Combination of spironolactone and sitagliptin improves clinical outcomes of outpatients with COVID-19: a prospective cohort study
et al., Journal of Endocrinological Investigation, doi:10.1007/s40618-023-02141-0, Jan 2022 (preprint)
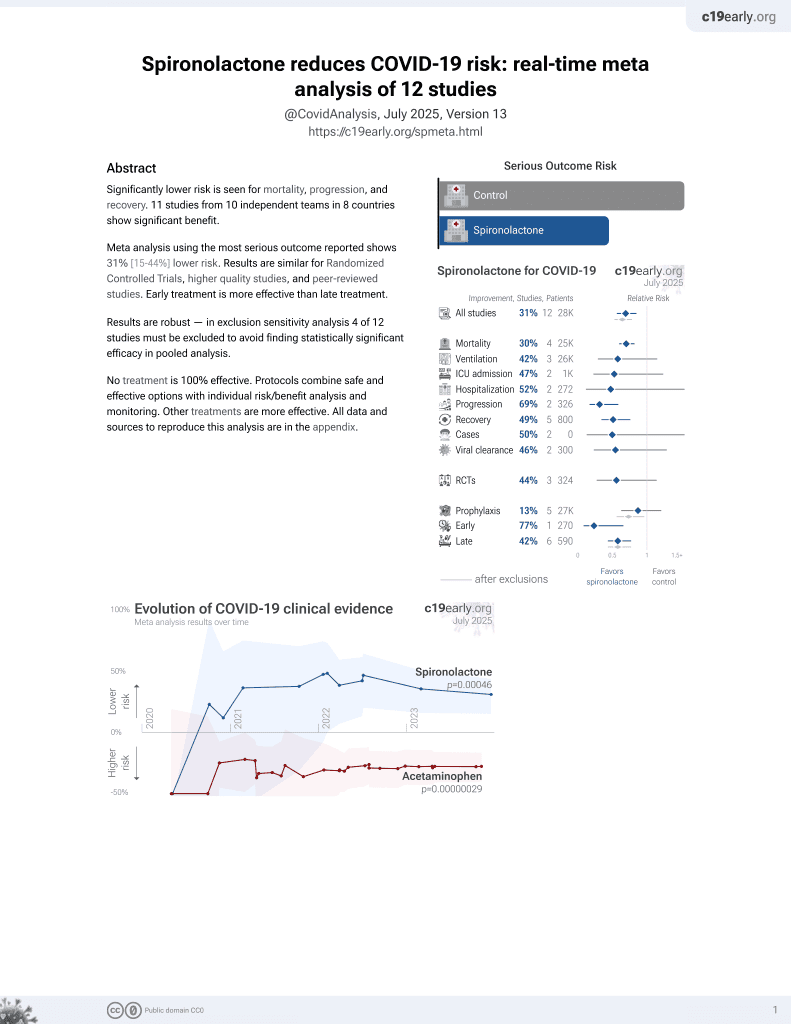
37th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2022, now with p = 0.00046 from 12 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Prospective study of 206 outpatients in Iran, 103 treated with spironolactone and sitagliptin, showing lower hospitalization and faster recovery with treatment. spironolactone 100mg and sitagliptin 100mg daily.
|
risk of hospitalization, 78.3% lower, RR 0.22, p < 0.001, treatment 6 of 103 (5.8%), control 23 of 103 (22.3%), NNT 6.1, adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk, multivariable.
|
|
ER visit, 66.7% lower, RR 0.33, p = 0.003, treatment 8 of 103 (7.8%), control 24 of 103 (23.3%), NNT 6.4.
|
|
recovery time, 64.4% lower, relative time 0.36, p < 0.001, treatment 103, control 103.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Davarpanah et al., 21 Jan 2022, prospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 9 authors, study period July 2021 - September 2021, average treatment delay 5.74 days, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with sitagliptin) - results of individual treatments may vary.
Combination of Spironolactone and Sitagliptin Improves Clinical Outcomes of Outpatients with COVID-19: A Prospective Cohort Study
doi:10.1101/2022.01.21.22269322
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) leads to hospitalization and death, especially in elderly and those with comorbidities. There are evidences showing that sitagliptin and spironolactone can potentially improve the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 cases. In this observational study on acutely symptomatic outpatient COVID-19 cases, we investigated the effects of spironolactone and sitagliptin on the outcomes of the disease. Methods: This prospective cohort study was conducted at Shiraz University of Medical Sciences Clinics during the fifth wave of the COVID-19 pandemic between July 2021 and September 2021. We followed mild to moderate symptomatic COVID-19 patients, who were treated with either combination (spironolactone 100 mg daily and sitagliptin 100 mg daily) or standard (steroid, antiviral and/or supportive care) therapy up to 30 days. Our primary outcome was hospitalization rate. The secondary outcomes included ER visit, duration of disease, and complications, such as hypoglycemia, low blood pressure or altered mental status.
Results: Of the 206 patients referred to clinics, 103 received standard therapy and 103 treated with combination therapy. There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics, except for slightly higher clinical score in control group (6.92 ± 4.01 control, 4.87 ± 2.92 combination; P <0.0001). Treatment with combination therapy was associated with lower admission rate (5.8% combination, 22.3% control; P = 0.0011), ER visits (7.8% combination, 23.3% control; P = 0.0021) and average duration of symptoms (6.67 ± 2.30 days combination, 18.71 ± 6.49 days control; P =<0.0001).
Conclusion: In this prospective cohort study of acutely ill outpatients with COVID-19, the combination of sitagliptin and spironolactone reduced duration of COVID infection and hospital visits better than standard therapeutic approaches. The effects of combination of sitagliptin and spironolactone in COVID-19 patients should be further verified in a double blind, randomized, placebocontrolled trial.
Additional Information Correspondence: Kamyar Asadipooya, MD, Department of Medicine, Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Barnstable Brown Diabetes and Obesity Center, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY 40504, USA. Email: kas224@uky.edu Disclosure Summary: The authors have no conflicts of interest to report. Authors' contributions: KA proposed the idea and designed the study. KA, RA, YM and RK wrote the manuscript. MAD, YM, HF, FSRR, AP, and MH collected the data. RA provided statistical analysis and wrote statistical part. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript. .
References
Al-Kuraishy, Gareeb, Qusty, Alexiou, Batiha, Impact of Sitagliptin in Non-Diabetic Covid-19 Patients, Current molecular pharmacology
Bardaweel, Hajjo, Sabbah, Sitagliptin: a potential drug for the treatment of COVID-19?, Acta pharmaceutica
Blair, Gotimukul, Wang, Mina, Bartels et al., Mild to moderate COVID-19 illness in adult outpatients: Characteristics, symptoms, and outcomes in the first 4 weeks of illness, Medicine
Cantuti-Castelvetri, Ojha, Pedro, Djannatian, Franz et al., Neuropilin-1 facilitates SARS-CoV-2 cell entry and infectivity, Science
Cases, Emergency Department Visits, Hospital Admissions, and Deaths Among Older Adults Following the Introduction of COVID-19
Chen, Zhang, Case, Winkler, Liu et al., Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants to neutralization by monoclonal and serum-derived polyclonal antibodies, Nature medicine
Christie, Henley, Mattocks, Fernando, Lansky et al., Decreases in COVID-19
Deacon, Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, Nature reviews Endocrinology
Dong, Fan, Ji, Yu, Wu et al., Spironolactone alleviates diabetic nephropathy through promoting autophagy in podocytes, Int Urol Nephrol
Edwards, New Horizons: Does Mineralocorticoid Receptor Activation by Cortisol Cause ATP Release and COVID-19 Complications?, The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism
Gao, Ding, Dong, Zhang, Azkur et al., Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: A review, Allergy
Garcia, Lipskiy, Tyson, Watkins, Esser et al., Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) information management: addressing national health-care and public health needs for standardized data definitions and codified vocabulary for data exchange, Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association
Goodacre, Thomas, Sutton, Burnsall, Lee et al., Derivation and validation of a clinical severity score for acutely ill adults with suspected COVID-19: The PRIEST observational cohort study, PloS one
Gupta, Gonzalez-Rojas, Juarez, Casal, Moya et al., Early Treatment for Covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Sotrovimab, The New England journal of medicine
Haga, Yamamoto, Nakai-Murakami, Osawa, Tokunaga et al., Modulation of TNF-alphaconverting enzyme by the spike protein of SARS-CoV and ACE2 induces TNF-alpha production and facilitates viral entry, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Harvey, Carabelli, Jackson, Gupta, Thomson et al., SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape, Nature reviews Microbiology
Heurich, Hofmann-Winkler, Gierer, Liepold, Jahn et al., TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 cleave ACE2 differentially and only proteolysis by TMPRSS2 augments entry driven by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein, Journal of virology
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell
Hopkins, Coronavirus resource center
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, Nature reviews Molecular cell biology
Jeffers, Tusell, Gillim-Ross, Hemmila, Achenbach et al., CD209L (L-SIGN) is a receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Jeon, Son, Choi, Effect of Spironolactone on COVID-19 in Patients With Underlying Liver Cirrhosis: A Nationwide Case-Control Study in South Korea, Frontiers in medicine
Keidar, Gamliel-Lazarovich, Kaplan, Pavlotzky, Hamoud et al., Mineralocorticoid receptor blocker increases angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activity in congestive heart failure patients, Circ Res
Kuba, Imai, Rao, Gao, Guo et al., A crucial role of angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced lung injury, Nat Med
Kustin, Harel, Finkel, Perchik, Harari et al., Evidence for increased breakthrough rates of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in BNT162b2-mRNA-vaccinated individuals, Nature medicine
Li, Liu, Zhou, Wang, On resistance to virus entry into host cells, Biophys J
Li, Zhang, Yang, Lian, Xie et al., The MERS-CoV Receptor DPP4 as a Candidate Binding Target of the SARS-CoV-2
Mareev, Orlova, Plisyk, Pavlikova, Matskeplishvili et al., Results of Open-Label non-Randomized Comparative Clinical Trial: "BromhexIne and Spironolactone for CoronаvirUs Infection requiring hospiTalization (BISCUIT), Kardiologiia
Martin, Anderson, Chang, Ehrmann, Lobo et al., Evaluation and Treatment of Hirsutism in Premenopausal Women: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline, The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism
Mccullough, Kelly, Ruocco, Lerma, Tumlin et al., Pathophysiological Basis and Rationale for Early Outpatient Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Infection, The American journal of medicine
Montastruc, Romano, Montastruc, Silva, Seguin et al., Pharmacological characteristics of patients infected with SARS-Cov-2 admitted to Intensive Care Unit in South of France, Therapie
Monteil, Kwon, Prado, Hagelkrüys, Wimmer et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Engineered Human Tissues Using Clinical-Grade Soluble Human ACE2, Cell
Patoulias, Doumas, Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and COVID-19-Related Deaths among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies, Endocrinology and metabolism
Peacocke, Heupink, Frønsdal, Dahl, Chola, Global access to COVID-19 vaccines: a scoping review of factors that may influence equitable access for low and middle-income countries, BMJ open
Qi, Qian, Zhang, Zhang, Single cell RNA sequencing of 13 human tissues identify cell types and receptors of human coronaviruses, Biochemical and biophysical research communications
Rahimi, Bezmin Abadi, Emergence of the Delta Plus variant of SARS-CoV-2 in Iran, Gene reports
Rahmanzade, Rahmanzadeh, Hashemian, Tabarsi, Iran's Approach to COVID-19: Evolving Treatment Protocols and Ongoing Clinical Trials, Frontiers in public health
Rakhmat, Kusmala, Handayani, Juliastuti, Nawangsih et al., Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) -A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression, Diabetes & metabolic syndrome
Satoh, Ishikawa, Minami, Akatsu, Nakamura, Eplerenone inhibits tumour necrosis factor alpha shedding process by tumour necrosis factor alpha converting enzyme in monocytes from patients with congestive heart failure, Heart
Shao, Xu, Yu, Pan, Chen, Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors and their potential immune modulatory functions, Pharmacology & therapeutics
Solerte, 'addio, Trevisan, Lovati, Rossi et al., Sitagliptin Treatment at the Time of Hospitalization Was Associated With Reduced Mortality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19: A Multicenter, Case-Control, Retrospective, Observational Study, Diabetes care
Stoian, Sachinidis, Stoica, Nikolic, Patti et al., The efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors compared to other oral glucose-lowering medications in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, Metabolism: clinical and experimental
Tomlins, Rhodes, Perner, Dhanasekaran, Mehra et al., Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS transcription factor genes in prostate cancer, Science
Tsang, Chan, Cho, Yu, Yim et al., An update on COVID-19 pandemic: the epidemiology, pathogenesis, prevention and treatment strategies, therapy
Vankadari, Wilce, Emerging WuHan (COVID-19) coronavirus: glycan shield and structure prediction of spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26, Emerg Microbes Infect
Verdecchia, Cavallini, Spanevello, Angeli, The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur J Intern Med
Walls, Park, Tortorici, Wall, Mcguire et al., Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein, Cell
Wang, Nair, Liu, Iketani, Luo et al., Antibody resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7, Nature
Wang, Qiu, Hou, Deng, Xu et al., AXL is a candidate receptor for SARS-CoV-2 that promotes infection of pulmonary and bronchial epithelial cells, Cell research
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Ali, Gao et al., REGEN-COV Antibody Combination and Outcomes in Outpatients with Covid-19, The New England journal of medicine
Weisblum, Schmidt, Zhang, Dasilva, Poston et al., Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants, eLife
Wilcox, Pitt, Is Spironolactone the Preferred Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Inhibitor for Protection Against COVID-19?, J Cardiovasc Pharmacol
Wrapp, Wang, Corbett, Goldsmith, Hsieh et al., Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation, Science
Wysocki, Ye, Hassler, Gupta, Wang et al., A Novel Soluble ACE2 Variant with Prolonged Duration of Action Neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Human Kidney Organoids, Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
Xie, Wang, Liang, Lin, Yang et al., Critical Review of the Scientific Evidence and Recommendations in COVID-19 Management Guidelines, Open forum infectious diseases
Xu, Xu, Jiang, Dua, Hansbro et al., SARS-CoV-2 induces transcriptional signatures in human lung epithelial cells that promote lung fibrosis, Respir Res
Zhang, Xiang, Huo, Zhou, Jiang et al., Molecular mechanism of interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and host cells and interventional therapy, Signal transduction and targeted therapy
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-023-02141-0",
"ISSN": [
"1720-8386"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40618-023-02141-0",
"alternative-id": [
"2141"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "6 February 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "16 June 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "24 June 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Iranian registry of clinical trial",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "IRCT registration number: IRCT20201003048904N2, Registration date: December 10, 2020."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Davarpanah",
"given": "M. A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adatorwovor",
"given": "R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mansoori",
"given": "Y.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ramsheh",
"given": "F. S. R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parsa",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hajiani",
"given": "M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Faramarzi",
"given": "H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kavuluru",
"given": "R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4484-1971",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Asadipooya",
"given": "K.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Endocrinological Investigation",
"container-title-short": "J Endocrinol Invest",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-24T11:59:54Z",
"timestamp": 1687607994000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-09T19:14:07Z",
"timestamp": 1704827647000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100013041",
"award": [
"IR.SUMS.MED.REC.1399.550"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Vice-Chancellor for Research, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-12T05:17:46Z",
"timestamp": 1718169466802
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
24
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springernature.com/gp/researchers/text-and-data-mining",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1687564800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springernature.com/gp/researchers/text-and-data-mining",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1687564800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40618-023-02141-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40618-023-02141-0/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40618-023-02141-0.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "235-243",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "2141_CR1",
"unstructured": "Hopkins J (2020) Coronavirus resource center. Im Internet (Stand: 1904 2020). https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14657",
"author": "YD Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "428",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "2141_CR2",
"unstructured": "Gao YD, Ding M, Dong X, Zhang JJ, KursatAzkur A, Azkur D, Gan H, Sun YL, Fu W, Li W, Liang HL, Cao YY, Yan Q, Cao C, Gao HY, Brüggen MC, van de Veen W, Sokolowska M, Akdis M, Akdis CA (2021) Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: a review. Allergy 76(2):428–455",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7023e2",
"author": "A Christie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "858",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "2141_CR3",
"unstructured": "Christie A, Henley SJ, Mattocks L, Fernando R, Lansky A, Ahmad FB, Adjemian J, Anderson RN, Binder AM, Carey K, Dee DL, Dias T, Duck WM, Gaughan DM, Lyons BC, McNaghten AD, Park MM, Reses H, Rodgers L, Van Santen K, Walker D, Beach MJ (2021) Decreases in COVID-19 cases, emergency department visits, hospital admissions, and deaths among older adults following the introduction of COVID-19 vaccine—United States, September 6, 2020-May 1, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 70(23):858–864",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "T Kustin",
"first-page": "236",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "2141_CR4",
"unstructured": "Kustin T, Harel N, Finkel U, Perchik S, Harari S, Tahor M, Caspi I, Levy R, Leshchinsky M, Ken Dror S, Bergerzon G, Gadban H, Gadban F, Eliassian E, Shimron O, Saleh L, Ben-Zvi H, Keren Taraday E, Amichay D, Ben-Dor A, Sagas D, Strauss M, Shemer Avni Y, Huppert A, Kepten E, Balicer RD, Netzer D, Ben-Shachar S, Stern A (2021) Evidence for increased breakthrough rates of SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern in BNT162b2-mRNA-vaccinated individuals. Nat Med 20(1):236",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofab376",
"author": "J Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "2141_CR5",
"unstructured": "Xie J, Wang Z, Liang J, Lin H, Yang Z, Wang Y, Liang H, Wu H, Chen R, Ou Y, Wang F, Wang Y, Wang Y, Luo W, Zhang J, Li N, Li Z, Jiang M, Li S, Li J (2021) Critical review of the scientific evidence and recommendations in COVID-19 management guidelines. Open Forum Infect Dis 8(8):ofab376",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2108163",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2141_CR6",
"unstructured": "Weinreich DM, Sivapalasingam S, Norton T, Ali S, Gao H, Bhore R, Xiao J, Hooper AT, Hamilton JD, Musser BJ, Rofail D, Hussein M, Im J, Atmodjo DY, Perry C, Pan C, Mahmood A, Hosain R, Davis JD, Turner KC, Baum A, Kyratsous CA, Kim Y, Cook A, Kampman W, Roque-Guerrero L, Acloque G, Aazami H, Cannon K, Simón-Campos JA, Bocchini JA, Kowal B, DiCioccio AT, Soo Y, Geba GP, Stahl N, Lipsich L, Braunstein N, Herman G, Yancopoulos GD (2021) REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with Covid-19. New Eng J Med"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0",
"author": "WT Harvey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "409",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "2141_CR7",
"unstructured": "Harvey WT, Carabelli AM, Jackson B, Gupta RK, Thomson EC, Harrison EM, Ludden C, Reeve R, Rambaut A, Peacock SJ, Robertson DL (2021) SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat Rev Microbiol 19(7):409–424",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01294-w",
"author": "RE Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "717",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "2141_CR8",
"unstructured": "Chen RE, Zhang X, Case JB, Winkler ES, Liu Y, VanBlargan LA, Liu J, Errico JM, Xie X, Suryadevara N, Gilchuk P, Zost SJ, Tahan S, Droit L, Turner JS, Kim W, Schmitz AJ, Thapa M, Wang D, Boon ACM, Presti RM, O’Halloran JA, Kim AHJ, Deepak P, Pinto D, Fremont DH, Crowe JE Jr, Corti D, Virgin HW, Ellebedy AH, Shi PY, Diamond MS (2021) Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants to neutralization by monoclonal and serum-derived polyclonal antibodies. Nat Med 27(4):717–726",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.02.19.956581",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2141_CR9",
"unstructured": "Walls AC, Park YJ, Tortorici MA, Wall A, McGuire AT, Veesler D (2020) Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1739565",
"author": "N Vankadari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "601",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "2141_CR10",
"unstructured": "Vankadari N, Wilce JA (2020) Emerging WuHan (COVID-19) coronavirus: glycan shield and structure prediction of spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26. Emerg Microbes Infect 9(1):601–604",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb2507",
"author": "D Wrapp",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1260",
"issue": "6483",
"journal-title": "Science (New York, NY)",
"key": "2141_CR11",
"unstructured": "Wrapp D, Wang N, Corbett KS, Goldsmith JA, Hsieh CL, Abiona O, Graham BS, McLellan JS (2020) Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science (New York, NY) 367(6483):1260–1263",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.576745",
"author": "D Zipeto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "2141_CR12",
"unstructured": "Zipeto D, Palmeira JDF, Argañaraz GA, Argañaraz ER (2020) ACE2/ADAM17/TMPRSS2 interplay may be the main risk factor for COVID-19. Front Immunol 11:576745",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.053",
"author": "ML Yeung",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2212",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2141_CR13",
"unstructured": "Yeung ML, Teng JLL, Jia L, Zhang C, Huang C, Cai JP, Zhou R, Chan KH, Zhao H, Zhu L, Siu KL, Fung SY, Yung S, Chan TM, To KK, Chan JF, Cai Z, Lau SKP, Chen Z, Jin DY, Woo PCY, Yuen KY (2021) Soluble ACE2-mediated cell entry of SARS-CoV-2 via interaction with proteins related to the renin-angiotensin system. Cell 184(8):2212-2228.e2212",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/FJC.0000000000000960",
"author": "CS Wilcox",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "323",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Cardiovasc Pharmacol",
"key": "2141_CR14",
"unstructured": "Wilcox CS, Pitt B (2020) Is spironolactone the preferred renin-angiotensin-aldosterone inhibitor for protection against COVID-19? J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 77(3):323–331",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/hrt.2005.071829",
"author": "M Satoh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "979",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Heart",
"key": "2141_CR15",
"unstructured": "Satoh M, Ishikawa Y, Minami Y, Akatsu T, Nakamura M (2006) Eplerenone inhibits tumour necrosis factor alpha shedding process by tumour necrosis factor alpha converting enzyme in monocytes from patients with congestive heart failure. Heart 92(7):979–980",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11255-019-02074-9",
"author": "D Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "755",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Int Urol Nephrol",
"key": "2141_CR16",
"unstructured": "Dong D, Fan TT, Ji YS, Yu JY, Wu S, Zhang L (2019) Spironolactone alleviates diabetic nephropathy through promoting autophagy in podocytes. Int Urol Nephrol 51(4):755–764",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.RES.0000187500.24964.7A",
"author": "S Keidar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "946",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Circ Res",
"key": "2141_CR17",
"unstructured": "Keidar S, Gamliel-Lazarovich A, Kaplan M, Pavlotzky E, Hamoud S, Hayek T, Karry R, Abassi Z (2005) Mineralocorticoid receptor blocker increases angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 activity in congestive heart failure patients. Circ Res 97(9):946–953",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2021.03.027",
"author": "II Rakhmat",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "777",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Diabet Metab Syndrome",
"key": "2141_CR18",
"unstructured": "Rakhmat II, Kusmala YY, Handayani DR, Juliastuti H, Nawangsih EN, Wibowo A, Lim MA, Pranata R (2021) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)—a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. Diabet Metab Syndrome 15(3):777–782",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jendso/bvac017",
"author": "F Abbasi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Endocr Soc",
"key": "2141_CR19",
"unstructured": "Abbasi F, Adatorwovor R, Davarpanah MA, Mansoori Y, Hajiani M, Azodi F, Sefidbakht S, Davoudi S, Rezaei F, Mohammadmoradi S, Asadipooya K (2022) A randomized trial of sitagliptin and spironolactone with combination therapy in hospitalized adults with COVID-19. J Endocr Soc 6(4):bvac017",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.genrep.2021.101341",
"author": "F Rahimi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Gene Reports",
"key": "2141_CR20",
"unstructured": "Rahimi F, TalebiBezmin Abadi A (2021) Emergence of the delta plus variant of SARS-CoV-2 in Iran. Gene Reports 25:101341",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jamia/ocaa141",
"author": "M Garcia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1476",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Am Med Inform Assoc",
"key": "2141_CR21",
"unstructured": "Garcia M, Lipskiy N, Tyson J, Watkins R, Esser ES, Kinley T (2020) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) information management: addressing national health-care and public health needs for standardized data definitions and codified vocabulary for data exchange. J Am Med Inform Assoc 27(9):1476–1487",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000026371",
"author": "JE Blair",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "24",
"journal-title": "Medicine",
"key": "2141_CR22",
"unstructured": "Blair JE, Gotimukul A, Wang F, Mina SA, Bartels HC, Burns MW, Kole AE, Vikram HR, Gea-Banacloche JC, Seville MT, Petty SAB, Vikram A, Orenstein R (2021) Mild to moderate COVID-19 illness in adult outpatients: characteristics, symptoms, and outcomes in the first 4 weeks of illness. Medicine 100(24):e26371",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2020.551889",
"author": "R Rahmanzade",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health",
"key": "2141_CR23",
"unstructured": "Rahmanzade R, Rahmanzadeh R, Hashemian SM, Tabarsi P (2020) Iran’s approach to COVID-19: evolving treatment protocols and ongoing clinical trials. Front Public Health 8:551889",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0245840",
"author": "S Goodacre",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2141_CR24",
"unstructured": "Goodacre S, Thomas B, Sutton L, Burnsall M, Lee E, Bradburn M, Loban A, Waterhouse S, Simmonds R, Biggs K, Marincowitz C, Schutter J, Connelly S, Sheldon E, Hall J, Young E, Bentley A, Challen K, Fitzsimmons C, Harris T, Lecky F, Lee A, Maconochie I, Walter D (2021) Derivation and validation of a clinical severity score for acutely ill adults with suspected COVID-19: the PRIEST observational cohort study. PLoS One 16(1):e0245840",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2021.1863146",
"author": "HF Tsang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "877",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther",
"key": "2141_CR25",
"unstructured": "Tsang HF, Chan LWC, Cho WCS, Yu ACS, Yim AKY, Chan AKC, Ng LPW, Wong YKE, Pei XM, Li MJW, Wong SC (2021) An update on COVID-19 pandemic: the epidemiology, pathogenesis, prevention and treatment strategies. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 19(7):877–888",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2021-049505",
"author": "EF Peacocke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "2141_CR26",
"unstructured": "Peacocke EF, Heupink LF, Frønsdal K, Dahl EH, Chola L (2021) Global access to COVID-19 vaccines: a scoping review of factors that may influence equitable access for low and middle-income countries. BMJ Open 11(9):e049505",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.07.003",
"author": "PA McCullough",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "16",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Am J Med",
"key": "2141_CR27",
"unstructured": "McCullough PA, Kelly RJ, Ruocco G, Lerma E, Tumlin J, Wheelan KR, Katz N, Lepor NE, Vijay K, Carter H, Singh B, McCullough SP, Bhambi BK, Palazzuoli A, De Ferrari GM, Milligan GP, Safder T, Tecson KM, Wang DD, McKinnon JE, O’Neill WW, Zervos M, Risch HA (2021) Pathophysiological basis and rationale for early outpatient treatment of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) infection. Am J Med 134(1):16–22",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "TC Lee",
"first-page": "763",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "2141_CR28",
"unstructured": "Lee TC, Bortolussi-Courval É, Belga S, Daneman N, Chan AK, Hanula R, Ezer N, McDonald EG (2022) Inhaled corticosteroids for outpatients with Covid-19: a meta-analysis. Eur Respir J 9:763",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"author": "A Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "509",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "New Eng J Med",
"key": "2141_CR29",
"unstructured": "Jayk Bernal A, Gomes da Silva MM, Musungaie DB, Kovalchuk E, Gonzalez A, Delos Reyes V, Martín-Quirós A, Caraco Y, Williams-Diaz A, Brown ML, Du J, Pedley A, Assaid C, Strizki J, Grobler JA, Shamsuddin HH, Tipping R, Wan H, Paschke A, Butterton JR, Johnson MG, De Anda C (2022) Molnupiravir for oral treatment of Covid-19 in nonhospitalized patients. New Eng J Med 386(6):509–520",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"author": "J Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2141_CR30",
"unstructured": "Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, Abreu P, Bao W, Wisemandle W, Baniecki M, Hendrick VM, Damle B, Simón-Campos A, Pypstra R, Rusnak JM (2022) Oral Nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 386(15):1397–1408",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116846",
"author": "RL Gottlieb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "305",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2141_CR31",
"unstructured": "Gottlieb RL, Vaca CE, Paredes R, Mera J, Webb BJ, Perez G, Oguchi G, Ryan P, Nielsen BU, Brown M, Hidalgo A, Sachdeva Y, Mittal S, Osiyemi O, Skarbinski J, Juneja K, Hyland RH, Osinusi A, Chen S, Camus G, Abdelghany M, Davies S, Behenna-Renton N, Duff F, Marty FM, Katz MJ, Ginde AA, Brown SM, Schiffer JT, Hill JA (2022) Early remdesivir to prevent progression to severe Covid-19 in outpatients. N Engl J Med 386(4):305–315",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "E Mahase",
"key": "2141_CR32",
"unstructured": "Mahase E (2021) Covid-19: Pfizer’s paxlovid is 89% effective in patients at risk of serious illness, company reports. British Medical Journal Publishing Group",
"volume-title": "Covid-19: Pfizer’s paxlovid is 89% effective in patients at risk of serious illness, company reports",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.27623",
"author": "WT Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2222",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "2141_CR33",
"unstructured": "Lin WT, Hung SH, Lai CC, Wang CY, Chen CH (2022) The impact of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies on the outcomes of COVID-19 outpatients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Med Virol 94(5):2222–2229",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2022.06.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2141_CR34",
"unstructured": "Coulson JM, Adams A, Gray LA, Evans A (2022) COVID-19 \"Rebound\" associated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir pre-hospital therapy. J Infect 85(4):436–480"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11845-021-02820-y",
"author": "A Vitiello",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2367",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Ir J Med Sci",
"key": "2141_CR35",
"unstructured": "Vitiello A (2022) Sars-Cov-2 and risk of antiviral drug resistance. Ir J Med Sci 191(5):2367–2368",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "A Komorowski",
"first-page": "57",
"journal-title": "Sci Brief Ontario COVID-19 Sci Advisory Table",
"key": "2141_CR36",
"unstructured": "Komorowski A, Tseng A, Vandersluis S (2022) Evidence-based recommendations on the use of nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid) for adults in Ontario. Sci Brief Ontario COVID-19 Sci Advisory Table 3:57",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00372-5",
"author": "AD Usher",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "779",
"issue": "10327",
"journal-title": "Lancet (London, England)",
"key": "2141_CR37",
"unstructured": "Usher AD (2022) The global COVID-19 treatment divide. Lancet (London, England) 399(10327):779–782",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac180",
"author": "LD Saravolatz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "165",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2141_CR38",
"unstructured": "Saravolatz LD, Depcinski S, Sharma M (2023) Molnupiravir and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir: oral coronavirus disease 2019 antiviral drugs. Clin Infect Dis 76(1):165–171",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.004",
"author": "V Monteil",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "905",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2141_CR39",
"unstructured": "Monteil V, Kwon H, Prado P, Hagelkrüys A, Wimmer RA, Stahl M, Leopoldi A, Garreta E, Hurtado Del Pozo C, Prosper F, Romero JP, Wirnsberger G, Zhang H, Slutsky AS, Conder R, Montserrat N, Mirazimi A, Penninger JM (2020) Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infections in engineered human tissues using clinical-grade soluble human ACE2. Cell 181(4):905-913.e907",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1681/ASN.2020101537",
"author": "J Wysocki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "795",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Am Soc Nephrol",
"key": "2141_CR40",
"unstructured": "Wysocki J, Ye M, Hassler L, Gupta AK, Wang Y, Nicoleascu V, Randall G, Wertheim JA, Batlle D (2021) A novel soluble ACE2 variant with prolonged duration of action neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 infection in human kidney organoids. J Am Soc Nephrol 32(4):795–803",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-020-01445-6",
"author": "J Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "182",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Respir Res",
"key": "2141_CR41",
"unstructured": "Xu J, Xu X, Jiang L, Dua K, Hansbro PM, Liu G (2020) SARS-CoV-2 induces transcriptional signatures in human lung epithelial cells that promote lung fibrosis. Respir Res 21(1):182",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2021.09.007",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2141_CR42",
"unstructured": "Angeli F, Zappa M, Reboldi G, Trapasso M, Cavallini C, Spanevello A, Verdecchia P (2021) The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection: one year later. Eur J Intern Med 93:28–34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2021.629176",
"author": "D Jeon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Med",
"key": "2141_CR43",
"unstructured": "Jeon D, Son M, Choi J (2021) Effect of spironolactone on COVID-19 in patients with underlying liver cirrhosis: a nationwide case-control study in South Korea. Front Med 8:629176",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18087/cardio.2020.11.n1440",
"author": "VY Mareev",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Kardiologiia",
"key": "2141_CR44",
"unstructured": "Mareev VY, Orlova YA, Plisyk AG, Pavlikova EP, Matskeplishvili ST, Akopyan ZA, Seredenina EM, Potapenko AV, Agapov MA, Asratyan DA, Dyachuk LI, Samokhodskaya LM, Mershina E, Sinitsyn VE, Pakhomov PV, Bulanova MM, Fuks AA, Mareev YV, Begrambekova YL, Kamalov A (2020) results of open-label non-randomized comparative clinical trial: “bromhexine and spironolactone for coronavirus infection requiring hospitalization” (BISCUIT). Kardiologiia 60(11):4–15",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"author": "CB Jackson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol",
"key": "2141_CR45",
"unstructured": "Jackson CB, Farzan M, Chen B, Choe H (2022) Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 23(1):3–20",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/CMR.00133-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2141_CR46",
"unstructured": "Synowiec A, Szczepański A, Barreto-Duran E, Lie LK, Pyrc K (2021) Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): a systemic infection. Clin Microbiol Rev 34(2):e00133–e00120"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00592-020-01539-z",
"author": "SB Solerte",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "779",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Acta Diabetol",
"key": "2141_CR47",
"unstructured": "Solerte SB, Di Sabatino A, Galli M, Fiorina P (2020) Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibition in COVID-19. Acta Diabetol 57(7):779–783",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1871530322666220104103325",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2141_CR48",
"unstructured": "Bakhtiari M, Asadipooya K (2022) Metainflammation in COVID-19. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 22(12):1154–1166"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/db21-0926",
"author": "M Ben Nasr",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1579",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Diabetes",
"key": "2141_CR49",
"unstructured": "Ben Nasr M, D’Addio F, Montefusco L, Usuelli V, Loretelli C, Rossi A, Pastore I, Abdelsalam A, Maestroni A, Dell’Acqua M, Ippolito E, Assi E, Seelam AJ, Fiorina RM, Chebat E, Morpurgo P, Lunati ME, Bolla AM, Abdi R, Bonventre JV, Rusconi S, Riva A, Corradi D, Santus P, Clark P, Nebuloni M, Baldi G, Finzi G, Folli F, Zuccotti GV, Galli M, Herold KC, Fiorina P (2022) Indirect and direct effects of SARS-CoV-2 on human pancreatic islets. Diabetes 71(7):1579–1590",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42255-021-00347-1",
"author": "JA Müller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "149",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nat Metab",
"key": "2141_CR50",
"unstructured": "Müller JA, Groß R, Conzelmann C, Krüger J, Merle U, Steinhart J, Weil T, Koepke L, Bozzo CP, Read C, Fois G, Eiseler T, Gehrmann J, van Vuuren J, Wessbecher IM, Frick M, Costa IG, Breunig M, Grüner B, Peters L, Schuster M, Liebau S, Seufferlein T, Stenger S, Stenzinger A, MacDonald PE, Kirchhoff F, Sparrer KMJ, Walther P, Lickert H, Barth TFE, Wagner M, Münch J, Heller S, Kleger A (2021) SARS-CoV-2 infects and replicates in cells of the human endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Nat Metab 3(2):149–165",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42255-021-00407-6",
"author": "L Montefusco",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "774",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nat Metab",
"key": "2141_CR51",
"unstructured": "Montefusco L, Ben Nasr M, D’Addio F, Loretelli C, Rossi A, Pastore I, Daniele G, Abdelsalam A, Maestroni A, Dell’Acqua M, Ippolito E, Assi E, Usuelli V, Seelam AJ, Fiorina RM, Chebat E, Morpurgo P, Lunati ME, Bolla AM, Finzi G, Abdi R, Bonventre JV, Rusconi S, Riva A, Corradi D, Santus P, Nebuloni M, Folli F, Zuccotti GV, Galli M, Fiorina P (2021) Acute and long-term disruption of glycometabolic control after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Metab 3(6):774–785",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.146701",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2141_CR52",
"unstructured": "Loretelli C, Abdelsalam A, D'Addio F, Ben Nasr M, Assi E, Usuelli V, Maestroni A, Seelam AJ, Ippolito E, Di Maggio S, Loreggian L, Radovanovic D, Vanetti C, Yang J, El Essawy B, Rossi A, Pastore I, Montefusco L, Lunati ME, Bolla AM, Biasin M, Antinori S, Santus P, Riva A, Zuccotti GV, Galli M, Rusconi S, Fiorina P (2021) PD-1 blockade counteracts post-COVID-19 immune abnormalities and stimulates the anti-SARS-CoV-2 immune response. JCI Insight 6(24):e146701"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/clinem/dgac450",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2141_CR53",
"unstructured": "Asadipooya K (2022) Letter to the editor from Asadipooya: “obesity and COVID-19: mechanistic insights from adipose tissue”. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 107(10):e4269"
},
{
"DOI": "10.22541/au.165403085.53671439/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2141_CR54",
"unstructured": "Davarpanah MA, Adatorwovor R, Mansoori Y, Ramsheh FSR, Parsa A, Hajiani M, Faramarzi H, Kavuluru R, Asadipooya K (2022) Combination of spironolactone and sitagliptin improves clinical outcomes of outpatients with COVID-19: a prospective cohort study. medRxiv. 2022.2001.2021.22269322"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-020-0399-8",
"author": "CF Deacon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "642",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Endocrinol",
"key": "2141_CR55",
"unstructured": "Deacon CF (2020) Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Endocrinol 16(11):642–653",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154295",
"author": "AP Stoian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "2141_CR56",
"unstructured": "Stoian AP, Sachinidis A, Stoica RA, Nikolic D, Patti AM, Rizvi AA (2020) The efficacy and safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors compared to other oral glucose-lowering medications in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 109:154295",
"volume": "109",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2018-00241",
"author": "KA Martin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1233",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "2141_CR57",
"unstructured": "Martin KA, Anderson RR, Chang RJ, Ehrmann DA, Lobo RA, Murad MH, Pugeat MM, Rosenfield RL (2018) Evaluation and treatment of hirsutism in premenopausal women: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 103(4):1233–1257",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2018"
}
],
"reference-count": 57,
"references-count": 57,
"relation": {
"has-preprint": [
{
"asserted-by": "object",
"id": "10.1101/2022.01.21.22269322",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40618-023-02141-0"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Combination of spironolactone and sitagliptin improves clinical outcomes of outpatients with COVID-19: a prospective cohort study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "47"
}
davarpanah