Feb 21 |
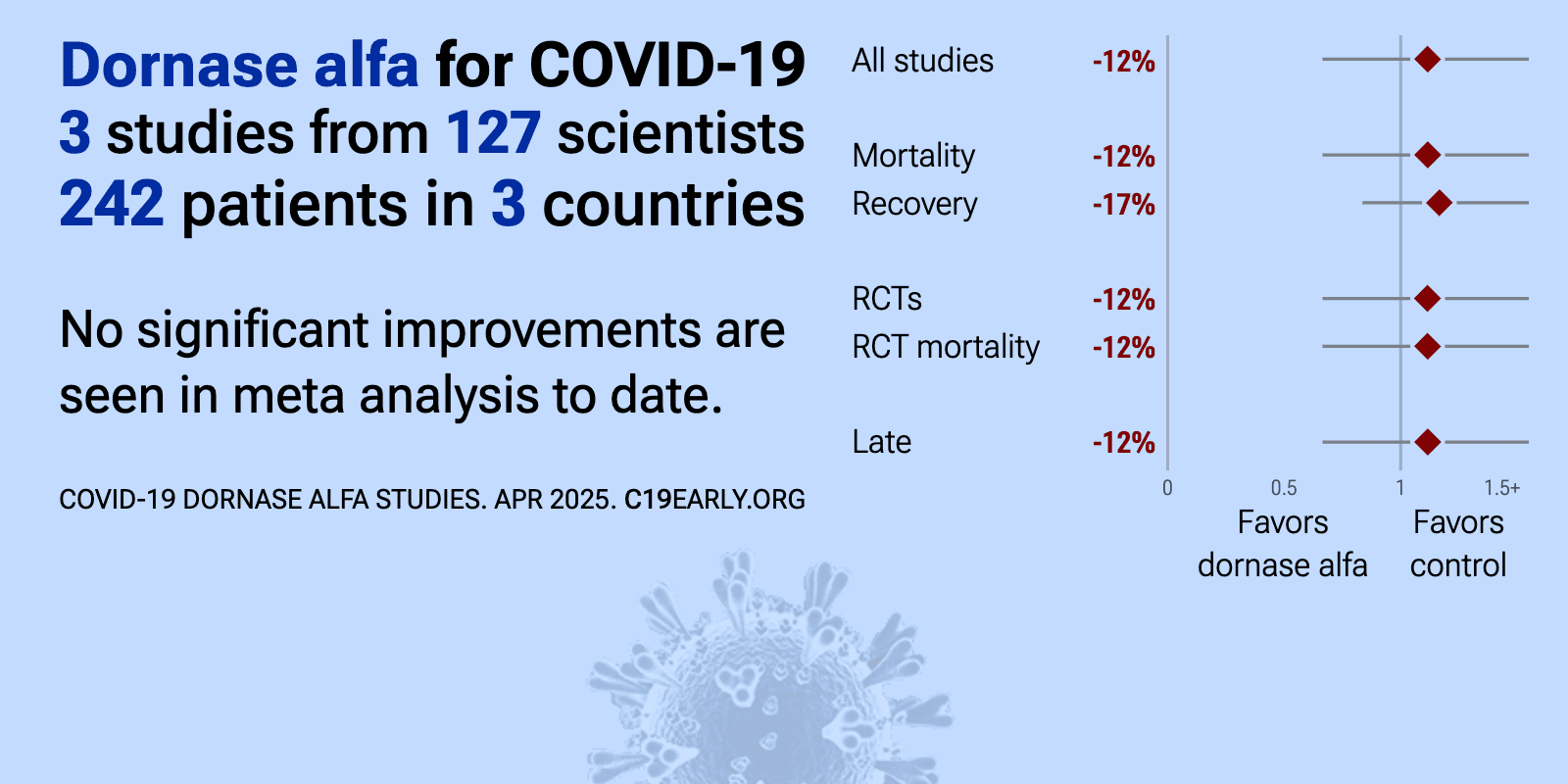
Dornase alfa for COVID-19: real-time meta-analysis of 3 studies (Version 2) | |
| Meta-analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 12% [-34‑87%] higher risk, without reaching statistical significance. Currently all studies are RCTs. Control Dornase alfa Currently there is limited data, with only 2.. | ||
Apr 24 2025 |
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf246 | Aerosolized dornase alfa (DNase I) for the treatment of severe respiratory failure in COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial |
| 11% higher mortality (p=1) and 2% worse recovery (p=0.94). RCT 76 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference with inhaled dornase alfa (DNase I) for resolution of hypoxia or other clinical outcomes. | ||
Jul 16 2024 |
et al., eLife, doi:10.7554/eLife.87030.4 | Anti-inflammatory therapy with nebulized dornase alfa for severe COVID-19 pneumonia: a randomized unblinded trial |
| 130% higher mortality (p=1) and 10% higher hospital discharge (p=1). RCT 99 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing significantly reduced C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and length of hospital stay with nebulized dornase alfa treatment in addition to standard of care (dexamethasone). Authors combine the ran.. | ||
Mar 3 2023 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101889 | Report of the first seven agents in the I-SPY COVID trial: a phase 2, open label, adaptive platform randomised controlled trial |
| 9% higher mortality (p=0.78) and 32% worse recovery (p=0.24). RCT severe COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in outcomes with dornase alfa. | ||
Apr 18 2022 |
et al., Clinical Immunology, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2022.109016 | Combined administration of inhaled DNase, baricitinib and tocilizumab as rescue treatment in COVID-19 patients with severe respiratory failure |
| 74% lower mortality (p=0.05), 76% lower ventilation (p=0.02), and 20% shorter hospitalization (p=0.02). Small retrospective study of hospitalized patients with severe respiratory failure, 22 treated with a combination of budesonide, tocilizumab, baricitinib, dornase alfa, and salbutamol or/and ipratropium, and 26 SOC patients, showing lower.. | ||
Dec 31 2021 |
et al., NCT04402944 | Pulmozyme to Improve COVID-19 ARDS Outcomes |
| Estimated 60 patient dornase alfa late treatment RCT with results not reported over 4 years after estimated completion. | ||
Dec 20 2021 |
et al., NCT04355364 | Efficacy and Safety of Dornase Alfa Aerosol in ARDS Secondary to SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Respiratory Infection - COVID-19 |
| 77 patient dornase alfa late treatment RCT with results not reported over 4 years after completion. | ||
Sep 25 2020 |
et al., NCT04432987 | Determination of Dornase Alpha Effectiveness in COVID-19 Treatment |
| Estimated 60 patient dornase alfa late treatment RCT with results not reported over 5 years after estimated completion. | ||
Jul 20 2020 |
et al., NCT04459325 | A Prospective Open-label Study of the Tigerase® Efficacy and Safety as Part of Complex Therapy in Patients With COVID-19 |
| 100 patient dornase alfa late treatment RCT with results not reported over 5 years after completion. | ||