Prevalence and risk factors of COVID-19 infection, mortality, and post-infection lung fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study
et al., Journal of International Medical Research, doi:10.1177/03000605231198413, Sep 2023
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
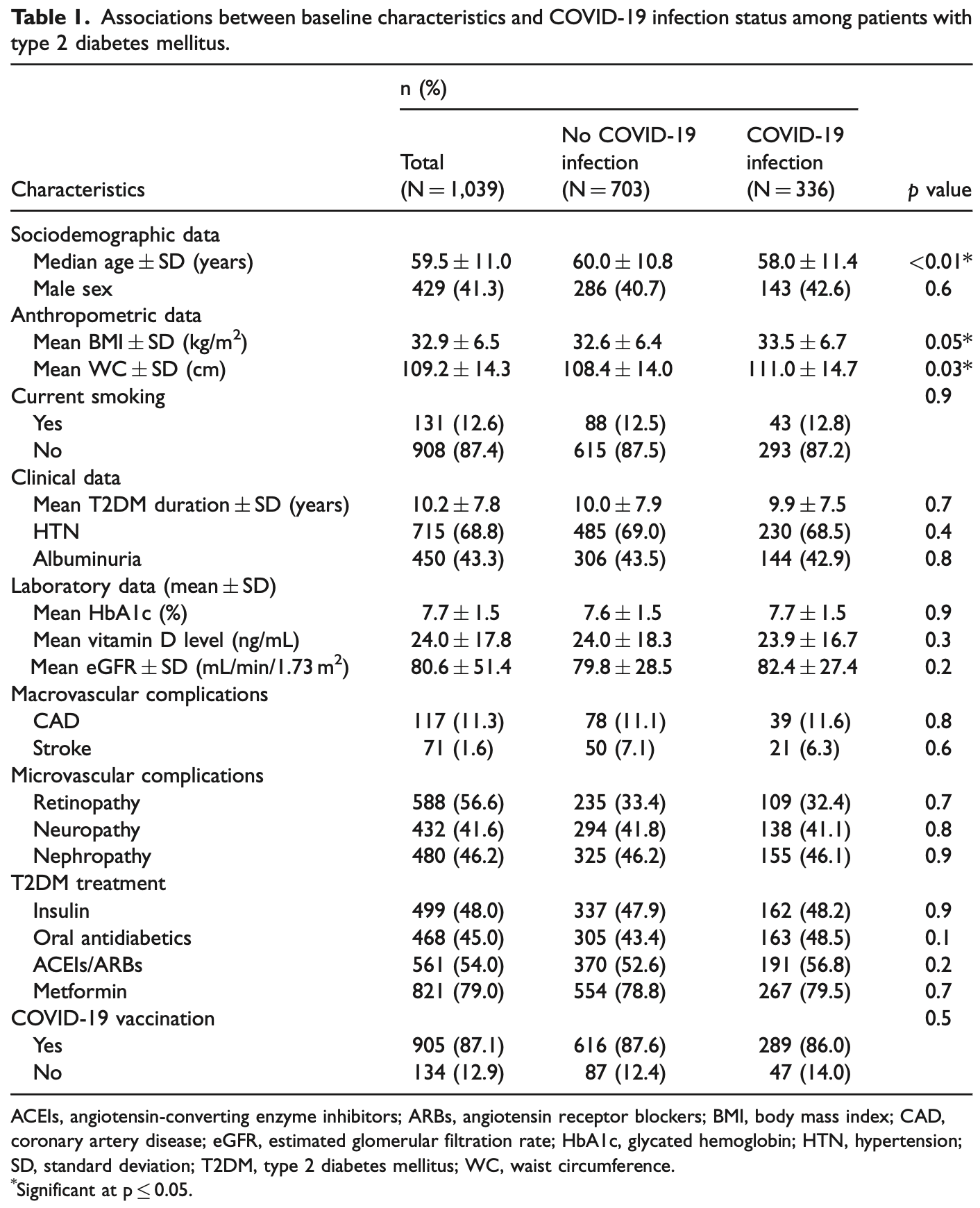
Retrospective 1,039 diabetes patients in Jordan, showing no significant difference in COVID-19 cases with metformin use in unadjusted results. Severity outcomes are not provided for metformin.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
|
risk of case, 2.7% higher, RR 1.03, p = 0.87, treatment 267 of 821 (32.5%), control 69 of 218 (31.7%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Farah et al., 20 Sep 2023, retrospective, Jordan, peer-reviewed, mean age 59.5, 10 authors.
Contact: r.farah@ju.edu.jo.
Prevalence and risk factors of COVID-19 infection, mortality, and post-infection lung fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study
Journal of International Medical Research, doi:10.1177/03000605231198413
Objectives: The clinical course of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection is often aggressive, with unfavorable outcomes for those with comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We aimed to assess the prevalence and risk factors of COVID-19 infection, mortality, and post-infection lung fibrosis in patients with COVID-19 infection who had T2DM. Methods: In this cross-sectional study, we included adult patients with T2DM who attended an endocrinology clinic and underwent testing for COVID-19 infection. Results: Among 1039 included patients, the mean age was 59.5 AE 11.0 years and 429 (41.3%) were men. Overall, 87.1% of patients had received COVID-19 vaccination and 32.3% had confirmed COVID-19 infection. The COVID-19-related mortality was 3.0% and rate of post-COVID-19 lung fibrosis was 19.1%. Vaccination was associated with lower COVID-19-related
Authors' contributions Randa I. Farah contributed to study conceptualization; formal analysis; methodology; supervision; and original writing, drafting, review, and editing of the manuscript. Hussam Al-Hawari contributed to study supervision and editing,
Declaration of conflicting interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
References
Abdi, Jalilian, Sarbarzeh, Diabetes and COVID-19: a systematic review on the current evidence, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108347
Antonelli, Penfold, Merino, Risk factors and disease profile of postvaccination SARS-CoV-2 infection in UK users of the COVID Symptom Study app: a prospective, community-based, nested, casecontrol study, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00460-6
Barron, Bakhai, Kar, Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: a whole-population study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2
Bereda, Dual insulin resistance causes: how frequently type 2 diabetes mellitus and COVID-19 infection caused diabetic ketoacidosis? a case report, Ann Med Surg (Lond), doi:10.1097/MS9.0000000000000341
Brosh-Nissimov, Orenbuch-Harroch, Chowers, BNT162b2 vaccine breakthrough: clinical characteristics of 152 fully vaccinated hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Israel, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2021.06.036
Cariou, Hadjadj, Wargny, Phenotypic characteristics and prognosis of inpatients with COVID-19 and diabetes: the CORONADO study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x
Cordero-Franco, De, Garza-Salinas, Gomez-Garcia, Risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection, pneumonia, intubation, and death in Northeast Mexico, Front Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2021.645739
Ejaz, Alsrhani, Zafar, COVID-19 and comorbidities: deleterious impact on infected patients, J Infect Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014
Faghir-Gangi, Moameri, Abdolmohamadi, The prevalence of type 2 diabetes in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Clin Diabetol, doi:10.5603/DK.2020.0041
Feldman, Savelieff, Hayek, COVID-19 and diabetes: a collision and collusion of two diseases, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/dbi20-0032
Gesesew, Koye, Fetene, Risk factors for COVID-19 infection, disease severity and related deaths in Africa: a systematic review, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044618
Gregg, Sophiea, Weldegiorgis, Diabetes and COVID-19: population impact 18 months into the pandemic, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dci21-0001
Harding, Ali, Gander, 174-LB: Diabetes as a risk factor for long-COVID-19: a scoping review, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/db22-174-LB
Hayek, Robert, Matar, Risk factors for hospital admission among COVID-19 patients with diabetes. A study from Saudi Arabia, Saudi Med J, doi:10.15537/smj.2020.10.25419
Jung, Park, Kim, Association between body mass index and risk of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a nationwide case-control study in South Korea, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa1257
Kumar, Arora, Sharma, Is diabetes mellitus associated with mortality and severity of COVID-19? A meta-analysis, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.044
Leon-Abarca, Portmann-Baracco, Alberti, Diabetes increases the risk of COVID-19 in an altitude dependent manner: an analysis of 1,280,806 Mexican patients, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0255144
Mahmud, Imam, Vinnakota, Vaccination intention against COVID-19 among the unvaccinated in Jordan during the early phase of the vaccination drive: a cross-sectional survey, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines10071159
Martellucci, Flacco, Soldato, Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines in the general population of an Italian region before and during the Omicron wave, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines10050662
Murillo-Zamora, Trujillo, Huerta, First-generation BNT162b2 and AZD1222 vaccines protect from COVID-19 pneumonia during the Omicron variant emergence, Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.puhe.2022.04.001
Notarte, Catahay, Velasco, Impact of COVID-19 vaccination on the risk of developing long-COVID and on existing long-COVID symptoms: a systematic review, EClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101624
Pal, Bhadada, COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: an unholy interaction of two pandemics, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.049
Pal, Sachdeva, Mukherjee, Impaired anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody response in non-severe COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus: a preliminary report, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.12.035
Raveendran, Misra, Post COVID-19 syndrome ("long COVID") and diabetes: challenges in diagnosis and management, Diabetes Metab Syndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102235
Shahbazi, Solgi, Khazaei, Predisposing risk factors for COVID-19 infection: a case-control study, Caspian J Intern Med, doi:10.22088/cjim.11.0.495
Shang, Shao, Guo, Diabetes mellitus is associated with severe infection and mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Arch Med Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.07.005
Stefan, Birkenfeld, Schulze, Obesity and impaired metabolic health in patients with COVID-19, Nat Rev Endocrinol, doi:10.1038/s41574-020-0364-6
Von Elm, Altman, Egger, The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies, Ann Intern Med
Zhang, Li, Zhang, The clinical characteristics and outcomes of patients with diabetes and secondary hyperglycaemia with coronavirus disease 2019: a singlecentre, retrospective, observational study in Wuhan, Diabetes Obes Metab, doi:10.1111/dom.14086
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1177/03000605231198413",
"ISSN": [
"0300-0605",
"1473-2300"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/03000605231198413",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Objectives</jats:title><jats:p> The clinical course of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection is often aggressive, with unfavorable outcomes for those with comorbidities such as type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We aimed to assess the prevalence and risk factors of COVID-19 infection, mortality, and post-infection lung fibrosis in patients with COVID-19 infection who had T2DM. </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p> In this cross-sectional study, we included adult patients with T2DM who attended an endocrinology clinic and underwent testing for COVID-19 infection. </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p> Among 1039 included patients, the mean age was 59.5 ± 11.0 years and 429 (41.3%) were men. Overall, 87.1% of patients had received COVID-19 vaccination and 32.3% had confirmed COVID-19 infection. The COVID-19-related mortality was 3.0% and rate of post-COVID-19 lung fibrosis was 19.1%. Vaccination was associated with lower COVID-19-related mortality (odds ratio [OR]: 0.03, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.0–0.3) and post-COVID-19 lung fibrosis risk (OR: 0.3, 95% CI: 0.1–0.9). </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p> Patients with T2DM exhibited a high prevalence of COVID-19 infection and associated mortality. However, COVID-19 vaccines were beneficial in reducing the risks of COVID-19-related mortality and post-infection lung fibrosis in these patients. COVID-19 vaccines and boosters are recommended for patients with T2DM. Further studies involving larger study populations are necessary to validate these findings. </jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1177/03000605231198413"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1638-9017",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Nephrology Division, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Farah",
"given": "Randa",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Endocrinology Division, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan"
}
],
"family": "Al-Hawari",
"given": "Hussam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pulmonary Division, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan"
}
],
"family": "Albtoush",
"given": "Asma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4011-1069",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Nofal",
"given": "Amani",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5021-8054",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hyasat",
"given": "Tala Basheer",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2291-8165",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Abu Jabeh",
"given": "Raghed Abdel Hay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan"
}
],
"family": "Suboh",
"given": "Lojayn Tareq",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4688-9728",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pulmonary Division, Department of Internal Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Toubasi",
"given": "Ahmad A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, The University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan"
}
],
"family": "Eqrai",
"given": "Tareq Fatah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Special Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan"
}
],
"family": "Abufaraj",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of International Medical Research",
"container-title-short": "J Int Med Res",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.sagepub.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-20T15:06:30Z",
"timestamp": 1695222390000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-20T15:06:36Z",
"timestamp": 1695222396000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-21T05:42:30Z",
"timestamp": 1695274950716
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1693526400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/03000605231198413",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1177/03000605231198413",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/03000605231198413",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "179",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
20
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "SAGE Publications",
"reference": [
{
"key": "bibr1-03000605231198413",
"unstructured": "Our World in Data. Cumulative confirmed COVID-19 cases and deaths, World. https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/cumulative-deaths-and-cases-covid-19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.049",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr2-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MS9.0000000000000341",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr3-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr4-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15537/smj.2020.10.25419",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr5-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dbi20-0032",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr6-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr7-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines10071159",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr8-03000605231198413"
},
{
"key": "bibr9-03000605231198413",
"unstructured": "UNC Gillings. COVID-19 Dashboard. https://gillingscovid19.unc.edu/definitions/covid-19-deaths."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc21-S002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr10-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-147-8-200710160-00010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr11-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dci21-0001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr12-03000605231198413"
},
{
"key": "bibr13-03000605231198413",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. COVID-19 dashboard: Jordan. https://covid19.who.int/region/emro/country/jo."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108347",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr14-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5603/DK.2020.0041",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr15-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1257",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr16-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-020-0364-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr17-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2021.645739",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr18-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044618",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr19-03000605231198413"
},
{
"author": "Shahbazi F",
"first-page": "495",
"journal-title": "Caspian J Intern Med",
"key": "bibr20-03000605231198413",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0255144",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr21-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.12.035",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr22-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.06.036",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr23-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.044",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr24-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.07.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr25-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00125-020-05180-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr26-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14086",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr27-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines10050662",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr28-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.puhe.2022.04.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr29-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db22-174-LB",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr30-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.102235",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr31-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00460-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr32-03000605231198413"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101624",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr33-03000605231198413"
}
],
"reference-count": 33,
"references-count": 33,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/03000605231198413"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Biochemistry (medical)",
"Cell Biology",
"Biochemistry",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Prevalence and risk factors of COVID-19 infection, mortality, and post-infection lung fibrosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/sage-journals-update-policy",
"volume": "51"
}
