Budesonide reduces COVID-19 risk: real-time meta analysis of 15 studies
, Dec 2025
Budesonide for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
April 2021, now with p = 0.0000011 from 15 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,300+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
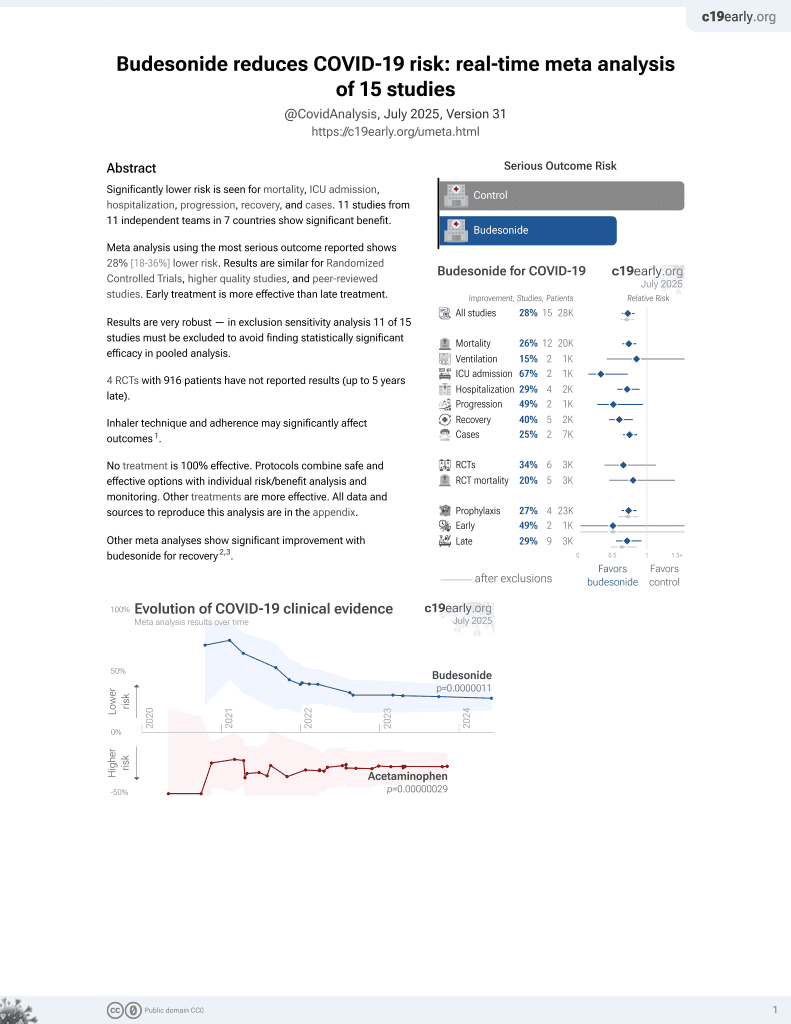
Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, ICU admission, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and cases. 11 studies from 11 independent teams in 7 countries show significant benefit.
Meta analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 28% [18‑36%] lower risk. Results are similar for Randomized Controlled Trials, higher quality studies, and peer-reviewed studies. Early treatment is more effective than late treatment.
Results are very robust — in exclusion sensitivity analysis 11 of 15 studies must be excluded to avoid finding statistically significant efficacy in pooled analysis.
Control Budesonide
4 RCTs with 916 patients have not reported results (up to 5 years late).
Inhaler technique and adherence may significantly affect outcomes1.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. Other treatments are more effective. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
Other meta analyses show significant improvement with budesonide for recovery2,3.
Covid Analysis et al., Dec 2025, preprint, 1 author.