Efficacy and Safety of Complementary Therapy With Jing Si Herbal Tea in Patients With Mild-To-Moderate COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study
et al., Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.832321, Mar 2022
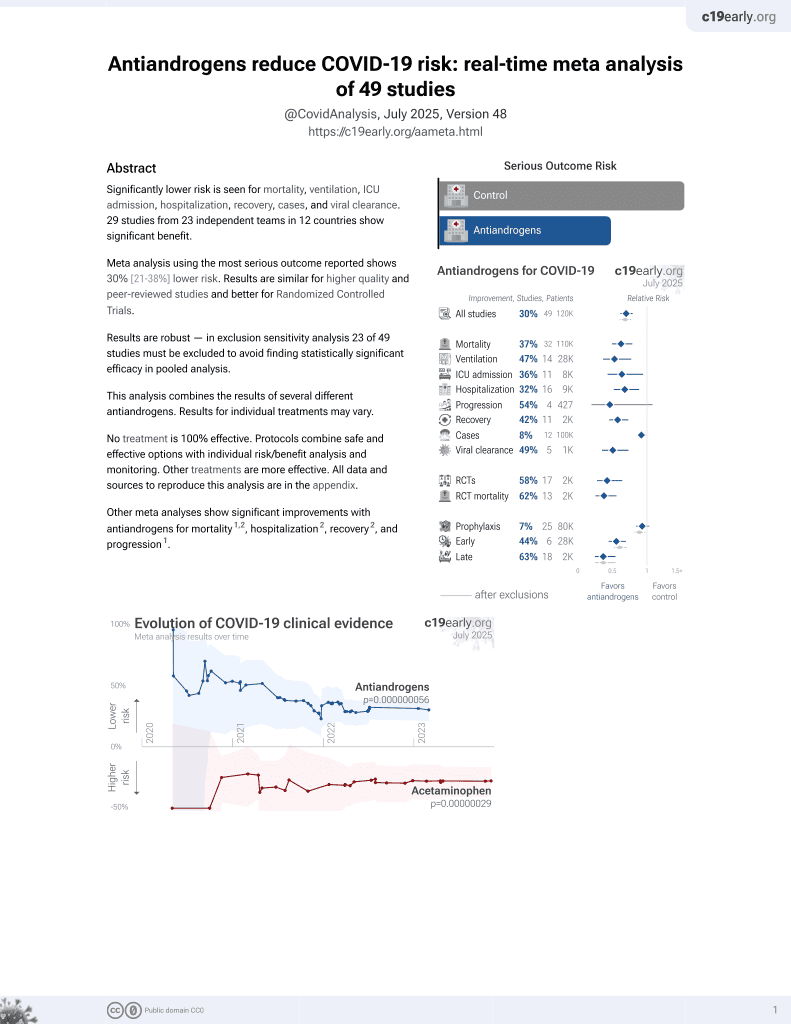
7th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000056 from 49 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
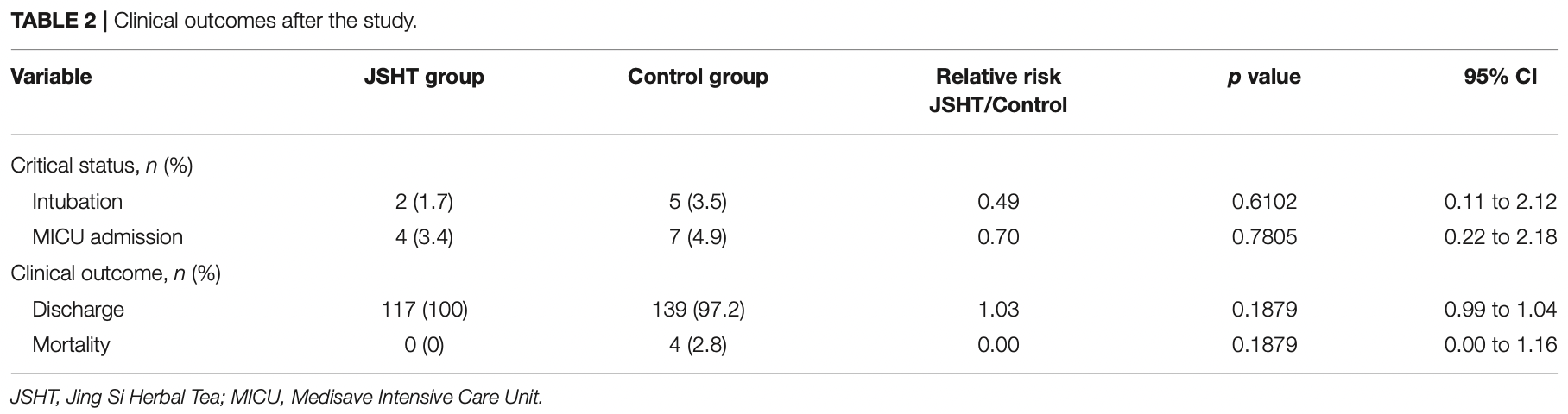
Prospective study of 260 hospitalized patients in Taiwan, 117 treated with herbal formula Jing Si Herbal Tea which includes antiandrogen glycyrrhiza glabra, showing improved recovery with treatment, with statistical significance for SpO2, Ct score, CRP, and Brixia score.
|
risk of death, 87.9% lower, RR 0.12, p = 0.13, treatment 0 of 117 (0.0%), control 4 of 143 (2.8%), NNT 36, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 51.1% lower, RR 0.49, p = 0.46, treatment 2 of 117 (1.7%), control 5 of 143 (3.5%), NNT 56.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 30.2% lower, RR 0.70, p = 0.76, treatment 4 of 117 (3.4%), control 7 of 143 (4.9%), NNT 68.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 87.9% lower, RR 0.12, p = 0.13, treatment 0 of 117 (0.0%), control 4 of 143 (2.8%), NNT 36, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
relative increase in Ct score, 36.1% better, RR 0.64, p < 0.001, treatment mean 8.14 (±4.9) n=117, control mean 5.2 (±6.99) n=143.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Hsieh et al., 14 Mar 2022, prospective, Taiwan, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period 1 May, 2021 - 31 August, 2021, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with multi-herbal formula) - results of individual treatments may vary.
Contact: drbfci@yahoo.com.tw.
Efficacy and Safety of Complementary Therapy With Jing Si Herbal Tea in Patients With Mild-To-Moderate COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study
Frontiers in Nutrition, doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.832321
Background: Since late 2019, there has been a global COVID-19 pandemic. To preserve medical capacity and decrease adverse health effects, preventing the progression of COVID-19 to severe status is essential. Jing-Si Herbal Tea (JSHT), a novel traditional Chinese medicine formula was developed to treat COVID-19. This study examined the clinical efficacy and safety of JSHT in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19.
Methods: In this prospective cohort study, we enrolled 260 patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. The enrolled patients were divided into the JSHT (n = 117) and control (n = 143) groups. Both groups received standard management. The JSHT group was treated with JSHT as a complementary therapy. Results: Compared with standard management alone, JSHT combined with standard management more effectively improved the reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction cycle threshold value, C-reactive protein level, and Brixia score in the adult patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, especially in the male and older patients (those aged ≥60 years). The results revealed that the patients treated with JSHT combined with standard management had 51, 70, and 100% lower risks of intubation, Medisave Care Unit admission, and mortality compared with those receiving standard management only. Conclusions: JSHT combined with standard management more effectively reduced the SARS-CoV-2 viral load and systemic inflammation and alleviated lung infiltrates in the patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, especially in the male and older patients (those aged ≥60 years). JSHT combined with standard management may prevent critical status and mortality in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. JSHT is a promising complementary therapy for patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19.
ETHICS STATEMENT The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Research Ethics Committee of Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital, Buddhist Tzu Chi Medical Foundation. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022. 832321/full#supplementary-material
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. Publisher's Note: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Araf, Akter, Tang, Fatemi, Parvez et al., Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2: Genomics, transmissibility, and responses to current COVID-19 vaccines, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.27588
Bhaskar, Sinha, Banach, Mittoo, Weissert et al., Cytokine Storm in COVID-19-immunopathological mechanisms, clinical considerations, and therapeutic approaches: the REPROGRAM Consortium Position Paper, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01648
Blumenthal, Fowler, Abrams, Collins, Covid-19 -Implications for the health care system, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMsb2021088
Cai, Yang, Zhang, Obesity is associated with severe disease and mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis, BMC Public Health, doi:10.1186/s12889-021-11546-6
Cruz, Mendes-Frias, Oliveira, Dias, Matos et al., Interleukin-6 Is a biomarker for the development of fatal severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 pneumonia, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.613422
Das, Mahanta, Tanti, Tag, Hui, Identification of phytocompounds from Houttuynia cordata Thunb. as potential inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 replication proteins through GC-MS/LC-MS characterization, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation, Mol Divers, doi:10.1007/s11030-021-10226-2
Du, Shi, Cao, Zuo, Zhou, Add-on effect of Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0256429
Frenck Rw, Klein, Kitchin, Gurtman, Absalon et al., Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the BNT162b2 Covid-19 vaccine in adolescents, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2107456
Gandhi, Lynch, Rio, Mild or moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMcp2009249
Han, Ma, Li, Liu, Zhao et al., Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129
Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7
Islam, Chamberlain, Mui, Little, Elevated Interleukin-10 Levels in COVID-19: Potentiation of Pro-Inflammatory Responses or Impaired Anti-Inflammatory Action?, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.677008
Islam, Quispe, Herrera, Khan, Bawazeer et al., Possible Mutation Pathways in SARS-CoV-2, Farmacia, doi:10.31925/farmacia.2021.6.1
Jan, Cheng, Juang, Ma, Wu et al., Identification of existing pharmaceuticals and herbal medicines as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.2021579118
Jin, Du, Xu, Deng, Liu et al., Structure of M(pro) from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2223-y
Kostoff, Calina, Kanduc, Briggs, Vlachoyiannopoulos et al., Why are we vaccinating children against COVID-19?, Toxicol Rep, doi:10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.08.010
Kou, Yu, Xu, Inhibitory effects of ethanol extract from Radix Ophiopogon japonicus on venous thrombosis linked with its endotheliumprotective and anti-adhesive activities, Vascul Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.vph.2005.06.004
Li, Jiang, Yue, Luan, Use of traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive treatment for COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000026641
Li, Li, Gao, Fan, Wang et al., Interleukin-8 as a biomarker for disease prognosis of coronavirus disease-2019 patients, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.602395
Lu, Zhang, Dauphars, He, A Potential Role of Interleukin 10 in COVID-19 Pathogenesis, Trends Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.it.2020.10.012
Ma, Zhang, Ye, Chen, Yu et al., High Levels of Circulating IL-8 and Soluble IL-2R Are Associated With Prolonged Illness in Patients With Severe COVID-19, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.626235
Merarchi, Dudha, Das, Garg, Natural products and phytochemicals as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs, Phytother Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.7151
Narkhede, Pise, Cheke, Shinde, Recognition of natural products as potential inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro): in-silico evidences, Nat Prod Bioprospect, doi:10.1007/s13659-020-00253-1
Ortega-Paz, Capodanno, Montalescot, Angiolillo, Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Thrombosis and Coagulopathy: Review of the Pathophysiological Characteristics and Implications for Antithrombotic Management, J Am Heart Assoc, doi:10.1161/JAHA.120.019650
Peckham, De Gruijter, Raine, Radziszewska, Ciurtin et al., Male sex identified by global COVID-19 metaanalysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6
Rao, Fang, Hsieh, Yeh, Tzeng, The constituents of anisomeles indica and their anti-inflammatory activities, J Ethnopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.jep.2008.10.032
Rct, A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing
Ritchie, Mathieu, Rodés-Guirao, Appel, Giattino et al., Taiwan: Coronavirus Pandemic Country Profile
Shin, Park, Ko, Ryu, Jeong et al., Artemisia argyi attenuates airway inflammation in lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury model, Lab Anim Res, doi:10.5625/lar.2017.33.3.209
Shingnaisui, Dey, Manna, Kalita, Therapeutic potentials of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. against inflammation and oxidative stress: a review, J Ethnopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.jep.2018.03.038
Signoroni, Savardi, Benini, Adami, Leonardi et al., BS-Net: Learning COVID-19 pneumonia severity on a large chest X-ray dataset, Med Image Anal, doi:10.1016/j.media.2021.102046
Song, Park, Cha, Seok, Kim et al., Clinical course and risk factors of fatal adverse outcomes in COVID-19 patients in Korea: a nationwide retrospective cohort study, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-021-89548-y
Tsai, Huang, Liaw, Tsai, Chiou et al., A traditional Chinese medicine formula NRICM101 to target COVID-19 through multiple pathways: a bedside-to-bench study, Biomed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111037
Vj, Illescas-Montes, Puerta-Puerta, Ruiz, Melguizo-Rodríguez, SARS-CoV-2 infection: the role of cytokines in COVID-19 disease, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.06.001
Wu, Chou, Lin, Hsieh, Wu et al., Epidemiological features of domestic and imported cases with COVID-19 between January 2020 and March 2021 in Taiwan, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000027360
Wu, Li, Qin, Xue, Huang et al., Traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive therapy for mild and common COVID-19: A systematic review and network meta-analysis, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000027372
Wu, Sun, Hou, Guan, Wang et al., Prospective: evolution of chinese medicine to treat COVID-19 patients in China, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.615287
Zhang, Hao, Ou, Ming, Liang et al., Serum interleukin-6 is an indicator for severity in 901 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a cohort study, J Transl Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02571-x
Zhang, Wang, Yang, Zhang, Zhang et al., Platycodon grandiflorus -an ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review, J Ethnopharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.052
Zhu, Zhang, Li, Yang, Song, A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001017
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2022.832321",
"ISSN": [
"2296-861X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.832321",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Since late 2019, there has been a global COVID-19 pandemic. To preserve medical capacity and decrease adverse health effects, preventing the progression of COVID-19 to severe status is essential. Jing-Si Herbal Tea (JSHT), a novel traditional Chinese medicine formula was developed to treat COVID-19. This study examined the clinical efficacy and safety of JSHT in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>In this prospective cohort study, we enrolled 260 patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. The enrolled patients were divided into the JSHT (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 117) and control (<jats:italic>n</jats:italic> = 143) groups. Both groups received standard management. The JSHT group was treated with JSHT as a complementary therapy.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Compared with standard management alone, JSHT combined with standard management more effectively improved the reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction cycle threshold value, C-reactive protein level, and Brixia score in the adult patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, especially in the male and older patients (those aged ≥60 years). The results revealed that the patients treated with JSHT combined with standard management had 51, 70, and 100% lower risks of intubation, Medisave Care Unit admission, and mortality compared with those receiving standard management only.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>JSHT combined with standard management more effectively reduced the SARS-CoV-2 viral load and systemic inflammation and alleviated lung infiltrates in the patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19, especially in the male and older patients (those aged ≥60 years). JSHT combined with standard management may prevent critical status and mortality in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. JSHT is a promising complementary therapy for patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fnut.2022.832321"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hsieh",
"given": "Po-Chun",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chao",
"given": "You-Chen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tsai",
"given": "Kuo-Wang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Chung-Hsien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tzeng",
"given": "I-Shiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Yao-Kuang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shih",
"given": "Cheng Yen",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Frontiers in Nutrition"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-14T07:52:02Z",
"timestamp": 1647244322000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-14T07:52:06Z",
"timestamp": 1647244326000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100008108",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Taipei Tzu Chi Hospital"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-14T08:12:31Z",
"timestamp": 1647245551966
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2296-861X"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
14
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1647216000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.832321/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
14
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
14
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China, 2019",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "727",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsb2021088",
"article-title": "Covid-19 - Implications for the health care system",
"author": "Blumenthal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1483",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7",
"article-title": "Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "141",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01648",
"article-title": "Cytokine Storm in COVID-19-immunopathological mechanisms, clinical considerations, and therapeutic approaches: the REPROGRAM Consortium Position Paper",
"author": "Bhaskar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1648",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "B5",
"unstructured": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31925/farmacia.2021.6.1",
"article-title": "Possible Mutation Pathways in SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Islam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1001",
"journal-title": "Farmacia.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "B7",
"unstructured": ""
},
{
"key": "B8",
"unstructured": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2107456",
"article-title": "Safety, immunogenicity, and efficacy of the BNT162b2 Covid-19 vaccine in adolescents",
"author": "Frenck RW",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "239",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.08.010",
"article-title": "Why are we vaccinating children against COVID-19?",
"author": "Kostoff",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1665",
"journal-title": "Toxicol Rep.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "B11",
"unstructured": "RitchieH\n MathieuE\n Rodés-GuiraoL\n AppelC\n GiattinoC\n Ortiz-OspinaE\n TaiwanCoronavirus Pandemic Country Profile2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000027360",
"article-title": "Epidemiological features of domestic and imported cases with COVID-19 between January 2020 and March 2021 in Taiwan",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e27360",
"journal-title": "Medicine (Baltimore).",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "B13",
"unstructured": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2020.111037",
"article-title": "A traditional Chinese medicine formula NRICM101 to target COVID-19 through multiple pathways: a bedside-to-bench study",
"author": "Tsai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "111037",
"journal-title": "Biomed Pharmacother.",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0256429",
"article-title": "Add-on effect of Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0256429",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000026641",
"article-title": "Use of traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive treatment for COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e26641",
"journal-title": "Medicine (Baltimore).",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000027372",
"article-title": "Traditional Chinese medicine as an adjunctive therapy for mild and common COVID-19: A systematic review and network meta-analysis",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e27372",
"journal-title": "Medicine (Baltimore).",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.615287",
"article-title": "Prospective: evolution of chinese medicine to treat COVID-19 patients in China",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "615287",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2021579118",
"article-title": "Identification of existing pharmaceuticals and herbal medicines as inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Jan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5625/lar.2017.33.3.209",
"article-title": "Artemisia argyi attenuates airway inflammation in lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury model",
"author": "Shin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "209",
"journal-title": "Lab Anim Res.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jep.2008.10.032",
"article-title": "The constituents of anisomeles indica and their anti-inflammatory activities",
"author": "Rao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "292",
"journal-title": "J Ethnopharmacol.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.052",
"article-title": "Platycodon grandiflorus - an ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "147",
"journal-title": "J Ethnopharmacol.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.vph.2005.06.004",
"article-title": "Inhibitory effects of ethanol extract from Radix Ophiopogon japonicus on venous thrombosis linked with its endothelium-protective and anti-adhesive activities",
"author": "Kou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "157",
"journal-title": "Vascul Pharmacol.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMcp2009249",
"article-title": "Mild or moderate Covid-19",
"author": "Gandhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1757",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Taiwan: Centers for Disease Control, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Taiwan",
"key": "B25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.media.2021.102046",
"article-title": "BS-Net: Learning COVID-19 pneumonia severity on a large chest X-ray dataset",
"author": "Signoroni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102046",
"journal-title": "Med Image Anal.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"journal-title": "R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 4.1.1",
"key": "B27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-89548-y",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors of fatal adverse outcomes in COVID-19 patients in Korea: a nationwide retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10066",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-021-11546-6",
"article-title": "Obesity is associated with severe disease and mortality in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a meta-analysis",
"author": "Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1505",
"journal-title": "BMC Public Health.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6",
"article-title": "Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission",
"author": "Peckham",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6317",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.06.001",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection: the role of cytokines in COVID-19 disease",
"author": "Costela-Ruiz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.613422",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 Is a biomarker for the development of fatal severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 pneumonia",
"author": "Santa Cruz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "613422",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-020-02571-x",
"article-title": "Serum interleukin-6 is an indicator for severity in 901 patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a cohort study",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "406",
"journal-title": "J Transl Med.",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.602395",
"article-title": "Interleukin-8 as a biomarker for disease prognosis of coronavirus disease-2019 patients",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "602395",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.626235",
"article-title": "High Levels of Circulating IL-8 and Soluble IL-2R Are Associated With Prolonged Illness in Patients With Severe COVID-19",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "626235",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.677008",
"article-title": "Elevated Interleukin-10 Levels in COVID-19: Potentiation of Pro-Inflammatory Responses or Impaired Anti-Inflammatory Action?",
"author": "Islam",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "677008",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.it.2020.10.012",
"article-title": "A Potential Role of Interleukin 10 in COVID-19 Pathogenesis",
"author": "Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Trends Immunol.",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1770129",
"article-title": "Profiling serum cytokines in COVID-19 patients reveals IL-6 and IL-10 are disease severity predictors",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1123",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect.",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11030-021-10226-2",
"article-title": "Identification of phytocompounds from Houttuynia cordata Thunb. as potential inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 replication proteins through GC-MS/LC-MS characterization, molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation",
"author": "Das",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Mol Divers",
"key": "B39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7151",
"article-title": "Natural products and phytochemicals as potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs",
"author": "Merarchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5384",
"journal-title": "Phytother Res.",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13659-020-00253-1",
"article-title": "Recognition of natural products as potential inhibitors of COVID-19 Main Protease (Mpro): in-silico evidences",
"author": "Narkhede",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "297",
"journal-title": "Nat Prod Bioprospect.",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2223-y",
"article-title": "Structure of M(pro) from SARS-CoV-2 and discovery of its inhibitors",
"author": "Jin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "289",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "582",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jep.2018.03.038",
"article-title": "Therapeutic potentials of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. against inflammation and oxidative stress: a review",
"author": "Shingnaisui",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "35",
"journal-title": "J Ethnopharmacol.",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "220",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/JAHA.120.019650",
"article-title": "Coronavirus Disease 2019-Associated Thrombosis and Coagulopathy: Review of the Pathophysiological Characteristics and Implications for Antithrombotic Management",
"author": "Ortega-Paz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e019650",
"journal-title": "J Am Heart Assoc.",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27588",
"article-title": "Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2: Genomics, transmissibility, and responses to current COVID-19 vaccines",
"author": "Araf",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol.",
"key": "B45",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 45,
"references-count": 45,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2022.832321/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Front. Nutr."
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism",
"Food Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Efficacy and Safety of Complementary Therapy With Jing Si Herbal Tea in Patients With Mild-To-Moderate COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "9"
}