Influence of inhibitors of the renin–angiotensin system on risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome in Danish hospitalized COVID-19 patients
et al., Journal of Hypertension, doi:10.1097/hjh.0000000000002515, May 2020
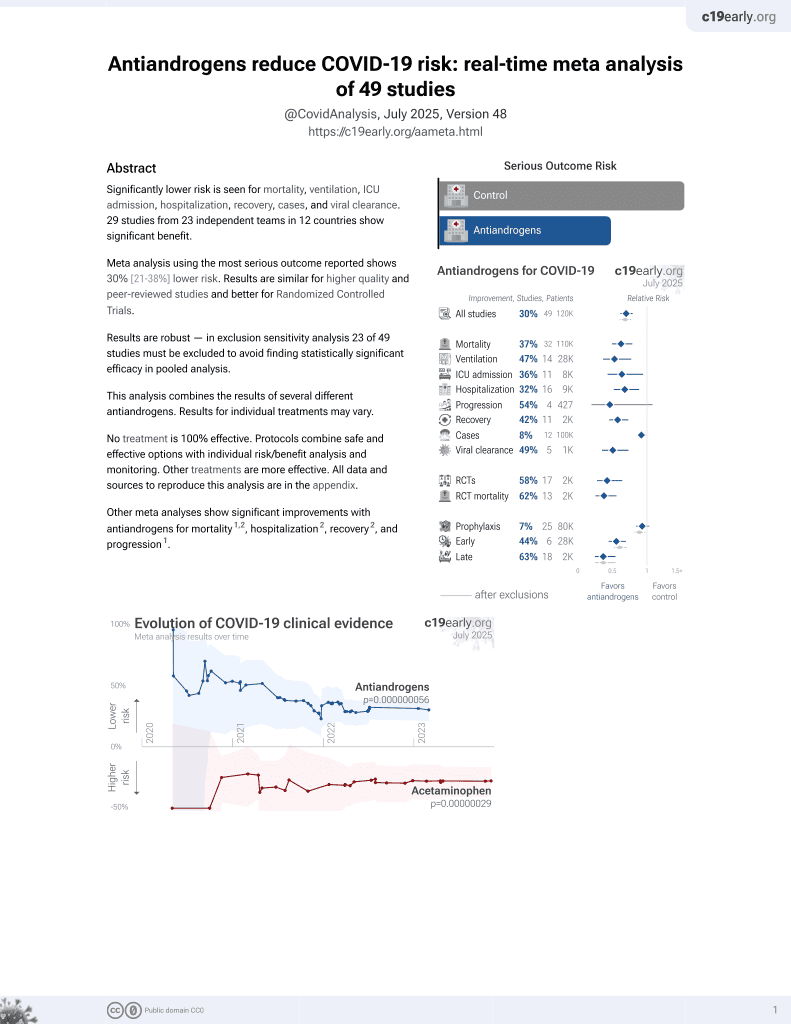
7th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000056 from 49 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
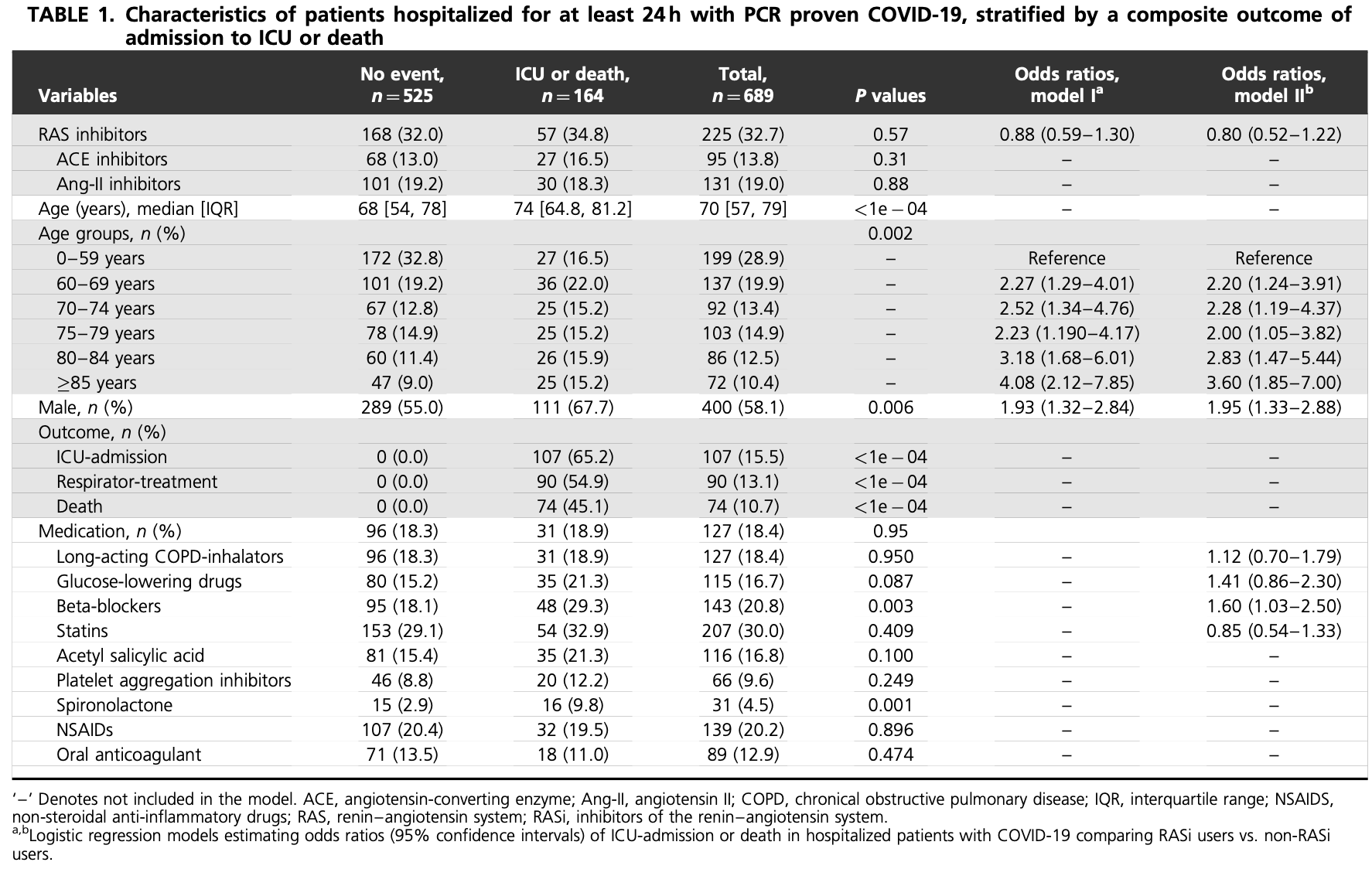
Retrospective 689 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Denmark, showing higher risk of ICU/death with spironolactone use in unadjusted results subject to confounding by indication.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
Study covers aspirin and spironolactone.
|
risk of death/ICU, 129.5% higher, RR 2.29, p < 0.001, treatment 16 of 31 (51.6%), control 148 of 658 (22.5%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Holt et al., 7 May 2020, retrospective, Denmark, peer-reviewed, median age 70.0, 4 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 1 April, 2020.
Influence of inhibitors of the renin–angiotensin system on risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome in Danish hospitalized COVID-19 patients
Journal of Hypertension, doi:10.1097/hjh.0000000000002515
OVID-19, the disease associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, is in some 20% of acutely affected patients associated with respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) often necessitating respirator treatment and associated with a high mortality [1] [2] [3] . Epidemics in Wuhan in China and Lombardy in Italy have been devastating, and SARS-CoV-2 has developed into a pandemic necessitating urgent worldwide co-operation. Until effective treatment of COVID-19 including a useful vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 is found, it is important to seek ways of limiting or avoiding ARDS. Virus-related ARDS is initiated from a high level of angiotensin II (Ang-II) via the type 1 receptor pathway [4], and Ang-II has already been demonstrated to be high in COVID-19 and linearly associated with lung injury [5] . Inhibitors of the renin-angiotensin system (RASi), cornerstones of treatment of patients with hypertension and heart failure, have attracted attention as they may in theory influence the Ang-II level in COVID-19 and thereby the risk of ARDS [4, 6] . In short, Ang-II activity is influenced by the balance of Ang-converting enzyme (ACE) and ACE2 receptor activity. The activity of ACE2 normally lowers the level of Ang-II, but SARS-CoV-2 virus binds to ACE2 receptors, lower their activity and hence increase Ang-II activity [1] . While RASi lower Ang-II levels, and may in this respect be helpful, chronic RASi treatment may on the other hand also increase pulmonary ACE2-receptor numbers hence providing a possible higher SARS-CoV-2 viral load. As suggested from animal experiments, chronic treatment with RASi can therefore, in theory, both increase and lower the risk of ARDS in SARS-CoV-2-infected patients. Studies early listed heart disease, hypertension, and diabetes as risk factors for ARDS [1-3], but unfortunately medication has not yet been reported on, and clinical data on the relative importance of RASi for outcome in COVID-19 are now urgently needed. Approved by the Danish Patient Safety Authority and the Danish Data Protection Agency, we related medication to outcome in all SARS-CoV-2 PCR positive patients, who,
References
Esler, Esler, Can angiotensin receptor-blocking drugs perhaps be harmful in the COVID-19 pandemic?, J Hypertens
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Antonelli, Cabrini et al., Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy, JAMA
Liu, Yang, Zhang, Huang, Wang et al., Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCOV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury, Sci China Life Sci
Vaduganathan, Vardeny, Michel, Mcmurray, Pfeffer et al., Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors in patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Yang, Zheng, Gou, Pu, Chen et al., Prevalence of comorbidities in the novel Wuhan coronavirus (COVID-19) infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int J Infect Dis
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/hjh.0000000000002515",
"ISSN": [
"0263-6352",
"1473-5598"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/hjh.0000000000002515",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Holt",
"given": "Anders",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mizrak",
"given": "Ikram",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lamberts",
"given": "Morten",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lav Madsen",
"given": "Per",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Hypertension",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2020-05-08T20:50:27Z",
"timestamp": 1588971027000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-24T10:32:13Z",
"timestamp": 1614162733000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-01T08:34:51Z",
"timestamp": 1662021291935
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 7,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
7
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/HJH.0000000000002515",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1612-1613",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
5,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.5394",
"article-title": "Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1574",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "R1-20210211",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1054",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "R2-20210211",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017",
"article-title": "Prevalence of comorbidities in the novel Wuhan coronavirus (COVID-19) infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "R3-20210211",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsr2005760",
"article-title": "Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system inhibitors in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Vaduganathan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1653",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R4-20210211",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11427-020-1643-8",
"article-title": "Clinical and biochemical indexes from 2019-nCOV infected patients linked to viral loads and lung injury",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "364",
"journal-title": "Sci China Life Sci",
"key": "R5-20210211",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/HJH.0000000000002450",
"article-title": "Can angiotensin receptor-blocking drugs perhaps be harmful in the COVID-19 pandemic?",
"author": "Esler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "781",
"journal-title": "J Hypertens",
"key": "R6-20210211",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 6,
"references-count": 6,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/HJH.0000000000002515"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cardiology and Cardiovascular Medicine",
"Physiology",
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Influence of inhibitors of the renin–angiotensin system on risk of acute respiratory distress syndrome in Danish hospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "38"
}