Rapid recovery of peripheral oxygen saturation in hypoxic COVID-19 patients with ivermectin/doxycycline/zinc multidrug therapy
et al., Preprint, 2025, Jul 2025
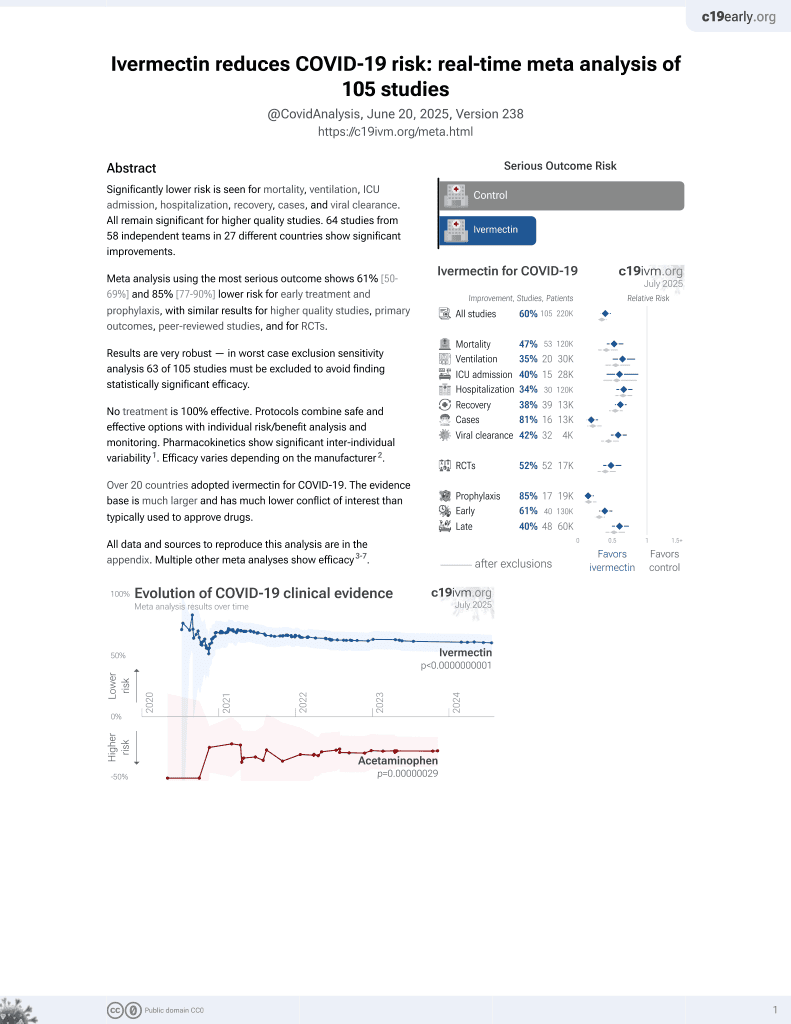
Ivermectin for COVID-19
4th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 106 studies, recognized in 24 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
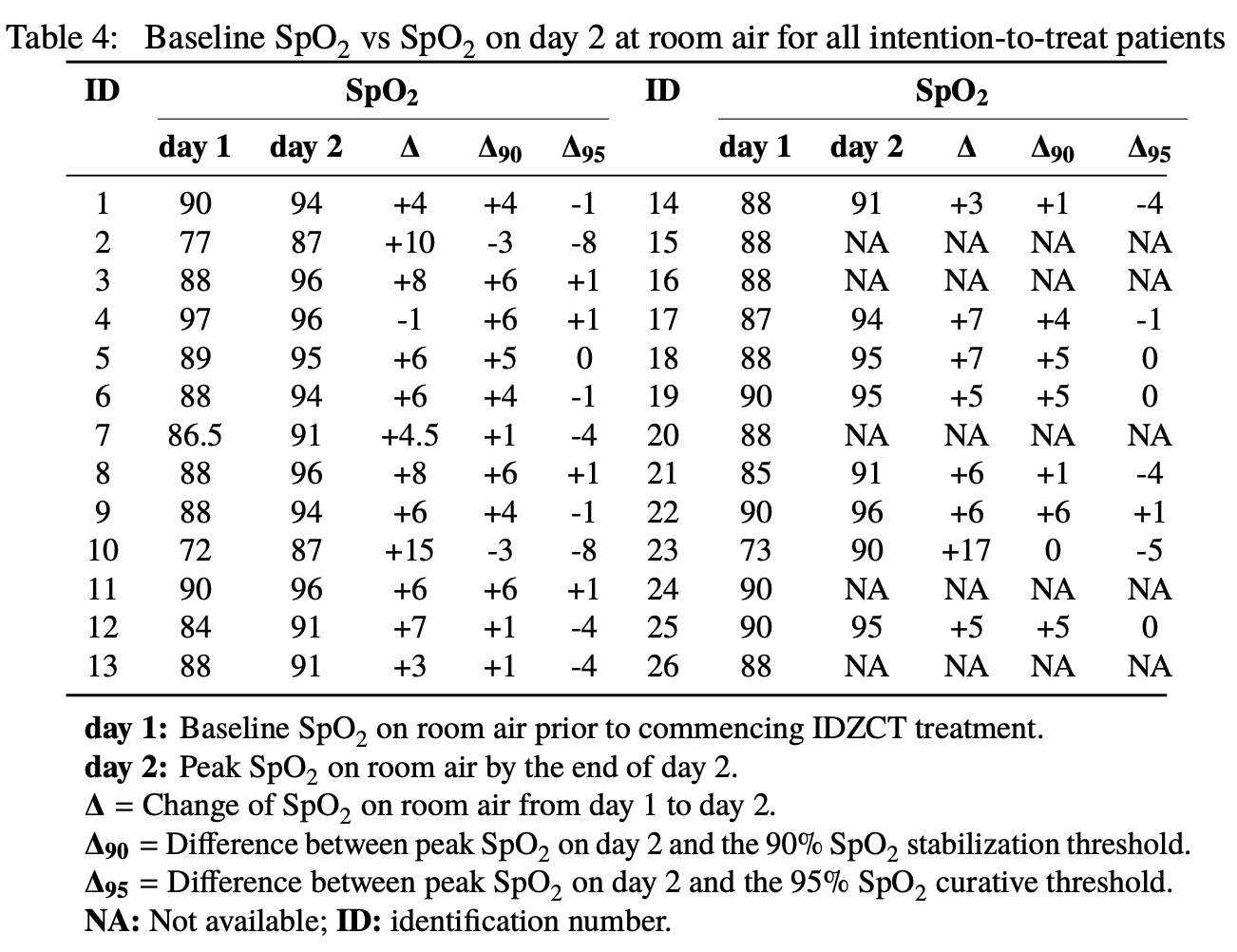
Retrospective 26 consecutive severe COVID-19 outpatients with hypoxia (25 with SpO2 ≤90%) showing rapid oxygen saturation recovery and survival with ivermectin/doxycycline/zinc/vitamin C/vitamin D combination therapy. All 24 patients completing the protocol survived without hospitalization, with median +6% SpO2 improvement within 24 hours and 18/21 patients achieving SpO2 >90% by day 2. Complete symptom resolution occurred within 20 days for 23/24 patients, with no long COVID symptoms reported. Two patients who declined or discontinued treatment died.
Hazan et al., 31 Jul 2025, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 8 authors, study period August 2020 - February 2021.
Contact: eleftherios.gkioulekas@utrgv.edu.
Rapid recovery of peripheral oxygen saturation in hypoxic COVID-19 patients with ivermectin/doxycycline/zinc multidrug therapy
Several combination therapies for the early outpatient treatment of COVID-19 were proposed by independent research groups at the onset of the pandemic during 2020 and 2021. In this observational study, we report on the outcomes of an off-label triple combination therapy, consisting of ivermectin, doxycycline, and zinc, with adjunct vitamin C and D3 supplementation, which was used on high-risk COVID-19 patients. These patients refused an initial recommendation to seek inpatient care, despite a high-risk presentation compounded with one or more comorbidities and/or severe hypoxia. Telemedicine was used to administer personalized treatment to patients at home, who did not have access to supplemental oxygen. Descriptive statistics was used to describe patient characteristics and outcomes. Of 26 consecutive patients, 25 presented with baseline SpO 2 ≤ 90% at room air. All 24 of 26 patients accepting the 10-day treatment survived without hospitalization. Within 24 hours on combination therapy, a rapid response of SpO 2 levels at room air was observed with median +6% (IQR 5% to 7%) increase between baseline (day 1) and day 2, with 18 patients stabilized at SpO 2 > 90% by day 2, and with full recovery of SpO 2 levels at room air within 10 days for all 24 patients who completed the 10-day treatment. All other symptoms were resolved within less than 20 days for 23 of 24 patients accepting treatment. All 24 patients fully recovered within 33 days, with no long covid symptoms after recovery. The rapid recovery of SpO 2 levels at room air provides temporality evidence in favor of the combination therapy. Furthermore, it has been replicated in two other studies and is further supported with experimental in-vitro studies and mechanistic evidence.
Ethics This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Ethical & Independent Review Services ( https://www.eandireview.com/ ) with IRB #21006. This study complied with the 2013 Declaration of Helsinki (World Medical Association, 2013) and applicable regulatory standards.
Competing interests Peter McCullough is the Founder and President of the McCullough Foundation. He is also the Chief Scientific Officer of the Wellness Company, who had no role in conducting this study. Sabine Hazan is the Chief Executive Officer of ProgenaBiome, LLC and Ventura Clinical Trials and she is the Founder of the Microbiome Research Foundation. She owns patents for the treatment and prophylaxis of COVID-19 and patents in the microbiome. She has a pecuniary interest in Topelia Aust Ltd in Australia and Topelia Therapeutics, Inc. in the USA where the development of treatment and prophylaxis options for COVID-19 are being pursued, including the combination therapy reported in this study. Thomas Borody has pecuniary interest in Topelia Aust Ltd in Australia and Topelia Therapeutics, Inc. in the USA. He has filed patents in the field of COVID-19 research and donated them to Topelia Aust Ltd in Australia for no compensation.
References
Aldous, Dancis, Dancis, Oldfield, Wheel replacing pyramid: Better paradigm representing totality of Evidence-Based Medicine, Annals of Global Health
Aldous, Gkioulekas, Oldfield, Ivermectin
Aminpour, Cannariato, Safaeeardebili, Preto, Moracchiato et al., In silico analysis of the multi-targeted mode of action of ivermectin and related compounds, Computation
Annunziata, Coppola, Carannante, Simioli, Lanza et al., Home management of patients with moderate or severe respiratory failure secondary to COVID-19, using remote monitoring and oxygen with or without HFNC, Pathogens
Aoki, Iwasawa, Hagiwara, Komatsu, Utsunomiya et al., Pulmonary vascular enlargement and lesion extent on computed tomography are correlated with COVID-19 disease severity, Japanese Journal of Radiology
Babalola, Ajayi, The place of ivermectin in the management of Covid-19: State of the evidence, Medical Research Archives, doi:10.18103/mra.v11i4.3778
Babalola, Ndanusa, Ajayi, Ogedengbe, Thairu et al., A randomized controlled trial of ivermectin monotherapy versus hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin, and azithromycin combination therapy in COVID-19 patients in Nigeria, Journal of Infectious Diseases and Epidemiology
Berndt, Kyle, Ling, The long shadow of patent expiration: generic entry and rx-to-OTC switches
Biancatelli, Berrill, Marik, The antiviral properties of vitamin C, Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy
Borsche, Glauner, Mendel, COVID-19 Mortality risk correlates inversely with vitamin D3 status, and a mortality rate close to zero could theoretically be achieved at 50 ng/mL 25(OH)D3: Results of a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrients
Boschi, Scheim, Bancod, Militello, Bideau et al., SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces hemagglutination: Implications for COVID-19 morbidities and therapeutics and for vaccine adverse effects, International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Bryant, Lawrie, Dowswell, Fordham, Mitchell et al., Ivermectin for prevention and treatment of COVID-19 infection: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis to inform clinical guidelines, American Journal of Therapeutics
Caly, Druce, Catton, Jans, Wagstaff, The FDA-approved drug ivermectin inhibits the replication of SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Antiviral Research
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Diaz, Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: A pilot randomized clinical study, Journal of steroid biochemistry and molecular biology
Chung, Yang, Wu, Deng, Tsai, Agricultural avermectins: An uncommon but potentially fatal cause of pesticide poisoning, Annals of Emergency Medicine
Core, R: A language and environment for statistical computing
De, Gregianin, Burger, Continuous high-dose ivermectin appears to be safe in patients with acute myelogenous leukemia and could inform clinical repurposing for COVID-19 infection, Leukemia and Lymphoma
Derwand, Scholz, Does zinc supplementation enhance the clinical efficacy of chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine to win today's battle against COVID-19?, Medical Hypotheses
Derwand, Scholz, Zelenko, COVID-19 outpatients -Early risk-stratified treatment with zinc plus low dose hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin: A retrospective case series study, International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents
Ding, Xu, Zhou, Long, Chest CT findings of COVID-19 pneumonia by duration of symptoms, European Journal of Radiology
Dolai, Hazan, Pagonis, Liu, Borody et al., Why multi-drug antiviral therapy is needed for COVID-19, SM Virology
George, Borody, Andrews, Devine, Moore-Jones et al., Cure of duodenal ulcer after eradication of Helicobacter pylori, The Medical Journal of Australia
Gkioulekas, Mccullough, Aldous, Critical appraisal of multi-drug therapy in the ambulatory management of patients with COVID-19 and hypoxemia. Part I. Evidence supporting the strength of association, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics
Gkioulekas, Mccullough, Aldous, Critical appraisal of multi-drug therapy in the ambulatory management of patients with COVID-19 and hypoxemia. Part II: Causal inference using the Bradford Hill criteria, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics
Guzzo, Furtek, Porras, Chen, Tipping et al., Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of escalating high doses of ivermectin in healthy adult subjects, Journal of Clinical Pharmacology
Heidary, Gharebaghi, Ivermectin: a systematic review from antiviral effects to COVID-19 complementary regimen, The Journal of Antibiotics
Hill, The environment and disease: Association or causation, Proceedings of the Royal Society of Medicine
Howick, Glasziou, Aronson, The evolution of evidence hierarchies: what can Bradford Hill's 'guidelines for causation' contribute?, Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine
Kory, Meduri, Gianfranco, Varon, Iglesias et al., Review of the emerging evidence demonstrating the efficacy of ivermectin in the prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19, American Journal of Therapeutics
Kow, Hasan, Ramachandram, The effect of vitamin C on the risk of mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Inflammopharmacology
Lange, Triple combinations: present and future, Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes and Human Retrovirology
Lehrer, Rheinstein, Ivermectin docks to the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain attached to ACE2, Vivo
Malek, Granwehr, Kontoyiannis, Doxycycline as a potential partner of COVID-19 therapies, IDCases
Marik, My journey to discovering ivermectin: Nature's gift to humanity
Marshall, Helicobacter connections
Mccullough, Alexander, Armstrong, Arvinte, Bain et al., Multifaceted highly targeted sequential multidrug treatment of early ambulatory high-risk SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19), Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine
Mccullough, Oskoui, Early multidrug regimens in new potentially fatal medical problems, Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine
Mcgonagle, Bridgewood, Meaney, A tricompartmental model of lung oxygenation disruption to explain pulmonary and systemic pathology in severe COVID-19, Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Mercola, Grant, Wagner, Evidence regarding vitamin D and risk of COVID-19 and its severity, Nutrients
Metwally, Basha, Zaitoun, Abdalla, Nofal et al., Clinical and radiological imaging as prognostic predictors in COVID-19 patients, The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine
Murchu, Byrne, Carty, Gascun, Keogan et al., Quantifying the risk of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection over time, Reviews in Medical Virology
Navarro, Camprubí, Requena-Mendez, Buonfrate, Giorli et al., Safety of high-dose ivermectin: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy
Niaee, Namdar, Allami, Zolghadr, Javadi et al., Ivermectin as an adjunct treatment for hospitalized adult COVID-19 patients: A randomized multi-center clinical trial, Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine
Osman, Farouk, Osman, Abdrabou, Longitudinal assessment of chest computerized tomography and oxygen saturation for patients with COVID-19, The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine
Procter, Ross, Pickard, Smith, Hanson et al., Clinical outcomes after early ambulatory multidrug therapy for high-risk SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection, Reviews in Cardiovascular Medicine
Procter, Ross, Pickard, Smith, Hanson et al., Early ambulatory multidrug therapy reduces hospitalization and death in high-risk patients with SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), International Journal of Innovative Research in Medical Science
Qin, Xu, Chen, Wen, Tang et al., Effects of vitamin C supplements on clinical outcomes and hospitalization duration for patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrition Reviews, doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuae154
Quispe-Cholan, Anticona-De-La-Cruz, Cornejo-Cruz, Quispe-Chirinos, Moreno-Lazaro et al., Tomographic findings in patients with COVID-19 according to evolution of the disease, The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine
Rajter, Sherman, Fatteh, Vogel, Sacks et al., Use of ivermectin is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with Coronavirus Disease, CHEST
Ravikirti, Pattadar, Raj, Agarwal, Biswas et al., Evaluation of ivermectin as a potential treatment for mild to moderate COVID-19: A double-blind randomized placebo controlled trial in Eastern India, Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences
Rheingold, Raval, Gordon, Hardigan, Zinc supplementation associated with a decrease in mortality in COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis, Cureus
Rizzo, Ivermectin, antiviral properties and COVID-19: a possible new mechanism of action, Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology
Santin, Scheim, Mccullough, Yagisawa, Borody, Ivermectin: a multifaceted drug of Nobel prize-honoured distinction with indicated efficacy against a new global scourge, COVID-19, New Microbes and New Infections
Scheim, A deadly embrace: Hemagglutination mediated by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein at its 22 N-glycosylation sites, red blood cell surface sialoglycoproteins, and antibody, International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Scheim, Parry, Rabbolini, Aldous, Yagisawa et al., Back to the basics of SARS-CoV-2 biochemistry: Microvascular occlusive glycan bindings govern its morbidities and inform therapeutic responses, Viruses
Scheim, Vottero, Santin, Hirsh, Sialylated glycan bindings from SARS-CoV-2 spike protein to blood and endothelial cells govern the severe morbidities of COVID-19, International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Skalny, Rink, Ajsuvakova, Aschner, Gritsenko et al., Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for COVID-19 (Review), International Journal of Molecular Medicine
Stone, Ndarukwa, Scheim, Dancis, Dancis et al., Changes in SpO2 on room air for 34 severe COVID-19 patients after ivermectin-based combination treatment: 62% normalization within 24 hours, Biologics
Tabatabaeizadeh, Zinc supplementation and COVID-19 mortality: a meta-analysis, European Journal of Medical Research
Thairu, Babalola, Ajayi, Ndanusa, Ogedengbe et al., A comparison of ivermectin and non ivermectin based regimen for COVID-19 in Abuja: Effects on virus clearance, days-to-discharge and mortality, Journal of Pharmaceutical Research International
Velthuis, Van Den Worm, Sims, Baric, Snijder et al., Zn2+ inhibits coronavirus and arterivirus RNA polymerase activity in vitro and zinc ionophores block the replication of these viruses in cell culture, PLoS Pathogens
Wang, Dong, Hu, Li, Ren et al., Temporal changes of CT findings in 90 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia: A longitudinal study, Radiology
Warren, Helicobacter -The ease and difficulty of a new discovery
Wong, Viswanathan, Wang, Sun, Clark et al., Current and future developments in the treatment of virus-induced hypercytokinemia, Future Medicinal Chemistry
Yagisawa, Foster, Hanaki, Omura, Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19 -Part 2, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics
Yagisawa, Foster, Hanaki, Omura, Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19, The Japanese Journal of Antibiotics
Yates, Newman, Oshry, Glassman, Leone et al., Doxycycline treatment of high-risk COVID-19-positive patients with comorbid pulmonary disease, Therapeutic Advances in Respiratory Disease
Zaidi, Dehgani-Mobaraki, The mechanisms of action of ivermectin against SARS-CoV-2. An extensive review, The Journal of Antibiotics