SAFEty Study of Early Infusion of Vitamin C for Treatment of Novel Coronavirus Acute Lung Injury (SAFE EVICT CORONA-ALI)
et al., NCT04344184, SAFE EVICT CORONA-ALI, NCT04344184, Apr 2024
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
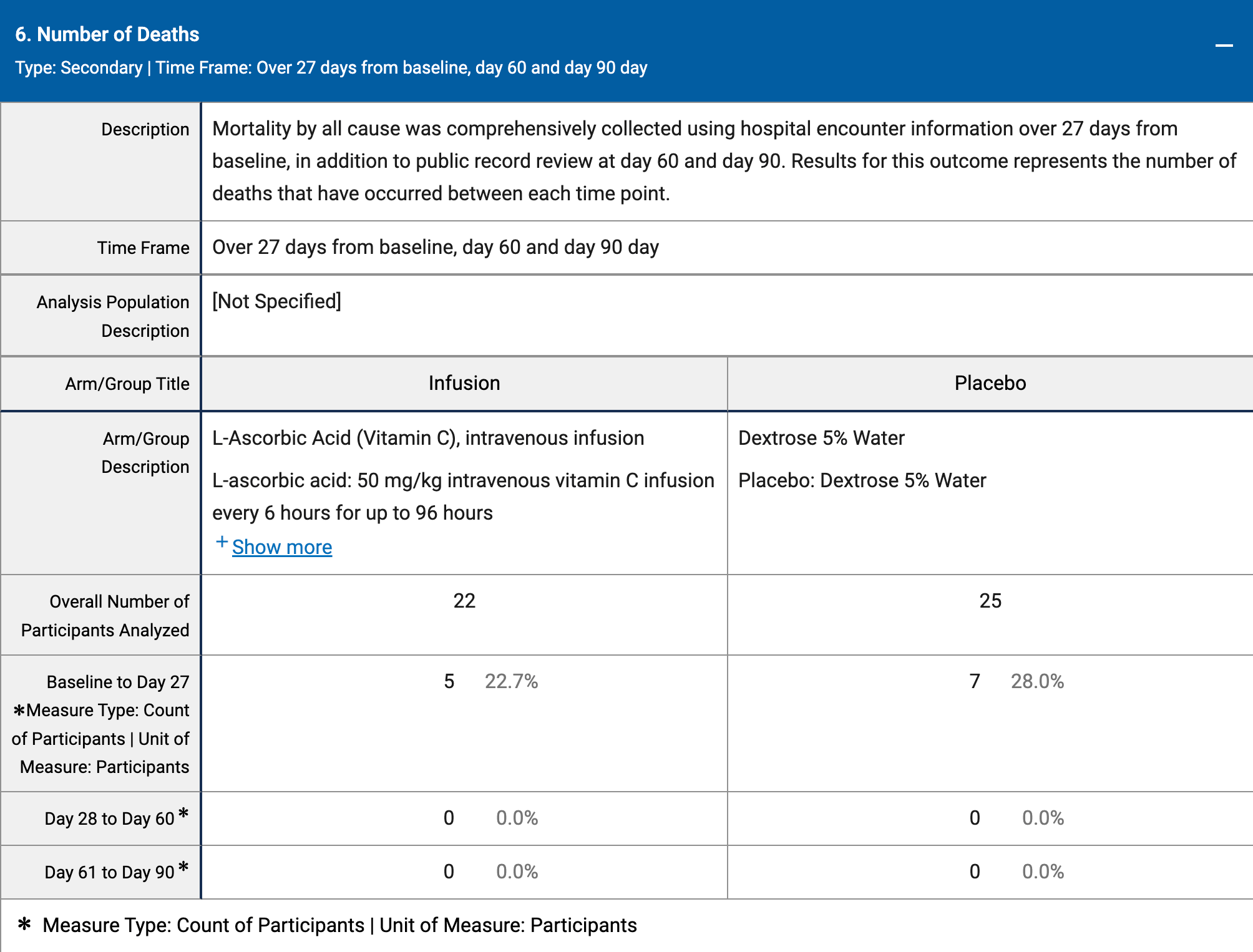
RCT 47 ICU patients showing no significant differences with vitamin C treatment.
Although the 19% lower mortality is not statistically significant, it is consistent with the significant 18% lower mortality [9‑27%] from meta-analysis of the 45 mortality results to date.
This is the 21st COVID-19 RCT for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.0012.
This is the 69th of 74 COVID-19 controlled studies for vitamin C, which collectively show efficacy with p=0.000000068.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
Results may differ in countries with improved SOC.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
very late stage, ICU patients.
|
risk of death, 18.8% lower, RR 0.81, p = 0.75, treatment 5 of 22 (22.7%), control 7 of 25 (28.0%), NNT 19.
|
|
relative WHO status, 1.7% worse, RR 1.02, p = 0.28, treatment mean 3.05 (±0.22) n=21, control mean 3.0 (±0.0) n=23, day 27.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Fowler et al., 4 Apr 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, preprint, 1 author, trial NCT04344184 (history) (SAFE EVICT CORONA-ALI).
