Vadadustat for the Prevention and Treatment of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) in Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)
et al., NCT04478071, VSTAT, NCT04478071, Mar 2025
RCT 448 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in the USA showing no significant differences with vadadustat.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
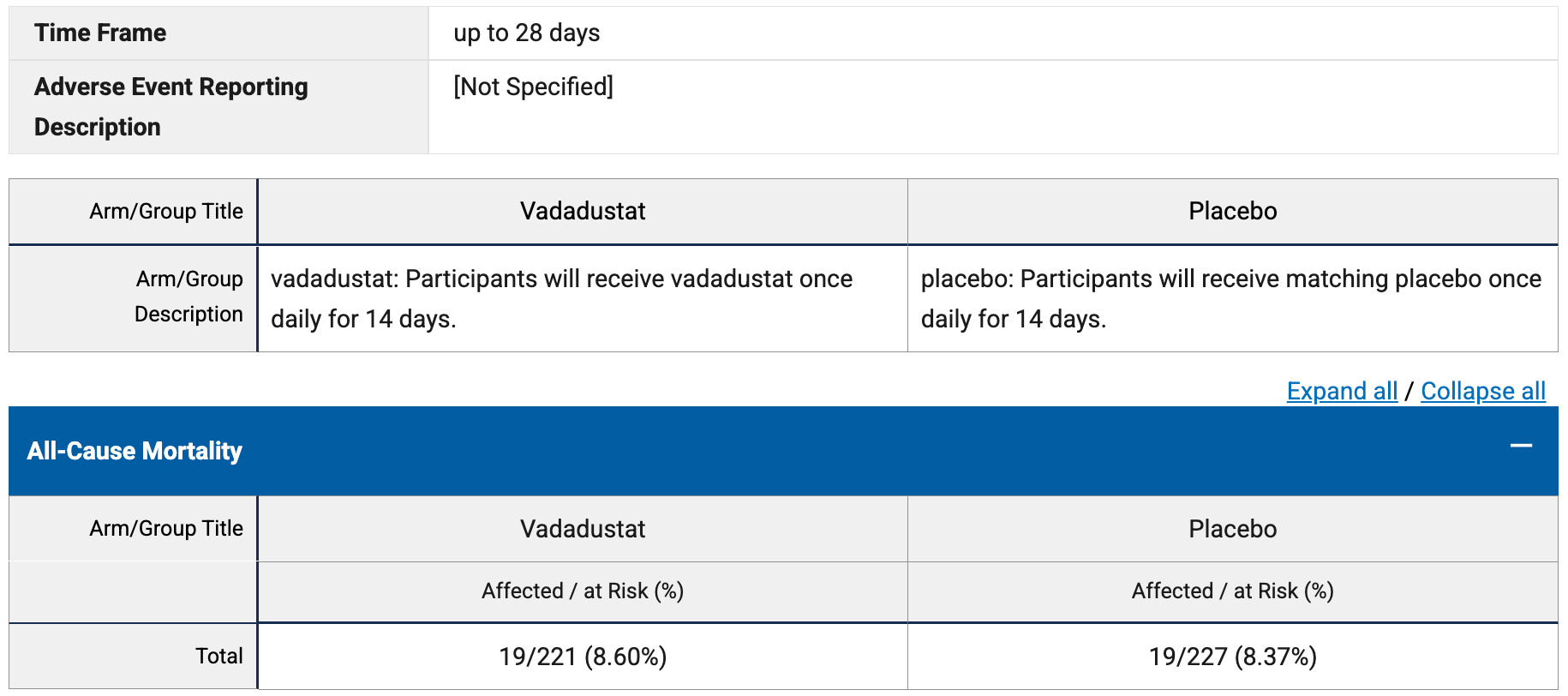
risk of death, 2.7% higher, RR 1.03, p = 1.00, treatment 19 of 221 (8.6%), control 19 of 227 (8.4%), day 28.
|
|
risk of progression, 16.2% lower, RR 0.84, p = 0.36, treatment 43 of 216 (19.9%), control 53 of 223 (23.8%), NNT 26, NIAID ordinal score ≥6, day 14.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 8.4% lower, RR 0.92, p = 0.60, treatment 58 of 214 (27.1%), control 66 of 223 (29.6%), NNT 40, MSOFA 0, day 14.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Bobrow et al., 25 Mar 2025, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, preprint, 1 author, average treatment delay 7.0 days, trial NCT04478071 (history) (VSTAT).
Contact: Bentley.J.Bobrow@uth.tmc.edu.