Cannabidiol for COVID-19 Patients with Mild to Moderate Symptoms (CANDIDATE Study): A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
et al., Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, doi:10.1089/can.2021.0093, NCT04467918, Oct 2021
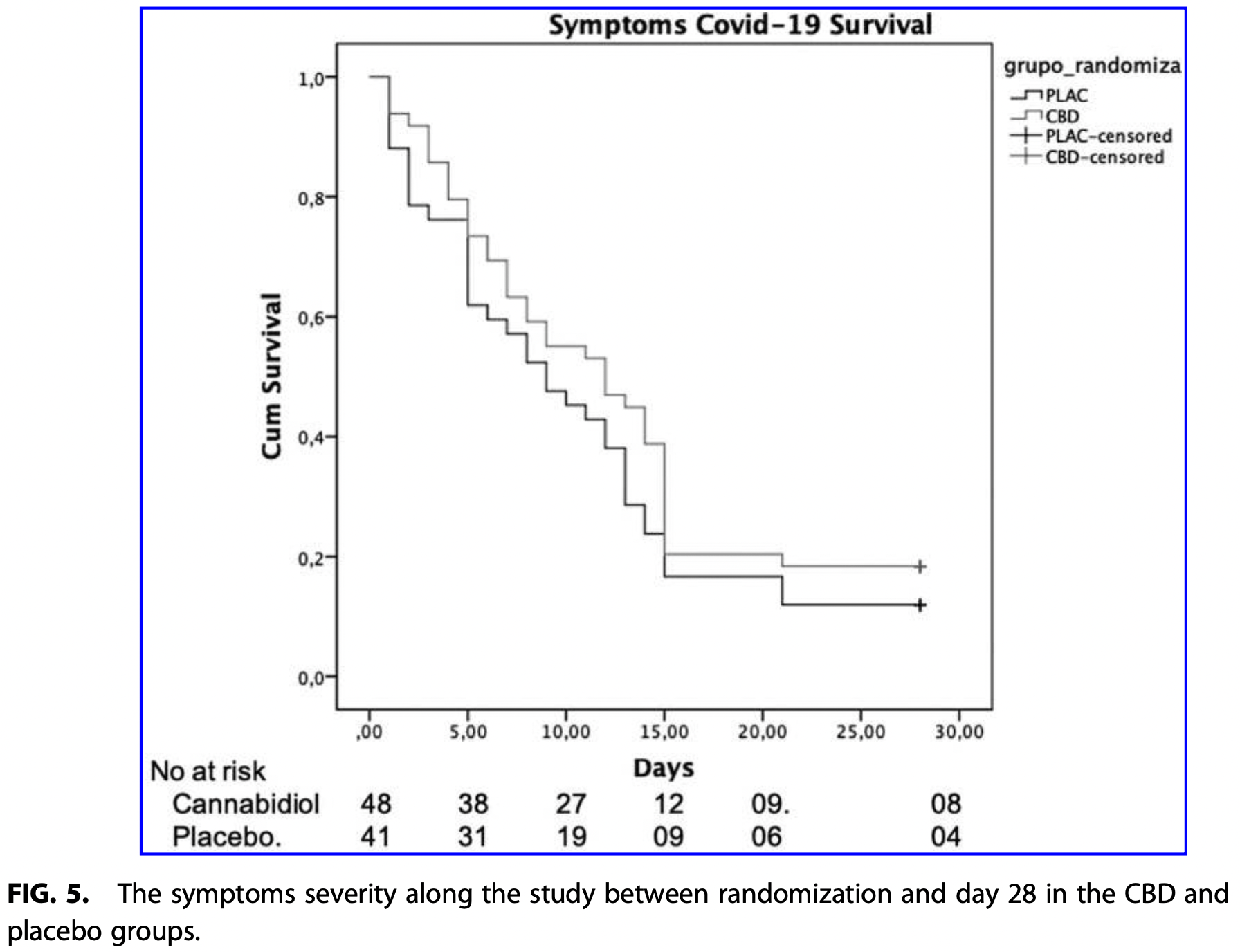
RCT 105 patients recruited in an ER in Brazil, 49 treated with CBD, showing no significant differences with treatment. 300mg CBD for 14 days.
For discussion see1.
|
risk of hospitalization, 557.1% higher, RR 6.57, p = 0.25, treatment 3 of 49 (6.1%), control 0 of 42 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
recovery time, 33.3% higher, relative time 1.33, p = 0.20, treatment 49, control 42.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Crippa et al., 7 Oct 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Brazil, peer-reviewed, 32 authors, study period 7 July, 2020 - 16 October, 2020, trial NCT04467918 (history).
Cannabidiol for COVID-19 Patients with Mild to Moderate Symptoms (CANDIDATE Study): A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial
Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, doi:10.1089/can.2021.0093
Importance: Owing to its anti-inflammatory properties and antiviral ''in vitro'' effect against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), cannabidiol (CBD) has been proposed as a potential treatment for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Objective: To investigate the safety and efficacy of CBD for treating patients with mild to moderate COVID-19. Design: Randomized, parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial conducted between July 7 and October 16, 2020, in two sites in Brazil. Setting: Patients were recruited in an emergency room. Participants: Block randomized patients (1:1 allocation ratio-by a researcher not directly involved in data collection) with mild and moderate COVID-19 living in Ribeira ˜o Preto, Brazil, seeking medical consultation, and those who voluntarily agreed to participate in the study. Interventions: Patients received 300 mg of CBD or placebo added to standard symptomatic care during 14 days. Main Outcome and Measure: The primary outcome was reduction or prevention of the deterioration in clinical status from mild/moderate to severe/critical measured with the COVID-19 Scale or the natural course of the resolution of typical clinical symptoms. Primary study outcome was assessed on days 14, 21, and 28 after enrollment. Results: A total of 321 patients were recruited and assessed for eligibility, and 105 were randomly allocated either in CBD (n = 49) or in placebo (n = 42) group. Ninety-one participants were included in the analysis of efficacy. There were no baseline between-group differences regarding disease severity (v 2 = 0.025, p = 0.988) and median time to symptom resolution (12 days [95% confidence interval, CI, 6.5-17.5] in the CBD group, 9 days [95% CI,
References
Anil, Shalev, Vinayaka, Cannabis compounds exhibit antiinflammatory activity in vitro in COVID-19-related inflammation in lung epithelial cells and pro-inflammatory activity in macrophages, Sci Rep
Bergamaschi, Queiroz, Chagas, Cannabidiol reduces the anxiety induced by simulated public speaking in treatmentnaı ¨ve social phobia patients, Neuropsychopharmacology
Biali, Broers, Besson, Cannabinoids and COVID-19, Med Cannabis Cannabinoids
Byrareddy, Mohan, SARS-CoV2 induced respiratory distress: can cannabinoids be added to anti-viral therapies to reduce lung inflammation?, Brain Behav Immun
Campos, Brant, Miranda, Cannabidiol increases survival and promotes rescue of cognitive function in a murine model of cerebral malaria, Neuroscience
Campos, Ferreira, Guimara, Fs, Cannabidiol blocks long-lasting behavioral consequences of predator threat stress: possible involvement of 5HT1A receptors, J Psychiatr Res
Campos, Ortega, Palazuelos, The anxiolytic effect of cannabidiol on chronically stressed mice depends on hippocampal neurogenesis: involvement of the endocannabinoid system, Int J Neuropsychopharmacol
China, National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China
Crippa, Guimara ˜es, Campos, Translational investigation of the therapeutic potential of cannabidiol (CBD): toward a new age, Front Immunol
Crippa, Pacheco, Zuardi, Guimara ˜es, Campos et al., for the Cannabidiol for COVID-19 Patients (CANDIDATE) Trial Investigators (2021) Cannabidiol for COVID-19 patients with mild to moderate symptoms (CANDIDATE study): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial, Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research X:X
Dong, Tang, Wang, The role of imaging in the detection and management of COVID-19: a review, IEEE Rev Biomed Eng
Dos-Santos-Pereira, ˜es, Bel, Cannabidiol prevents LPS-induced microglial inflammation by inhibiting ROS/ NF-jB-dependent signaling and glucose consumption, Glia
Esposito, Pesce, Seguella, The potential of cannabidiol in the COVID-19 pandemic, Br J Pharmacol
Fu, Kong, Wang, The clinical implication of dynamic neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and D-dimer in COVID-19: a retrospective study in Suzhou China, Thromb Res
Jimeno, Ventura, Castellano, Prognostic implications of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in COVID-19, Eur J Clin Invest
Khodadadi, Salles, ´l, Jarrahi, Cannabidiol modulates cytokine storm in acute respiratory distress syndrome induced by simulated viral infection using synthetic RNA, Cannabis Cannabinoid Res
Long, Zeng, Zhang, Short-term outcomes of COVID-19 and risk factors for progression, Eur Respir J
Mabou Tagne, Pacchetti, Sodergren, Cannabidiol for viral diseases: hype or hope? Cannabis Cannabinoid, Res
Malinowska, Baranowska-Kuczko, Kicman, Opportunities, challenges and pitfalls of using cannabidiol as an adjuvant drug in COVID-19, Int J Mol Sci
Masataka, Anxiolytic effects of repeated cannabidiol treatment in teenagers with social anxiety disorders, Front Psychol
Mecha, Feliu, ˜igo, Cannabidiol provides long-lasting protection against the deleterious effects of inflammation in a viral model of multiple sclerosis: a role for A2A receptors, Neurobiol Dis
Moreno, Desousa, Souza, Factor structure, reliability, and item parameters of the Brazilian-Portuguese version of the GAD-7 questionnaire, Temas Psicol
Oso, Vilela Mendes, Crippa, Study of the discriminative validity of the PHQ-9 and PHQ-2 in a sample of Brazilian women in the context of primary health care, Perspect Psychiatr Care
Pacheco, Souza, Hallak, Cannabidiol as a treatment for mental health outcomes among health care workers during the coronavirus disease pandemic, J Clin Psychopharmacol
Raj, Park, Cho, Assessment of antiviral potencies of cannabinoids against SARS-CoV-2 using computational and in vitro approaches, Int J Biol Macromol
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area, JAMA
Salles, ´l, Khodadadi, Jarrahi, Cannabidiol (CBD) modulation of apelin in acute respiratory distress syndrome, J Cell Mol Med
Sonego, Prado, Vale, Cannabidiol prevents haloperidolinduced vacuos chewing movements and inflammatory changes in mice via PPARc receptors, Brain Behav Immun
Stamps, Bartoshuk, Heilman, A brief olfactory test for Alzheimer's disease, J Neurol Sci
Suryavanshi, Kovalchuk, Kovalchuk, Cannabinoids as key regulators of inflammasome signaling: a current perspective, Front Immunol
Vuolo, Abreu, Michels, Cannabidiol reduces airway inflammation and fibrosis in experimental allergic asthma, Eur J Pharmacol
Zanelati, Biojone, Moreira, Antidepressant-like effects of cannabidiol in mice: possible involvement of 5-HT 1A receptors, Br J Pharmacol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1089/can.2021.0093",
"ISSN": [
"2578-5125",
"2378-8763"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1089/can.2021.0093",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1089/can.2021.0093"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9520-6746",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience and Behavior, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
},
{
"name": "National Institute for Science and Technology—Translational Medicine, São Paulo, Brazil."
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Crippa",
"given": "José Alexandre S.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience and Behavior, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Pacheco",
"given": "Julia Cozar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience and Behavior, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
},
{
"name": "National Institute for Science and Technology—Translational Medicine, São Paulo, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Zuardi",
"given": "Antonio W.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Institute for Science and Technology—Translational Medicine, São Paulo, Brazil."
},
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Guimarães",
"given": "Francisco S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Campos",
"given": "Alline Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience and Behavior, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
},
{
"name": "National Institute for Science and Technology—Translational Medicine, São Paulo, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Osório",
"given": "Flávia de Lima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience and Behavior, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Loureiro",
"given": "Sonia Regina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience and Behavior, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
},
{
"name": "National Institute for Science and Technology—Translational Medicine, São Paulo, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "dos Santos",
"given": "Rafael G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience and Behavior, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Souza",
"given": "José Diogo S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience and Behavior, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Ushirohira",
"given": "Juliana Mayumi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Ferreira",
"given": "Rafael Rinaldi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Mancini Costa",
"given": "Karla Cristinne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Scomparin",
"given": "Davi Silveira",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Scarante",
"given": "Franciele Franco",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pharmacology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Pires-Dos-Santos",
"given": "Isabela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicinal Chemistry and Natural Products, The Institute for Drug Research, School of Pharmacy, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, Israel."
}
],
"family": "Mechoulam",
"given": "Raphael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Institute for Science and Technology—Translational Medicine, São Paulo, Brazil."
},
{
"name": "Department of Psychiatry and Behavioural Neurosciences, McMaster University and St. Joseph's Healthcare Hamilton, Hamilton, Canada."
},
{
"name": "Graduate Program in Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, Department of Psychiatry, Faculty of Medicine, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Kapczinski",
"given": "Flávio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Fonseca",
"given": "Benedito A.L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Internal Medicine, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Esposito",
"given": "Danillo L.A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Social Medicine, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Passos",
"given": "Afonso Dinis Costa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Social Medicine, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Dal Fabbro",
"given": "Amaury Lelis",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Social Medicine, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Bellissimo-Rodrigues",
"given": "Fernando",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Cell and Molecular Biology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Arruda",
"given": "Eurico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Surgery and Anatomy, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Scarpelini",
"given": "Sandro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Chromatox Laboratory Ltda., São Paulo, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Andraus",
"given": "Maristela Haddad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Imaging, Hematology, and Clinical Oncology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Nather Junior",
"given": "Julio Cesar",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Imaging, Hematology, and Clinical Oncology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Wada",
"given": "Danilo Tadao",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Imaging, Hematology, and Clinical Oncology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Koenigkam-Santos",
"given": "Marcel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Imaging, Hematology, and Clinical Oncology, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Santos",
"given": "Antonio Carlos",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Psychiatric Neuroimaging (LIM 21), Department of Psychiatry, Faculty of Medicine, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Busatto Filho",
"given": "Geraldo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Neuroscience and Behavior, Ribeirão Preto Medical School, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil."
},
{
"name": "National Institute for Science and Technology—Translational Medicine, São Paulo, Brazil."
}
],
"family": "Hallak",
"given": "Jaime E.C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "for the Cannabidiol for COVID-19 Patients (CANDIDATE) Trial Investigators",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-09T21:02:13Z",
"timestamp": 1633813333000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-09T21:02:18Z",
"timestamp": 1633813338000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-16T12:25:53Z",
"timestamp": 1642335953220
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "2578-5125"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "2378-8763"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
7
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.liebertpub.com/nv/resources-tools/text-and-data-mining-policy/121/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-07T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633564800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1089/can.2021.0093",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/pdf/10.1089/can.2021.0093",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "278",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1089",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
7
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
7
]
]
},
"publisher": "Mary Ann Liebert Inc",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000510799",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2020.04.079",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.15157",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/can.2019.0060",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms22041986",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.613613",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/can.2020.0043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B7"
},
{
"author": "Khodadadi H",
"first-page": "251",
"journal-title": "J Cell Mol Med",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "843",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.12.051",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nbd.2013.06.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/glia.23738",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbi.2018.09.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-81049-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.11.029",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B15"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00521.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jpsychires.2012.08.012",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S1461145712001502",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/npp.2011.6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02466",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/JCP.0000000000001405",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jns.2013.06.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00990-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1109/RBME.2020.2990959",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.9788/TP2016.1-25",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1744-6163.2009.00224.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2020.05.006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/eci.13404",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.02009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "B32"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology (medical)",
"Complementary and alternative medicine",
"Pharmacology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Cannabidiol for COVID-19 Patients with Mild to Moderate Symptoms (CANDIDATE Study): A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}