Effect of Antithrombotic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes in Outpatients With Clinically Stable Symptomatic COVID-19
et al., JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.1727283, ACTIV-4B, NCT04498273, Oct 2021
Early terminated RCT with 164 aspirin and 164 control patients in the USA with very few events, showing no significant difference with aspirin treatment for the combined endpoint of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, and hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary indication. There was no mortality and no major bleeding events among participants that started treatment (there was one ITT placebo death).
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
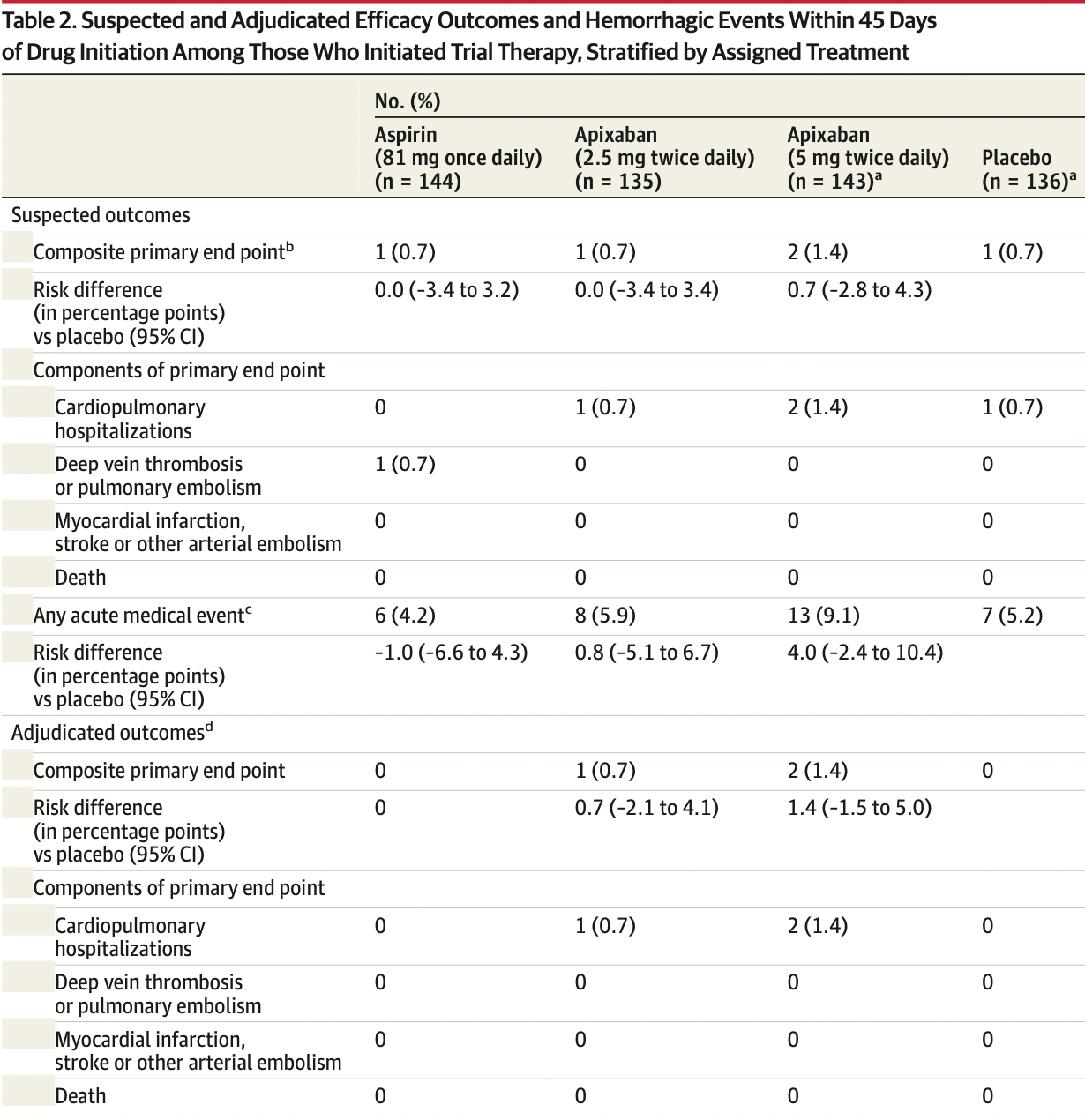
risk of hospitalization, 67.3% lower, RR 0.33, p = 0.49, treatment 0 of 144 (0.0%), control 1 of 136 (0.7%), NNT 136, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary indication, suspected, started treatment.
|
|
risk of progression, 19.0% lower, RR 0.81, p = 0.78, treatment 6 of 144 (4.2%), control 7 of 136 (5.1%), NNT 102, acute medical event, suspected, started treatment.
|
|
risk of progression, 5.6% lower, RR 0.94, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 144 (0.7%), control 1 of 136 (0.7%), NNT 2448, combined endpoint of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, and hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary indication, suspected, started treatment, primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Connors et al., 11 Oct 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, 27 authors, study period September 2020 - June 2021, trial NCT04498273 (history) (ACTIV-4B).
Effect of Antithrombotic Therapy on Clinical Outcomes in Outpatients With Clinically Stable Symptomatic COVID-19 The ACTIV-4B Randomized Clinical Trial
doi:10.1001/jama.2021.17272
IMPORTANCE Acutely ill inpatients with COVID-19 typically receive antithrombotic therapy, although the risks and benefits of this intervention among outpatients with COVID-19 have not been established. OBJECTIVE To assess whether anticoagulant or antiplatelet therapy can safely reduce major adverse cardiopulmonary outcomes among symptomatic but clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19.
DESIGN, SETTING, AND PARTICIPANTS The ACTIV-4B Outpatient Thrombosis Prevention Trial was designed as a minimal-contact, adaptive, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to compare anticoagulant and antiplatelet therapy among 7000 symptomatic but clinically stable outpatients with COVID-19. The trial was conducted at 52 US sites between September 2020 and June 2021; final follow-up was August 5, 2021. Prior to initiating treatment, participants were required to have platelet count greater than 100 000/mm 3 and estimated glomerular filtration rate greater than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . INTERVENTIONS Random allocation in a 1:1:1:1 ratio to aspirin (81 mg orally once daily; n = 164), prophylactic-dose apixaban (2.5 mg orally twice daily; n = 165), therapeutic-dose apixaban (5 mg orally twice daily; n = 164), or placebo (n = 164) for 45 days.
MAIN OUTCOMES AND MEASURES The primary end point was a composite of all-cause mortality, symptomatic venous or arterial thromboembolism, myocardial infarction, stroke, or hospitalization for cardiovascular or pulmonary cause. The primary analyses for efficacy and bleeding events were limited to participants who took at least 1 dose of trial medication.
RESULTS On June 18, 2021, the trial data and safety monitoring board recommended early terminationbecauseoflowerthananticipatedeventrates;atthattime,657symptomaticoutpatients with COVID-19 had been randomized (median age, 54 years [IQR, 46-59]; 59% women). The median times from diagnosis to randomization and from randomization to initiation of study treatment were 7 days and 3 days, respectively. Twenty-two randomized participants (3.3%) were hospitalized for COVID-19 prior to initiating treatment. Among the 558 patients who initiated treatment, the adjudicated primary composite end point occurred in 1 patient (0.7%) in the aspirin group, 1 patient (0.7%) in the 2.5-mg apixaban group, 2 patients (1.4%) in the 5-mg apixaban group, and 1 patient (0.7%) in the placebo group. The risk differences compared with placebo for the primary end point were 0.0% (95% CI not calculable) in the aspirin group, 0.7% (95% CI, -2.1% to 4.1%) in the 2.5-mg apixaban group, and 1.4% (95% CI, -1.5% to 5.0%) in the 5-mg apixaban group. Risk differences compared with placebo for bleeding events were 2.0% (95% CI, -2.7% to 6.8%), 4.5% (95% CI, -0.7% to 10.2%), and 6.9% (95% CI, 1.4% to 12.9%) among participants who initiated therapy in the aspirin, prophylactic apixaban, and therapeutic apixaban groups, respectively, although none were major. Findings inclusive of all randomized patients were..
The trial drugs and matching placebo were donated by the Bristol Myers Squibb-Pfizer Alliance.
Role of the Funder/Sponsor: The NHLBI funded the ACTIV-4B trial and had a collaborative role in the trial design. The NHLBI had no role in the collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; or the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Disclaimer: The views and conclusions contained in this document are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as representing the official policies, either express or implied, of the NIH.
Group Information: A complete list of all protocol development committee members, data and safety monitoring board members, contributors from the research communications center, the data coordinating center, the drug shipment center, NHLBI Executive and Steering Committee members, and all participating sites is provided in Supplement 3 and Supplement 4.
Data Sharing
References
Agnelli, Buller, Cohen, AMPLIFY Investigators. Oral apixaban for the treatment of acute venous thromboembolism, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1302507
Agnelli, Buller, Cohen, AMPLIFY-EXT Investigators. Apixaban for extended treatment of venous thromboembolism, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1207541
Attacc Investigators, Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in critically ill patients with Covid-19
Baden, Sahly, Essink, Efficacy and safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2035389
Chen, Nirula, Heller, None
Cohen, Spiro, Büller, Rivaroxaban for thromboprophylaxis in acutely ill medical patients, J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1111096
Contributions, Brooks, Connors, Sciurba, Krishnan et al., access to all of the data in the study and take responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.4152?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2021.17272
Dagan, Barda, Kepten, BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine in a nationwide mass vaccination setting, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2101765
Goligher, Bradbury, Mcverry, None
Gottlieb, Nirula, Chen, Effect of bamlanivimab as monotherapy or in combination with etesevimab on viral load in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.0202?utm_campaign=articlePDF%26utm_medium=articlePDFlink%26utm_source=articlePDF%26utm_content=jama.2021.17272
Investigators, SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2029849
Kaatz, Ahmad, Spyropoulos, Schulman, Subcommittee on Control of Anticoagulation. Definition of clinically relevant non-major bleeding in studies of anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation and venous thromboembolic disease in non-surgical patients: communication from the SSC of the ISTH, J Thromb Haemost, doi:10.1111/jth.13140
Lawler, Goligher, Berger, Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in noncritically ill patients with Covid-19
Lopes, De, Silva, Furtado, ACTION Coalition COVID-19 Brazil IV Investigators. Therapeutic versus prophylactic anticoagulation for patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 and elevated D-dimer concentration (ACTION): an open-label, multicentre, randomised, controlled trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01203-4
Polack, Thomas, Kitchin, Clinical Trial Group. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 vaccine, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2034577
Spyropoulos, Ageno, Albers, Post-discharge prophylaxis with rivaroxaban reduces fatal and major thromboembolic events in medically ill patients, J Am Coll Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2020.04.071
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, Trial Investigators. REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail