Early Convalescent Plasma Therapy and Mortality Among US Veterans Hospitalized With Nonsevere COVID-19: An Observational Analysis Emulating a Target Trial
et al., The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab330, NCT04545047, Jun 2021
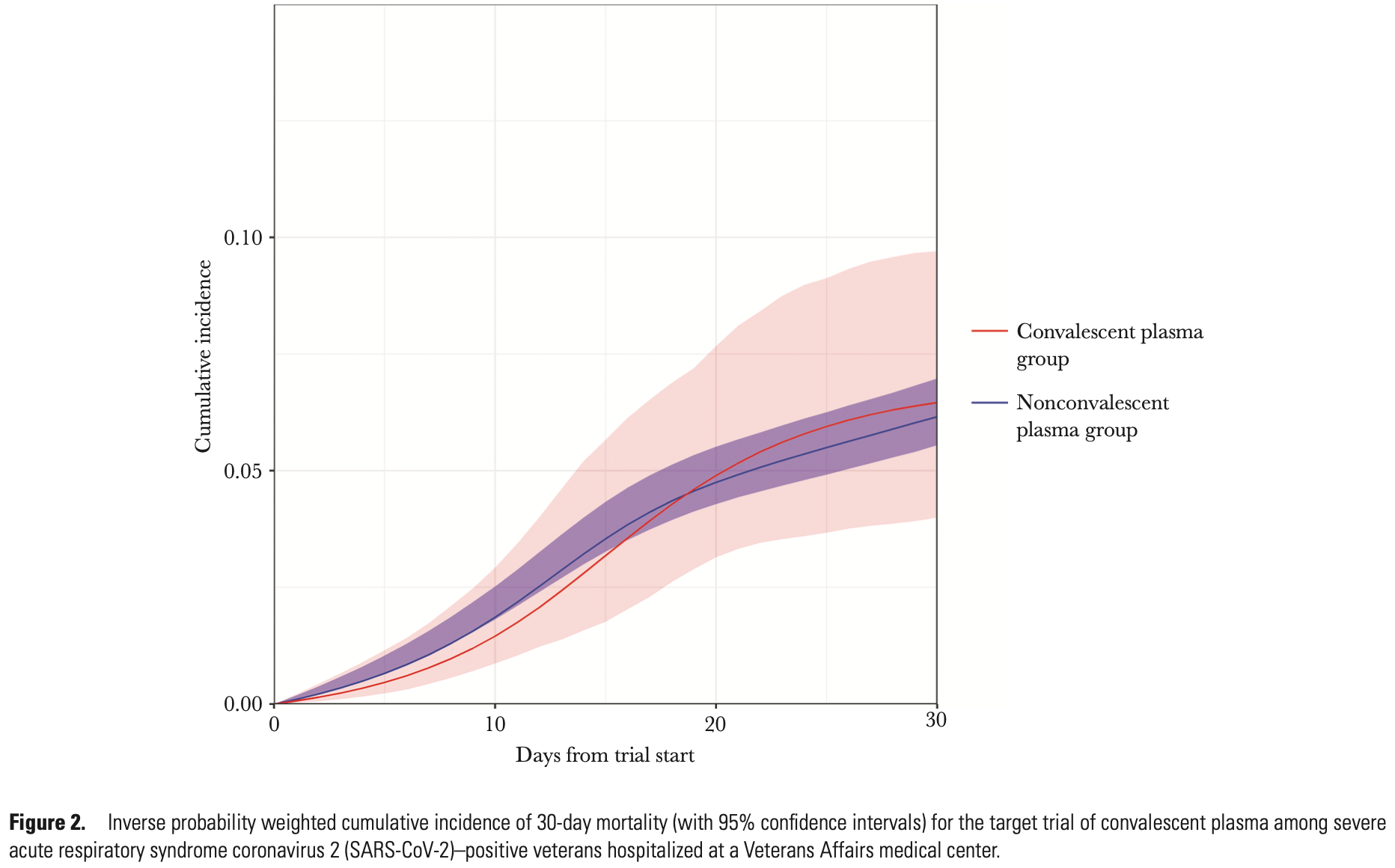
Target trial emulation with 4,755 patients showing no significant difference in 30-day mortality with convalescent plasma.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 4.0% higher, HR 1.04, p = 0.88, treatment 402, control 4,642.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Cho et al., 21 Jun 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 24 authors, trial NCT04545047 (history).
Contact: kelly.cho@va.gov.
Early Convalescent Plasma Therapy and Mortality Among US Veterans Hospitalized With Nonsevere COVID-19: An Observational Analysis Emulating a Target Trial
The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiab330
Background. Early convalescent plasma transfusion may reduce mortality in patients with nonsevere coronavirus disease 2019 . Methods. This study emulates a (hypothetical) target trial using observational data from a cohort of US veterans admitted to a Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) facility between 1 May and 17 November 2020 with nonsevere COVID-19. The intervention was convalescent plasma initiated within 2 days of eligibility. Thirty-day mortality was compared using cumulative incidence curves, risk differences, and hazard ratios estimated from pooled logistic models with inverse probability weighting to adjust for confounding. Results. Of 11 269 eligible person-trials contributed by 4755 patients, 402 trials were assigned to the convalescent plasma group. Forty and 671 deaths occurred within the plasma and nonplasma groups, respectively. The estimated 30-day mortality risk was 6.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.0%-9.7%) in the plasma group and 6.2% (95% CI, 5.6%-7.0%) in the nonplasma group. The associated risk difference was 0.30% (95% CI, -2.30% to 3.60%) and the hazard ratio was 1.04 (95% CI, .64-1.62). Conclusions. Our target trial emulation estimated no meaningful differences in 30-day mortality between nonsevere COVID-19 patients treated and untreated with convalescent plasma. Clinical Trials Registration. NCT04545047.
Supplementary Data Supplementary materials are available at The Journal of Infectious Diseases online. Consisting of data provided by the authors to benefit the reader, the posted materials are not copyedited and are the sole responsibility of the authors, so questions or comments should be addressed to the corresponding author. Notes Author contributions. The study was conceptualized by KC, SCK, KEK, ALM, HG, KJ, MK, GDH, JPC, DRG, MAH, NLS, and JMG. Full access to all the data in the study and responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis are affirmed by KK and HMW. Data curation was performed by KC, SCK., KEK, ALM, HG, HMW, AD, ERT, JP, AH, and DRG. Analyses were performed by KC, SCK, KEK, ALM, HG, HMW, AD, ERT, JP, AH, ERG, MAH, NLS, and JMG.
References
Agarwal, Mukherjee, Kumar, Chatterjee, Bhatnagar et al., Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate covid-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID Trial), BMJ
Alqahtani, Abdulrahman, Almadani, Randomized controlled trial of convalescent plasma therapy against standard therapy in patients with severe COVID-19 disease, Sci Rep
Avendano-Sola, Ramos-Martinez, Munez-Rubio, Convalescent plasma for COVID-19: a multicenter, randomized clinical trial, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.26.20182444
Balcells, Rojas, Corre, Early versus deferred anti-SARS-CoV-2 convalescent plasma in patients admitted for COVID-19: a randomized phase II clinical trial, PLoS Med
Bennett-Guerrero, Romeiser, Talbot, Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 convalescent plasma versus standard plasma in coronavirus disease 2019 infected hospitalized patients in New York: a double-blind randomized trial, Crit Care Med
Budhiraja, Dewan, Aggarwal, Effectiveness of convalescent plasma in Indian patients with COVID-19, Blood Cells Mol Dis
Gharbharan, Jordans, Geurtsvankessel, Effects of potent neutralizing antibodies from convalescent plasma in patients hospitalized for severe SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nat Commun
Hernán, Logan, Observational studies analyzed like randomized experiments: an application to postmenopausal hormone therapy and coronary heart disease, Epidemiology
Hernán, Robins, Using big data to emulate a target trial when a randomized trial is not available, Am J Epidemiol
Hernán, Sauer, Hernández-Díaz, Platt, Shrier, Specifying a target trial prevents immortal time bias and other self-inflicted injuries in observational analyses, J Clin Epidemiol
Joyner, Carter, Senefeld, Convalescent plasma antibody levels and the risk of death from Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Klassen, Senefeld, Johnson, The effect of convalescent plasma therapy on mortality among patients with COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Mayo Clin Proc
Li, Zhang, Hu, Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Libster, Marc, Wappner, Fundación INFANT-COVID-19 Group. Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe Covid-19 in older adults, N Engl J Med
Luchsinger, Ransegnola, Jin, Serological assays estimate highly variable SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody activity in recovered COVID-19 patients, J Clin Microbiol
Ngwa, Cabral, Cheng, A comparison of time dependent Cox regression, pooled logistic regression and cross sectional pooling with simulations and an application to the Framingham heart study, BMC Med Res Methodol
Rasheed, Fatak, Hashim, The therapeutic potential of convalescent plasma therapy on treating criticallyill COVID-19 patients residing in respiratory care units in hospitals in Baghdad, Iraq, Infez Med
Rodríguez, Novelli, Rojas, Autoinflammatory and autoimmune conditions at the crossroad of COVID-19, J Autoimmun
Rojas, Anaya, Why will it never be known if convalescent plasma is effective for COVID-19, J Transl Autoimmun
Rojas, Rodríguez, Monsalve, Convalescent plasma in Covid-19: possible mechanisms of action, Autoimmun Rev
Salazar, Christensen, Graviss, Significantly decreased mortality in a large cohort of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients transfused early with convalescent plasma containing high-titer anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein IgG, Am J Pathol
Salazar, Christensen, Graviss, Treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 patients with convalescent plasma reveals a signal of significantly decreased mortality, Am J Pathol
Sethuraman, Jeremiah, Ryo, Interpreting diagnostic tests for SARS-CoV-2, JAMA
Simonovich, Pratx, Scibona, A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Wang, Cao, Zeng, Zhang, Luo, The collective wisdom in the COVID-19 research: comparison and synthesis of epidemiological parameter estimates in preprints and peer-reviewed articles, Int J Infect Dis
Wang, Huo, Dai, Convalescent plasma may be a possible treatment for COVID-19: a systematic review, Int Immunopharmacol
Wang, Zhang, Sang, Kinetics of viral load and antibody response in relation to COVID-19 severity, J Clin Invest
Woolf, Chapman, Lee, COVID-19 as the leading cause of death in the United States, JAMA
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab330",
"ISSN": [
"0022-1899",
"1537-6613"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiab330",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Early convalescent plasma transfusion may reduce mortality in patients with nonsevere coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>This study emulates a (hypothetical) target trial using observational data from a cohort of US veterans admitted to a Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) facility between 1 May and 17 November 2020 with nonsevere COVID-19. The intervention was convalescent plasma initiated within 2 days of eligibility. Thirty-day mortality was compared using cumulative incidence curves, risk differences, and hazard ratios estimated from pooled logistic models with inverse probability weighting to adjust for confounding.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Of 11 269 eligible person-trials contributed by 4755 patients, 402 trials were assigned to the convalescent plasma group. Forty and 671 deaths occurred within the plasma and nonplasma groups, respectively. The estimated 30-day mortality risk was 6.5% (95% confidence interval [CI], 4.0%–9.7%) in the plasma group and 6.2% (95% CI, 5.6%–7.0%) in the nonplasma group. The associated risk difference was 0.30% (95% CI, −2.30% to 3.60%) and the hazard ratio was 1.04 (95% CI, .64–1.62).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>Our target trial emulation estimated no meaningful differences in 30-day mortality between nonsevere COVID-19 patients treated and untreated with convalescent plasma.</jats:p><jats:p>Clinical Trials Registration. NCT04545047.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1727-7076",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts Veterans Epidemiology Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cho",
"given": "Kelly",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Seattle Epidemiologic Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Seattle, Washington, USA"
}
],
"family": "Keithly",
"given": "Sarah C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts Veterans Epidemiology Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"family": "Kurgansky",
"given": "Katherine E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1258-7278",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departments of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Madenci",
"given": "Arin L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6700-2129",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts Veterans Epidemiology Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gerlovin",
"given": "Hanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts Veterans Epidemiology Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"family": "Marucci-Wellman",
"given": "Helen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Seattle Epidemiologic Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Seattle, Washington, USA"
}
],
"family": "Doubleday",
"given": "Annie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Seattle Epidemiologic Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Seattle, Washington, USA"
}
],
"family": "Thomas",
"given": "Eva R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts Veterans Epidemiology Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"family": "Park",
"given": "Yojin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts Veterans Epidemiology Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"family": "Ho",
"given": "Yuk-Lam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Seattle Epidemiologic Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Seattle, Washington, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, School of Public Health, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, USA"
},
{
"name": "Vaccine and Infectious Disease Division, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, Washington, USA"
}
],
"family": "Sugimoto",
"given": "Jonathan D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Seattle Epidemiologic Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Seattle, Washington, USA"
}
],
"family": "Moore",
"given": "Kathryn P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Seattle Epidemiologic Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Seattle, Washington, USA"
}
],
"family": "Peterson",
"given": "Alexander C",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts Veterans Epidemiology Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"family": "Hoag",
"given": "Constance",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Boston Healthcare System, Department of Veterans Affairs, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Boston University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"family": "Gupta",
"given": "Kalpana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Washington, District of Columbia, USA"
}
],
"family": "Jeans",
"given": "Karen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Washington, District of Columbia, USA"
}
],
"family": "Klote",
"given": "Molly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Washington, District of Columbia, USA"
}
],
"family": "Ramoni",
"given": "Rachel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Washington, District of Columbia, USA"
}
],
"family": "Huang",
"given": "Grant D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts Veterans Epidemiology Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"family": "Casas",
"given": "Juan P",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts Veterans Epidemiology Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Biostatistics, Boston University School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"family": "Gagnon",
"given": "David R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Departments of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"family": "Hernán",
"given": "Miguel A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Seattle Epidemiologic Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Seattle, Washington, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Epidemiology, School of Public Health, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, USA"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Nicholas L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts Veterans Epidemiology Research and Information Center, Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA"
}
],
"family": "Gaziano",
"given": "J Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-19T11:08:01Z",
"timestamp": 1624100881000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-05T03:44:24Z",
"timestamp": 1699155864000
},
"funder": [
{
"name": "Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Office of Research and Development"
},
{
"name": "VA-CAUSAL Methods Core"
},
{
"name": "VA Boston Healthcare System"
},
{
"name": "VA Puget Sound Healthcare System"
},
{
"award": [
"VA HSR RES 13–457"
],
"name": "VA Informatics and Computing Infrastructure"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000738",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Department of Veterans Affairs"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-21T05:40:55Z",
"timestamp": 1710999655881
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 14,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
21
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
21
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
17
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiab330/39354334/jiab330.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/jid/article-pdf/224/6/967/40406164/jiab330.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "http://academic.oup.com/jid/article-pdf/224/6/967/40406164/jiab330.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "967-975",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
21
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
15
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
17
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.24865",
"article-title": "COVID-19 as the leading cause of death in the United States",
"author": "Woolf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "123",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0001",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102506",
"article-title": "Autoinflammatory and autoimmune conditions at the crossroad of COVID-19",
"author": "Rodríguez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102506",
"journal-title": "J Autoimmun",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0002",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102554",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma in Covid-19: possible mechanisms of action",
"author": "Rojas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102554",
"journal-title": "Autoimmun Rev",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0003",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.8259",
"article-title": "Interpreting diagnostic tests for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Sethuraman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2249",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0004",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.10044",
"article-title": "Effect of convalescent plasma therapy on time to clinical improvement in patients with severe and life-threatening COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "460",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0005",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI138759",
"article-title": "Kinetics of viral load and antibody response in relation to COVID-19 severity",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5235",
"journal-title": "J Clin Invest",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0006",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107262",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma may be a possible treatment for COVID-19: a systematic review",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107262",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0007",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtauto.2020.100069",
"article-title": "Why will it never be known if convalescent plasma is effective for COVID-19",
"author": "Rojas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100069",
"journal-title": "J Transl Autoimmun",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0008",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/EDE.0b013e3181875e61",
"article-title": "Observational studies analyzed like randomized experiments: an application to postmenopausal hormone therapy and coronary heart disease",
"author": "Hernán",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "Epidemiology",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0009",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/aje/kwv254",
"article-title": "Using big data to emulate a target trial when a randomized trial is not available",
"author": "Hernán",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "758",
"journal-title": "Am J Epidemiol",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0010",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30483-7",
"article-title": "A minimal common outcome measure set for COVID-19 clinical research",
"author": "WHO Working Group on the Clinical Characterisation and Management of COVID-19 infection",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e192",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0011",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12874-016-0248-6",
"article-title": "A comparison of time dependent Cox regression, pooled logistic regression and cross sectional pooling with simulations and an application to the Framingham heart study",
"author": "Ngwa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "148",
"journal-title": "BMC Med Res Methodol",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0012",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"author": "US Food and Drug Administration",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jclinepi.2016.04.014",
"article-title": "Specifying a target trial prevents immortal time bias and other self-inflicted injuries in observational analyses",
"author": "Hernán",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "70",
"journal-title": "J Clin Epidemiol",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0014",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00897-7",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2049",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0015",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-89444-5",
"article-title": "Randomized controlled trial of convalescent plasma therapy against standard therapy in patients with severe COVID-19 disease",
"author": "AlQahtani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9927",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0016",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000005066",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 convalescent plasma versus standard plasma in coronavirus disease 2019 infected hospitalized patients in New York: a double-blind randomized trial",
"author": "Bennett-Guerrero",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1015",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0017",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3939",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma in the management of moderate covid-19 in adults in India: open label phase II multicentre randomised controlled trial (PLACID Trial)",
"author": "Agarwal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m3939",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0018",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma for COVID-19: a multicenter, randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Avendano-Sola",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0019",
"year": "29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003415",
"article-title": "Early versus deferred anti-SARS-CoV-2 convalescent plasma in patients admitted for COVID-19: a randomized phase II clinical trial",
"author": "Balcells",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1003415",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0020",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of potent neutralizing antibodies from convalescent plasma in patients hospitalized for severe SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Gharbharan",
"first-page": "2021; 12:3189.",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033700",
"article-title": "Early high-titer plasma therapy to prevent severe Covid-19 in older adults",
"author": "Libster",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "610",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0022",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The therapeutic potential of convalescent plasma therapy on treating critically-ill COVID-19 patients residing in respiratory care units in hospitals in Baghdad, Iraq",
"author": "Rasheed",
"first-page": "357",
"journal-title": "Infez Med",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0023",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031304",
"article-title": "A randomized trial of convalescent plasma in Covid-19 severe pneumonia",
"author": "Simonovich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "619",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0024",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2021.02.008",
"article-title": "The effect of convalescent plasma therapy on mortality among patients with COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Klassen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1262",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0025",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031893",
"article-title": "Convalescent plasma antibody levels and the risk of death from Covid-19",
"author": "Joyner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1015",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0026",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.08.001",
"article-title": "Treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 patients with convalescent plasma reveals a signal of significantly decreased mortality",
"author": "Salazar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2290",
"journal-title": "Am J Pathol",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0027",
"volume": "190",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajpath.2020.10.008",
"article-title": "Significantly decreased mortality in a large cohort of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients transfused early with convalescent plasma containing high-titer anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein IgG",
"author": "Salazar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "90",
"journal-title": "Am J Pathol",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0028",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JCM.02005-20",
"article-title": "Serological assays estimate highly variable SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody activity in recovered COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Luchsinger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e02005",
"journal-title": "J Clin Microbiol",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0029",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "US Food and Drug Administration",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0030"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.040",
"article-title": "The collective wisdom in the COVID-19 research: comparison and synthesis of epidemiological parameter estimates in preprints and peer-reviewed articles",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0031",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcmd.2021.102548",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of convalescent plasma in Indian patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Budhiraja",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102548",
"journal-title": "Blood Cells Mol Dis",
"key": "2021091718343679700_CIT0032",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 32,
"references-count": 32,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/article/224/6/967/6307367"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Early Convalescent Plasma Therapy and Mortality Among US Veterans Hospitalized With Nonsevere COVID-19: An Observational Analysis Emulating a Target Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "224"
}