Mouthwash Effects on the Oral Microbiome: Are They Good, Bad, or Balanced?
et al., International Dental Journal, doi:10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010, Nov 2023
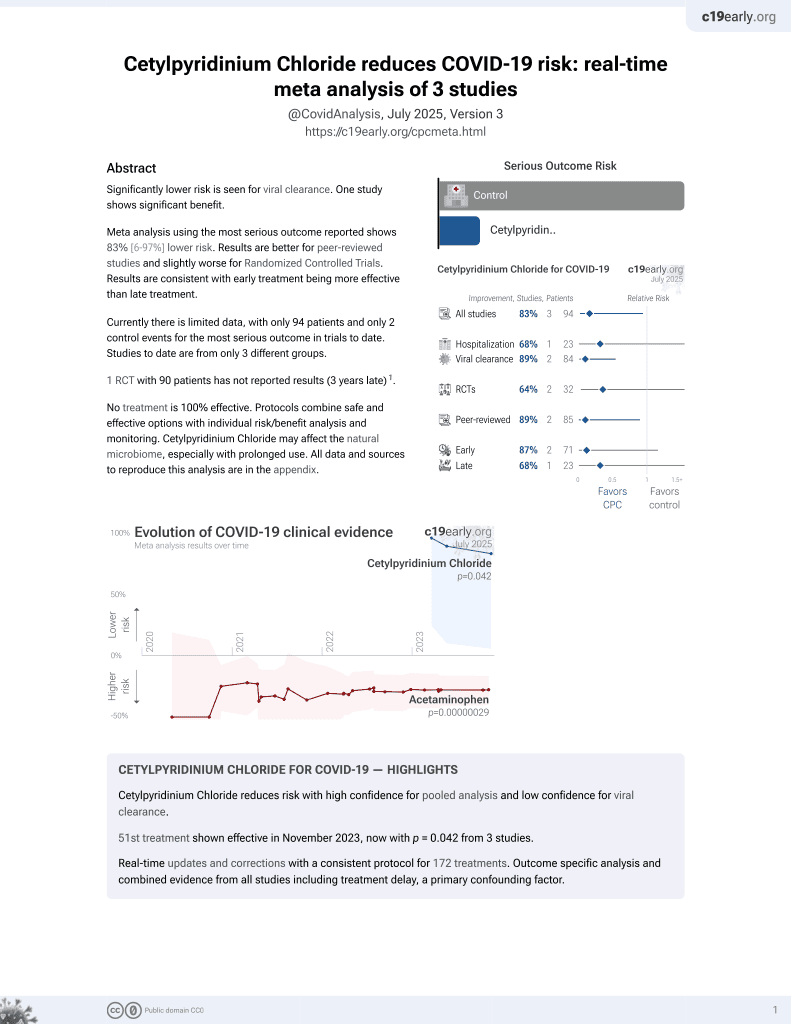
58th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2025, now with p = 0.0035 from 4 studies.
Lower risk for recovery and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
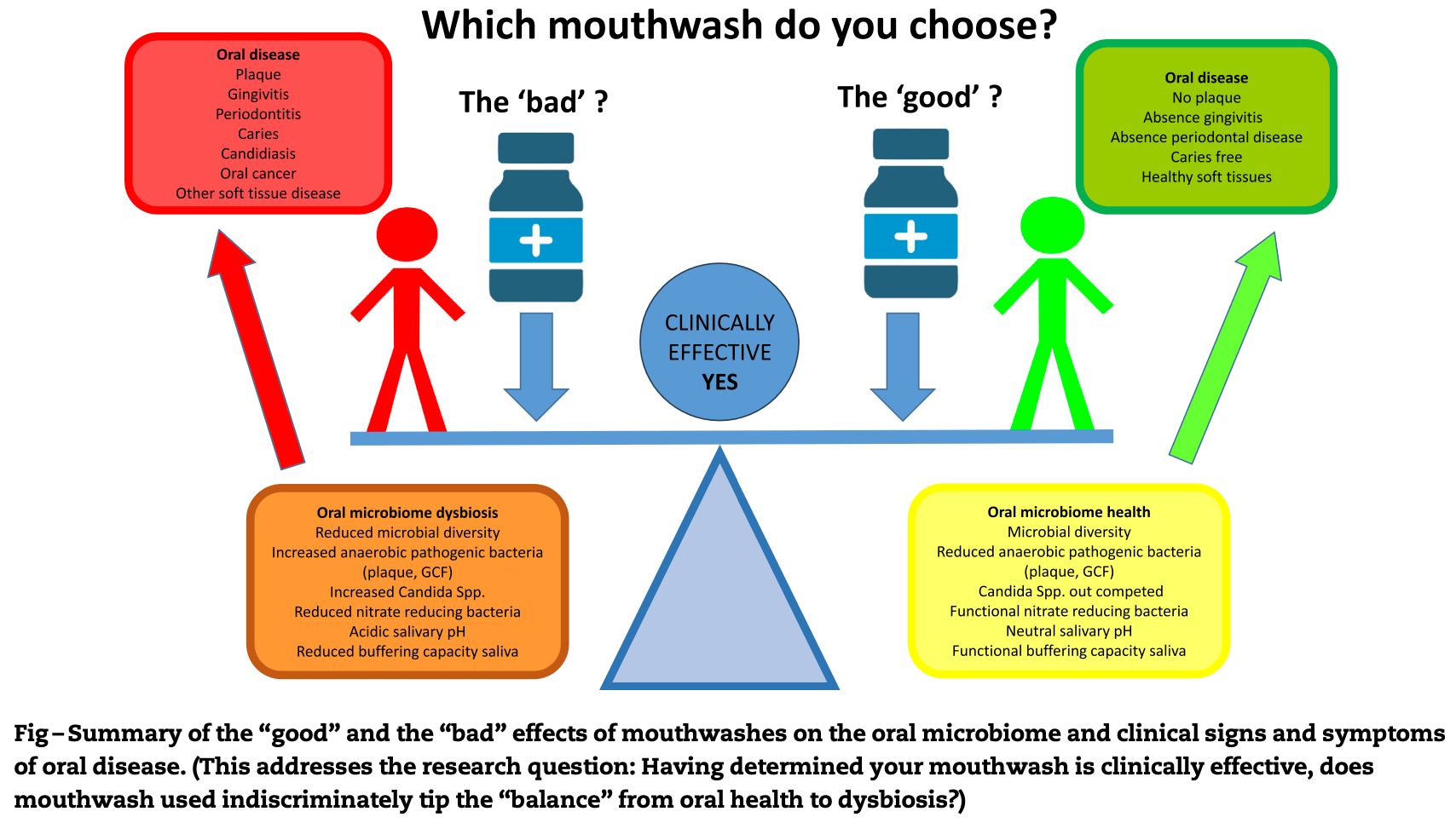
Review of the effects of commonly used mouthwashes on the oral microbiome, which includes bacteria, viruses, bacteriophages, and fungi. While certain mouthwashes have proven antimicrobial actions and clinical effectiveness, more recent metagenomics evidence suggests that mouthwashes such as chlorhexidine may cause "dysbiosis," whereby certain species of bacteria are killed, leaving others, sometimes unwanted, to predominate. This suggests that the ideal mouthwash should minimize negative effects on the oral microbiome.
Brookes et al., 30 Nov 2023, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: zoe.brookes@plymouth.ac.uk.
Mouthwash Effects on the Oral Microbiome: Are They Good, Bad, or Balanced?
doi:10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.0100020-6539/
This narrative review describes the oral microbiome, and its role in oral health and disease, before considering the impact of commonly used over-the-counter (OTC) mouthwashes on oral bacteria, viruses, bacteriophages, and fungi that make up these microbial communities in different niches of the mouth. Whilst certain mouthwashes have proven antimicrobial actions and clinical effectiveness supported by robust evidence, this review reports more recent metagenomics evidence, suggesting that mouthwashes such as chlorhexidine may cause "dysbiosis," whereby certain species of bacteria are killed, leaving others, sometimes unwanted, to predominate. There is little known about the effects of mouthwashes on fungi and viruses in the context of the oral microbiome (virome) in vivo, despite evidence that they "kill" certain viral pathogens ex vivo. Evidence for mouthwashes, much like antibiotics, is also emerging with regards to antimicrobial resistance, and this should further be considered in the context of their widespread use by clinicians and patients. Therefore, considering the potential of currently available OTC mouthwashes to alter the oral microbiome, this article finally proposes that the ideal mouthwash, whilst combatting oral disease, should "balance" antimicrobial communities, especially those associated with health. Which antimicrobial mouthwash best fits this ideal remains uncertain.
Conflict of interest None disclosed.
References
Alemany, Perez-Zsolt, ¨ch-Regu E D, Cetylpyridinium chloride mouthwash to reduce shedding of infectious SARS-CoV-2: a double-blind randomized clinical trial, J Dent Res
Alshehri, The use of mouthwash containing essential oils (LISTERINE Ò ) to improve oral health: a systematic review, Saudi Dent J
Amtha, Kj, Povidone-iodine in dental and oral health: a narrative review, J Int Oral Health
Anchez Barrueco, Mv, Inez-Beneyto, Effect of oral antiseptics in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infectivity: evidence from a randomized double-blind clinical trial, Emerg Microbes Infect
Ardizzoni, Pericolini, Paulone, In vitro effects of commercial mouthwashes on several virulence traits of Candida albicans, viridans streptococci and Enterococcus faecalis colonizing the oral cavity, PLoS One
Atanasova, Sen Cilo A, Pietil€ A Mk, Roine, Oksanen, Bamford, Comparison of lipid-containing bacterial and archaeal viruses, Adv Virus Res
Bandara, Panduwawala, Samaranayake, Biodiversity of the human oral mycobiome in health and disease, Oral Dis
Bescos, Ashworth, Cutler, Effects of chlorhexidine mouthwash on the oral microbiome, Sci Rep
Bonn, Rohrhofer, Audebert, Efficacy of a mouthwash containing CHX and CPC in SARS-CoV-2-positive patients: a randomized controlled clinical trial, J Dent Res
Carrouel, Gonçalves, Conte, Antiviral activity of reagents in mouth rinses against SARS-CoV-2, J Dent Res
Chaudhary, Melkonyan, Meethil, Estimating salivary carriage of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in nonsymptomatic people and efficacy of mouthrinse in reducing viral load: a randomized controlled trial, J Am Dent Assoc
Chen, Lee, Ma, Jang, Fong et al., The efficacy of different sanitizers against MS2 bacteriophage introduced onto plastic or stainless steel surfaces, Curr Res Food Sci
Cieplik, Jakubovics, Buchalla, Maisch, Hellwig, Resistance toward chlorhexidine in oral bacteriais there cause for concern?, Front Microbiol
Cieplik, Jakubovics, Preprocedural mouthwashes for reduction of SARS-CoV-2 viral load and infectivity, J Dent Res
Cieplik, Kara, Muehler, Antimicrobial efficacy of alternative compounds for use in oral care toward biofilms from caries-associated bacteria in vitro, Microbiologyopen
Collins, Dawes, The surface area of the adult human mouth and thickness of the salivary film covering the teeth and oral mucosa, J Dent Res
Conceição, De Lencastre, Aires-De-Sousa, Prevalence of biocide resistance genes and chlorhexidine and mupirocin non-susceptibility in Portuguese hospitals during a 31-year period (1985-2016), J Glob Antimicrob Resist
Cosyn, Princen, Miremadi, Decat, Vaneechoutte et al., A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled study on the clinical and microbial effects of an essential oil mouth rinse used by patients in supportive periodontal care, Int J Dent Hyg
Darveau, Tanner, Page, The microbial challenge in periodontitis, Periodontol
De Faveri, Pupio, Koo, The effect of Brazilian propolis type-3 against oral microbiota and volatile sulfur compounds in subjects with morning breath malodor, Clin Oral Investig
Dogra, Dor E, Damak, Gut microbiota resilience: definition, link to health and strategies for intervention, Front Microbiol
Dudek-Wicher, Junka, Migda, Korzeniowska-Kowal, Wzorek et al., The antibiofilm activity of selected substances used in oral health prophylaxis, BMC Oral Health
Emilson, Ericson, Lilja, Heyden, Effect of chlorhexidine on human oral streptococci, J Periodontal Res
Fan, Peters, Jacobs, Drinking alcohol is associated with variation in the human oral microbiome in a large study of American adults, Microbiome
Fernandez, Guedes, Langa, Cavagni, Muniz, Virucidal efficacy of chlorhexidine: a systematic review, Odontology
Gedam, Katre, Efficacy of probiotic, chlorhexidine, and sodium fluoride mouthrinses on mutans streptococci in 8-to 12-year-old children: a crossover randomized trial, Lifestyle Genom
Ghannoum, Jurevic, Mukherjee, Characterization of the oral fungal microbiome (mycobiome) in healthy individuals, PLoS Pathog
Giertsen, Emberland, Scheie, Effects of mouth rinses with xylitol and fluoride on dental plaque and saliva, Caries Res
Gusberti, Sampathkumar, Siegrist, Lang, Microbiological and clinical effects of chlorhexidine digluconate and hydrogen peroxide mouthrinses on developing plaque and gingivitis, J Clin Periodontol
Hartzell, Henrici, The dental path: its importance as an avenue to infection, Public Health J
Herrera, Serrano, Rold An, Sanz, Is the oral cavity relevant in SARS-CoV-2 pandemic?, Clin Oral Investig
Imabayashi, Moriyama, Takeshita, Molecular analysis of fungal populations in patients with oral candidiasis using next-generation sequencing, Sci Rep
James, Worthington, Parnell, Chlorhexidine mouthrinse as an adjunctive treatment for gingival health, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Jones, Chlorhexidine: is it still the gold standard?, Periodontology
Joshi, Matthews, Aspiras, De Jager, Ward et al., Smoking decreases structural and functional resilience in the subgingival ecosystem, J Clin Periodontol
Kampf, Acquired resistance to chlorhexidine -is it time to establish an 'antiseptic stewardship' initiative?, J Hosp Infect
Kitagawa, Izutani, Kitagawa, Maezono, Yamaguchi et al., Evolution of resistance to cationic biocides in Streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus faecalis, J Dent
Kulik, Waltimo, Weiger, Development of resistance of mutans streptococci and Porphyromonas gingivalis to chlorhexidine digluconate and amine fluoride/stannous fluoride-containing mouthrinses, in vitro, Clin Oral Investig
Kumar, Dabdoub, Ganesan, Probing periodontal microbial dark matter using metataxonomics and metagenomics, Periodontol
Kumar, Microbial dysbiosis: the root cause of periodontal disease, J Periodontol
Lachenmeier, Gumbel-Mako, Sohnius, Keck-Wilhelm, Kratz et al., Salivary acetaldehyde increase due to alcohol-containing mouthwash use: a risk factor for oral cancer, Int J Cancer
Lassalle, Spagnoletti, Fumagalli, Oral microbiomes from hunter-gatherers and traditional farmers reveal shifts in commensal balance and pathogen load linked to diet, Mol Ecol
Liang, Bushman, The human virome: assembly, composition and host interactions, Nat Rev Microbiol
Mao, Auer, Buchalla, Cetylpyridinium chloride: mechanism of action, antimicrobial efficacy in biofilms, and potential risks of resistance, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Mart Inez, Kuraji, Kapila, The human oral virome: shedding light on the dark matter, Periodontol
Mason, Chambers, Dabdoub, Thikkurissy, Kumar, Characterizing oral microbial communities across dentition states and colonization niches, Microbiome
Mcdonnell, Russell, Antiseptics and disinfectants: activity, action, and resistance, Clin Microbiol Rev
Meister, Gottsauner, Schmidt, Mouthrinses against SARS-CoV-2 -high antiviral effectivity by membrane disruption in vitro translates to mild effects in a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial, Virus Res
Menendez, Li, Michalek, Kirk, Makhija et al., Comparative analysis of the antibacterial effects of combined mouthrinses on Streptococcus mutans, Oral Microbiol Immunol
Millhouse, Sherry, Development of an in vitro periodontal biofilm model for assessing antimicrobial and host modulatory effects of bioactive molecules, BMC Oral Health
Moazzez, Thompson, Palmer, Wilson, Proctor et al., Effect of rinsing with ethanol-containing mouthrinses on the production of salivary acetaldehyde, Eur J Oral Sci
Mokili, Rohwer, Dutilh, Metagenomics and future perspectives in virus discovery, Curr Opin Virol
Morawiec, Mertas, Tanasiewicz, Dziedzic, Kr Ol W, Influence of propolis on hygiene, gingival condition, and oral microflora in patients with cleft lip and palate treated with fixed orthodontic appliances, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
M€ Antynen, Sundberg, Oksanen, Poranen, Half a century of research on membrane-containing bacteriophages: bringing new concepts to modern virology, Viruses
Nagappan, Champakesan, Tirupati, Cruz, Ramasubramanian et al., Antimicrobial efficacy of two mouthrinses against Candida albicans: an in vitro study, J Pharm Bioallied Sci
Nakagawa, Hosaka, Ishihara, The efficacy of povidone-iodine products against periodontopathic bacteria, Dermatology
Netto, Marcucci, Paulino, Effects of typified propolis on mutans streptococci and lactobacilli: a randomized clinical trial, Braz Dent Sci
O'donnell, Thomas, Stanton, Potential role of oral rinses targeting the viral lipid envelope in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Function (Oxf)
Otręba, Tyczy Nska, Stojko, Propolis as natural product in the oral cavity bacterial infections treatment: a systematic review, Appl Sci
Parras-Molt O, Opez-Bueno, Methods for enrichment and sequencing of oral viral assemblages: saliva, oral mucosa, and dentalplaqueviromes, MethodsMolBiol
Pereira, Da Silva, Silva, Clinical evidence of the efficacy of a mouthwash containing propolis for the control of plaque and gingivitis: a phase II study, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
Pignatelli, Fabietti, Ricci, Piattelli, Curia, How periodontal disease and presence of nitric oxide reducing oral bacteria can affect blood pressure, Int J Mol Sci
Pride, Salzman, Haynes, Evidence of a robust resident bacteriophage population revealed through analysis of the human salivary virome, ISME J
Quintas, Prada-L Opez, Donos, Su Arez-Quintanilla, As, In situ neutralisation of the antibacterial effect of 0.2% chlorhexidine on salivary microbiota: quantification of substantivity, Arch Oral Biol
Raangs, Winkel, Van Winkelhoff, In vitro antimicrobial effects of two antihalitosis mouth rinses on oral pathogens and human tongue microbiota, Int J Dent Hyg
Radford, Beighton, Nugent, Jackson, Effect of use of 0.05% cetylpyridinium chloride mouthwash on normal oral flora, J Dent
Rahmani-Badi, Sepehr, Babaie-Naiej, A combination of cis-2-decenoic acid and chlorhexidine removes dental plaque, Arch Oral Biol
Reilly, Goettl, Steinmetz, Nikrad, Jones, Short-term effects of povidone iodine and sodium fluoride therapy on plaque levels and microbiome diversity, Oral Dis
Relman, The human microbiome: ecosystem resilience and health, Nutr Rev
Rocha, Duarte, De Oliveira Corrêa, Nampo, De et al., Chemical cleaning methods for prostheses colonized by Candida spp.: A systematic review, J Prosthet Dent
Sajedinejad, Paknejad, Houshmand, Lactobacillus salivarius NK02: a potent probiotic for clinical application in mouthwash, ProbioticsAntimicrobProteins
Saleem, Seers, Sabri, Reynolds, Dental plaque bacteria with reduced susceptibility to chlorhexidine are multidrug resistant, BMC Microbiol
Sauerbrei, Bactericidal and virucidal activity of ethanol and povidone-iodine, Microbiologyopen
Schiott, The sensitivity of oral streptococci to chlorhexidine, J Periodontal Res
Sharma, Charles, Lynch, Adjunctive benefit of an essential oil-containing mouthrinse in reducing plaque and gingivitis in patients who brush and floss regularly: a sixmonth study, J Am Dent Assoc
Shiraishi, Nakagawa, Evaluation of the bactericidal activity of povidone-iodine and commercially available gargle preparations, Dermatology
Shrestha, Rao, Sequeira, Doshi, Bhat, In vitro antifungal effect of mouth rinses containing chlorhexidine and thymol, J Dent Sciences
Skaba, Morawiec, Tanasiewicz, Influence of the toothpaste with Brazilian ethanol extract propolis on the oral cavity health, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
Stewart, Antimicrobial tolerance in biofilms, Microbiol Spectr
Sukumar, Roberts, Martin, Adler, Metagenomic insights into transferable antibiotic resistance in oral bacteria, J Dent Res
Szafra Nski, Slots, Stiesch, The human oral phageome, Periodontol
Tamai, Sugamata, Kiyoura, Candida albicans enhances invasion of human gingival epithelial cells and gingival fibroblasts by Porphyromonas gingivalis, Microb Pathog
Tarrag O-Gil, Mj, Salcedo, Randomized clinical trial to assess the impact of oral intervention with cetylpyridinium chloride to reduce salivary SARS-CoV-2 viral load, J Clin Periodontol, doi:10.1111/jcpe.13746
Teles, Teles, Frias-Lopez, Paster, Haffajee, Lessons learned and unlearned in periodontal microbiology, Periodontol
Teng, He, Huang, Cetylpyridinium chloride mouth rinses alleviate experimental gingivitis by inhibiting dental plaque maturation, Int J Oral Sci
Tezel, Pavlostathis, Quaternary ammonium disinfectants: microbial adaptation, degradation and ecology, Curr Opin Biotechnol
Thurnheer, Belibasakis, Effect of sodium fluoride on oral biofilm microbiota and enamel demineralization, Arch Oral Biol
Tribble, Angelov, Weltman, Frequency of tongue cleaning impacts the human tongue microbiome composition and enterosalivary circulation of nitrate, Front Cell Infect Microbiol
Van Leeuwen, Rosema, Versteeg, Slot, Winkelhoff et al., Long-term efficacy of a 0.07% cetylpyridinium chloride mouth rinse in relation to plaque and gingivitis: a 6-month randomized, vehicle-controlled clinical trial, Int J Dent Hyg
Verspecht, Herrero, Khodaparast, Development of antiseptic adaptation and cross-adapatation in selected oral pathogens in vitro, Sci Rep
Vlachojannis, Chrubasik-Hausmann, Hellwig, A preliminary investigation on the antimicrobial activity of o r a l m i c r o b i o m e a n d m o u t h w a s h e s listerine Ò , its components, and of mixtures thereof, Phytother Res
Wade, Addy, In vitro activity of a chlorhexidine-containing mouthwash against subgingival bacteria, J Periodontol
Wand, Bock, Bonney, Sutton, Mechanisms of increased resistance to chlorhexidine and cross-resistance to colistin following exposure of klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates to chlorhexidine, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Weber, Bonn, Auer, Preprocedural mouthwashes for infection control in dentistry-an update, Clin Oral Investig
Yamamoto, Tamura, Yokota, Antiseptic and antibiotic resistance plasmid in Staphylococcus aureus that possesses ability to confer chlorhexidine and acrinol resistance, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010",
"ISSN": [
"0020-6539"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010",
"alternative-id": [
"S0020653923004550"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Mouthwash Effects on the Oral Microbiome: Are They Good, Bad, or Balanced?"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "International Dental Journal"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.014"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.012"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of FDI World Dental Federation."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8096-6256",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Brookes",
"given": "Zoë",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Teoh",
"given": "Leanne",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cieplik",
"given": "Fabian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Purnima",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Dental Journal",
"container-title-short": "International Dental Journal",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-17T20:37:15Z",
"timestamp": 1697575035000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-19T09:21:08Z",
"timestamp": 1702977668000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100023813",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "FDI World Dental Federation"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-02T16:03:24Z",
"timestamp": 1712073804760
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 5,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1698796800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1692662400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0020653923004550?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0020653923004550?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "S74-S81",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1177/00220345870660080201",
"article-title": "The surface area of the adult human mouth and thickness of the salivary film covering the teeth and oral mucosa",
"author": "Collins",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1300",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Dent Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0001",
"volume": "66",
"year": "1987"
},
{
"article-title": "The dental path: its importance as an avenue to infection",
"author": "Hartzell",
"first-page": "254",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Public Health J",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0002",
"volume": "7",
"year": "1916"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40168-018-0443-2",
"article-title": "Characterizing oral microbial communities across dentition states and colonization niches",
"author": "Mason",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "67",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Microbiome",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0003",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-0757.1997.tb00190.x",
"article-title": "The microbial challenge in periodontitis",
"author": "Darveau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Periodontol 2000",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0004",
"volume": "14",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/prd.12010",
"article-title": "Lessons learned and unlearned in periodontal microbiology",
"author": "Teles",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "95",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Periodontol 2000",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0005",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jcpe.12300",
"article-title": "Smoking decreases structural and functional resilience in the subgingival ecosystem",
"author": "Joshi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1037",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Clin Periodontol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0006",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2020.572921",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota resilience: definition, link to health and strategies for intervention",
"author": "Dogra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0007",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1753-4887.2012.00489.x",
"article-title": "The human microbiome: ecosystem resilience and health",
"author": "Relman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S2",
"issue": "Suppl 1",
"journal-title": "Nutr Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0008",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/mec.14435",
"article-title": "Oral microbiomes from hunter-gatherers and traditional farmers reveal shifts in commensal balance and pathogen load linked to diet",
"author": "Lassalle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "182",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mol Ecol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0009",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/JPER.21-0245",
"article-title": "Microbial dysbiosis: the root cause of periodontal disease",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1079",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Periodontol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0010",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/prd.12349",
"article-title": "Probing periodontal microbial dark matter using metataxonomics and metagenomics",
"author": "Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Periodontol 2000",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0011",
"volume": "85",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1472-6831-14-80",
"article-title": "Development of an in vitro periodontal biofilm model for assessing antimicrobial and host modulatory effects of bioactive molecules",
"author": "Millhouse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "80",
"journal-title": "BMC Oral Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0012",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-61912-4",
"article-title": "Effects of chlorhexidine mouthwash on the oral microbiome",
"author": "Bescos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5254",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0013",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.04.002",
"article-title": "In situ neutralisation of the antibacterial effect of 0.2% chlorhexidine on salivary microbiota: quantification of substantivity",
"author": "Quintas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1109",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Arch Oral Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0014",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2019.00039",
"article-title": "Frequency of tongue cleaning impacts the human tongue microbiome composition and enterosalivary circulation of nitrate",
"author": "Tribble",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0015",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Chlorhexidine mouthrinse as an adjunctive treatment for gingival health",
"author": "James",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0016",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0017",
"unstructured": "Periodontology EFo. EFP clinical guideline. 2023. Available from: https://www.efp.org/education/continuing-education/clinical-guidelines/. Accessed 1 February 2023."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21207538",
"article-title": "How periodontal disease and presence of nitric oxide reducing oral bacteria can affect blood pressure",
"author": "Pignatelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0018",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/CMR.12.1.147",
"article-title": "Antiseptics and disinfectants: activity, action, and resistance",
"author": "McDonnell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "147",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0019",
"volume": "12",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-051X.1988.tb01556.x",
"article-title": "Microbiological and clinical effects of chlorhexidine digluconate and hydrogen peroxide mouthrinses on developing plaque and gingivitis",
"author": "Gusberti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "60",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Clin Periodontol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0020",
"volume": "15",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1399-302X.2004.00189.x",
"article-title": "Comparative analysis of the antibacterial effects of combined mouthrinses on Streptococcus mutans",
"author": "Menendez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "31",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Oral Microbiol Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0021",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/idh.12082",
"article-title": "Long-term efficacy of a 0.07% cetylpyridinium chloride mouth rinse in relation to plaque and gingivitis: a 6-month randomized, vehicle-controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Van Leeuwen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "93",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Int J Dent Hyg",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0022",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ijos.2016.18",
"article-title": "Cetylpyridinium chloride mouth rinses alleviate experimental gingivitis by inhibiting dental plaque maturation",
"author": "Teng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "182",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Int J Oral Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0023",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/jioh.jioh_89_20",
"article-title": "Povidone-iodine in dental and oral health: a narrative review",
"author": "Amtha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "407",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Int Oral Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0024",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000089208",
"article-title": "The efficacy of povidone-iodine products against periodontopathic bacteria",
"author": "Nakagawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109",
"issue": "Suppl 1",
"journal-title": "Dermatology",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0025",
"volume": "212",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000057723",
"article-title": "Evaluation of the bactericidal activity of povidone-iodine and commercially available gargle preparations",
"author": "Shiraishi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "37",
"issue": "Suppl 1",
"journal-title": "Dermatology",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0026",
"volume": "204",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/odi.12407",
"article-title": "Short-term effects of povidone iodine and sodium fluoride therapy on plaque levels and microbiome diversity",
"author": "Reilly",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "155",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Oral Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0027",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.5399",
"article-title": "A preliminary investigation on the antimicrobial activity of listerine®, its components, and of mixtures thereof",
"author": "Vlachojannis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1590",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Phytother Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0028",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mbo3.695",
"article-title": "Antimicrobial efficacy of alternative compounds for use in oral care toward biofilms from caries-associated bacteria in vitro",
"author": "Cieplik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e00695",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Microbiologyopen",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0029",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12903-022-02532-4",
"article-title": "The antibiofilm activity of selected substances used in oral health prophylaxis",
"author": "Dudek-Wicher",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Oral Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0030",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sdentj.2017.12.004",
"article-title": "The use of mouthwash containing essential oils (LISTERINE®) to improve oral health: a systematic review",
"author": "Alshehri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Saudi Dent J",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0031",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14219/jada.archive.2004.0217",
"article-title": "Adjunctive benefit of an essential oil-containing mouthrinse in reducing plaque and gingivitis in patients who brush and floss regularly: a six-month study",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "496",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "J Am Dent Assoc",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0032",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/idh.12000",
"article-title": "A double-blind randomized placebo-controlled study on the clinical and microbial effects of an essential oil mouth rinse used by patients in supportive periodontal care",
"author": "Cosyn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "53",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Int J Dent Hyg",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0033",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mbo3.1097",
"article-title": "Bactericidal and virucidal activity of ethanol and povidone-iodine",
"author": "Sauerbrei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e1097",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Microbiologyopen",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0034",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40168-018-0448-x",
"article-title": "Drinking alcohol is associated with variation in the human oral microbiome in a large study of American adults",
"author": "Fan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "59",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Microbiome",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0035",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-0722.2011.00886.x",
"article-title": "Effect of rinsing with ethanol-containing mouthrinses on the production of salivary acetaldehyde",
"author": "Moazzez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "441",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Eur J Oral Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0036",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ijc.24381",
"article-title": "Salivary acetaldehyde increase due to alcohol-containing mouthwash use: a risk factor for oral cancer",
"author": "Lachenmeier",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "730",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Int J Cancer",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0037",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.02.010",
"article-title": "Effect of sodium fluoride on oral biofilm microbiota and enamel demineralization",
"author": "Thurnheer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Arch Oral Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0038",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000016492",
"article-title": "Effects of mouth rinses with xylitol and fluoride on dental plaque and saliva",
"author": "Giertsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Caries Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0039",
"volume": "33",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/idh.12014",
"article-title": "In vitro antimicrobial effects of two antihalitosis mouth rinses on oral pathogens and human tongue microbiota",
"author": "Raangs",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "203",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Int J Dent Hyg",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0040",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12602-017-9296-4",
"article-title": "Lactobacillus salivarius NK02: a potent probiotic for clinical application in mouthwash",
"author": "Sajedinejad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "485",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0041",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000519916",
"article-title": "Efficacy of probiotic, chlorhexidine, and sodium fluoride mouthrinses on mutans streptococci in 8- to 12-year-old children: a crossover randomized trial",
"author": "Gedam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Lifestyle Genom",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0042",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/app121910123",
"article-title": "Propolis as natural product in the oral cavity bacterial infections treatment: a systematic review",
"author": "Otręba MM",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10123",
"journal-title": "Appl Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0043",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2011/750249",
"article-title": "Clinical evidence of the efficacy of a mouthwash containing propolis for the control of plaque and gingivitis: a phase II study",
"author": "Pereira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Evid Based Complement Alternat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0044",
"volume": "2011",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2013/215391",
"article-title": "Influence of the toothpaste with Brazilian ethanol extract propolis on the oral cavity health",
"author": "Skaba",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Evid Based Complement Alternat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0045",
"volume": "2013",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2013/183915",
"article-title": "Influence of propolis on hygiene, gingival condition, and oral microflora in patients with cleft lip and palate treated with fixed orthodontic appliances",
"author": "Machorowska-Pieniążek",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Evid Based Complement Alternat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0046",
"volume": "2013",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14295/bds.2013.v16i2.879",
"article-title": "Effects of typified propolis on mutans streptococci and lactobacilli: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Anauate Netto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "31",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Braz Dent Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0047",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00784-021-04125-x",
"article-title": "The effect of Brazilian propolis type-3 against oral microbiota and volatile sulfur compounds in subjects with morning breath malodor",
"author": "de Faveri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1531",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Clin Oral Investig",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0048",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/odi.12899",
"article-title": "Biodiversity of the human oral mycobiome in health and disease",
"author": "Bandara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "363",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Oral Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0049",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1000713",
"article-title": "Characterization of the oral fungal microbiome (mycobiome) in healthy individuals",
"author": "Ghannoum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0050",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep28110",
"article-title": "Molecular analysis of fungal populations in patients with oral candidiasis using next-generation sequencing",
"author": "Imabayashi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28110",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0051",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/JPBS.JPBS_16_19",
"article-title": "Antimicrobial efficacy of two mouthrinses against Candida albicans: an in vitro study",
"author": "Nagappan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S293",
"issue": "Suppl 2",
"journal-title": "J Pharm Bioallied Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0052",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jds.2011.02.001",
"article-title": "In vitro antifungal effect of mouth rinses containing chlorhexidine and thymol",
"author": "Shrestha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Dent Sciences",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0053",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micpath.2011.06.009",
"article-title": "Candida albicans enhances invasion of human gingival epithelial cells and gingival fibroblasts by Porphyromonas gingivalis",
"author": "Tamai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "250",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Microb Pathog",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0054",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.08.006",
"article-title": "A combination of cis-2-decenoic acid and chlorhexidine removes dental plaque",
"author": "Rahmani-Badi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1655",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Arch Oral Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0055",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0207262",
"article-title": "In vitro effects of commercial mouthwashes on several virulence traits of Candida albicans, viridans streptococci and Enterococcus faecalis colonizing the oral cavity",
"author": "Ardizzoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0056",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.prosdent.2019.10.004",
"article-title": "Chemical cleaning methods for prostheses colonized by Candida spp.: A systematic review",
"author": "Ribeiro Rocha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "653",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Prosthet Dent",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0057",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00536-5",
"article-title": "The human virome: assembly, composition and host interactions",
"author": "Liang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "514",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0058",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4939-8682-8_11",
"article-title": "Methods for enrichment and sequencing of oral viral assemblages: saliva, oral mucosa, and dental plaque viromes",
"author": "Parras-Moltó",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "143",
"journal-title": "Methods Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0059",
"volume": "1838",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/prd.12396",
"article-title": "The human oral virome: shedding light on the dark matter",
"author": "Martínez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "282",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Periodontol 2000",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0060",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00784-020-03413-2",
"article-title": "Is the oral cavity relevant in SARS-CoV-2 pandemic?",
"author": "Herrera",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2925",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Clin Oral Investig",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0061",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/prd.12363",
"article-title": "The human oral phageome",
"author": "Szafrański",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "79",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Periodontol 2000",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0062",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ismej.2011.169",
"article-title": "Evidence of a robust resident bacteriophage population revealed through analysis of the human salivary virome",
"author": "Pride",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "ISME J",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0063",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/function/zqaa002",
"article-title": "Potential role of oral rinses targeting the viral lipid envelope in SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "O'Donnell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "zqaa002",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Function (Oxf)",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0064",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2022.198791",
"article-title": "Mouthrinses against SARS-CoV-2 - high antiviral effectivity by membrane disruption in vitro translates to mild effects in a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Meister",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Virus Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0065",
"volume": "316",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v11010076",
"article-title": "Half a century of research on membrane-containing bacteriophages: bringing new concepts to modern virology",
"author": "Mäntynen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0066",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/bs.aivir.2014.11.005",
"article-title": "Comparison of lipid-containing bacterial and archaeal viruses",
"author": "Atanasova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Adv Virus Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0067",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.crfs.2022.01.004",
"article-title": "The efficacy of different sanitizers against MS2 bacteriophage introduced onto plastic or stainless steel surfaces",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "175",
"journal-title": "Curr Res Food Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0068",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10266-021-00660-x",
"article-title": "Virucidal efficacy of chlorhexidine: a systematic review",
"author": "Fernandez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "376",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Odontology",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0069",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0022034520967933",
"article-title": "Antiviral activity of reagents in mouth rinses against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Carrouel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "124",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Dent Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0070",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/00220345221110444",
"article-title": "Preprocedural mouthwashes for reduction of SARS-CoV-2 viral load and infectivity",
"author": "Cieplik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1421",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J Dent Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0071",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/00220345221102310",
"article-title": "Cetylpyridinium chloride mouthwash to reduce shedding of infectious SARS-CoV-2: a double-blind randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Alemany",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1450",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "J Dent Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0072",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2022.2098059",
"article-title": "Effect of oral antiseptics in reducing SARS-CoV-2 infectivity: evidence from a randomized double-blind clinical trial",
"author": "Sánchez Barrueco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1833",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0073",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Randomized clinical trial to assess the impact of oral intervention with cetylpyridinium chloride to reduce salivary SARS-CoV-2 viral load",
"author": "Tarragó-Gil",
"journal-title": "J Clin Periodontol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0074",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.adaj.2021.05.021",
"article-title": "Estimating salivary carriage of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in nonsymptomatic people and efficacy of mouthrinse in reducing viral load: a randomized controlled trial",
"author": "Chaudhary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "903",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "J Am Dent Assoc",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0075",
"volume": "152",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/00220345231156415",
"article-title": "Efficacy of a mouthwash containing CHX and CPC in SARS-CoV-2-positive patients: a randomized controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Bonn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Dent Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0076",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"article-title": "Preprocedural mouthwashes for infection control in dentistry-an update",
"author": "Weber",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin Oral Investig",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0077",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coviro.2011.12.004",
"article-title": "Metagenomics and future perspectives in virus discovery",
"author": "Mokili",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "63",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0078",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0022034516648944",
"article-title": "Metagenomic insights into transferable antibiotic resistance in oral bacteria",
"author": "Sukumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "969",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Dent Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0079",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2019.00587",
"article-title": "Resistance toward chlorhexidine in oral bacteria - is there cause for concern?",
"author": "Cieplik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "587",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0080",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhin.2016.08.018",
"article-title": "Acquired resistance to chlorhexidine - is it time to establish an ‘antiseptic stewardship’ initiative?",
"author": "Kampf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "213",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Hosp Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0081",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-0765.1972.tb00645.x",
"article-title": "The sensitivity of oral streptococci to chlorhexidine",
"author": "Schiott",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "192",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Periodontal Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0082",
"volume": "7",
"year": "1972"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-0765.1972.tb00644.x",
"article-title": "Effect of chlorhexidine on human oral streptococci",
"author": "Emilson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "189",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Periodontal Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0083",
"volume": "7",
"year": "1972"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1902/jop.1989.60.9.521",
"article-title": "In vitro activity of a chlorhexidine-containing mouthwash against subgingival bacteria",
"author": "Wade",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "521",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Periodontol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0084",
"volume": "60",
"year": "1989"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00784-014-1379-y",
"article-title": "Development of resistance of mutans streptococci and Porphyromonas gingivalis to chlorhexidine digluconate and amine fluoride/stannous fluoride-containing mouthrinses, in vitro",
"author": "Kulik",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1547",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Clin Oral Investig",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0085",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12866-016-0833-1",
"article-title": "Dental plaque bacteria with reduced susceptibility to chlorhexidine are multidrug resistant",
"author": "Saleem",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "214",
"journal-title": "BMC Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0086",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.32.6.932",
"article-title": "Antiseptic and antibiotic resistance plasmid in Staphylococcus aureus that possesses ability to confer chlorhexidine and acrinol resistance",
"author": "Yamamoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "932",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0087",
"volume": "32",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jgar.2020.12.010",
"article-title": "Prevalence of biocide resistance genes and chlorhexidine and mupirocin non-susceptibility in Portuguese hospitals during a 31-year period (1985-2016)",
"author": "Conceição",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "169",
"journal-title": "J Glob Antimicrob Resist",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0088",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.01162-16",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of increased resistance to chlorhexidine and cross-resistance to colistin following exposure of klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates to chlorhexidine",
"author": "Wand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0089",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.copbio.2015.03.018",
"article-title": "Quaternary ammonium disinfectants: microbial adaptation, degradation and ecology",
"author": "Tezel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "296",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Biotechnol",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0090",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdent.2016.02.008",
"article-title": "Evolution of resistance to cationic biocides in Streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus faecalis",
"author": "Kitagawa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "18",
"journal-title": "J Dent",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0091",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-019-44822-y",
"article-title": "Development of antiseptic adaptation and cross-adapatation in selected oral pathogens in vitro",
"author": "Verspecht",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8326",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0092",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0300-5712(95)00116-6",
"article-title": "Effect of use of 0.05% cetylpyridinium chloride mouthwash on normal oral flora",
"author": "Radford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Dent",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0093",
"volume": "25",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00576-20",
"article-title": "Cetylpyridinium chloride: mechanism of action, antimicrobial efficacy in biofilms, and potential risks of resistance",
"author": "Mao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0094",
"volume": "64",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1600-0757.1997.tb00105.x",
"article-title": "Chlorhexidine: is it still the gold standard?",
"author": "Jones",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Periodontology 2000",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0095",
"volume": "15",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/microbiolspec.MB-0010-2014",
"article-title": "Antimicrobial tolerance in biofilms",
"author": "Stewart",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Microbiol Spectr",
"key": "10.1016/j.identj.2023.08.010_bib0096",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2015"
}
],
"reference-count": 96,
"references-count": 96,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0020653923004550"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Dentistry"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Mouthwash Effects on the Oral Microbiome: Are They Good, Bad, or Balanced?",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "73"
}