Improved survival in intensive care unit in severe COVID-19 associated with amantadine use - retrospective study
et al., International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026, Nov 2022
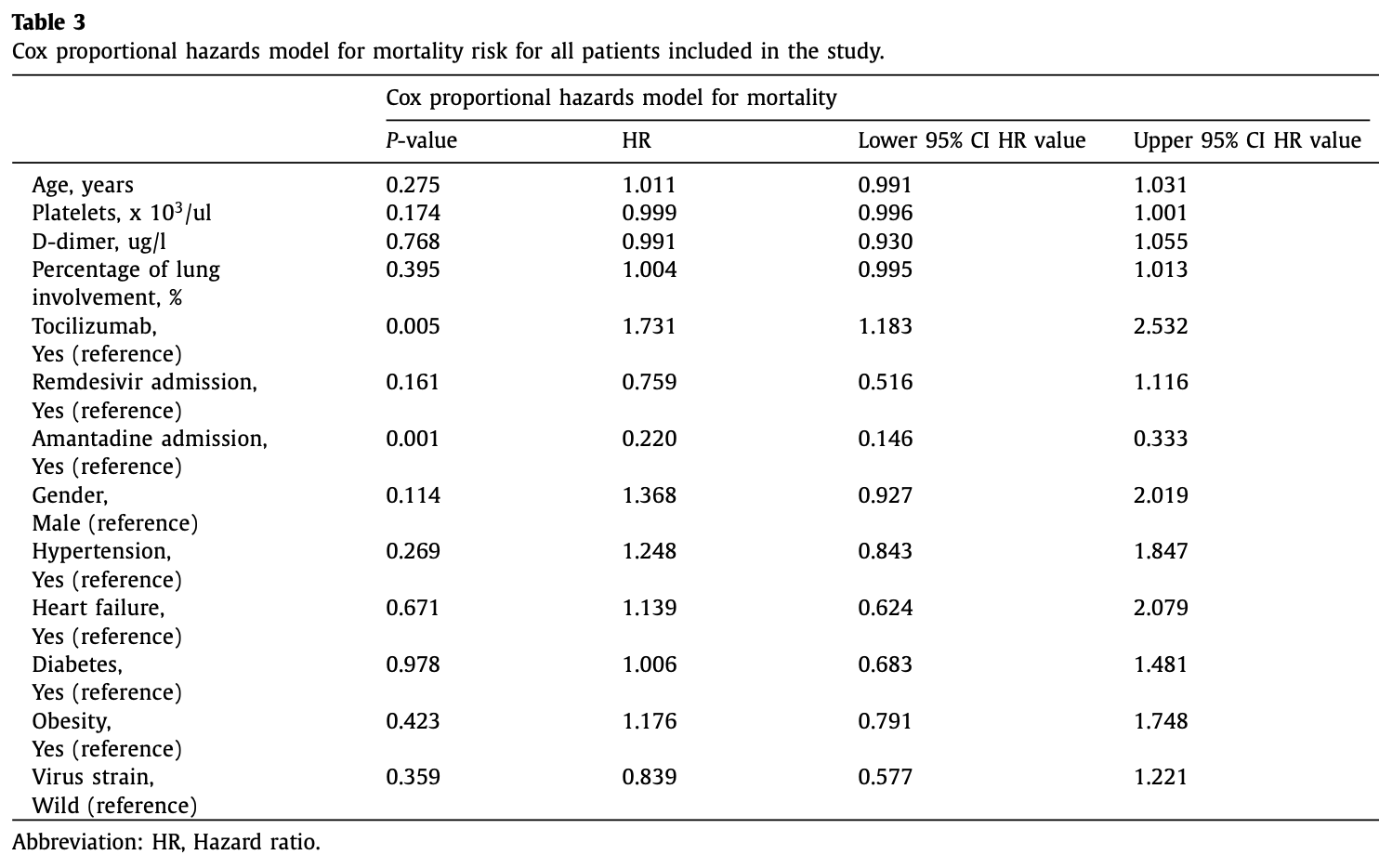
Retrospective 241 COVID-19 ICU patients requiring mechanical ventilation showing significantly lower mortality with intravenous amantadine. However the KM plot shows very high control deaths on day 1 and no treatment deaths days 2-4. Given biological plausibility and the median three-day lag before the first amantadine dose, this early divergence is best explained by immortal-time and baseline-severity confounding rather than a causal drug effect.
Chober et al., 30 Nov 2022, retrospective, Poland, peer-reviewed, 10 authors, study period 4 March, 2020 - 23 January, 2022.
Contact: daniel.chober@pum.edu.pl.
Improved survival in intensive care unit in severe COVID-19 associated with amantadine use - retrospective study
International Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026
Objectives: Possible immunomodulatory effect of amantadine in patients treated in intensive care unit (ICU), mostly among patients with brain injuries or vascular diseases was observed in several studies. The potential antiviral effect of amantadine against SARS-CoV-2 was discarded in clinical trials; however, immunomodulatory potential was not studied. The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of immunomodulatory amantadine therapy on mortality in patients with respiratory insufficiency due to COVID-19 requiring mechanical ventilation in ICU. Methods: Retrospective analysis of 241 cases of 141 (58.5%) receiving intravenous amantadine sulfate vs 100 (41.5%) controls on standard of care only was performed. Results: Overall mortality was 72.6%, being notably lower among amantadine treated patients (59.5%, n = 84) compared with controls (91%, n = 91), P -value = 0.001. In multivariate models administration of amantadine was independently associated with lower mortality rate (hazard ratio: 0.220, CI: 0.146-0.333 P -value = 0.001). Furthermore, survival was improved in patients who received amantadine; late administration of amantadine after 5th day was independently associated with lower mortality (hazard ratio: 0.560, CI: 0.313-0.999, P -value = 0.050).
Conclusion: In patients treated in ICU with severe respiratory failure, administration of amantadine is associated with lower mortality, which may be associated with the potential anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of this agent.
Declaration of competing interest The authors have no competing interests to declare.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
References
Abbasivash, Hasanloei, Kazempour, Mahdkhah, Ghoreishi et al., The effect of oral administration of amantadine on neurological outcome of patients with diffuse axonal injury in ICU, J Exp Neurosci
Biran, Ip, Ahn, Go, Wang et al., Tocilizumab among patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care unit: a multicentre observational study, Lancet Rheumatol
Chen, Han, Yang, Kim, Nair et al., SARS-CoV-2 infection causes dopaminergic neuron senescence, Research Square
Chober, Ąs, Bobrek-Lesiakowska, Budny-Finster, Hołda et al., Effectiveness of tocilizumab in patients with severe or critical lung involvement in COVID-19: a retrospective study, J Clin Med
Fj, Navarro, García-Martín, Agúndez, Anti-inflammatory effects of amantadine and memantine: possible therapeutics for the treatment of Covid-19?, J Pers Med
Gaskill, Yano, Kalpana, Javitch, Berman, Dopamine receptor activation increases HIV entry into primary human macrophages, PLoS One
Geisler, Sliwinski, Coyle, Masur, Doscher et al., The effects of amantadine and pemoline on cognitive functioning in multiple sclerosis, Arch Neurol
Ghalaenovi, Fattahi, Koohpayehzadeh, Khodadost, Fatahi et al., The effects of amantadine on traumatic brain injury outcome: a double-blind, randomized, controlled, clinical trial, Brain Inj
Giacino, Whyte, Bagiella, Kalmar, Childs et al., Placebocontrolled trial of amantadine for severe traumatic brain injury, N Engl J Med
Gualtieri, Chandler, Coons, Brown, Amantadine: a new clinical profile for traumatic brain injury, Clin Neuropharmacol
Hubsher, Haider, Okun, Amantadine: the journey from fighting flu to treating Parkinson disease, Neurology
Kraus, Smith, Butters, Donnell, Dixon et al., Effects of the dopaminergic agent and NMDA receptor antagonist amantadine on cognitive function, cerebral glucose metabolism and D2 receptor availability in chronic traumatic brain injury: a study using positron emission tomography (PET), Brain Inj
Kubera, Maes, Budziszewska, Basta-Kaim, Grygier, Inhibitory effects of amantadine on the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by stimulated in vitro human blood, Pharmacol Rep
Leclerc, Riker, Brown, May, Nocella et al., Amantadine and modafinil as neurostimulants following acute stroke: a retrospective study of intensive care unit patients, Neurocrit Care
Li, Zhang, Liu, Wu, Yi et al., Early amantadine treatment reduces the risk of death in patients with large hemisphere infarctions:a Chinese hospital-based study, BMC Neurol
Monto, Arden, Implications of viral resistance to amantadine in control of influenza, Clin Infect Dis
Peeters, Romieu, Su, Maloteaux, Hermans, Involvement of the sigma 1 receptor in the modulation of dopaminergic transmission by amantadine, Eur J Neurosci
Saniova, Drobny, Kneslova, Minarik, The outcome of patients with severe head injuries treated with amantadine sulphate, J Neural Transm
Shafiee, Ehteshami, Moosazadeh, Aghapour, Haddadi, Placebo-controlled trial of oral amantadine and zolpidem efficacy on the outcome of patients with acute severe traumatic brain injury and diffuse axonal injury, Caspian J Intern Med
Simanjuntak, Liang, Lee, Lin, Japanese encephalitis virus exploits dopamine D2 receptor-phospholipase C to target dopaminergic human neuronal cells, Front Microbiol
Stelmaschuk, Will, Meyers, Amantadine to treat cognitive dysfunction in moderate to severe traumatic brain injury, J Trauma Nurs
Stoof, Booij, Drukarch, Amantadine as N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor antagonist: new possibilities for therapeutic applications?, Clin Neurol Neurosurg
Wandinger, Hagenah, Klüter, Rothermundt, Peters et al., Effects of amantadine treatment on in vitro production of interleukin-2 in de-novo patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease, J Neuroimmunol
Zhong, Li, Ni, Zuo, Amantadine alleviates postoperative cognitive dysfunction possibly by preserving neurotrophic factor expression and dendritic arborization in the hippocampus of old rodents, Front Aging Neurosci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026",
"ISSN": [
"1201-9712"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026",
"alternative-id": [
"S1201971222005252"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Improved survival in intensive care unit in severe COVID-19 associated with amantadine use - retrospective study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of International Society for Infectious Diseases."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6775-4152",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Chober",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Czajkowski",
"given": "Zenon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2092-3737",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Aksak-Wąs",
"given": "Bogusz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dalewska-Kucharczyk",
"given": "Katarzyna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hołubczak",
"given": "Katarzyna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karasińska-Milchert",
"given": "Sylwia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jaremko",
"given": "Mateusz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Skowron",
"given": "Miłosz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karasińska-Cieślak",
"given": "Malwina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parczewski",
"given": "Miłosz",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"ijidonline.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-21T17:47:21Z",
"timestamp": 1663782441000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-27T04:08:30Z",
"timestamp": 1666843710000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100005632",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Narodowe Centrum Badań i Rozwoju"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
10,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-10-28T04:46:03Z",
"timestamp": 1666932363343
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667260800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-18T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1663459200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1201971222005252?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1201971222005252?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "143-151",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1179069518824851",
"article-title": "The effect of oral administration of amantadine on neurological outcome of patients with diffuse axonal injury in ICU",
"author": "Abbasivash",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Exp Neurosci",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0001",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30277-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab among patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care unit: a multicentre observational study",
"author": "Biran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e603",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0002",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 infection causes dopaminergic neuron senescence",
"author": "Chen",
"journal-title": "Research Square",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0003",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm11092286",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of tocilizumab in patients with severe or critical lung involvement in COVID-19: a retrospective study",
"author": "Chober",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2286",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0004",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0108232",
"article-title": "Dopamine receptor activation increases HIV entry into primary human macrophages",
"author": "Gaskill",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0005",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archneur.1996.00550020101021",
"article-title": "The effects of amantadine and pemoline on cognitive functioning in multiple sclerosis",
"author": "Geisler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "185",
"journal-title": "Arch Neurol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0006",
"volume": "53",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/02699052.2018.1476733",
"article-title": "The effects of amantadine on traumatic brain injury outcome: a double-blind, randomized, controlled, clinical trial",
"author": "Ghalaenovi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1050",
"journal-title": "Brain Inj",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0007",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1102609",
"article-title": "Placebo-controlled trial of amantadine for severe traumatic brain injury",
"author": "Giacino",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "819",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0008",
"volume": "366",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00002826-198908000-00003",
"article-title": "Amantadine: a new clinical profile for traumatic brain injury",
"author": "Gualtieri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "258",
"journal-title": "Clin Neuropharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0009",
"volume": "12",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0010",
"unstructured": "How long does it take for amantadine to start working? Drugs.com. https://www.drugs.com/medical-answers/long-amantadine-start-working-3546573/, 2022 (accessed 22 May 2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1212/WNL.0b013e31824e8f0d",
"article-title": "Amantadine: the journey from fighting flu to treating Parkinson disease",
"author": "Hubsher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1096",
"journal-title": "Neurology",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0011",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0012",
"unstructured": "Influenza antiviral drug resistance, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/flu/treatment/antiviralresistance.htm, 2021 (accessed 22 May 2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jpm10040217",
"article-title": "Anti-inflammatory effects of amantadine and memantine: possible therapeutics for the treatment of Covid-19?",
"author": "Jiménez-Jiménez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "J Pers Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0013",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/02699050400025059",
"article-title": "Effects of the dopaminergic agent and NMDA receptor antagonist amantadine on cognitive function, cerebral glucose metabolism and D2 receptor availability in chronic traumatic brain injury: a study using positron emission tomography (PET)",
"author": "Kraus",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "471",
"journal-title": "Brain Inj",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0014",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1734-1140(09)70173-2",
"article-title": "Inhibitory effects of amantadine on the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by stimulated in vitro human blood",
"author": "Kubera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1105",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0015",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12028-020-00986-4",
"article-title": "Amantadine and modafinil as neurostimulants following acute stroke: a retrospective study of intensive care unit patients",
"author": "Leclerc",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102",
"journal-title": "Neurocrit Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0016",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12883-021-02444-w",
"article-title": "Early amantadine treatment reduces the risk of death in patients with large hemisphere infarctions:a Chinese hospital-based study",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "419",
"journal-title": "BMC Neurol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0017",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/clinids/15.2.362",
"article-title": "Implications of viral resistance to amantadine in control of influenza",
"author": "Monto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "362",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0019",
"volume": "15",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.0953-816X.2004.03297.x",
"article-title": "Involvement of the sigma 1 receptor in the modulation of dopaminergic transmission by amantadine",
"author": "Peeters",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2212",
"journal-title": "Eur J Neurosci",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0020",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00702-004-0112-4",
"article-title": "The outcome of patients with severe head injuries treated with amantadine sulphate",
"author": "Saniova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "511",
"journal-title": "J Neural Transm (Vienna)",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0021",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"article-title": "Placebo-controlled trial of oral amantadine and zolpidem efficacy on the outcome of patients with acute severe traumatic brain injury and diffuse axonal injury",
"author": "Shafiee",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "Caspian J Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0022",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2017.00651",
"article-title": "Japanese encephalitis virus exploits dopamine D2 receptor-phospholipase C to target dopaminergic human neuronal cells",
"author": "Simanjuntak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "651",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0023",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/JTN.0000000000000138",
"article-title": "Amantadine to treat cognitive dysfunction in moderate to severe traumatic brain injury",
"author": "Stelmaschuk",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "194",
"journal-title": "J Trauma Nurs",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0024",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/0303-8467(92)90006-O",
"article-title": "Amantadine as N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor antagonist: new possibilities for therapeutic applications?",
"author": "Stoof",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S4",
"journal-title": "Clin Neurol Neurosurg",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0025",
"volume": "94",
"year": "1992"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0165-5728(99)00093-4",
"article-title": "Effects of amantadine treatment on in vitro production of interleukin-2 in de-novo patients with idiopathic Parkinson's disease",
"author": "Wandinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "214",
"journal-title": "J Neuroimmunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0026",
"volume": "98",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnagi.2020.605330",
"article-title": "Amantadine alleviates postoperative cognitive dysfunction possibly by preserving neurotrophic factor expression and dendritic arborization in the hippocampus of old rodents",
"author": "Zhong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "427",
"journal-title": "Front Aging Neurosci",
"key": "10.1016/j.ijid.2022.09.026_bib0027",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 26,
"references-count": 26,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1201971222005252"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Improved survival in intensive care unit in severe COVID-19 associated with amantadine use - retrospective study",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "124"
}