EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate) is a small molecule polyphenol derived from Camellia sinensis that exhibits antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 via dual mechanisms: blocking viral entry by interfering with the Spike-ACE2 receptor interaction and inhibiting the viral 3CL protease (Mpro). Additionally, EGCG provides anti-inflammatory effects by modulating cytokine production, potentially mitigating the cytokine storm associated with severe COVID-19.
Recent:Zhu.
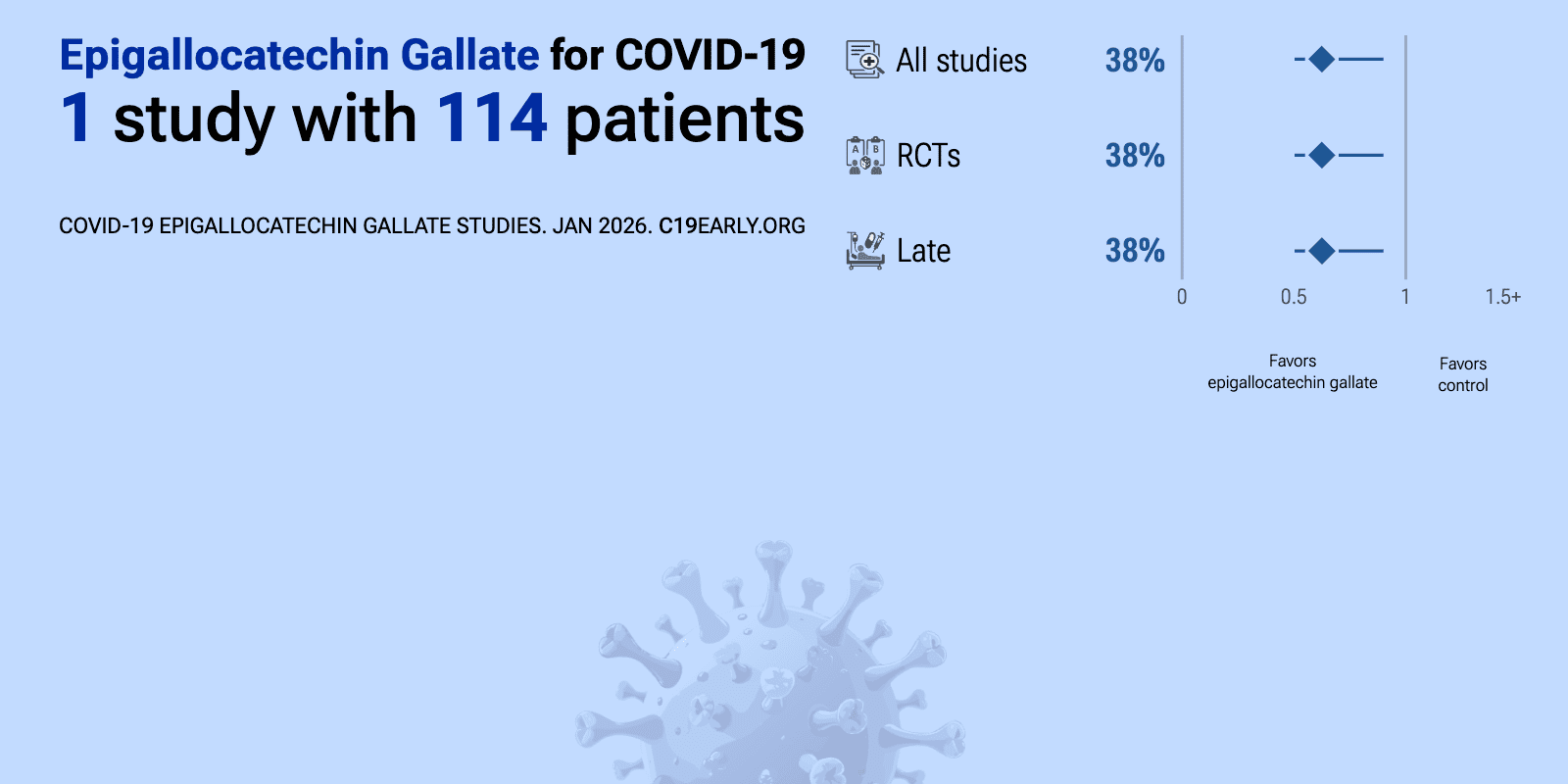
Jan 19 |
et al., BMC Cancer, doi:10.1186/s12885-026-15553-x | Efficacy and safety of 7-day aerosolized epigallocatechin-3-gallate in oncologic patients with COVID-19 pneumonia |
| 38% greater improvement (p=0.002). RCT 108 hospitalized oncologic patients with COVID-19 pneumonia showing significant benefit with aerosolized epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). The EGCG group showed significantly greater CT imaging improvement (64.8% vs 40.5%, P=0.004) a.. | ||
Jan 9 2025 |
, R., Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.77188 | COVID-19 Humic/Fulvic Acid Plus Epigallocatechin Gallate Treatment: A Retrospective Chart Review |
| 97% lower mortality (p<0.0001). Retrospective 60 COVID-19 patients in a nursing home facility showing no mortality with EGCG (from green tea extract), humic/fulvic acid, and vitamin C treatment, compared to 55% mortality in the control group not receiving treatment. The.. | ||
Apr 17 2024 |
et al., BMC Cancer, doi:10.1186/s12885-024-12228-3 | Phase I/II clinical trial of efficacy and safety of EGCG oxygen nebulization inhalation in the treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia patients with cancer |
| Phase I/II trial of EGCG nebulization inhalation in 54 COVID-19 pneumonia patients with cancer showing good tolerability and improvement in CT scans in 56% of patients after 7 days, with non-progression of pneumonia in 82% of patients. Th.. | ||
Dec 31 2023 |
et al., Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens13010039 | The Role of the NRF2 Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Viral Respiratory Infections |
| Review discussing the role of the NRF2 antioxidant pathway in regulating viral replication and associated inflammation and cell damage pathways during respiratory viral infections. Authors summarize evidence showing that respiratory virus.. | ||
Apr 13 2023 |
et al., Indian Journal of Medical Research, doi:10.4103/ijmr.ijmr_1701_22 | Indian food habit & food ingredients may have a role in lowering the severity & high death rate from COVID-19 in Indians: findings from the first nutrigenomic analysis |
| Nutrigenomics study of blood transcriptomes from Indian and western COVID-19 patients, showing Indian dietary habits and food ingredients including higher zinc, iron, curcumin, fiber, catechins, and EGCG may be associated with reduced sev.. | ||
Jun 7 2022 |
, M., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.06.06.22276060 | COVID-19 and per capita green tea consumption: update |
| Ecological study comparing 134 countries/territories showing lower COVID-19 morbidity and mortality associated with higher per capita green tea consumption. The differences remained significant when excluding countries with low human deve.. | ||