Turning up the heat on COVID-19: heat as a therapeutic intervention
, M., F1000Research, doi:10.12688/f1000research.23299.2, Jul 2020
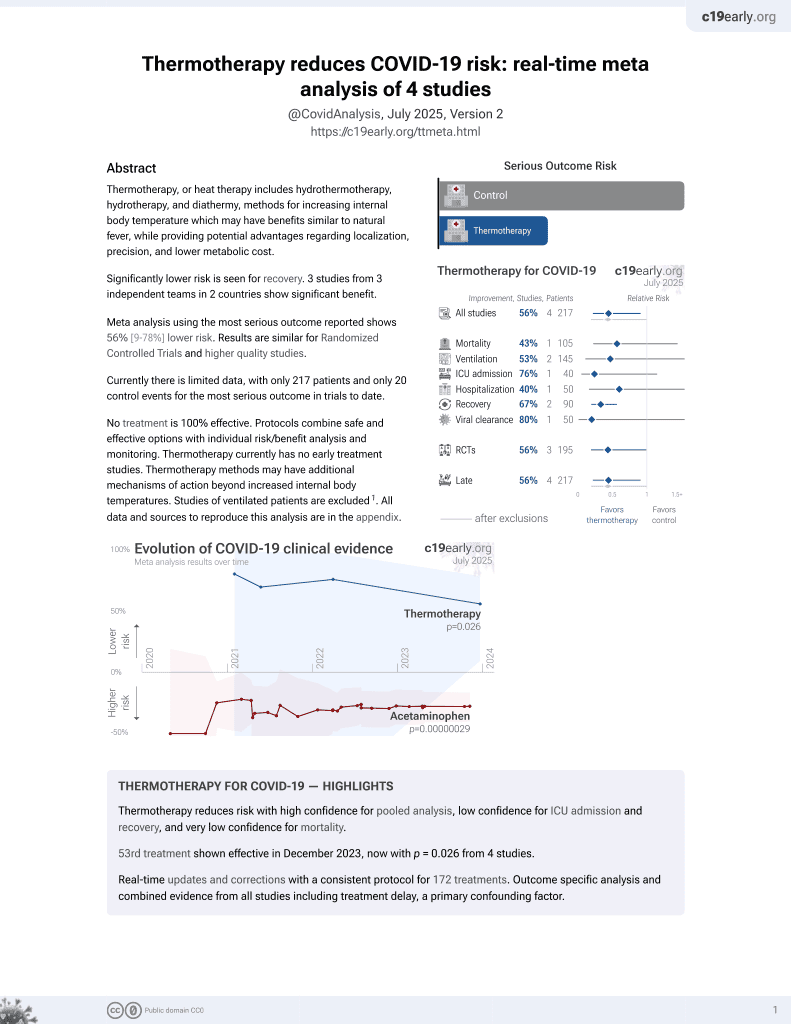
54th treatment shown to reduce risk in
December 2023, now with p = 0.026 from 4 studies.
Lower risk for recovery.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Review of the evidence supporting the use of heat therapy to treat and prevent viral respiratory infections like COVID-19. Author explains that enveloped viruses like coronaviruses are heat-sensitive and destroyed by temperatures tolerable to humans. Author discusses how mammals use fever and humans use practices like saunas and steam inhalation to fight infections. Heat is proposed to combat viruses through direct deactivation, supporting mucociliary clearance, mimicking fever, activating immune defenses, and building physiological resilience. Psychological benefits are also noted.
1.
Smadja et al., Hyperthermia and targeting heat shock proteins: innovative approaches for neurodegenerative disorders and Long COVID, Frontiers in Neuroscience, doi:10.3389/fnins.2025.1475376.
2.
Kunutsor et al., Finnish sauna and COVID-19, Le Infezioni in Medicina, 1, www.infezmed.it/index.php/article?Anno=2021&numero=1&ArticoloDaVisualizzare=Vol_29_1_2021_160.
3.
Ramirez et al., Hydrothermotherapy in prevention and treatment of mild to moderate cases of COVID-19, Medical Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110363.
4.
Mancilla-Galindo et al., Exploring the rationale for thermotherapy in COVID-19, International Journal of Hyperthermia, doi:10.1080/02656736.2021.1883127.
5.
Larenas-Linnemann et al., Enhancing innate immunity against virus in times of COVID-19: Trying to untangle facts from fictions, World Allergy Organization Journal, doi:10.1016/j.waojou.2020.100476.
Cohen et al., 20 Jul 2020, peer-reviewed, 1 author.
Contact: drmarc@extremewellness.co.
Turning up the heat on COVID-19: heat as a therapeutic intervention
F1000Research, doi:10.12688/f1000research.23299.1
Enveloped viruses such as SAR-CoV-2 are sensitive to heat and are destroyed by temperatures tolerable to humans. All mammals use fever to deal with infections and heat has been used throughout human history in the form of hot springs, saunas, hammams, steamrooms, sweat-lodges, steam inhalations, hot mud and poultices to prevent and treat respiratory infections and enhance health and wellbeing. This paper reviews the evidence for using heat to treat and prevent viral infections and discusses potential cellular, physiological and psychological mechanisms of action. In the initial phase of infection, heat applied to the upper airways can support the immune system's first line of defence by supporting muco-ciliary clearance and inhibiting or deactivating virions where they first lodge. This may be further enhanced by the inhalation of steam containing essential oils with anti-viral, mucolytic and anxiolytic properties. Heat applied to the whole body can further support the immune system's second line of defence by mimicking fever and activating innate and acquired immune defences and building physiological resilience. Heat-based treatments also offer psychological benefits and enhanced mental wellness by focusing attention on positive action, enhancing relaxation and sleep, inducing 'forced-mindfulness', and invoking the power of positive thinking and 'remembered wellness'. Heat is a cheap, convenient and widely accessible therapeutic modality and while no clinical protocols exist for using heat to treat COVID-19, protocols that draw from traditional practices and consider contraindications, adverse effects and infection control measures could be developed and implemented rapidly and inexpensively on a wide scale. While there are significant challenges in implementing heat-based therapies during the current pandemic, these therapies present an opportunity to integrate natural medicine, conventional medicine and traditional wellness practices, and support the wellbeing of both patients and medical staff, while building community resilience and reducing the likelihood and impact of future pandemics.
Author Response 12 Jul 2020
Marc Cohen I agree that this is a timely and interesting topic that covers a wide range of literature and am grateful for your comments, which have led to improvements in the paper's content and flow. I have now modified the wording to better reflect the difference between fever and externally applied heat stress and have referenced a review of the different forms of heat treatment that are currently being used or are under investigation for cancer therapy and suggest they may be useful for treating COVID-19. I have also added more detail on the adverse effects of heat and have reorganised some sections to improve the flow of information and make the paper more cohesive. Competing Interests: All competing interests have been declared in the authorship statement.
Comments on this article
References
Ali, Wabel, Shams, Essential oils used in aromatherapy: A systemic review, Asian Pac J Trop Biomed
Benson, Friedman, Harnessing the power of the placebo effect and renaming it "remembered wellness, Annu Rev Med
Hannuksela, Ellahham, Benefits and risks of sauna bathing, Am J Med, doi:10.1016/S0002-9343(00)00671-9
Heinonen, Laukkanen, Effects of heat and cold on health, with special reference to Finnish sauna bathing, Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00115.2017
Heinonen, Laukkanen, Effects of heat and cold on health, with special reference to Finnish sauna bathing, American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00115.2017
Hu, Trefethen, Zeng, Biophysical characterization and conformational stability of Ebola and Marburg virus-like particles, J Pharm Sci, doi:10.1002/jps.22724
Huang, Li, Instability of Nucleic Acids in Airborne Microorganisms under Far Infrared Radiation, doi:10.20944/preprints202002.0332.v1
Hussain, Cohen, Clinical Effects of Regular Dry Sauna Bathing: A Systematic Review, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, doi:10.1155/2018/1857413
Hussain, Greaves, Cohen, A hot topic for health: Results of the Global Sauna Survey, Complement Ther Med, doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2019.03.012
Iguchi, Littmann, Chang, Heat stress and cardiovascular, hormonal, and heat shock proteins in humans, J Athl Train, doi:10.4085/1062-6050-47.2.184
Irwin, Opp, Sleep Health: Reciprocal Regulation of Sleep and Innate Immunity, Neuropsychopharmacology, doi:10.1038/npp.2016.148
Kampf, Voss, Scheithauer, Inactivation of coronaviruses by heat, J Hosp Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jhin.2020.03.025
Kappel, Stadeager, Tvede, Effects of in vivo hyperthermia on natural killer cell activity, in vitro proliferative responses and blood mononuclear cell subpopulations, Clin Exp Immunol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb08144.x
Kudo, Song, Yockey, Low ambient humidity impairs barrier function and innate resistance against influenza infection, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1902840116
Kunutsor, Laukkanen, Laukkanen, Frequent sauna bathing may reduce the risk of pneumonia in middle-aged Caucasian men: The KIHD prospective cohort study, Respir Med, doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2017.10.018
Kunutsor, Laukkanen, Laukkanen, Longitudinal associations of sauna bathing with inflammation and oxidative stress: the KIHD prospective cohort study, Ann Med, doi:10.1080/07853890.2018.1489143
Kunutsor, Laukkanen, Laukkanen, Longitudinal associations of sauna bathing with inflammation and oxidative stress: the KIHD prospective cohort study, Ann Med, doi:10.1080/07853890.2018.1489143
Kunutsor, Laukkanen, Laukkanen, Sauna bathing reduces the risk of respiratory diseases: a long-term prospective cohort study, Eur J Epidemiol, doi:10.1007/s10654-017-0311-6
Kunutsor, Laukkanen, Laukkanen, Sauna bathing reduces the risk of respiratory diseases: a long-term prospective cohort study, European Journal of Epidemiology, doi:10.1007/s10654-017-0311-6
Laitinen, Lindqvist, Heino, Effect of pH and temperature on the infectivity of human coronavirus 229E, Can J Microbiol, doi:10.1139/m89-160
Laukkanen, Khan, Zaccardi, Association Between Sauna Bathing and Fatal Cardiovascular and All-Cause Mortality Events, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.8187
Laukkanen, Khan, Zaccardi, Laukkanen, Association between sauna bathing and fatal cardiovascular and all-cause mortality events, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.8187
Laukkanen, Kunutsor, Is sauna bathing protective of sudden cardiac death? A review of the evidence, Prog Cardiovasc Dis, doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2019.05.001
Laukkanen, Kunutsor, Is sauna bathing protective of sudden cardiac death? A review of the evidence, Prog Cardiovasc Dis, doi:10.1016/j.pcad.2019.05.001
Laukkanen, Laukkanen, Kunutsor, Cardiovascular and Other Health Benefits of Sauna Bathing: A Review of the Evidence, Mayo Clin Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.04.008
Laukkanen, Laukkanen, Kunutsor, Cardiovascular and Other Health Benefits of Sauna Bathing: A Review of the Evidence, Mayo Clin Proc, doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.04.008
Laukkanen, Laukkanen, Sauna bathing and systemic inflammation, European Journal of Epidemiology, doi:10.1007/s10654-017-0335-y
Lelie, Reesink, Lucas, Inactivation of 12 viruses by heating steps applied during manufacture of a hepatitis B vaccine, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.1890230313
Leyk, Hoitz, Becker, Health Risks and Interventions in Exertional Heat Stress, Deutsches Arzteblatt international, doi:10.3238/arztebl.2019.0537
Mace, Zhong, Kilpatrick, Differentiation of CD8+ T cells into effector cells is enhanced by physiological range hyperthermia, J Leukoc Biol, doi:10.1189/jlb.0511229
Mather, Kaups, Effects of steam inhalation on nasal patency and nasal symptoms in patients with the common cold, Am J Otolaryngol, doi:10.1016/s0196-0709(87)80037-6
Mk, Lim, Song, The effects of aromatherapy essential oil inhalation on stress, sleep quality and immunity in healthy adults: Randomized controlled trial, Eur J Integr Med, doi:10.1016/j.eujim.2017.04.009
Mäkinen, Juvonen, Jokelainen, Cold temperature and low humidity are associated with increased occurrence of respiratory tract infections, Respir Med, doi:10.1016/j.rmed.2008.09.011
Pilch, Pokora, Szyguła, Effect of a single finnish sauna session on white blood cell profile and cortisol levels in athletes and non-athletes, J Hum Kinet, doi:10.2478/hukin-2013-0075
Sajadi, Habibzadeh, Vintzeleos, Reference Source Schieber AMP, Ayres JS: Thermoregulation as a disease tolerance defense strategy, Pathog Dis, doi:10.1093/femspd/ftw106
Shemilt, Bagabir, Lang, Potential mechanisms for the effects of farinfrared on the cardiovascular system -a review, Vasa, doi:10.1024/0301-1526/a000752
Singh, Hasday, Fever, hyperthermia and the heat shock response, Int J Hyperthermia, doi:10.3109/02656736.2013.808766
Sobajima, Nozawa, Ihori, Repeated Low-Temperature Sauna Therapy Improves Cardiac and Exercise Capacity as well as Immune Competence in Patients with Heart Failure, Circulation, doi:10.1161/circ.126.suppl_21.a10868
Soni, Nayak, Effect of inspiration cycle and ventilation rate on heat exchange in human respiratory airways, J Therm Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jtherbio.2019.07.026
Sturman, Ricard, Holmes, Conformational change of the coronavirus peplomer glycoprotein at pH 8.0 and 37 degrees C correlates with virus aggregation and virus-induced cell fusion, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.64.6.3042-3050.1990
Tomiyama, Watanabe, Honma, The effect of repetitive mild hyperthermia on body temperature, the autonomic nervous system, and innate and adaptive immunity, Biomed Res, doi:10.2220/biomedres.36.135
Tsan, Gao, Heat shock proteins and immune system, J Leukoc Biol, doi:10.1189/jlb.0109005
Tsuchiya, Shimizu, Tazawa, Effects of hot deep seawater bathing on the immune cell distribution in peripheral blood from healthy young men, Environ Health Prev Med, doi:10.1007/BF02897909
Tsuji, Hayashi, Kondo, Characteristics of hyperthermia-induced hyperventilation in humans, Temperature, doi:10.1080/23328940.2016.1143760
Tyrrell, Barrow, Arthur, Local hyperthermia benefits natural and experimental common colds, Annu Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.000343
Uzunoglu, Yentur, Kayar, Effect of mild heat stress on heat shock protein 70 in a balneotherapy model, Eur J Integr Med, doi:10.1016/j.eujim.2016.11.014
Wang, Crisis and Opportunities for the Chinese Hot Springs Industry in Year 2020
Wang, Tang, Feng, High Temperature and High Humidity Reduce the Transmission of COVID-19
Zellner, Hergovics, Roth, Human monocyte stimulation by experimental whole body hyperthermia, Wien Klin Wochenschr
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.12688/f1000research.23299.2",
"ISSN": [
"2046-1402"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.23299.2",
"abstract": "<ns4:p>Enveloped viruses such as SAR-CoV-2 are sensitive to heat and are destroyed by temperatures tolerable to humans. All mammals use fever to deal with infections and heat has been used throughout human history in the form of hot springs, saunas, hammams, steam-rooms, sweat-lodges, steam inhalations, hot mud and poultices to prevent and treat respiratory infections and enhance health and wellbeing. This paper reviews the evidence for using heat to treat and prevent viral infections and discusses potential cellular, physiological and psychological mechanisms of action. In the initial phase of infection, heat applied to the upper airways can support the immune system’s first line of defence by supporting muco-ciliary clearance and inhibiting or deactivating virions where they first lodge. This may be further enhanced by the inhalation of steam containing essential oils with anti-viral, mucolytic and anxiolytic properties. Heat applied to the whole body can further support the immune system’s second line of defence by mimicking fever and activating innate and acquired immune defences and building physiological resilience. Heat-based treatments also offer psychological benefits and enhanced mental wellness by focusing attention on positive action, enhancing relaxation and sleep, inducing 'forced-mindfulness', and invoking the power of positive thinking and ‘remembered wellness’. Heat is a cheap, convenient and widely accessible therapeutic modality and while no clinical protocols exist for using heat to treat COVID-19, protocols that draw from traditional practices and consider contraindications, adverse effects and infection control measures could be developed and implemented rapidly and inexpensively on a wide scale. While there are significant challenges in implementing heat-based therapies during the current pandemic, these therapies present an opportunity to integrate natural medicine, conventional medicine and traditional wellness practices, and support the wellbeing of both patients and medical staff, while building community resilience and reducing the likelihood and impact of future pandemics.</ns4:p>",
"assertion": [
{
"URL": "https://f1000research.com/articles/9-292/v2#article-reports",
"group": {
"label": "Current Referee Status",
"name": "current-referee-status"
},
"label": "Referee status",
"name": "referee-status",
"order": 0,
"value": "Indexed"
},
{
"URL": "https://f1000research.com/articles/9-292/v1#referee-response-62783",
"group": {
"label": "Article Reports",
"name": "article-reports"
},
"label": "Referee Report",
"name": "referee-response-62783",
"order": 0,
"value": "10.5256/f1000research.25720.r62783, Elizabeth A. Repasky, Department of Immunology, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, Buffalo, NY, USA, 13 May 2020, version 1, 1 approved, 1 approved with reservations"
},
{
"URL": "https://f1000research.com/articles/9-292/v2#referee-response-67436",
"group": {
"label": "Article Reports",
"name": "article-reports"
},
"label": "Referee Report",
"name": "referee-response-67436",
"order": 1,
"value": "10.5256/f1000research.28030.r67436, Jari Laukkanen, Institute of Clinical Medicine, Department of Medicine, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland, 20 Jul 2020, version 2, indexed"
},
{
"label": "Grant Information",
"name": "grant-information",
"order": 2,
"value": "The author(s) declared that no grants were involved in supporting this work"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright-info",
"order": 0,
"value": "This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Licence, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-5876-6565",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cohen",
"given": "Marc",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": "F1000Research",
"container-title-short": "F1000Res",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"f1000research.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-20T12:15:07Z",
"timestamp": 1595247307000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-20T15:15:29Z",
"timestamp": 1595258129000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-18T11:49:40Z",
"timestamp": 1695037780340
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 6,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
20
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1595203200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://f1000research.com/articles/9-292/v2/xml",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://f1000research.com/articles/9-292/v2/pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://f1000research.com/articles/9-292/v2/iparadigms",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "2560",
"original-title": [],
"page": "292",
"prefix": "10.12688",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
20
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
20
]
]
},
"publisher": "F1000 Research Ltd",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.05.007",
"article-title": "Essential oils used in aromatherapy: A systemic review.",
"author": "B Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "601-611",
"journal-title": "Asian Pac J Trop Biomed.",
"key": "ref-1",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.med.47.1.193",
"article-title": "Harnessing the power of the placebo effect and renaming it \"remembered wellness\".",
"author": "H Benson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "193-199",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Med.",
"key": "ref-2",
"volume": "47",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nyas.12998",
"article-title": "Mindfulness meditation and the immune system: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.",
"author": "D Black",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13-24",
"journal-title": "Ann N Y Acad Sci.",
"key": "ref-3",
"volume": "1373",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/jappl.1999.87.2.699",
"article-title": "Immune changes in humans during cold exposure: effects of prior heating and exercise.",
"author": "I Brenner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "699-710",
"journal-title": "J Appl Physiol (1985).",
"key": "ref-4",
"volume": "87",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0161749",
"article-title": "The Effect of Cold Showering on Health and Work: A Randomized Controlled Trial.",
"author": "G Buijze",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0161749",
"journal-title": "PLoS One.",
"key": "ref-5",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2011/734690",
"article-title": "The Effects of Temperature and Relative Humidity on the Viability of the SARS Coronavirus.",
"author": "K Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "734690",
"journal-title": "Adv Virol.",
"key": "ref-6",
"volume": "2011",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1507-1367(10)60065-X",
"article-title": "Hyperthermia – description of a method and a review of clinical applications.",
"author": "A Chicheł",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "267-275",
"journal-title": "Reports of Practical Oncology & Radiotherapy.",
"key": "ref-60",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10941665.2016.1276946",
"article-title": "Indulgence or therapy? Exploring the characteristics, motivations and experiences of hot springs bathers in Victoria, Australia.",
"author": "J Clark-Kennedy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "501-511",
"journal-title": "Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research.",
"key": "ref-7",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ptsp.2003.10.002",
"article-title": "Alternating hot and cold water immersion for athlete recovery: a review.",
"author": "D Cochrane",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "26-32",
"journal-title": "Physical Therapy in Sport.",
"key": "ref-8",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/aac.43.4.822",
"article-title": "Antiviral effect of hyperthermic treatment in rhinovirus infection.",
"author": "C Conti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "822-829",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother.",
"key": "ref-9",
"volume": "43",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"article-title": "Sauna as a valuable clinical tool for cardiovascular, autoimmune, toxicant- induced and other chronic health problems.",
"author": "W Crinnion",
"first-page": "215-225",
"journal-title": "Altern Med Rev.",
"key": "ref-10",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jviromet.2004.06.006",
"article-title": "Inactivation of the coronavirus that induces severe acute respiratory syndrome, SARS-CoV.",
"author": "M Darnell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "85-91",
"journal-title": "J Virol Methods.",
"key": "ref-11",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jir.1988.8.143",
"article-title": "Hyperthermia in humans enhances interferon-gamma synthesis and alters the peripheral lymphocyte population.",
"author": "J Downing",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "143-150",
"journal-title": "J Interferon Res.",
"key": "ref-12",
"volume": "8",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"article-title": "Stability of SARS coronavirus in human specimens and environment and its sensitivity to heating and UV irradiation.",
"author": "S Duan",
"first-page": "246-255",
"journal-title": "Biomed Environ Sci.",
"key": "ref-13",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.1978.58.3.529",
"article-title": "Renal effects of head-out water immersion in man: implications for an understanding of volume homeostasis.",
"author": "M Epstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "529-581",
"journal-title": "Physiol Rev.",
"key": "ref-14",
"volume": "58",
"year": "1978"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/07853899009148930",
"article-title": "Regular sauna bathing and the incidence of common colds.",
"author": "E Ernst",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "225-227",
"journal-title": "Ann Med.",
"key": "ref-15",
"volume": "22",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri3843",
"article-title": "Fever and the thermal regulation of immunity: the immune system feels the heat.",
"author": "S Evans",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "335-349",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol.",
"key": "ref-16",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra0910061",
"article-title": "Airway mucus function and dysfunction.",
"author": "J Fahy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2233-2247",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "ref-17",
"volume": "363",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms19061687",
"article-title": "Balneotherapy, Immune System, and Stress Response: A Hormetic Strategy?",
"author": "I Gálvez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci.",
"key": "ref-18",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00244-010-9611-5",
"article-title": "Blood, urine, and sweat (BUS) study: monitoring and elimination of bioaccumulated toxic elements.",
"author": "S Genuis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "344-357",
"journal-title": "Arch Environ Contam Toxicol.",
"key": "ref-19",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Effect of Steam Inhalation on Nasal Mucociliary Clearance in Normal Individuals and Nasal Disease State.",
"author": "A Gujrathi",
"first-page": "1262-1264",
"journal-title": "Journal of Contemporary Medical Research.",
"key": "ref-20",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0002-9343(00)00671-9",
"article-title": "Benefits and risks of sauna bathing.",
"author": "M Hannuksela",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "118-126",
"journal-title": "Am J Med.",
"key": "ref-21",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpregu.00115.2017",
"article-title": "Effects of heat and cold on health, with special reference to Finnish sauna bathing.",
"author": "I Heinonen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "R629-R638",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.",
"key": "ref-61",
"volume": "314",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jps.22724",
"article-title": "Biophysical characterization and conformational stability of Ebola and Marburg virus-like particles.",
"author": "L Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5156-5173",
"journal-title": "J Pharm Sci.",
"key": "ref-22",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202002.0332.v1",
"article-title": "Instability of Nucleic Acids in Airborne Microorganisms under Far Infrared Radiation.",
"author": "W Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref-23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2018/1857413",
"article-title": "Clinical Effects of Regular Dry Sauna Bathing: A Systematic Review.",
"author": "J Hussain",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1857413",
"journal-title": "Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.",
"key": "ref-24",
"volume": "2018",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ctim.2019.03.012",
"article-title": "A hot topic for health: Results of the Global Sauna Survey.",
"author": "J Hussain",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "223-234",
"journal-title": "Complement Ther Med.",
"key": "ref-25",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4085/1062-6050-47.2.184",
"article-title": "Heat stress and cardiovascular, hormonal, and heat shock proteins in humans.",
"author": "M Iguchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "184-190",
"journal-title": "J Athl Train.",
"key": "ref-56",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/npp.2016.148",
"article-title": "Sleep Health: Reciprocal Regulation of Sleep and Innate Immunity.",
"author": "M Irwin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "129-155",
"journal-title": "Neuropsychopharmacology.",
"key": "ref-26",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhin.2020.03.025",
"article-title": "Inactivation of coronaviruses by heat.",
"author": "G Kampf",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Hosp Infect.",
"key": "ref-27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2249.1991.tb08144.x",
"article-title": "Effects of in vivo hyperthermia on natural killer cell activity, in vitro proliferative responses and blood mononuclear cell subpopulations.",
"author": "M Kappel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "175-180",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Immunol.",
"key": "ref-28",
"volume": "84",
"year": "1991"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1902840116",
"article-title": "Low ambient humidity impairs barrier function and innate resistance against influenza infection.",
"author": "E Kudo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10905-10910",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.",
"key": "ref-29",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2017.10.018",
"article-title": "Frequent sauna bathing may reduce the risk of pneumonia in middle-aged Caucasian men: The KIHD prospective cohort study.",
"author": "S Kunutsor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "161-163",
"journal-title": "Respir Med.",
"key": "ref-30",
"volume": "132",
"year": "2017a"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10654-017-0311-6",
"article-title": "Sauna bathing reduces the risk of respiratory diseases: a long-term prospective cohort study.",
"author": "S Kunutsor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1107-1111",
"journal-title": "Eur J Epidemiol.",
"key": "ref-63",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2017b"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07853890.2018.1489143",
"article-title": "Longitudinal associations of sauna bathing with inflammation and oxidative stress: the KIHD prospective cohort study.",
"author": "S Kunutsor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "437-442",
"journal-title": "Ann Med.",
"key": "ref-64",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Lungs and ventilation in sauna.",
"author": "L Laitinen",
"first-page": "244-248",
"journal-title": "Ann Clin Res.",
"key": "ref-65",
"volume": "20",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1139/m89-160",
"article-title": "Effect of pH and temperature on the infectivity of human coronavirus 229E.",
"author": "A Lamarre",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "972-974",
"journal-title": "Can J Microbiol.",
"key": "ref-31",
"volume": "35",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pcad.2019.05.001",
"article-title": "Is sauna bathing protective of sudden cardiac death? A review of the evidence.",
"author": "J Laukkanen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "288-293",
"journal-title": "Prog Cardiovasc Dis.",
"key": "ref-66",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2018.04.008",
"article-title": "Cardiovascular and Other Health Benefits of Sauna Bathing: A Review of the Evidence.",
"author": "J Laukkanen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1111-1121",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc.",
"key": "ref-67",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.8187",
"article-title": "Association Between Sauna Bathing and Fatal Cardiovascular and All-Cause Mortality Events.",
"author": "T Laukkanen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "542-8",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med.",
"key": "ref-68",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eujim.2017.04.009",
"article-title": "The effects of aromatherapy essential oil inhalation on stress, sleep quality and immunity in healthy adults: Randomized controlled trial.",
"author": "M Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "79-86",
"journal-title": "Eur J Integr Med.",
"key": "ref-32",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.1890230313",
"article-title": "Inactivation of 12 viruses by heating steps applied during manufacture of a hepatitis B vaccine.",
"author": "P Lelie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "297-301",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol.",
"key": "ref-33",
"volume": "23",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3238/arztebl.2019.0537",
"article-title": "Health Risks and Interventions in Exertional Heat Stress.",
"author": "D Leyk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "537-544",
"journal-title": "Deutsches Arzteblatt international.",
"key": "ref-69",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Handbook of COVID-19 Preventionand Treatment China",
"author": "T Liang",
"key": "ref-34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1189/jlb.0511229",
"article-title": "Differentiation of CD8+ T cells into effector cells is enhanced by physiological range hyperthermia.",
"author": "T Mace",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "951-962",
"journal-title": "J Leukoc Biol.",
"key": "ref-35",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.rmed.2008.09.011",
"article-title": "Cold temperature and low humidity are associated with increased occurrence of respiratory tract infections.",
"author": "T Mäkinen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "456-462",
"journal-title": "Respir Med.",
"key": "ref-36",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"article-title": "The Finnish Sauna: A cultural index to settlement.",
"author": "C Mather",
"first-page": "494-504",
"journal-title": "A Assoc Am Geog.",
"key": "ref-37",
"volume": "53",
"year": "1963"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0196-0709(87)80037-6",
"article-title": "Effects of steam inhalation on nasal patency and nasal symptoms in patients with the common cold.",
"author": "D Ophir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "149-153",
"journal-title": "Am J Otolaryngol.",
"key": "ref-38",
"volume": "8",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2478/hukin-2013-0075",
"article-title": "Effect of a single finnish sauna session on white blood cell profile and cortisol levels in athletes and non-athletes.",
"author": "W Pilch",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "127-135",
"journal-title": "J Hum Kinet.",
"key": "ref-39",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3550308",
"article-title": "Temperature and Latitude Analysis to Predict Potential Spread and Seasonality for COVID-19",
"author": "M Sajadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref-40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/femspd/ftw106",
"article-title": "Thermoregulation as a disease tolerance defense strategy.",
"author": "A Schieber",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pathog Dis.",
"key": "ref-41",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1024/0301-1526/a000752",
"article-title": "Potential mechanisms for the effects of far-infrared on the cardiovascular system - a review.",
"author": "R Shemilt",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "303-312",
"journal-title": "Vasa.",
"key": "ref-42",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3109/02656736.2013.808766",
"article-title": "Fever, hyperthermia and the heat shock response.",
"author": "I Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "423-435",
"journal-title": "Int J Hyperthermia.",
"key": "ref-43",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Repeated Low-Temperature Sauna Therapy Improves Cardiac and Exercise Capacity as well as Immune Competence in Patients with Heart Failure.",
"author": "M Sobajima",
"first-page": "A10868",
"journal-title": "Circulation.",
"key": "ref-57",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtherbio.2019.07.026",
"article-title": "Effect of inspiration cycle and ventilation rate on heat exchange in human respiratory airways.",
"author": "B Soni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "357-367",
"journal-title": "J Therm Biol.",
"key": "ref-44",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.64.6.3042-3050.1990",
"article-title": "Conformational change of the coronavirus peplomer glycoprotein at pH 8.0 and 37 degrees C correlates with virus aggregation and virus-induced cell fusion.",
"author": "L Sturman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3042-50",
"journal-title": "J Virol.",
"key": "ref-45",
"volume": "64",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2220/biomedres.36.135",
"article-title": "The effect of repetitive mild hyperthermia on body temperature, the autonomic nervous system, and innate and adaptive immunity.",
"author": "C Tomiyama",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "135-142",
"journal-title": "Biomed Res.",
"key": "ref-46",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1189/jlb.0109005",
"article-title": "Heat shock proteins and immune system.",
"author": "M Tsan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "905-910",
"journal-title": "J Leukoc Biol.",
"key": "ref-58",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF02897909",
"article-title": "Effects of hot deep seawater bathing on the immune cell distribution in peripheral blood from healthy young men.",
"author": "Y Tsuchiya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "161-165",
"journal-title": "Environ Health Prev Med.",
"key": "ref-47",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/23328940.2016.1143760",
"article-title": "Characteristics of hyperthermia-induced hyperventilation in humans.",
"author": "B Tsuji",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "146-160",
"journal-title": "Temperature (Austin).",
"key": "ref-48",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.298.6683.1280",
"article-title": "Local hyperthermia benefits natural and experimental common colds.",
"author": "D Tyrrell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1280-1283",
"journal-title": "BMJ.",
"key": "ref-49",
"volume": "298",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.000343",
"article-title": "Hot news on the common cold.",
"author": "D Tyrrell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "35-47",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Microbiol.",
"key": "ref-50",
"volume": "42",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eujim.2016.11.014",
"article-title": "Effect of mild heat stress on heat shock protein 70 in a balneotherapy model.",
"author": "E Uzunoglu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "86-90",
"journal-title": "Eur J Integr Med.",
"key": "ref-51",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Crisis and Opportunities for the Chinese Hot Springs Industry in Year 2020.",
"author": "J Wang",
"key": "ref-52",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3551767",
"article-title": "High Temperature and High Humidity Reduce the Transmission of COVID-19",
"author": "J Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref-53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "First data on stability and resistance of SARS coronavirus compiled by members of WHO laboratory network, WHO Multi-center Collaborative Network on SARS Diagnosis",
"key": "ref-54",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"article-title": "Human monocyte stimulation by experimental whole body hyperthermia.",
"author": "M Zellner",
"first-page": "102-107",
"journal-title": "Wien Klin Wochenschr.",
"key": "ref-55",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2002"
}
],
"reference-count": 67,
"references-count": 67,
"relation": {
"has-review": [
{
"asserted-by": "subject",
"id": "10.5256/f1000research.28030.r67436",
"id-type": "doi"
}
]
},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://f1000research.com/articles/9-292/v2"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Pharmacology, Toxicology and Pharmaceutics",
"General Immunology and Microbiology",
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Turning up the heat on COVID-19: heat as a therapeutic intervention",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.crossmark-policy",
"update-to": [
{
"DOI": "10.12688/f1000research.23299.1",
"label": "New version",
"type": "new_version",
"updated": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-20T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1595203200000
}
}
],
"volume": "9"
}