Antiandrogens reduce COVID-19 risk: real-time meta analysis of 49 studies (Version 48)
, Jan 2026
7th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000056 from 49 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,300+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
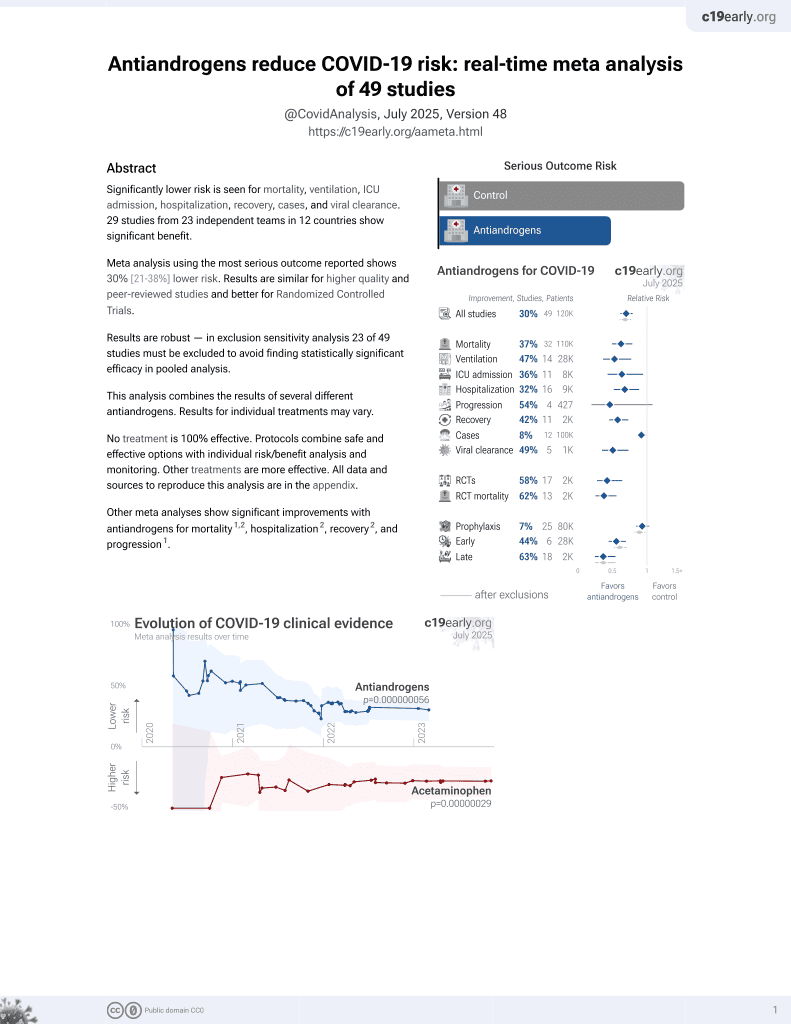
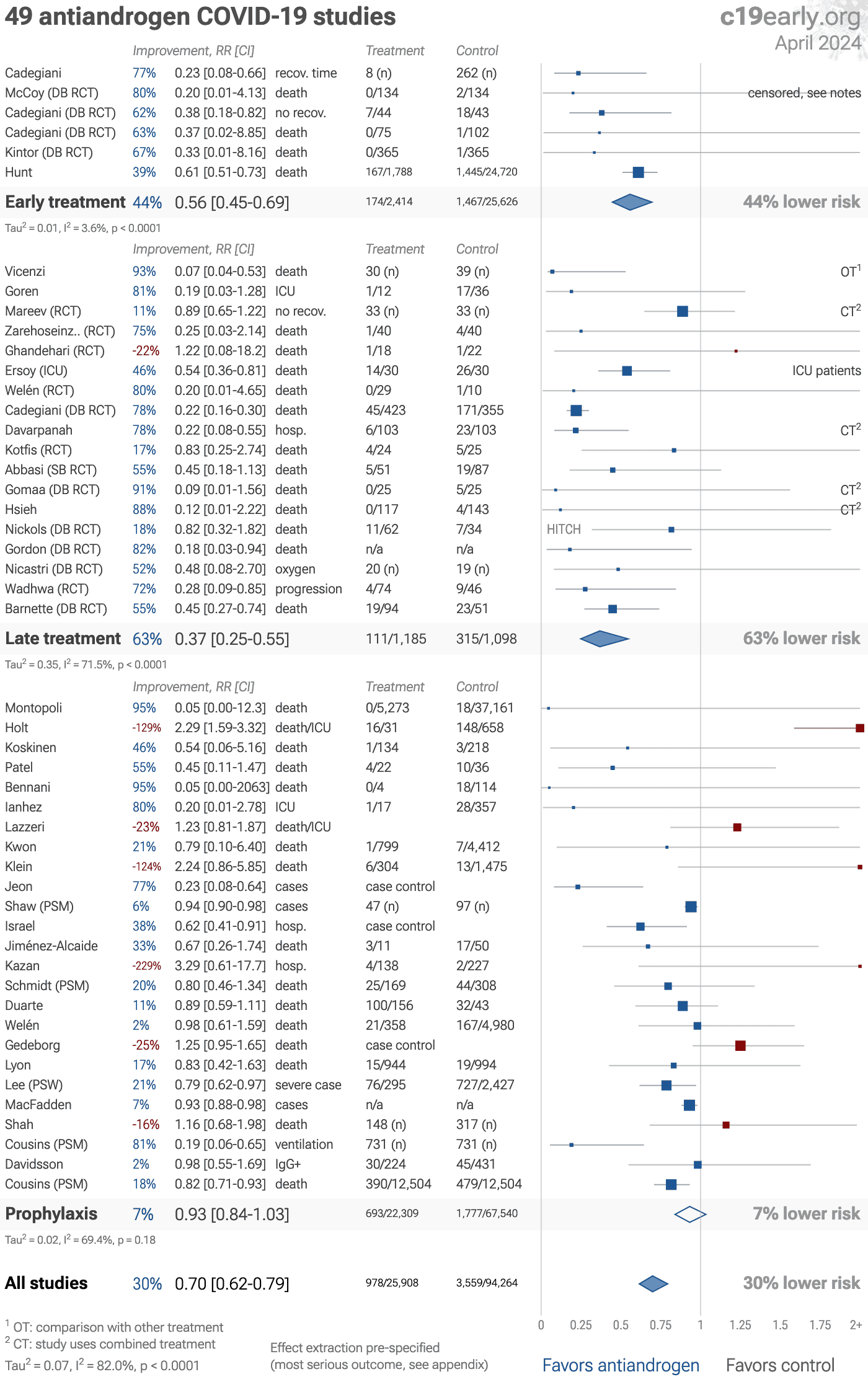
Significantly lower risk is seen for mortality, ventilation, ICU admission, hospitalization, recovery, cases, and viral clearance. 29 studies from 23 independent teams in 12 countries show significant benefit.
Meta analysis using the most serious outcome reported shows 30% [21‑38%] lower risk. Results are similar for higher quality and peer-reviewed studies and better for Randomized Controlled Trials.
Results are robust — in exclusion sensitivity analysis 23 of 49 studies must be excluded to avoid finding statistically significant efficacy in pooled analysis.
Control Antiandrogens
This analysis combines the results of several different antiandrogens. Results for individual treatments may vary.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols combine safe and effective options with individual risk/benefit analysis and monitoring. Other treatments are more effective. All data and sources to reproduce this analysis are in the appendix.
Other meta analyses show significant improvements with antiandrogens for mortality1,2, hospitalization2, recovery2, and progression1.
2 meta analyses show significant improvements with antiandrogens for mortality1,2,
hospitalization2,
recovery2, and
progression1.
Covid Analysis et al., Jan 2026, preprint, 1 author.