Ongoing Treatment with a Spore-Based Probiotic Containing Five Strains of Bacillus Improves Outcomes of Mild COVID-19
et al., Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030488, Jan 2023
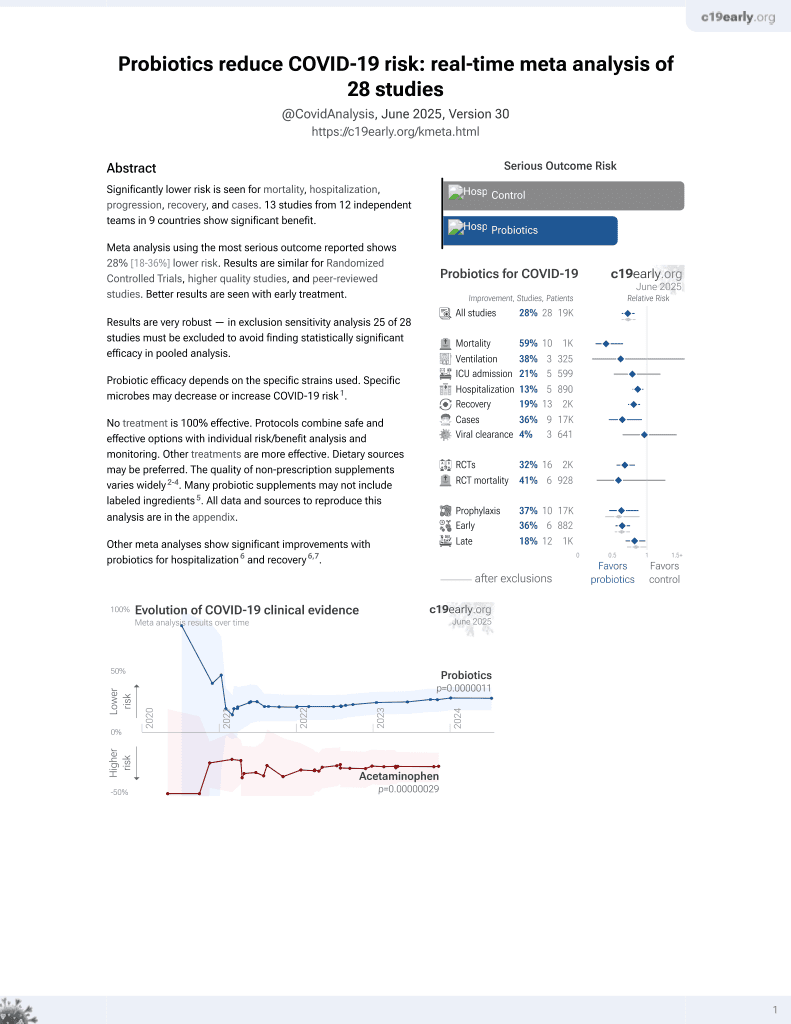
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
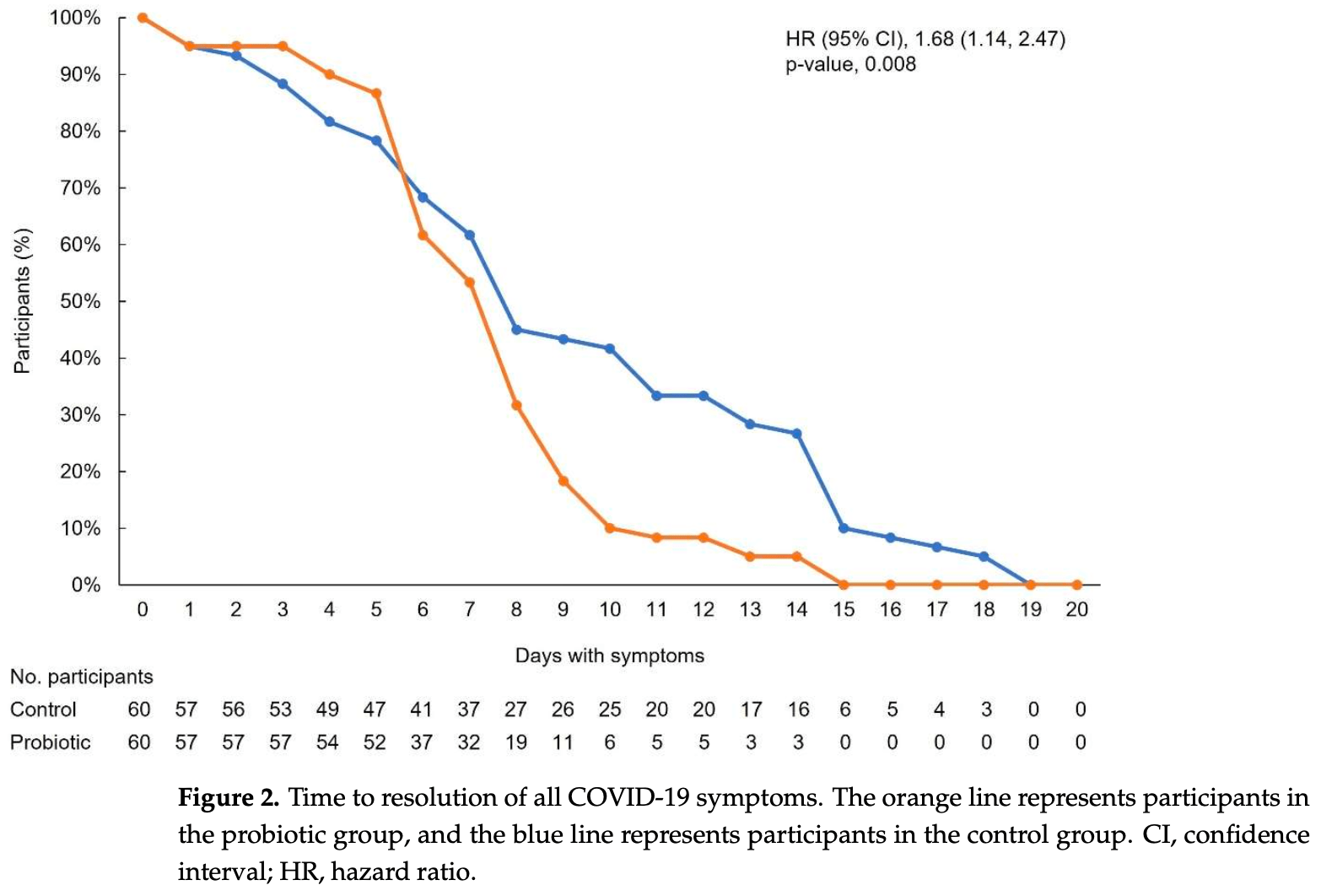
Retrospective 60 patients in Romania taking probiotics and 60 matched controls, showing faster symptom resolution with the use of probiotics. Spore-based probiotic containing five strains of Bacillus.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk1.
|
symptom resolution, 40.5% lower, HR 0.60, p = 0.008, treatment 60, control 60, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment.
|
|
resolution of fever, 37.5% lower, HR 0.62, p = 0.02, treatment 60, control 60, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, fever.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Catinean et al., 17 Jan 2023, retrospective, Romania, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, study period 15 September, 2020 - 15 February, 2021.
Contact: ana.sida04@gmail.com (corresponding author).
Ongoing Treatment with a Spore-Based Probiotic Containing Five Strains of Bacillus Improves Outcomes of Mild COVID-19
Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu15030488
Spore-based Bacillus probiotic treatment improves intestinal health. The intestinal microbiota influences both the innate and adaptive immune responses. As such, the influence of ongoing spore-based probiotic treatment (five probiotic strains of Bacillus) on the clinical outcomes of mild COVID-19 was evaluated in this retrospective, observational study. Demographics, medical history, probiotic use, and COVID-19 symptom information were collected. The study included 120 patients with a PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and mild COVID-19 symptoms. The probiotic group (n = 60) comprised patients with ongoing probiotic treatment (≥1 month); the control group comprised patients not taking probiotics (n = 60). The primary outcome was time to symptom resolution; secondary outcomes included time to fever resolution and presence of digestive symptoms. The probiotic group had a significantly shorter time to symptom resolution (mean (95% confidence interval) days: control group, 8.48 (6.56, 10.05); probiotic group, 6.63 (5.56; 6.63); p = 0.003) and resolution of fever (control group, 2.67 (1.58, 3.61); probiotic group, 1.48 (1.21, 2.03); p < 0.001). More patients in the probiotic group (n = 53) than in the control group (n = 34) did not have digestive symptoms (p < 0.001). Among adults with mild COVID-19, participants receiving ongoing probiotic treatment had a shorter clinical course, and fewer had digestive symptoms compared with those not taking probiotics.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose.
References
Akour, Probiotics and COVID-19: Is there any link?, Lett. Appl. Microbiol, doi:10.1111/lam.13334
Belon, Skidmore, Mehra, Walter, Effect of a fever in viral infections-The 'Goldilocks' phenomenon?, World J. Clin. Cases, doi:10.12998/wjcc.v9.i2.296
Beyerstedt, Casaro, Rangel, COVID-19: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6
Blackett, Wainberg, Elkind, Freedberg, Potential long coronavirus disease 2019 gastrointestinal symptoms 6 months after coronavirus infection are associated with mental health symptoms, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.040
Boeck, Cauwenberghs, Spacova, Gehrmann, Eilers et al., Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of a Throat Spray with Selected Lactobacilli in COVID-19
Carsetti, Zaffina, Piano Mortari, Terreri, Corrente et al., Different Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Asymptomatic, Mild, and Severe Cases, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.610300
Catinean, Neag, Krishnan, Muntean, Bocsan et al., Probiotic Bacillus Spores Together with Amino Acids and Immunoglobulins Exert Protective Effects on a Rat Model of Ulcerative Colitis, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12123607
Clemente, Manasson, Scher, The role of the gut microbiome in systemic inflammatory disease, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.j5145
Copaescu, Smibert, Gibson, Phillips, Trubiano, The role of IL-6 and other mediators in the cytokine storm associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.07.001
Deleu, Machiels, Raes, Verbeke, Vermeire, Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: An overlooked therapy for IBD?, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103293
Dound, Jadhav, Devale, Bayne, Krishnan et al., The effect of Probiotic Bacillus Subtilis HU58 on Immune Function in Healthy Human, Indian Pract
El-Radhi, Pathogenesis of fever
Garbers, Heink, Korn, Rose-John, Interleukin-6: Designing specific therapeutics for a complex cytokine, Nat. Rev. Drug Discov, doi:10.1038/nrd.2018.45
Geva-Zatorsky, Sefik, Kua, Pasman, Tan et al., Mining the Human Gut Microbiota for Immunomodulatory Organisms, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.022
Gu, Chen, Wu, Chen, Gao et al., Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 or H1N1 Influenza, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa709
Hamming, Timens, Bulthuis, Lely, Navis et al., Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis, J. Pathol, doi:10.1002/path.1570
Han, Shin, Lee, Kim, Yang et al., Lactobacillus rhamnosus HDB1258 modulates gut microbiota-mediated immune response in mice with or without lipopolysaccharide-induced systemic inflammation, BMC Microbiol, doi:10.1186/s12866-021-02192-4
Kageyama, Nishizaki, Aida, Yayama, Ebisui et al., Lactobacillus plantarum induces innate cytokine responses that potentially provide a protective benefit against COVID-19: A single-arm, double-blind, prospective trial combined with an in vitro cytokine response assay, Exp. Ther. Med, doi:10.3892/etm.2021.10942
Kaiser, Upton, Mocarski, Viral modulation of programmed necrosis, Curr. Opin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2013.05.019
Kalman, Schwartz, Alvarez, Feldman, Pezzullo et al., A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel-group dual site trial to evaluate the effects of a Bacillus coagulans-based product on functional intestinal gas symptoms, BMC Gastroenterol, doi:10.1186/1471-230X-9-85
Kurian, Unnikrishnan, Miraj, Bagchi, Banerjee et al., Probiotics in Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19: Current Perspective and Future Prospects, Arch. Med. Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002
Lau, Ng, Yu, Targeting the Gut Microbiota in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Hype or Hope?, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.009
Leal-Martinez, Abarca-Bernal, Garcia-Perez, Gonzalez-Tolosa, Cruz-Cazares et al., Effect of a Nutritional Support System to Increase Survival and Reduce Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 in Stage III and Comorbidities: A Blinded Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial, Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, doi:10.3390/ijerph19031172
Leon, White, Kluger, Role of IL-6 and TNF in thermoregulation and survival during sepsis in mice, Am. J. Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpregu.1998.275.1.R269
Li, Qiao, You, Zong, Peng et al., SARS-CoV-2 Nsp5 Activates NF-kappaB Pathway by Upregulating SUMOylation of MAVS, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.750969
Magleby, Westblade, Trzebucki, Simon, Rajan et al., Impact of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Viral Load on Risk of Intubation and Mortality among Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa851
Mao, Qiu, He, Tan, Li et al., Manifestations and prognosis of gastrointestinal and liver involvement in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol, doi:10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30126-6
Marsland, Trompette, Gollwitzer, The Gut-Lung Axis in Respiratory Disease, Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc, doi:10.1513/AnnalsATS.201503-133AW
Marzorati, Abbeele, Bubeck, Bayne, Krishnan et al., Bacillus subtilis HU58 and Bacillus coagulans SC208 Probiotics Reduced the Effects of Antibiotic-Induced Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis in an M-SHIME ® Model, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms8071028
Marzorati, Bubeck, Bayne, Krishnan, Giusto, Effects of combined prebiotic, probiotic, IgG and amino acid supplementation on the gut microbiome of patients with inflammatory bowel disease, Future Microbiol
Marzorati, Van Den Abbeele, Bubeck, Bayne, Krishnan et al., Treatment with a spore-based probiotic containing five strains of Bacillus induced changes in the metabolic activity and community composition of the gut microbiota in a SHIME(R) model of the human gastrointestinal system, Food Res. Int, doi:10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110676
Mcelvaney, Mcevoy, Mcelvaney, Carroll, Murphy et al., Characterization of the Inflammatory Response to Severe COVID-19 Illness, Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med, doi:10.1164/rccm.202005-1583OC
Mcfarlin, Henning, Bowman, Gary, Carbajal, Oral spore-based probiotic supplementation was associated with reduced incidence of post-prandial dietary endotoxin, triglycerides, and disease risk biomarkers, World J. Gastrointest Pathophysiol, doi:10.4291/wjgp.v8.i3.117
Miyauchi, Shimokawa, Steimle, Desai, Ohno, The impact of the gut microbiome on extra-intestinal autoimmune diseases, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-022-00727-y
Nguyen, Chong, Hor, Lew, Rather et al., Role of Probiotics in the Management of COVID-19: A Computational Perspective, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14020274
Oba, Rongduo, Saito, Okabayashi, Yokota et al., Natto extract, a Japanese fermented soybean food, directly inhibits viral infections including SARS-CoV-2 in vitro, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.07.034
Pan, Mu, Yang, Sun, Wang et al., Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients With Digestive Symptoms in Hubei, China: A Descriptive, Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study, Am. J. Gastroenterol, doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000620
Qian, Lei, Patel, Lee, Monaghan-Nichols et al., Direct Activation of Endothelial Cells by SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Is Blocked by Simvastatin, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01396-21
Rodriguez, Bifano, Roca Goma, Plasencia, Torralba et al., Effect and Tolerability of a Nutritional Supplement Based on a Synergistic Combination of beta-Glucans and Selenium-and Zinc-Enriched Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ABB C1((R))) in Volunteers Receiving the Influenza or the COVID-19 Vaccine: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study, Nutrients
Rossini, Tolosa-Enguis, Frances-Cuesta, Sanz, Gut microbiome and anti-viral immunity in COVID-19, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2022.2143476
Russo, Giudici, Fiorindi, Ficari, Scaringi et al., Immunomodulating Activity and Therapeutic Effects of Short Chain Fatty Acids and Tryptophan Post-Biotics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.02754
Safiabadi Tali, Leblanc, Sadiq, Oyewunmi, Camargo et al., Tools and Techniques for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)/COVID-19 Detection, Clin. Microbiol. Rev, doi:10.1128/CMR.00228-20
Tan, Liu, Zhou, Deng, Li et al., Immunopathological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 cases in Guangzhou, China, Immunology, doi:10.1111/imm.13223
Tanikawa, Kiba, Yu, Hsu, Chen et al., Degradative Effect of Nattokinase on Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules27175405
Teijaro, Type I interferons in viral control and immune regulation, Curr. Opin. Virol, doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2016.01.001
Umakanthan, Sahu, Ranade, Bukelo, Rao et al., Origin, transmission, diagnosis and management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Postgrad. Med. J
Venegas-Borsellino, Sankararaman, Roche, Burns, Landis, Impact of COVID-19 on the Intestinal Microbiome, Curr. Nutr. Rep, doi:10.1007/s13668-021-00375-z
Vollenbroich, Ozel, Vater, Kamp, Pauli, Mechanism of inactivation of enveloped viruses by the biosurfactant surfactin from Bacillus subtilis, Biologicals, doi:10.1006/biol.1997.0099
Who, Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard
Wiersinga, Rhodes, Cheng, Peacock, Prescott, Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.12839
Williams, Probiotics, None, Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm, doi:10.2146/ajhp090168
Wu, Wu, The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity, Gut Microbes, doi:10.4161/gmic.19320
Xu, Ren, Cao, Li, Yang et al., Boosting Vaccine-Elicited Respiratory Mucosal and Systemic COVID-19 Immunity in Mice with the Oral Lactobacillus Plantarum, Front. Nutr
Yang, Xie, Tu, Fu, Xu et al., The signal pathways and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00679-0
Zuo, Zhang, Lui, Yeoh, Li et al., Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients with COVID-19 during Time of Hospitalization, Gastroenterology, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu15030488",
"ISSN": [
"2072-6643"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/nu15030488",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Spore-based Bacillus probiotic treatment improves intestinal health. The intestinal microbiota influences both the innate and adaptive immune responses. As such, the influence of ongoing spore-based probiotic treatment (five probiotic strains of Bacillus) on the clinical outcomes of mild COVID-19 was evaluated in this retrospective, observational study. Demographics, medical history, probiotic use, and COVID-19 symptom information were collected. The study included 120 patients with a PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection and mild COVID-19 symptoms. The probiotic group (n = 60) comprised patients with ongoing probiotic treatment (≥1 month); the control group comprised patients not taking probiotics (n = 60). The primary outcome was time to symptom resolution; secondary outcomes included time to fever resolution and presence of digestive symptoms. The probiotic group had a significantly shorter time to symptom resolution (mean (95% confidence interval) days: control group, 8.48 (6.56, 10.05); probiotic group, 6.63 (5.56; 6.63); p = 0.003) and resolution of fever (control group, 2.67 (1.58, 3.61); probiotic group, 1.48 (1.21, 2.03); p < 0.001). More patients in the probiotic group (n = 53) than in the control group (n = 34) did not have digestive symptoms (p < 0.001). Among adults with mild COVID-19, participants receiving ongoing probiotic treatment had a shorter clinical course, and fewer had digestive symptoms compared with those not taking probiotics.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"nu15030488"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6327-6608",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Catinean",
"given": "Adrian",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sida",
"given": "Anamaria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Silvestru",
"given": "Celina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Balan",
"given": "Gheorghe G.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrients",
"container-title-short": "Nutrients",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-18T07:31:11Z",
"timestamp": 1674027071000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-18T07:56:49Z",
"timestamp": 1674028609000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-19T06:09:29Z",
"timestamp": 1674108569894
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "3",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
17
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "3",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
2
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-17T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1673913600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/3/488/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "488",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
17
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
17
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.048",
"article-title": "Alterations in Gut Microbiota of Patients with COVID-19 during Time of Hospitalization",
"author": "Zuo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "944",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "ref_1",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_2",
"unstructured": "WHO (2023, January 16). Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/#:~:text=Globally%2C%20as%20of%204%3A54pm,vaccine%20doses%20have%20been%20administered."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.j5145",
"article-title": "The role of the gut microbiome in systemic inflammatory disease",
"author": "Clemente",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "j5145",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "360",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-022-00727-y",
"article-title": "The impact of the gut microbiome on extra-intestinal autoimmune diseases",
"author": "Miyauchi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_4",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4161/gmic.19320",
"article-title": "The role of gut microbiota in immune homeostasis and autoimmunity",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4",
"journal-title": "Gut Microbes",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12866-021-02192-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_6",
"unstructured": "Han, S.K., Shin, Y.J., Lee, D.Y., Kim, K.M., Yang, S.J., Kim, D.S., Choi, J.W., Lee, S., and Kim, D.H. (2021). Lactobacillus rhamnosus HDB1258 modulates gut microbiota-mediated immune response in mice with or without lipopolysaccharide-induced systemic inflammation. BMC Microbiol., 21."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.750969",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Nsp5 Activates NF-kappaB Pathway by Upregulating SUMOylation of MAVS",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "750969",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_7",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/lam.13334",
"article-title": "Probiotics and COVID-19: Is there any link?",
"author": "Akour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "229",
"journal-title": "Lett. Appl. Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/CMR.00228-20",
"article-title": "Tools and Techniques for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)/COVID-19 Detection",
"author": "LeBlanc",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00228-20",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Rev.",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.040",
"article-title": "Potential long coronavirus disease 2019 gastrointestinal symptoms 6 months after coronavirus infection are associated with mental health symptoms",
"author": "Blackett",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "648",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "ref_10",
"volume": "162",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000620",
"article-title": "Clinical Characteristics of COVID-19 Patients With Digestive Symptoms in Hubei, China: A Descriptive, Cross-Sectional, Multicenter Study",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "766",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Gastroenterol.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14020274",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Nguyen, Q.V., Chong, L.C., Hor, Y.Y., Lew, L.C., Rather, I.A., and Choi, S.B. (2022). Role of Probiotics in the Management of COVID-19: A Computational Perspective. Nutrients, 14."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2022.2143476",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_13",
"unstructured": "Rossini, V., Tolosa-Enguis, V., Frances-Cuesta, C., and Sanz, Y. (2022). Gut microbiome and anti-viral immunity in COVID-19. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr., 1–16."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.03.002",
"article-title": "Probiotics in Prevention and Treatment of COVID-19: Current Perspective and Future Prospects",
"author": "Kurian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "582",
"journal-title": "Arch. Med. Res.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2146/ajhp090168",
"article-title": "Probiotics",
"author": "Williams",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "449",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13124347",
"article-title": "Effect and Tolerability of a Nutritional Supplement Based on a Synergistic Combination of beta-Glucans and Selenium-and Zinc-Enriched Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ABB C1((R))) in Volunteers Receiving the Influenza or the COVID-19 Vaccine: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study",
"author": "Rodriguez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4347",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijerph19031172",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_17",
"unstructured": "Leal-Martinez, F., Abarca-Bernal, L., Garcia-Perez, A., Gonzalez-Tolosa, D., Cruz-Cazares, G., Montell-Garcia, M., and Ibarra, A. (2022). Effect of a Nutritional Support System to Increase Survival and Reduce Mortality in Patients with COVID-19 in Stage III and Comorbidities: A Blinded Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 19."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/spectrum.01682-22",
"article-title": "Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of a Throat Spray with Selected Lactobacilli in COVID-19 Outpatients",
"author": "Cauwenberghs",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0168222",
"journal-title": "Microbiol. Spectr.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms8071028",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_19",
"unstructured": "Marzorati, M., Abbeele, P.V.D., Bubeck, S.S., Bayne, T., Krishnan, K., Young, A., Mehta, D., and DeSouza, A. (2020). Bacillus subtilis HU58 and Bacillus coagulans SC208 Probiotics Reduced the Effects of Antibiotic-Induced Gut Microbiome Dysbiosis in an M-SHIME® Model. Microorganisms, 8."
},
{
"article-title": "The effect of Probiotic Bacillus Subtilis HU58 on Immune Function in Healthy Human",
"author": "Dound",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Indian Pract.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4291/wjgp.v8.i3.117",
"article-title": "Oral spore-based probiotic supplementation was associated with reduced incidence of post-prandial dietary endotoxin, triglycerides, and disease risk biomarkers",
"author": "McFarlin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "117",
"journal-title": "World J. Gastrointest Pathophysiol.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fmb-2022-0066",
"article-title": "Effects of combined prebiotic, probiotic, IgG and amino acid supplementation on the gut microbiome of patients with inflammatory bowel disease",
"author": "Marzorati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1307",
"journal-title": "Future Microbiol.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110676",
"article-title": "Treatment with a spore-based probiotic containing five strains of Bacillus induced changes in the metabolic activity and community composition of the gut microbiota in a SHIME(R) model of the human gastrointestinal system",
"author": "Marzorati",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110676",
"journal-title": "Food Res. Int.",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-230X-9-85",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_24",
"unstructured": "Kalman, D.S., Schwartz, H.I., Alvarez, P., Feldman, S., Pezzullo, J.C., and Krieger, D.R. (2009). A prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled parallel-group dual site trial to evaluate the effects of a Bacillus coagulans-based product on functional intestinal gas symptoms. BMC Gastroenterol., 9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-020-04138-6",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression and tissue susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Beyerstedt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.1570",
"article-title": "Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in understanding SARS pathogenesis",
"author": "Hamming",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "631",
"journal-title": "J. Pathol.",
"key": "ref_26",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27175405",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Tanikawa, T., Kiba, Y., Yu, J., Hsu, K., Chen, S., Ishii, A., Yokogawa, T., Suzuki, R., Inoue, Y., and Kitamura, M. (2022). Degradative Effect of Nattokinase on Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2. Molecules, 27."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.07.034",
"article-title": "Natto extract, a Japanese fermented soybean food, directly inhibits viral infections including SARS-CoV-2 in vitro",
"author": "Oba",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "21",
"journal-title": "Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "570",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.12839",
"article-title": "Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review",
"author": "Wiersinga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "782",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2468-1253(20)30126-6",
"article-title": "Manifestations and prognosis of gastrointestinal and liver involvement in patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Mao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "667",
"journal-title": "Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol.",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01396-21",
"article-title": "Direct Activation of Endothelial Cells by SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein Is Blocked by Simvastatin",
"author": "Qian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0139621",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12123607",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_32",
"unstructured": "Catinean, A., Neag, M.A., Krishnan, K., Muntean, D.M., Bocsan, C.I., Pop, R.M., Mitre, A.O., Melincovici, C.S., and Buzoianu, A.D. (2020). Probiotic Bacillus Spores Together with Amino Acids and Immunoglobulins Exert Protective Effects on a Rat Model of Ulcerative Colitis. Nutrients, 12."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-319-92336-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "El-Radhi, A.S. (2019). Clinical Manual of Fever in Children, Springer."
},
{
"DOI": "10.12998/wjcc.v9.i2.296",
"article-title": "Effect of a fever in viral infections—The ‘Goldilocks’ phenomenon?",
"author": "Belon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "296",
"journal-title": "World J. Clin. Cases",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coviro.2016.01.001",
"article-title": "Type I interferons in viral control and immune regulation",
"author": "Teijaro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "31",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Virol.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coviro.2013.05.019",
"article-title": "Viral modulation of programmed necrosis",
"author": "Kaiser",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "296",
"journal-title": "Curr. Opin. Virol.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00679-0",
"article-title": "The signal pathways and treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "255",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target. Ther.",
"key": "ref_37",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Role of IL-6 and TNF in thermoregulation and survival during sepsis in mice",
"author": "Leon",
"first-page": "R269",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "275",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/etm.2021.10942",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus plantarum induces innate cytokine responses that potentially provide a protective benefit against COVID-19: A single-arm, double-blind, prospective trial combined with an in vitro cytokine response assay",
"author": "Kageyama",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Exp. Ther. Med.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.789242",
"article-title": "Boosting Vaccine-Elicited Respiratory Mucosal and Systemic COVID-19 Immunity in Mice with the Oral Lactobacillus Plantarum",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "789242",
"journal-title": "Front. Nutr.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2021.09.009",
"article-title": "Targeting the Gut Microbiota in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Hype or Hope?",
"author": "Lau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "162",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13668-021-00375-z",
"article-title": "Impact of COVID-19 on the Intestinal Microbiome",
"author": "Sankararaman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "300",
"journal-title": "Curr. Nutr. Rep.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "ref_43",
"unstructured": "(2022, September 28). Probiotics in Food: Health and Nutritional Properties and Guidelines for Evaluation. Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/a0512e/a0512e.pdf."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa709",
"article-title": "Alterations of the Gut Microbiota in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 or H1N1 Influenza",
"author": "Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2669",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1513/AnnalsATS.201503-133AW",
"article-title": "The Gut-Lung Axis in Respiratory Disease",
"author": "Marsland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S150",
"journal-title": "Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2019.02754",
"article-title": "Immunomodulating Activity and Therapeutic Effects of Short Chain Fatty Acids and Tryptophan Post-Biotics in Inflammatory Bowel Disease",
"author": "Russo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2754",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_46",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103293",
"article-title": "Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: An overlooked therapy for IBD?",
"author": "Deleu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "103293",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.022",
"article-title": "Mining the Human Gut Microbiota for Immunomodulatory Organisms",
"author": "Sefik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "928",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "ref_48",
"volume": "168",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/biol.1997.0099",
"article-title": "Mechanism of inactivation of enveloped viruses by the biosurfactant surfactin from Bacillus subtilis",
"author": "Vollenbroich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "289",
"journal-title": "Biologicals",
"key": "ref_49",
"volume": "25",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202005-1583OC",
"article-title": "Characterization of the Inflammatory Response to Severe COVID-19 Illness",
"author": "McElvaney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "812",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med.",
"key": "ref_50",
"volume": "202",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.610300",
"article-title": "Different Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection of Asymptomatic, Mild, and Severe Cases",
"author": "Carsetti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "610300",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_51",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaci.2020.07.001",
"article-title": "The role of IL-6 and other mediators in the cytokine storm associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Copaescu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "518",
"journal-title": "J. Allergy Clin. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_52",
"volume": "146",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/imm.13223",
"article-title": "Immunopathological characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 cases in Guangzhou, China",
"author": "Tan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "261",
"journal-title": "Immunology",
"key": "ref_53",
"volume": "160",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa851",
"article-title": "Impact of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Viral Load on Risk of Intubation and Mortality among Hospitalized Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019",
"author": "Magleby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e4197",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_54",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrd.2018.45",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6: Designing specific therapeutics for a complex cytokine",
"author": "Garbers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "395",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.",
"key": "ref_55",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Origin, transmission, diagnosis and management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "Umakanthan",
"first-page": "753",
"journal-title": "Postgrad. Med. J.",
"key": "ref_56",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 56,
"references-count": 56,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/15/3/488"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science",
"Nutrition and Dietetics"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Ongoing Treatment with a Spore-Based Probiotic Containing Five Strains of Bacillus Improves Outcomes of Mild COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "15"
}