Beyond probiotic legend: ESSAP gut microbiota health score to delineate SARS-COV-2 infection severity
et al., British Journal of Nutrition, doi:10.1017/S0007114521001926, NCT04447144, Jun 2021
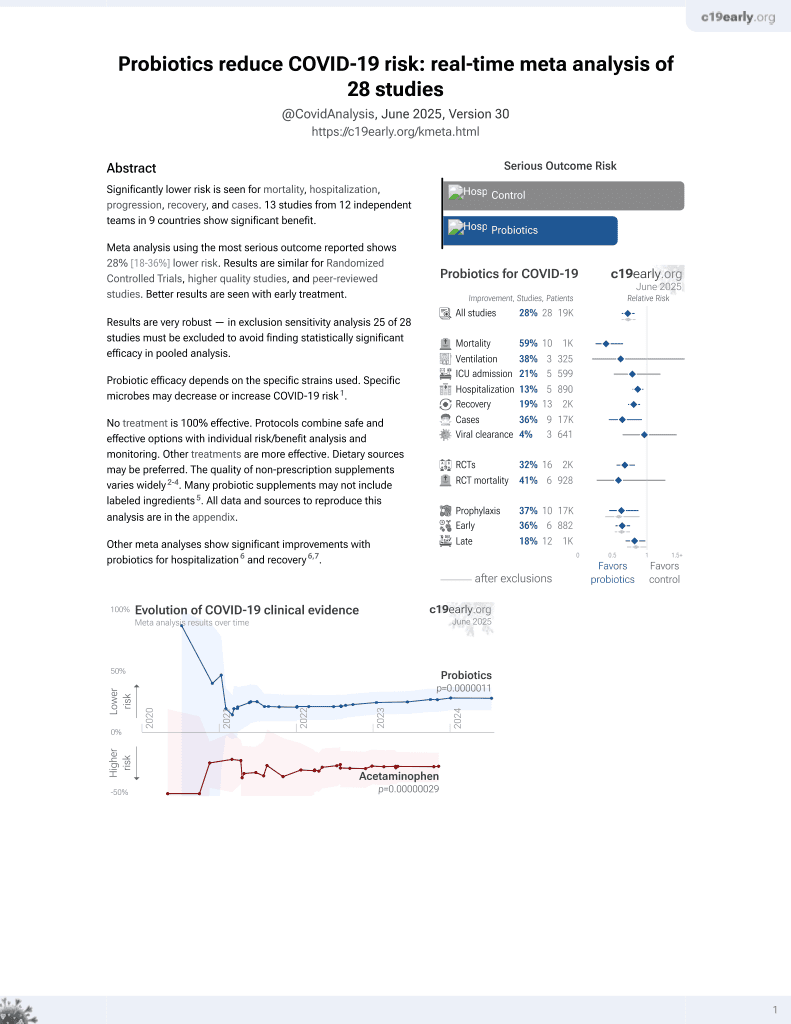
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
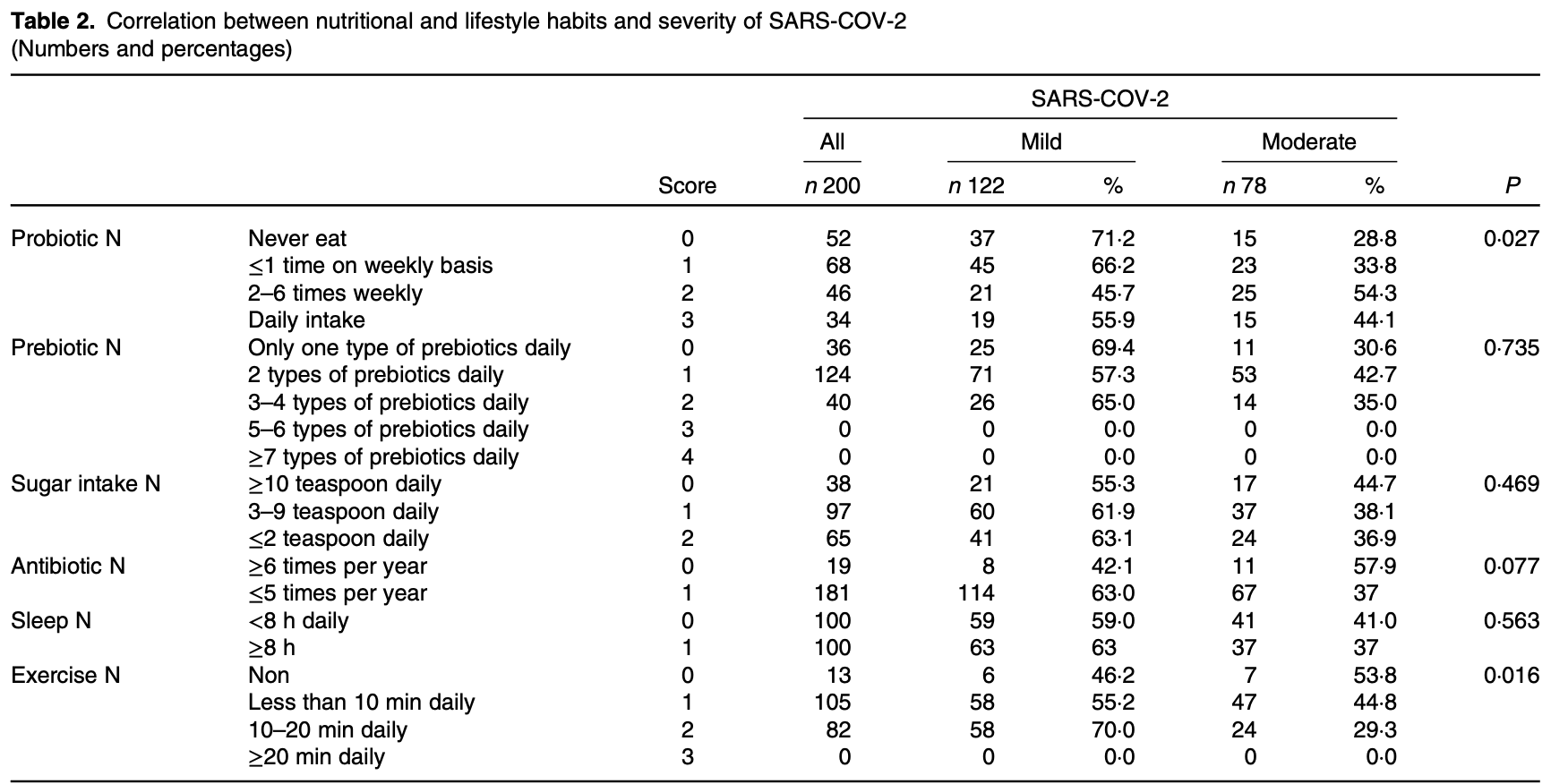
Analysis of 200 mild and moderate COVID-19 outpatients showing an association between higher ESSAP scores (measuring exercise, sugar and prebiotic consumption, sleep, and antibiotic use) and milder COVID-19 disease. Authors find increased risk with daily yogurt containing probiotics. Probiotic intake based on yogurt only may be inaccurate. Authors hypothesize that commercial yogurt products may not contain sufficient beneficial bacteria or may be contaminated. Other research shows that probiotic food labels are often misleading—of 26 probiotic foods tested, only 5 contained Bifidobacterium in sufficient concentration for exhibiting a therapeutic effect1. For sleep, authors compare <8 hours and ≥8 hours, while sleep for less than or longer than a recommended range may indicate increased risk.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk2.
Study covers exercise and probiotics.
Hegazy et al., 7 Jun 2021, retrospective, Egypt, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, trial NCT04447144 (history).
Contact: monahegazy@cu.edu.eg.
Beyond probiotic legend: ESSAP gut microbiota health score to delineate SARS-COV-2 infection severity
British Journal of Nutrition, doi:10.1017/s0007114521001926
COVID-19 pandemic continues to be a global health crisis. The gut microbiome critically affects the immune system, and some respiratory infections are associated with changes in the gut microbiome; here, we evaluated the role of nutritional and lifestyle habits that modulate gut microbiota on COVID-19 outcomes in a longitudinal cohort study that included 200 patients infected with COVID-19. Of these, 122 cases were mild and seventy-eight were moderate, according to WHO classification. After detailed explanation by a consultant in clinical nutrition, participants responded to a written questionnaire on daily sugar, prebiotic intake in food, sleeping hours, exercise duration and antibiotic prescription, during the past 1 year before infection. Daily consumption of prebiotic-containing foods, less sugar, regular exercise, adequate sleep and fewer antibiotic prescriptions led to a milder disease and rapid virus clearance. Additionally, data on these factors were compiled into a single score, the ESSAP score (Exercise, Sugar consumption, Sleeping hours, Antibiotics taken, and Prebiotics consumption; 0-11 points), median ESSAP score was 5 for both mild and moderate cases; however, the range was 4-8 in mild cases, but 1-6 in moderate (P = 0•001, OR: 4•2, 95 % CI 1•9, 9•1); our results showed a negative correlation between regular consumption of yogurt containing probiotics and disease severity (P = 0•007, OR: 1•6, 95 % CI 1•1, 2•1). Mild COVID-19 disease was associated with 10-20 min of daily exercise (P = 0•016), sleeping at least 8 h daily, prescribed antibiotics less than 5 times per year (P = 0•077) and ate plenty of prebiotic-containing food.
References
Arrieta, Meddings, Field, The immunomodulatory effects of dietary fiber and prebiotics in the gastrointestinal tract
Bakirci, A study on the occurrence of aflatoxin M1 in milk and milk products produced in Van province of Turkey, Food Control
Bassuoni, Soliman, Hussein, Bio-efficiencies of probiotic yoghurt and fermented sour soya supplements on gut microbial health and other associated health biomarkers among Egyptian pre-school to school age children, Int J Clin Nutr Diet
Becattini, Taur, Pamer, Antibiotic-induced changes in the intestinal microbiota and disease, Trends Mol Med
Benedict, Vogel, Gut microbiota and glucometabolic alterations in response to recurrent partial sleep deprivation in normal-weight young individuals, J Mol Metab
Bermon, Petriz, Kajeniene, The microbiota: an exercise immunology perspective, Exerc Immunol Rev
Clemente, Ursell, Parfrey, The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: an integrative view, Cell
Coakes, Steed, SPSS: Analysis without Anguish using SPSS Ion 14.0 for Windows, Statistics in Medicine
Conlon, Bird, The impact of diet and lifestyle on gut microbiota and human health, Nutrients
Dimitrov, Lange, Gouttefangeas, Gαs-coupled receptor signaling and sleep regulate integrin activation of human antigen-specific T cells, J Exp Med
Dominika, Arjan, Karyn, The study on the impact of glycated pea proteins on human intestinal bacteria, Int J Food Microbiol
Dominika, Arjan, Karyn, The study on the impact of glycated pea proteins on human intestinal bacteria, Int J Food Microbiol
Drakes, Blanchard, Czinn, Bacterial probiotic modulation of dendritic cells, Infect Immun
Ellulu, Patimah, Khaza'ai, Obesity and inflammation: the linking mechanism and the complications, Arch Med Sci
Elsheikh, Tinay, Fadul, Effect of nutritional status of fava bean on proximate composition, antinutritional factors and in vitro protein digestibility (IVPD), Food Chem
Everard, Belzer, Geurts, Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Frølich, Aman, Tetens, Whole grain foods and health a Scandinavian perspective, Food Nutr Res
Groves, Higham, Moffatt, Respiratory viral infection alters the gut microbiota by inducing inappetence, mBio
Groves, Higham, Moffatt, Respiratory viral infection alters the gut microbiota by inducing inappetence, mBio
Harsch, Konturek, The role of gut microbiota in obesity and type 2 and type 1 diabetes mellitus: new insights into 'Old' diseases, Med Sci
Jespersen, Tranow, Eskesen, Effect of Lactobacillus. paracasei, L. casei 431 on immune response to influenza vaccination and upper respiratory tract infections in healthy adult volunteers: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study, Am J Clin Nutr
Johnson, Appel, Brands, Dietary sugars intake and cardiovascular health: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association, Circulation
Jones, Davison, Exercise, Immunity, and Illness, Muscle Exercise Physiology, doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-814593-7.00015-3
Kabak, Var, Factors affecting the removal of aflatoxin M1 from food model by Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains, J Environ Sci Health Part B Pesticides
Khan, Sievenpiper, Controversies about sugars: results from systematic reviews and meta-analyses on obesity, cardiometabolic disease and diabetes, Eur J Nutr
Ku, Probiotics provoked D-lactic acidosis in short bowel syndrome: case report and literature review, HK J Paediatr
Lin, Fung, Wu, Molecular characterization of a plasmid-borne (pTC82) chloramphenicol resistance determinant (cat-TC) from Lactobacillus reuteri G4, Plasmid
Lourens-Hattingh, Viljoen, Yoghurt as probiotic carrier food, Int Dairy J
Lourens-Hattingh, Viljoen, Yogurt as a probiotic carrier food, Int Dairy J
Luoto, Ruuskanen, Waris, Prebiotic and probiotic supplementation prevents rhinovirus infections in preterm infants: a randomized placebo-controlled trial, J Allergy Clin Immunol
Mackay, Taylor, Kibbler, Lactobacillus endocarditis caused by a probiotic organism, Clin Microbiol Infect
Matsumoto, Inoue, Tsukahara, Voluntary running exercise alters microbiota composition and increases n-butyrate concentration in the rat cecum, Biosci Biotechnol Biochem
Maynard, Rich, Fleisher, The Microbiota in Immunity and Inflammation, Clinical Immunology
Mika, Van Treuren, González, Exercise is more effective at altering gut microbial composition and producing stable changes in lean mass in juvenile v. adult male F344 rats, PLoS ONE
Mogensen, Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses, Clin Microbiol Rev
Montaseri, Arjmandtalab, Dehghanzadeh, Effect of production and storage of probiotic yogurt on aflatoxin M1 residue, J Food Qual Hazards Control
Negi, Das, Pahari, Potential role of gut microbiota in induction and regulation of innate immune memory, Front Immunol
Pan, Mu, Yang, Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, china. A descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study, Am J Gastroenterol
Peake, Exercise-induced alterations in neutrophil degranulation and respiratory burst activity: possible mechanisms of action, Exerc Immunol Rev
Perrotta, Corbi, Mazzeo, COVID-19 and the elderly: insights into pathogenesis and clinical decision-making, Aging Clin Exp Res
Presterl, Kneifel, Mayer, Endocarditis by Lactobacillus rhamnosus due to yogurt ingestion?, J Infect Dis
Quercia, Candela, Giuliani, From lifetime to evolution: timescales of human gut microbiota adaptation, Front Microbiol
Rienzi, Britton, Adaptation of the gut microbiota to modern dietary sugars and sweeteners, Adv Nutr
Robak, Heimesaat, Kruglov, Antibiotic treatment-induced secondary IgA deficiency enhances susceptibility to Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia, J Clin Invest
Round, Mazmanian, Mazmanian Inducible Foxp3þ regulatory T-cell development by a commensal bacterium of the intestinal microbiota, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Salari, Nikfar, Abdollahi, A meta-analysis and systematic review on the effect of probiotics in acute diarrhea, Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets
Sanders, Akkermans, Haller, Safety assessment of probiotics for human use, Gut Microbes
Schley, Field, The immune-enhancing effects of dietary fibers and prebiotics, Br J Nutr
Shah, Functional cultures and health benefits, Int Dairy J
Smith, Easson, Lyle, Gut microbiome diversity is associated with sleep physiology in humans, PLoS One
Tlaskova-Hogenova, Stepankova, Hudcovic, Commensal bacteria (normal microflora), mucosal immunity and chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, Immunol Lett
Trompette, Gollwitzer, Pattaroni, Dietary fiber confers protection against flu by shaping Ly6c-patrolling monocyte hematopoiesis and CD8 T cell metabolism, Immunity
Trompette, Gollwitzer, Yadava, Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis, Nat Med
West, Dzidic, Prescott, Bugging allergy; role of pre-, pro-and symbiotic in allergy prevention, Allergol Int
Who, Egypt: WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard
Williams, Probiotics, Am J Health-System Pharm
Willing, Russell, Finlay, Shifting the balance: antibiotic effects on host-microbiota mutualism, Nat Rev Microbiol
Zakaria, Amin, Khalil, Rapid detection of aflatoxin M1 residues in market milk in Aswan Province, Egypt and effect of probiotics on its residues concentration, J Adv Vet Anim Res
Zheng, Peng, Xu, Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis, J Infect
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1017/s0007114521001926",
"ISSN": [
"0007-1145",
"1475-2662"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/S0007114521001926",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>COVID-19 pandemic continues to be a global health crisis. The gut microbiome critically affects the immune system, and some respiratory infections are associated with changes in the gut microbiome; here, we evaluated the role of nutritional and lifestyle habits that modulate gut microbiota on COVID-19 outcomes in a longitudinal cohort study that included 200 patients infected with COVID-19. Of these, 122 cases were mild and seventy-eight were moderate, according to WHO classification. After detailed explanation by a consultant in clinical nutrition, participants responded to a written questionnaire on daily sugar, prebiotic intake in food, sleeping hours, exercise duration and antibiotic prescription, during the past 1 year before infection. Daily consumption of prebiotic-containing foods, less sugar, regular exercise, adequate sleep and fewer antibiotic prescriptions led to a milder disease and rapid virus clearance. Additionally, data on these factors were compiled into a single score, the ESSAP score (Exercise, Sugar consumption, Sleeping hours, Antibiotics taken, and Prebiotics consumption; 0–11 points), median ESSAP score was 5 for both mild and moderate cases; however, the range was 4–8 in mild cases, but 1–6 in moderate (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0·001, OR: 4·2, 95 % CI 1·9, 9·1); our results showed a negative correlation between regular consumption of yogurt containing probiotics and disease severity (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0·007, OR: 1·6, 95 % CI 1·1, 2·1). Mild COVID-19 disease was associated with 10–20 min of daily exercise (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0·016), sleeping at least 8 h daily, prescribed antibiotics less than 5 times per year (<jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = 0·077) and ate plenty of prebiotic-containing food.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"S0007114521001926"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Copyright and Licensing",
"name": "copyright_and_licensing"
},
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© The Author(s), 2021. Published by Cambridge University Press on behalf of The Nutrition Society"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hegazy",
"given": "Mona",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed Ashoush",
"given": "Omar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tharwat Hegazy",
"given": "Mohamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wahba",
"given": "Mahmoud",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lithy",
"given": "Rania M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdel-Hamid",
"given": "Hoda M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed Abd elshafy",
"given": "Samah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdelfatah",
"given": "Dalia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "El-Din Ibrahim",
"given": "Maha Hossam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0408-7994",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Abdelghani",
"given": "Ahmed",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "British Journal of Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Br J Nutr",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"cambridge.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-07T10:33:33Z",
"timestamp": 1623062013000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-15T02:28:32Z",
"timestamp": 1684117712000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
10,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2024-10-06T01:08:19Z",
"timestamp": 1728176899884
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 18,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
7
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
28
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cambridge.org/core/terms",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1623024000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.cambridge.org/core/services/aop-cambridge-core/content/view/S0007114521001926",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "56",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1180-1189",
"prefix": "10.1017",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
7
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
28
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cambridge University Press (CUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000620",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 patients with digestive symptoms in Hubei, china. A descriptive, cross-sectional, multicenter study",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref2",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Maynard",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref4",
"volume-title": "The Microbiota in Immunity and Inflammation, Clinical Immunology",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-016-1345-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/ajcn.114.103531",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.04.021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref28"
},
{
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref17",
"unstructured": "17. Committee (DGAC) (2010) The Dietary Guidelines for Americans 2010 (USDA and HHS, 2011). https://health.gov/our-work/food-nutrition/previous-dietary-guidelines/2010 (accessed April 2021)."
},
{
"article-title": "Probiotics provoked D-lactic acidosis in short bowel syndrome: case report and literature review",
"author": "Ku",
"first-page": "246",
"journal-title": "HK J Paediatr",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref55",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"article-title": "The role of gut microbiota in obesity and type 2 and type 1 diabetes mellitus: new insights into ‘Old’ diseases",
"author": "Harsch",
"first-page": "32",
"journal-title": "Med Sci",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref31",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.0909122107",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20181169",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref42"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1079/BJNBJN/2002541",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2013.08.020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmz118",
"article-title": "Adaptation of the gut microbiota to modern dietary sugars and sweeteners",
"author": "Di Rienzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "616",
"journal-title": "Adv Nutr",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref36",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.01.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.03236-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0958-6946(01)00036-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0125889",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molmed.2016.04.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref46"
},
{
"article-title": "Exercise, Immunity, and Illness",
"author": "Jones",
"first-page": "317",
"journal-title": "Muscle Exercise Physiology",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref41",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/03601230802234740",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref60"
},
{
"article-title": "Endocarditis by Lactobacillus rhamnosus due to yogurt ingestion?",
"author": "Presterl",
"first-page": "710",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref54",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/187152812798889394",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref49"
},
{
"article-title": "‘The microbiota: an exercise immunology perspective’",
"author": "Bermon",
"first-page": "70",
"journal-title": "Exerc Immunol Rev",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref37",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15344/2456-8171/2019/145",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref16"
},
{
"article-title": "Exercise-induced alterations in neutrophil degranulation and respiratory burst activity: possible mechanisms of action",
"author": "Peake",
"first-page": "49",
"journal-title": "Exerc Immunol Rev",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref40",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2146/ajhp090168",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref64"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1469-0691.1999.tb00144.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref53"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2012.01.035",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/plas.1996.0039",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref57"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2014.00587",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0956-7135(00)00020-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref59"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.01.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref7"
},
{
"article-title": "Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "J Am Coll Dent",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref14",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0958-6946(01)00036-X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref63"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/CMR.00046-08",
"article-title": "Pathogen recognition and inflammatory signaling in innate immune defenses",
"author": "Mogensen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "240",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Rev",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref24",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.192627",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/IAI.72.6.3299-3309.2004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref56"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref32"
},
{
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref13",
"volume-title": "Diagnosis and Treatment Protocol for COVID 19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrmicro2536",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imlet.2004.02.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/gmic.1.3.12127",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40520-020-01631-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.03236-19",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molmet.2016.10.003",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.02441",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref5"
},
{
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref21",
"volume-title": "Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1219451110",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref30"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of production and storage of probiotic yogurt on aflatoxin M1 residue",
"author": "Montaseri",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "J Food Qual Hazards Control",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref61",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.alit.2017.08.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref8"
},
{
"article-title": "SPSS: Analysis without Anguish using SPSS Ion 14.0 for Windows",
"author": "Coakes",
"journal-title": "Statistics in Medicine",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref22",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3402/fnr.v57i0.18503",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1271/bbb.70474",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0222394",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI97065",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5455/javar.2019.f332",
"article-title": "Rapid detection of aflatoxin M1 residues in market milk in Aswan Province, Egypt and effect of probiotics on its residues concentration",
"author": "Zakaria",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "197",
"journal-title": "J Adv Vet Anim Res",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref62",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref1",
"unstructured": "1. WHO (2021) Egypt: WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/region/emro/country/eg/ (accessed April 2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.5114/aoms.2016.58928",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref29"
},
{
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref12",
"unstructured": "12. World Health Organization (2020) Clinical Management of COVID-19: Interim Guidance. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/clinical-management-of-covid-19 (accessed May 2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/9780470958186.ch3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.idairyj.2007.01.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref58"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nm.3444",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7010017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0308-8146(99)00127-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "S0007114521001926_ref18"
}
],
"reference-count": 64,
"references-count": 64,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.cambridge.org/core/product/identifier/S0007114521001926/type/journal_article"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Beyond probiotic legend: ESSAP gut microbiota health score to delineate SARS-COV-2 infection severity",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1017/policypage",
"volume": "127"
}
hegazy2