Efficacy of a Low Dose of Melatonin as an Adjunctive Therapy in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-blind Clinical Trial
et al., Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006, Jun 2021
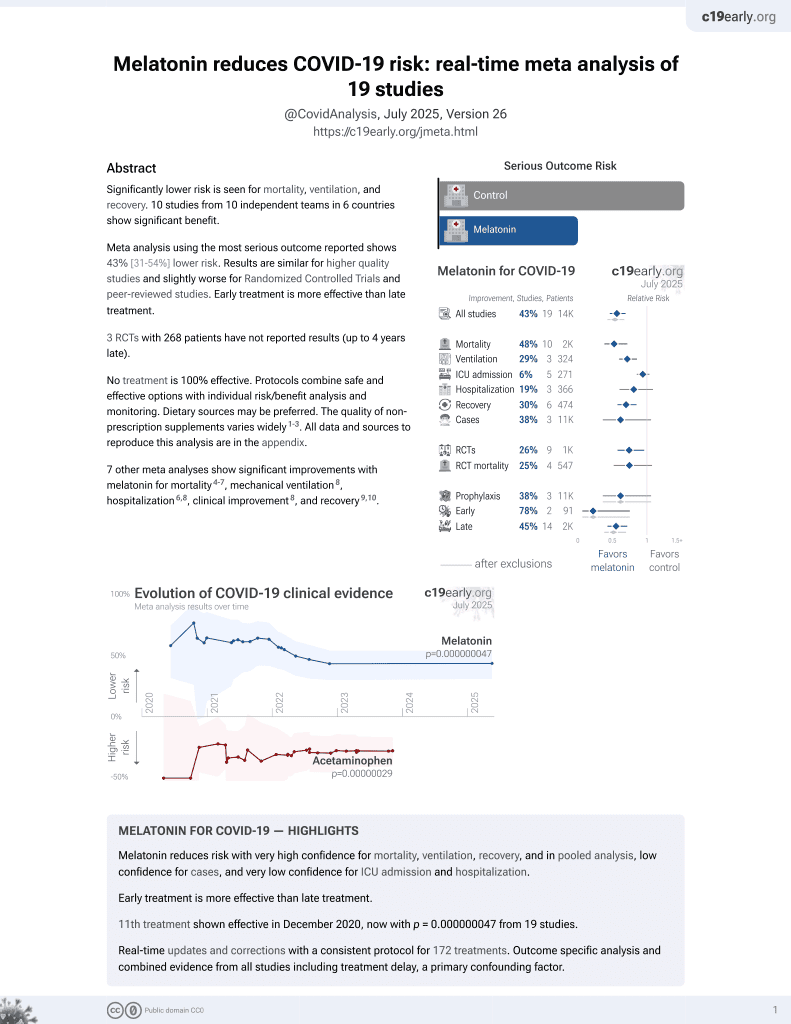
Melatonin for COVID-19
12th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2020, now with p = 0.000000015 from 18 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
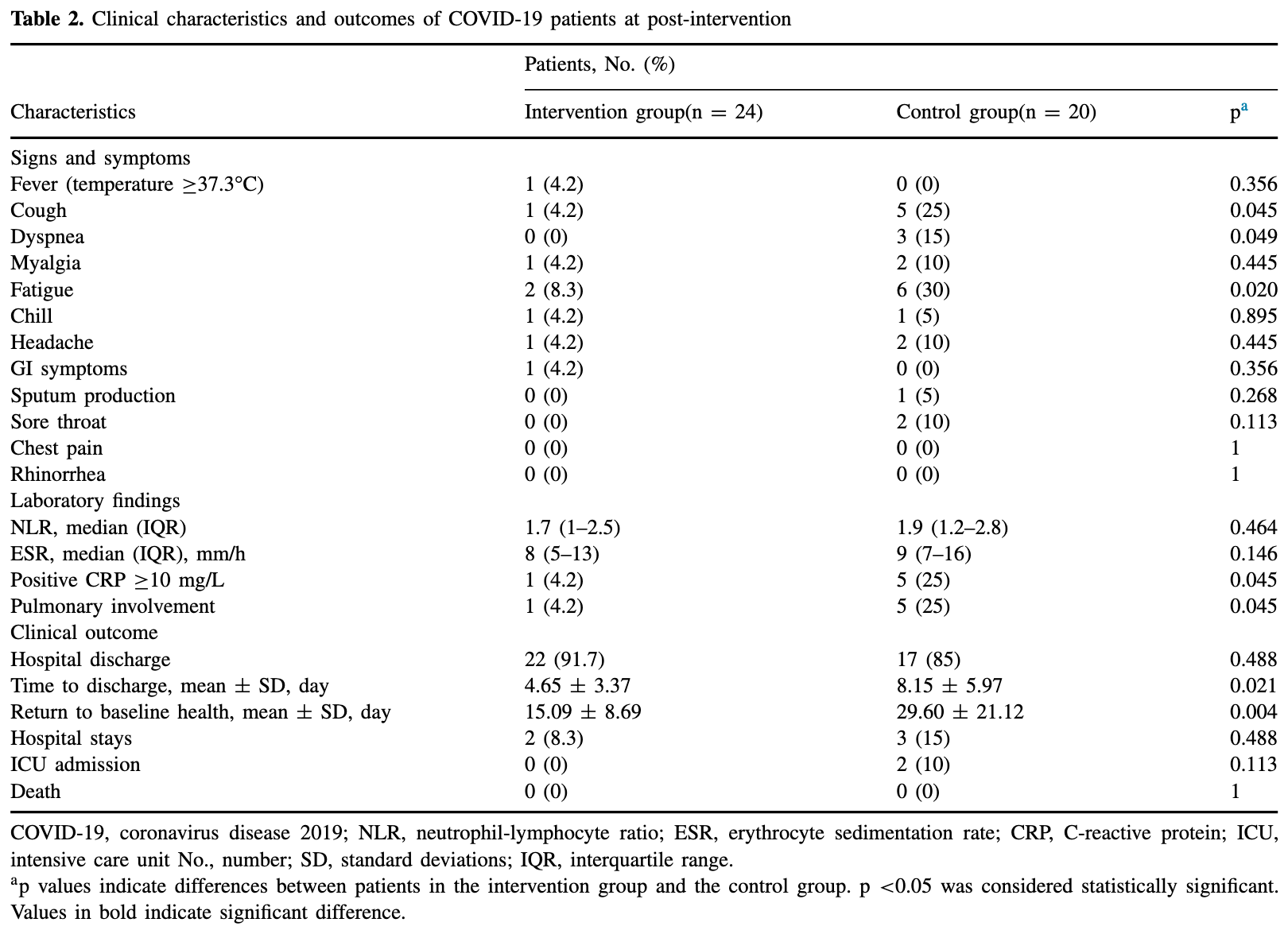
RCT 44 hospitalized patients in Iran, 24 treated with melatonin, showing faster recovery with treatment. There was no mortality.
|
risk of ICU admission, 81.5% lower, RR 0.19, p = 0.20, treatment 0 of 24 (0.0%), control 2 of 20 (10.0%), NNT 10.0, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
recovery time, 49.0% lower, relative time 0.51, p = 0.004, treatment 24, control 20.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 44.4% lower, RR 0.56, p = 0.65, treatment 2 of 24 (8.3%), control 3 of 20 (15.0%), NNT 15.
|
|
time to discharge, 42.9% lower, relative time 0.57, p = 0.02, treatment 24, control 20.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Farnoosh et al., 23 Jun 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, study period 25 April, 2020 - 5 June, 2020, average treatment delay 7.0 days.
Efficacy of a Low Dose of Melatonin as an Adjunctive Therapy in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-blind Clinical Trial
Archives of Medical Research, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006
Background. Melatonin has been known as an anti-inflammatory agent and immune modulator that may address progressive pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 .Aim of the study. To evaluate the clinical efficacy of adjuvant, use of melatonin in patients with COVID-19. Methods. This single-center, double-blind, randomized clinical trial included 74 hospitalized patients with confirmed mild to moderate COVID-19 at Baqiyatallah Hospital in Tehran, Iran, from April 25, 2020-June 5, 2020. Patients were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to receive standard of care and standard of care plus melatonin at a dose of 3 mg three times daily for 14 d. Clinical characteristics, laboratory, and radiological findings were assessed and compared between two study groups at baseline and post-intervention. Safety and clinical outcomes were followed up for four weeks. Results. A total of 24 patients in the intervention group and 20 patients in the control group completed the treatment. Compared with the control group, the clinical symptoms such as cough, dyspnea, and fatigue, as well as the level of CRP and the pulmonary involvement in the intervention group had significantly improved (p < 0.05). The mean time of hospital discharge of patients and return to baseline health was significantly shorter in the intervention group compared to the control group (p < 0.05). No deaths and adverse events were observed in both groups. Conclusions. Adjuvant use of melatonin has a potential to improve clinical symptoms of COVID-19 patients and contribute to a faster return of patients to baseline health.
ARTICLE IN PRESS
Declaration of Competing Interests All authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
References
Akbariqomi, Hosseini, Rashidiani, Clinical characteristics and outcome of hospitalized COVID-19 patients with diabetes: A single-center, retrospective study in Iran, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
Biancatelli, Berrill, Mohammed, Melatonin for the treatment of sepsis: the scientific rationale, J Thorac Dis
Davoodi, Abedi, Salehifar, Febuxostat therapy in outpatients with suspected COVID-19: A clinical trial, Int J Clin Pract
Farnoosh, Efficacy of a Low Dose of Melatonin as an Adjunctive Therapy in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-blind Clinical Trial, Archives of Medical Research
Habtemariam, Daglia, Sureda, Melatonin and respiratory diseases: a review, Curr Top Med Chem
Huang, Liao, Chen, Melatonin possesses an anti-influenza potential through its immune modulatory effect, J Funct Foods
Ibrahim, Potential repurposed SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection drugs, RSC Adv
Kleszczyński, Slominski, Steinbrink, Clinical Trials for Use of Melatonin to Fight against COVID-19 Are Urgently Needed, Nutrients
Li, Li, Zhang, Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues, Infect Dis Poverty
Li, Li, Zhou, Melatonin for the prevention and treatment of cancer, Oncotarget
Liu, Li, Xu, Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with COVID-19, J Clin Virol
Mousavizadeh, Ghasemi, Genotype and phenotype of COVID-19: Their roles in pathogenesis, J Microbiol Immunol Infect
Nikpouraghdam, Farahani, Alishiri, Epidemiological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients in IRAN: A single center study, J Clin Virol
Potempa, Rajab, Hart, Insights into the use of C-Reactive protein as a diagnostic index of disease severity in COVID-19 infections, Am J Trop Med Hyg
Ragab, Salah Eldin, Taeimah, The COVID-19 cytokine storm; what we know so far, Front Immunol
Shneider, Kudriavtsev, Vakhrusheva, Can melatonin reduce the severity of COVID-19 pandemic?, Int Rev Immunol
Tan, Hardeland, Potential utility of melatonin in deadly infectious diseases related to the overreaction of innate immune response and destructive inflammation: focus on COVID-19, Melatonin Res
Wang, Horby, Hayden, A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern, Lancet
Wang, Zhang, Du, Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet
Wu, Wang, Kuo, An update on current therapeutic drugs treating COVID-19, Curr Pharmacol Reports
Zhang, Wang, Ni, COVID-19: Melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment, Life Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006",
"ISSN": [
"0188-4409"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006",
"alternative-id": [
"S0188440921001417"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Efficacy of a Low Dose of Melatonin as an Adjunctive Therapy in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-blind Clinical Trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Archives of Medical Research"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social (IMSS). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Farnoosh",
"given": "Gholamreza",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3533-2393",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Akbariqomi",
"given": "Mostafa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Badri",
"given": "Taleb",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bagheri",
"given": "Mahdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Izadi",
"given": "Morteza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saeedi-Boroujeni",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rezaie",
"given": "Ehsan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ghaleh",
"given": "Hadi Esmaeili Gouvarchin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aghamollaei",
"given": "Hossein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fasihi-ramandi",
"given": "Mahdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hassanpour",
"given": "Kazem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alishiri",
"given": "GholamHossein",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Archives of Medical Research",
"container-title-short": "Archives of Medical Research",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-23T15:51:54Z",
"timestamp": 1624463514000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T23:11:34Z",
"timestamp": 1712272294000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T23:40:16Z",
"timestamp": 1712274016409
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 41,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1640995200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0188440921001417?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0188440921001417?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "79-85",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30185-9",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "470",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0001",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104378",
"article-title": "Epidemiological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients in IRAN: A single center study",
"author": "Nikpouraghdam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0002",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0003",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19-4-may-2021. (Accessed May 4, 2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108467",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and outcome of hospitalized COVID-19 patients with diabetes: A single-center, retrospective study in Iran",
"author": "Akbariqomi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Res Clin Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0004",
"volume": "169",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31022-9",
"article-title": "Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1569",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0005",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/D0RA05821A",
"article-title": "Potential repurposed SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection drugs",
"author": "Abuo-Rahma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "26895",
"journal-title": "RSC Adv",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0006",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.13600",
"article-title": "Febuxostat therapy in outpatients with suspected COVID-19: A clinical trial",
"author": "Davoodi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e13600",
"journal-title": "Int J Clin Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0007",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40495-020-00216-7",
"article-title": "An update on current therapeutic drugs treating COVID-19",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "56",
"journal-title": "Curr Pharmacol Reports",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0008",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmii.2020.03.022",
"article-title": "Genotype and phenotype of COVID-19: Their roles in pathogenesis",
"author": "Mousavizadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "159",
"journal-title": "J Microbiol Immunol Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0009",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x",
"article-title": "Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Poverty",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0010",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01446",
"article-title": "The COVID-19 cytokine storm; what we know so far",
"author": "Ragab",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1446",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0011",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092561",
"article-title": "Clinical Trials for Use of Melatonin to Fight against COVID-19 Are Urgently Needed",
"author": "Kleszczyński",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2561",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0012",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "COVID-19: Melatonin as a potential adjuvant treatment",
"author": "Zhang",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0013",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08830185.2020.1756284",
"article-title": "Can melatonin reduce the severity of COVID-19 pandemic?",
"author": "Shneider",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Int Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0014",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.32794/mr11250052",
"article-title": "Potential utility of melatonin in deadly infectious diseases related to the overreaction of innate immune response and destructive inflammation: focus on COVID-19",
"author": "Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "120",
"journal-title": "Melatonin Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0015",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/oncotarget.16379",
"article-title": "Melatonin for the prevention and treatment of cancer",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39896",
"journal-title": "Oncotarget",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0016",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jff.2019.04.062",
"article-title": "Melatonin possesses an anti-influenza potential through its immune modulatory effect",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "189",
"journal-title": "J Funct Foods",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0017",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21037/jtd.2019.12.85",
"article-title": "Melatonin for the treatment of sepsis: the scientific rationale",
"author": "Biancatelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S54",
"journal-title": "J Thorac Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0018",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1568026616666160824120338",
"article-title": "Melatonin and respiratory diseases: a review",
"author": "Habtemariam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "467",
"journal-title": "Curr Top Med Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0019",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104370",
"article-title": "Prognostic value of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, and procalcitonin in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0020",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4269/ajtmh.20-0473",
"article-title": "Insights into the use of C-Reactive protein as a diagnostic index of disease severity in COVID-19 infections",
"author": "Potempa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "561",
"journal-title": "Am J Trop Med Hyg",
"key": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.06.006_bib0021",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 21,
"references-count": 21,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0188440921001417"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Efficacy of a Low Dose of Melatonin as an Adjunctive Therapy in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Randomized, Double-blind Clinical Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "53"
}