Incidence of COVID-19 Symptom Rebound After Treatment with Remdesivir
et al., Infectious Disease Reports, doi:10.3390/idr17030043, May 2025
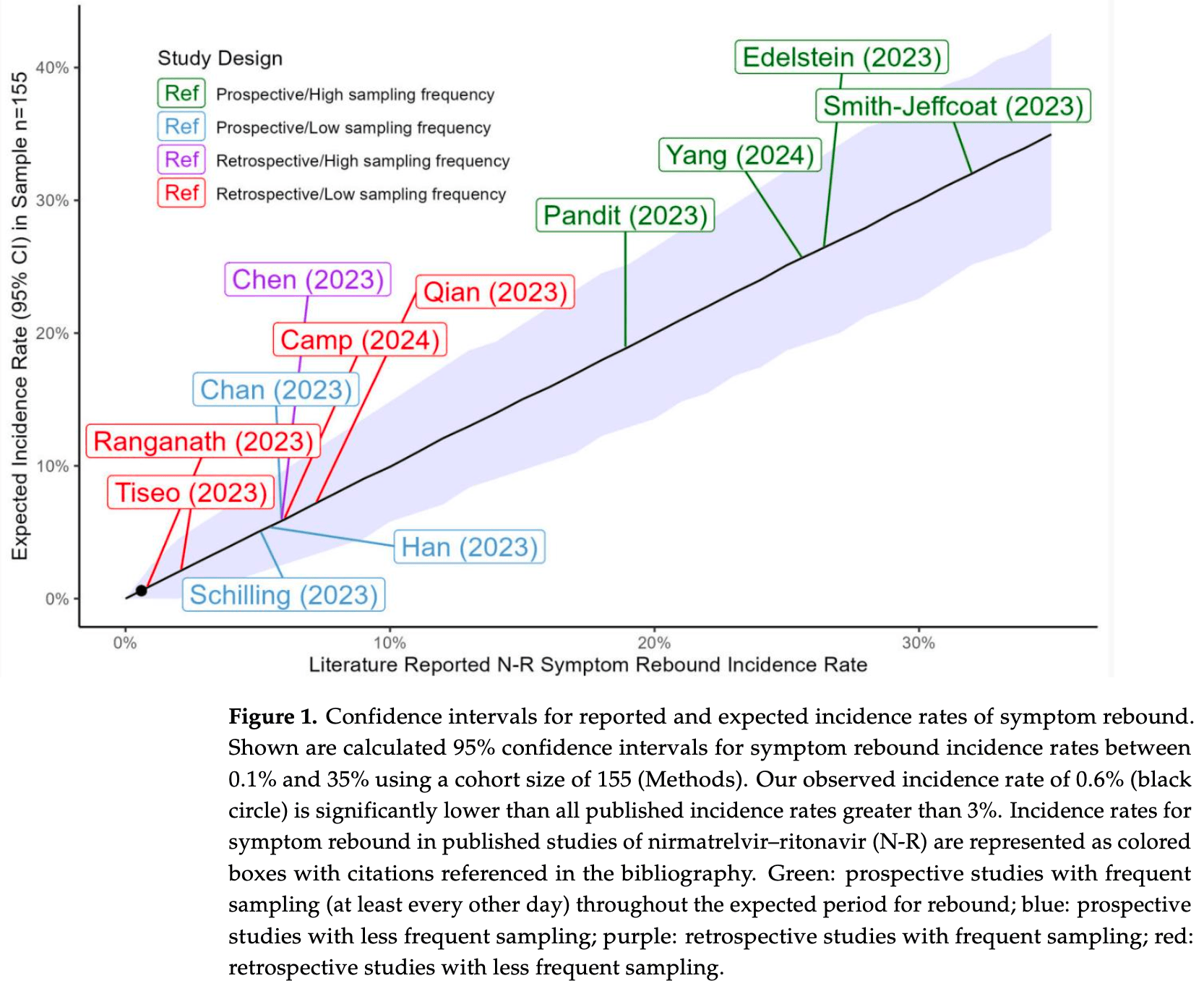
Retrospective 155 patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 showing significantly lower symptom rebound rates with remdesivir compared with paxlovid. Authors provide an analysis of rebound with paxlovid, showing higher rates in prospective studies with high frequency sampling.
Study covers paxlovid and remdesivir.
Gupta et al., 1 May 2025, peer-reviewed, 7 authors.
Contact: michael.charness@va.gov (corresponding author), kalpana.gupta@va.gov, william.obrien@va.gov, judith.strymish@va.gov, anna.chen2@va.gov, katherine.linsenmeyer@va.gov, rebecca.madjarov@va.gov.
Incidence of COVID-19 Symptom Rebound After Treatment with Remdesivir
Infectious Disease Reports, doi:10.3390/idr17030043
Background/Objectives: Recent in vitro data suggest that remdesivir might be less likely than nirmatrelvir-ritonavir to be associated with COVID-19 rebound. We compared the incidence of symptom rebound in our remdesivir-treated cohort with rates reported in the literature for nirmatrelvir-ritonavir. Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study of VA Boston Healthcare System patients who were nursing home residents or inpatients treated with remdesivir for mild to moderate COVID-19 that met clinical criteria for nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment between 05/2022 and 10/2024. Electronic health records were reviewed for evidence of symptom rebound in daily clinical evaluations and outside hospital care notes for 15-20 days after the diagnosis of COVID-19. Rates for nirmatrelvir-ritonavir were identified via a literature review. Results: Among 194 patients treated with remdesivir, 39 were excluded due to concurrent antiviral use, hypoxia, or ICU-level care. The average age of the remaining 155 patients was 75.1 ± 11.9 years; 147 patients (95%) were male. Evidence of symptom rebound was found in 1 of 155 (0.6%) remdesivir-treated patients, which is a rate lower than that reported in all 12 studies of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir symptom rebound during the Omicron era. Conclusions: Our finding of low rates of COVID-19 symptom rebound after treatment with remdesivir are consistent with the hypothesis that rebound may be less frequent after treatment with remdesivir than with nirmatrelvir-ritonavir.
Abbreviations The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
ICU Intensive care unit EHR Electronic health record VA Veterans Affairs
References
Anderson, Caubel, Rusnak, Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir and Viral Load Rebound in COVID-19, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2205944
Bennett, Magagnoli, Gundabolu, Georgantopoulos, Lebby et al., A SONAR report on Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir-associated rebound COVID-19: Using new databases for evaluating new diseases, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0308205
Camp, Caputo, Echevarria, Achenbach, Clinical rebound after treatment with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in COVID-19, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-024-09842-8
Chan, Lui, Wong, Yip, Li et al., Safety Profile and Clinical and Virological Outcomes of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Treatment in Patients With Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease and Coronavirus Disease, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad371
Charness, Gupta, Stack, Strymish, Adams et al., Rebound of SARS-CoV-2 Infection after Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Treatment, N. Engl. J. Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2206449
Chen, Wang, Chang, Hung, Fang et al., Factors associated with viral rebound among COVID-19 patients receiving oral antivirals, J. Formos. Med. Assoc, doi:10.1016/j.jfma.2023.02.008
Deo, Choudhary, Moser, Ritz, Daar et al., Symptom and Viral Rebound in Untreated SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Ann. Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/M22-2381
Du, Wang, Bai, Liu, Lau et al., A retrospective cohort study of Paxlovid efficacy depending on treatment time in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.89801
Durstenfeld, Peluso, Lin, Peyser, Isasi et al., Association of nirmatrelvir for acute SARS-CoV-2 infection with subsequent Long COVID symptoms in an observational cohort study, J. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.29333
Edelstein, Boucau, Uddin, Marino, Liew et al., SARS-CoV-2 Virologic Rebound With Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Therapy: An Observational Study, Ann. Intern. Med, doi:10.7326/M23-1756
Esmaeili, Owens, Wagoner, Polyak, White et al., A unifying model to explain frequent SARS-CoV-2 rebound after nirmatrelvir treatment and limited prophylactic efficacy, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-024-49458-9
Haddad, Hachem, Moussa, Jiang, Dagher et al., Comparing Molnupiravir to Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir (Paxlovid) in the Treatment of Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19 in Immunocompromised Cancer Patients, Cancers, doi:10.3390/cancers16051055
Han, Bae, Jung, Kim, Chong et al., Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 rebound after nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or molnupiravir therapy: A prospective cohort study, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000035094
Hay, Kissler, Fauver, Mack, Tai et al., Quantifying the impact of immune history and variant on SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and infection rebound: A retrospective cohort study, eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.81849
Li, Zhang, Liu, Wang, Liu, Adverse Events Associated with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis Based on FAERS, Pharmaceuticals, doi:10.3390/ph15121455
Marchetti, Rovito, Bono, Bonara, Bai et al., Immunologic characterization of a patient with clinical and virologic rebound upon Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir treatment: The unfortunate epilogue of COVID-19, Clin. Microbiol. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2023.01.016
Nair, Luck, Huang, Sabo, Ho, Persistence of an infectious form of SARS-CoV-2 post protease inhibitor treatment of permissive cells in vitro, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiae385
Pandit, Radin, Chiang, Spencer, Pawelek et al., The COVID-19 Rebound Study: A Prospective Cohort Study to Evaluate Viral and Symptom Rebound Differences in Participants Treated with Nirmatrelvir Plus Ritonavir Versus Untreated Controls, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad102
Phan, Ribeiro, Edelstein, Boucau, Uddin et al., Modeling suggests SARS-CoV-2 rebound after nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment is driven by target cell preservation coupled with incomplete viral clearance, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi.01623-24
Qian, Wang, Patel, Kawano, Fu et al., Outcomes with and without outpatient SARS-CoV-2 treatment for patients with COVID-19 and systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases: A retrospective cohort study, Lancet Rheumatol, doi:10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00006-1
Ranganath, O'horo, Challener, Tulledge-Scheitel, Pike et al., Rebound Phenomenon After Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in High-Risk Persons, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciac481
Schilling, Jittamala, Watson, Boyd, Luvira et al., Antiviral efficacy of molnupiravir versus ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir in patients with early symptomatic COVID-19 (PLATCOV): An open-label, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive trial, Lancet Infect. Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00493-0
Smith, Li, Moser, Yeh, Currier et al., Recurrence of Symptoms Following a 2-Day Symptom Free Period in Patients With COVID-19, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.38867
Smith-Jeffcoat, Biddle, Talbot, Morrissey, Stockwell et al., Symptoms, viral loads, and rebound among COVID-19 outpatients treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir compared to propensity score matched untreated individuals, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad696
Tiseo, Barbieri, Galfo, Occhineri, Matucci et al., Efficacy and Safety of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir, Molnupiravir, and Remdesivir in a Real-World Cohort of Outpatients with COVID-19 at High Risk of Progression: The PISA Outpatient Clinic Experience, Infect. Dis. Ther, doi:10.1007/s40121-022-00729-2
Wong, Lau, Au, Lau, Hung et al., Optimal timing of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment after COVID-19 symptom onset or diagnosis: Target trial emulation, Nat. Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-43706-0
Yang, Xu, Zheng, Ye, Lv et al., COVID-19 Rebound After VV116 vs Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Treatment: A Randomized Clinical Trial, JAMA Netw. Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.1765
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/idr17030043",
"ISSN": [
"2036-7449"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/idr17030043",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background/Objectives: Recent in vitro data suggest that remdesivir might be less likely than nirmatrelvir–ritonavir to be associated with COVID-19 rebound. We compared the incidence of symptom rebound in our remdesivir-treated cohort with rates reported in the literature for nirmatrelvir–ritonavir. Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study of VA Boston Healthcare System patients who were nursing home residents or inpatients treated with remdesivir for mild to moderate COVID-19 that met clinical criteria for nirmatrelvir–ritonavir treatment between 05/2022 and 10/2024. Electronic health records were reviewed for evidence of symptom rebound in daily clinical evaluations and outside hospital care notes for 15–20 days after the diagnosis of COVID-19. Rates for nirmatrelvir–ritonavir were identified via a literature review. Results: Among 194 patients treated with remdesivir, 39 were excluded due to concurrent antiviral use, hypoxia, or ICU-level care. The average age of the remaining 155 patients was 75.1 ± 11.9 years; 147 patients (95%) were male. Evidence of symptom rebound was found in 1 of 155 (0.6%) remdesivir-treated patients, which is a rate lower than that reported in all 12 studies of nirmatrelvir–ritonavir symptom rebound during the Omicron era. Conclusions: Our finding of low rates of COVID-19 symptom rebound after treatment with remdesivir are consistent with the hypothesis that rebound may be less frequent after treatment with remdesivir than with nirmatrelvir–ritonavir.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"idr17030043"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "VA Boston Healthcare System, West Roxbury, MA 02132, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, Boston, MA 02111, USA"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Kalpana",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "VA Boston Healthcare System, West Roxbury, MA 02132, USA"
},
{
"name": "Veterans Affairs Informatics and Computing Infrastructure, George E. Wahlen Department of Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Salt Lake City, UT 84148, USA"
}
],
"family": "O’Brien",
"given": "William J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "VA Boston Healthcare System, West Roxbury, MA 02132, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA"
}
],
"family": "Strymish",
"given": "Judith",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "VA Boston Healthcare System, West Roxbury, MA 02132, USA"
}
],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Anna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "VA Boston Healthcare System, West Roxbury, MA 02132, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, Boston, MA 02111, USA"
}
],
"family": "Linsenmeyer",
"given": "Katherine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "VA Boston Healthcare System, West Roxbury, MA 02132, USA"
}
],
"family": "Madjarov",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3301-8966",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "VA Boston Healthcare System, West Roxbury, MA 02132, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Neurology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Neurology, Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, Boston, MA 02111, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Charness",
"given": "Michael E.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Infectious Disease Reports",
"container-title-short": "Infectious Disease Reports",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-01T13:16:12Z",
"timestamp": 1746105372000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-01T14:13:38Z",
"timestamp": 1746108818000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-02T04:09:40Z",
"timestamp": 1746158980536,
"version": "3.40.4"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1746057600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2036-7449/17/3/43/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "43",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2206449",
"article-title": "Rebound of SARS-CoV-2 Infection after Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Treatment",
"author": "Charness",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1045",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M23-1756",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Virologic Rebound With Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Therapy: An Observational Study",
"author": "Edelstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1577",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad102",
"article-title": "The COVID-19 Rebound Study: A Prospective Cohort Study to Evaluate Viral and Symptom Rebound Differences in Participants Treated with Nirmatrelvir Plus Ritonavir Versus Untreated Controls",
"author": "Pandit",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "25",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Symptoms, viral loads, and rebound among COVID-19 outpatients treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir compared to propensity score matched untreated individuals",
"author": "Biddle",
"first-page": "1175",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000035094",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of COVID-19 rebound after nirmatrelvir-ritonavir or molnupiravir therapy: A prospective cohort study",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e35094",
"journal-title": "Medicine",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-024-09842-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_6",
"unstructured": "Camp, D., Caputo, M., Echevarria, F.M., and Achenbach, C.J. (2024). Clinical rebound after treatment with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir in COVID-19. BMC Infect. Dis., 24."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiae385",
"article-title": "Persistence of an infectious form of SARS-CoV-2 post protease inhibitor treatment of permissive cells in vitro",
"author": "Nair",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e68",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "231",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-43706-0",
"article-title": "Optimal timing of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment after COVID-19 symptom onset or diagnosis: Target trial emulation",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8377",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-024-49458-9",
"article-title": "A unifying model to explain frequent SARS-CoV-2 rebound after nirmatrelvir treatment and limited prophylactic efficacy",
"author": "Esmaeili",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5478",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.89801",
"article-title": "A retrospective cohort study of Paxlovid efficacy depending on treatment time in hospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e89801",
"journal-title": "eLife",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.01623-24",
"article-title": "Modeling suggests SARS-CoV-2 rebound after nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment is driven by target cell preservation coupled with incomplete viral clearance",
"author": "Phan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0162324",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2023.01.016",
"article-title": "Immunologic characterization of a patient with clinical and virologic rebound upon Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir treatment: The unfortunate epilogue of COVID-19",
"author": "Marchetti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "660",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Infect.",
"key": "ref_12",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2205944",
"article-title": "Nirmatrelvir–Ritonavir and Viral Load Rebound in COVID-19",
"author": "Anderson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1047",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "387",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.1765",
"article-title": "COVID-19 Rebound After VV116 vs Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Treatment: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e241765",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00493-0",
"article-title": "Antiviral efficacy of molnupiravir versus ritonavir-boosted nirmatrelvir in patients with early symptomatic COVID-19 (PLATCOV): An open-label, phase 2, randomised, controlled, adaptive trial",
"author": "Schilling",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad371",
"article-title": "Safety Profile and Clinical and Virological Outcomes of Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir Treatment in Patients With Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease and Coronavirus Disease 2019",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1406",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cancers16051055",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "Haddad, A.J., Hachem, R.Y., Moussa, M., Jiang, Y., Dagher, H.R., Chaftari, P., Chaftari, A.-M., and Raad, I.I. (2024). Comparing Molnupiravir to Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir (Paxlovid) in the Treatment of Mild-to-Moderate COVID-19 in Immunocompromised Cancer Patients. Cancers, 16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00006-1",
"article-title": "Outcomes with and without outpatient SARS-CoV-2 treatment for patients with COVID-19 and systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Qian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e139",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-2381",
"article-title": "Symptom and Viral Rebound in Untreated SARS-CoV-2 Infection",
"author": "Deo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "348",
"journal-title": "Ann. Intern. Med.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.38867",
"article-title": "Recurrence of Symptoms Following a 2-Day Symptom Free Period in Patients With COVID-19",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2238867",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29333",
"article-title": "Association of nirmatrelvir for acute SARS-CoV-2 infection with subsequent Long COVID symptoms in an observational cohort study",
"author": "Durstenfeld",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e29333",
"journal-title": "J. Med. Virol.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jfma.2023.02.008",
"article-title": "Factors associated with viral rebound among COVID-19 patients receiving oral antivirals",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "J. Formos. Med. Assoc.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.81849",
"article-title": "Quantifying the impact of immune history and variant on SARS-CoV-2 viral kinetics and infection rebound: A retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Hay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e81849",
"journal-title": "eLife",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac481",
"article-title": "Rebound Phenomenon After Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in High-Risk Persons",
"author": "Ranganath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e537",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-022-00729-2",
"article-title": "Efficacy and Safety of Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir, Molnupiravir, and Remdesivir in a Real-World Cohort of Outpatients with COVID-19 at High Risk of Progression: The PISA Outpatient Clinic Experience",
"author": "Tiseo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "257",
"journal-title": "Infect. Dis. Ther.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0308205",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Bennett, C.L., Magagnoli, J., Gundabolu, K., Georgantopoulos, P., Lebby, A., Watson, G., Knopf, K., Martin, L., Carson, K.R., and Hrushesky, W.J. (2024). A SONAR report on Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir-associated rebound COVID-19: Using new databases for evaluating new diseases. PLoS ONE, 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph15121455",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Li, M., Zhang, Q.S., Liu, X.L., Wang, H.L., and Liu, W. (2022). Adverse Events Associated with Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir: A Pharmacovigilance Analysis Based on FAERS. Pharmaceuticals, 15."
}
],
"reference-count": 27,
"references-count": 27,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2036-7449/17/3/43"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Incidence of COVID-19 Symptom Rebound After Treatment with Remdesivir",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "17"
}