID-19 Among Residents and Staff of Skilled Nursing and Assisted Living Facilities: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.8828
Hansen, Baum, Pascal, Russo, Giordano et al., Studies in humanized mice and convalescent humans yield a SARS-CoV-2 antibody cocktail, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abd0827
Jian, Feng, Yang, Yu, Wang et al., Convergent evolution of SARS-CoV-2 XBB lineages on receptor-binding domain 455-456 synergistically enhances antibody evasion and ACE2 binding, PLoS Pathogens, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1011868
Jian, Yu, Song, Yisimayi, Yu et al., Further humoral immunity evasion of emerging SARS-CoV-2 BA.4 and BA.5 subvariants, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00642-9
Li, Hilgenfeld, Whitley, De Clercq, Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: Progress and lessons learned, Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov, doi:10.1038/s41573-023-00672-y
Li, Peng, Deng, Yang, Chen et al., Real-world effectiveness of an intranasal spray A8G6 antibody cocktail in the post-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01656-5
Lin, Yue, Yang, Yang, Pan et al., Nasal Spray of Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody 35B5 Confers Potential Prophylaxis Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Variants of Concern: A Small-Scale Clinical Trial, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac448
Loo, Mctamney, Arends, Abram, Aksyuk et al., The SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody combination, AZD7442, is protective in nonhuman primates and has an extended half-life in humans, Sci. Transl. Med, doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abl8124
Park, Pinto, Walls, Liu, De Marco et al., Imprinted antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages, Science, doi:10.1126/science.adc9127
Pinto, Park, Beltramello, Walls, Tortorici et al., Cross-neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by a human monoclonal SARS-CoV antibody, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2349-y
Prather, Wang, Schooley, Reducing transmission of SARS-CoV-2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abc6197
Qu, Yi, Shen, Lin, Chen et al., Circular RNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.03.044
Shi, Shan, Duan, Chen, Liu et al., A human neutralizing antibody targets the receptor-binding site of SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2381-y
Si, Jin, Li, Cao, Kan et al., Safety and Effectiveness of SA58 Nasal Spray Against COVID-19 Infection in Medical Personnel: An Open-Label, Blank-Controlled Study-Hohhot City, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China, China CDC Wkly, doi:10.46234/ccdcw2023.040
Song, Zeng, Yu, Meng, Chen et al., Post-exposure prophylaxis with SA58 (anti-SARS-COV-2 monoclonal antibody) nasal spray for the prevention of symptomatic COVID-19 in healthy adult workers: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2023.2212806
Tuekprakhon, Nutalai, Dijokaite-Guraliuc, Zhou, Ginn et al., Antibody escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 from vaccine and BA.1 serum, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.005
Wang, Guo, Iketani, Nair, Li et al., Antibody evasion by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.2.12, BA.4 and BA.5, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05053-w
Westendorf, Zentelis, Wang, Foster, Vaillancourt et al., LY-CoV1404 (bebtelovimab) potently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110812
Who, COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker and Landscape
Who, WHO Director-General's Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19-11
Yang, Yu, Jian, Song, Yisimayi et al., Antigenicity and infectivity characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00573-X
Yang, Yu, Xu, Jian, Song et al., Fast evolution of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2•86 to JN.1 under heavy immune pressure, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00744-2
Yisimayi, Song, Wang, Jian, Yu et al., Repeated Omicron exposures override ancestral SARS-CoV-2 immune imprinting, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06753-7
Yue, Song, Wang, Jian, Chen et al., ACE2 binding and antibody evasion in enhanced transmissibility of XBB.1.5, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00010-5
Zost, Gilchuk, Case, Binshtein, Chen et al., Potently neutralizing and protective human antibodies against SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2548-6
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics17010043",
"ISSN": [
"1999-4923"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics17010043",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: A broad-spectrum anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody (mAb), SA55, is highly effective against SARS-CoV-2 variants. This trial aimed at demonstrating the safety, tolerability, local drug retention and neutralizing activity, systemic exposure level, and immunogenicity of the SA55 nasal spray in healthy individuals. Methods: This phase I, dose-escalation clinical trial combined an open-label design with a randomized, controlled, double-blind design. Healthy participants aged 18–65 years were enrolled and received a single dose of the SA55 nasal spray (1 mg or 2 mg) or multiple doses of SA55 nasal spray/placebo for 7 days (1 or 2 mg/dose, 3 or 6 doses/day). Safety monitoring was conducted throughout the study. Nasal swabs and venous blood samples were collected to analyze local drug concentration/neutralization, systemic exposure, and immunogenicity. Results: From 2 June to 11 August 2023, 80 participants were enrolled and received study intervention. The severity of adverse reactions (ADRs) reported during the study was mild in all cases, and all ADRs were laboratory test abnormalities without corresponding symptoms or vital signs. A total of 9 ADRs were reported, of which all were mild in severity. Overall ADR incidence rate was 16.67% (8/48) in single-dose groups and 4.17% (1/24) in multiple-dose groups. The nasal local drug concentration and neutralizing activity were generally stable within 4–8 h, with favorable neutralization activity against Omicron BF.7 and XBB strains. Conclusions: This study demonstrated favorable safety and tolerability of the SA55 nasal spray in healthy volunteers, exhibited satisfactory neutralizing activity against Omicron variants intranasally, and indicated low systemic toxicity risk.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"pharmaceutics17010043"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Phase I Clinical Trial Unit, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100015, China"
}
],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Chaoying",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Phase I Clinical Trial Unit, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100015, China"
}
],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Yibo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5309-7681",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Research and Development Center, Sinovac Biotech Co., Ltd., Beijing 100085, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Meng",
"given": "Xing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9216-4699",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Zhejiang Key Laboratory of Public Health Detection and Pathogenesis Research, Hangzhou 310051, China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jianhua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Research and Development Center, Sinovac Life Sciences Co., Ltd., Beijing 102601, China"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Jinxia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Respiratory Virus Vaccine, National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, Beijing 100061, China"
}
],
"family": "Ying",
"given": "Zhifang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biomedical Pioneering Innovation Center (BIOPIC), Peking University, Beijing 100871, China"
},
{
"name": "Changping Laboratory, Beijing 102206, China"
}
],
"family": "Xie",
"given": "Xiaoliang Sunney",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Clinical Research and Development Center, Sinovac Life Sciences Co., Ltd., Beijing 102601, China"
}
],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Yaling",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Biomedical Pioneering Innovation Center (BIOPIC), Peking University, Beijing 100871, China"
},
{
"name": "Changping Laboratory, Beijing 102206, China"
}
],
"family": "Cao",
"given": "Yunlong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Phase I Clinical Trial Unit, Beijing Ditan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100015, China"
}
],
"family": "Jin",
"given": "Ronghua",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Pharmaceutics",
"container-title-short": "Pharmaceutics",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-31T18:26:25Z",
"timestamp": 1735669585000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-31T18:39:07Z",
"timestamp": 1735670347000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Sinovac Life Sciences Co., Ltd."
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-01-01T05:25:45Z",
"timestamp": 1735709145796,
"version": "3.32.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-12-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1735603200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/17/1/43/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "43",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "WHO (2020, January 30). Statement on the Second Meeting of the International Health Regulations (2005) Emergency Committee Regarding the Outbreak of Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV), Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/30-01-2020-statement-on-the-second-meeting-of-the-international-health-regulations-(2005)-emergency-committee-regarding-the-outbreak-of-novel-coronavirus-(2019-ncov)."
},
{
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "WHO (2020, March 11). WHO Director-General’s Opening Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19—11 March 2020, Available online: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-covid-19%2D%2D-11-march-2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41573-023-00672-y",
"article-title": "Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19: Progress and lessons learned",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "449",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.03.044",
"article-title": "Circular RNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and emerging variants",
"author": "Qu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1728",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "ref_5",
"unstructured": "WHO (2023, March 30). COVID-19 Vaccine Tracker and Landscape, Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/draft-landscape-of-covid-19-candidate-vaccines."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.8828",
"article-title": "Effect of Bamlanivimab vs. Placebo on Incidence of COVID-19 Among Residents and Staff of Skilled Nursing and Assisted Living Facilities: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Cohen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "46",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110812",
"article-title": "LY-CoV1404 (bebtelovimab) potently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants",
"author": "Westendorf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110812",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2349-y",
"article-title": "Cross-neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by a human monoclonal SARS-CoV antibody",
"author": "Pinto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "290",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2548-6",
"article-title": "Potently neutralizing and protective human antibodies against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Zost",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "443",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd0827",
"article-title": "Studies in humanized mice and convalescent humans yield a SARS-CoV-2 antibody cocktail",
"author": "Hansen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1010",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2381-y",
"article-title": "A human neutralizing antibody targets the receptor-binding site of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Shi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "120",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btab856",
"article-title": "CoV-Spectrum: Analysis of globally shared SARS-CoV-2 data to identify and characterize new variants",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1735",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05053-w",
"article-title": "Antibody evasion by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "603",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "608",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04387-1",
"article-title": "Omicron extensively but incompletely escapes Pfizer BNT162b2 neutralization",
"author": "Cele",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "654",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.06.005",
"article-title": "Antibody escape of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.4 and BA.5 from vaccine and BA.1 serum",
"author": "Tuekprakhon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2422",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04386-2",
"article-title": "Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron antigenic shift",
"author": "Cameroni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "664",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00642-9",
"article-title": "Further humoral immunity evasion of emerging SARS-CoV-2 BA.4 and BA.5 subvariants",
"author": "Jian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1535",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00573-X",
"article-title": "Antigenicity and infectivity characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2.86",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e457",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00744-2",
"article-title": "Fast evolution of SARS-CoV-2 BA.2·86 to JN.1 under heavy immune pressure",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e70",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00010-5",
"article-title": "ACE2 binding and antibody evasion in enhanced transmissibility of XBB.1.5",
"author": "Yue",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "278",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.08.30.555211",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_21",
"unstructured": "Jian, F., Feng, L., Yang, S., Yu, Y., Wang, L., Song, W., Yisimayi, A., Chen, X., Xu, Y., and Wang, P. (2023). Convergent evolution of SARS-CoV-2 XBB lineages on receptor-binding domain 455–456 synergistically enhances antibody evasion and ACE2 binding. PLoS Pathogens, 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.adc9127",
"article-title": "Imprinted antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "619",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "378",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3",
"article-title": "Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "657",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abl8124",
"article-title": "The SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody combination, AZD7442, is protective in nonhuman primates and has an extended half-life in humans",
"author": "Loo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabl8124",
"journal-title": "Sci. Transl. Med.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac448",
"article-title": "Nasal Spray of Neutralizing Monoclonal Antibody 35B5 Confers Potential Prophylaxis Against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Variants of Concern: A Small-Scale Clinical Trial",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e336",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-023-01656-5",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of an intranasal spray A8G6 antibody cocktail in the post-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "403",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "(2022, May 03). Efficacy and Safety of Nasal Spray Solution Containing Human IgG1 Anti-COVID-19 Antibody Cocktail, Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05358873?term=Efficacy%20%20and%20Safety%20of%20Nasal%20Spray%20Solution%20Containing%20Human%20IgG1%20Anti-COVID-19%20Antibody%20Cocktail&rank=1."
},
{
"DOI": "10.46234/ccdcw2023.040",
"article-title": "Safety and Effectiveness of SA58 Nasal Spray Against COVID-19 Infection in Medical Personnel: An Open-Label, Blank-Controlled Study—Hohhot City, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China, 2022",
"author": "Si",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "218",
"journal-title": "China CDC Wkly",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2023.2212806",
"article-title": "Post-exposure prophylaxis with SA58 (anti-SARS-COV-2 monoclonal antibody) nasal spray for the prevention of symptomatic COVID-19 in healthy adult workers: A randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study",
"author": "Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2212806",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111845",
"article-title": "Rational identification of potent and broad sarbecovirus-neutralizing antibody cocktails from SARS convalescents",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111845",
"journal-title": "Cell Reports",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06753-7",
"article-title": "Repeated Omicron exposures override ancestral SARS-CoV-2 immune imprinting",
"author": "Yisimayi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "148",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "625",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc6197",
"article-title": "Reducing transmission of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Prather",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1422",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Aleem, A., and Vaqar, S. (2023). Monoclonal Antibody Therapy for High-Risk Coronavirus (COVID 19) Patients With Mild To Moderate Disease Presentations. StatPearls, StatPearls Publishing."
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4923/17/1/43"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Safety and Intranasal Retention of a Broad-Spectrum Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibody SA55 Nasal Spray in Healthy Volunteers: A Phase I Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "17"
}