SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibody Treatment Followed by Vaccination Shifts Human Memory B-Cell Epitope Recognition, Suggesting Antibody Feedback
et al., The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiae371, Jul 2024
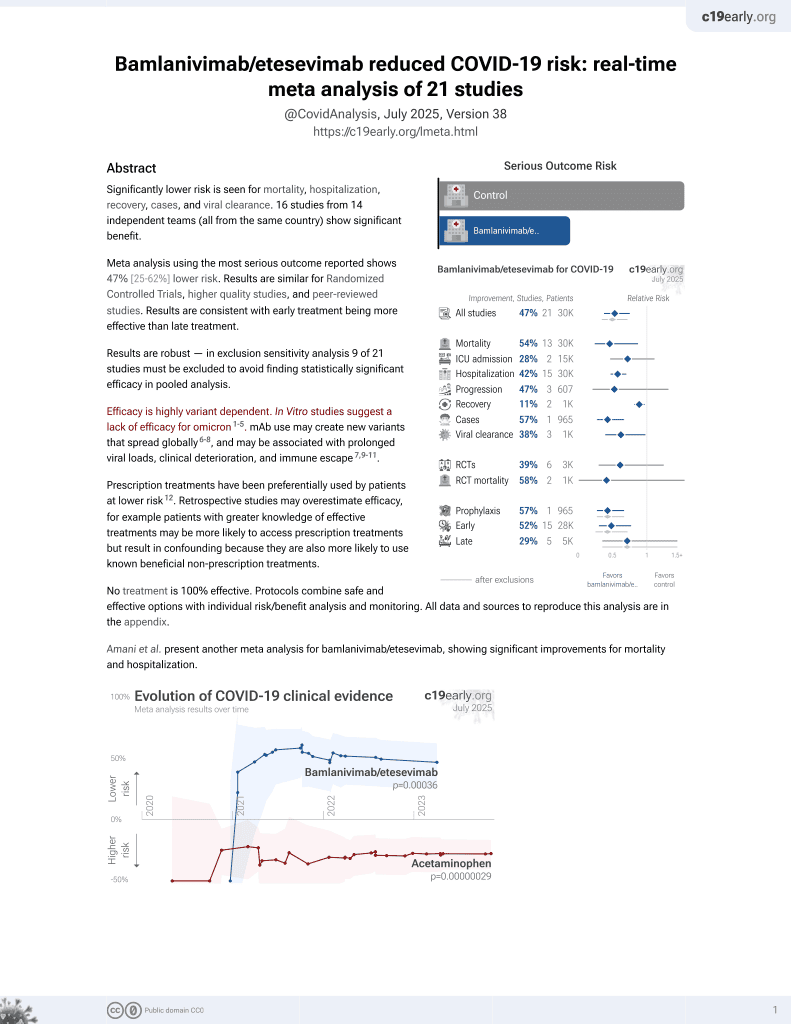
25th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2021, now with p = 0.00049 from 22 studies, recognized in 11 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
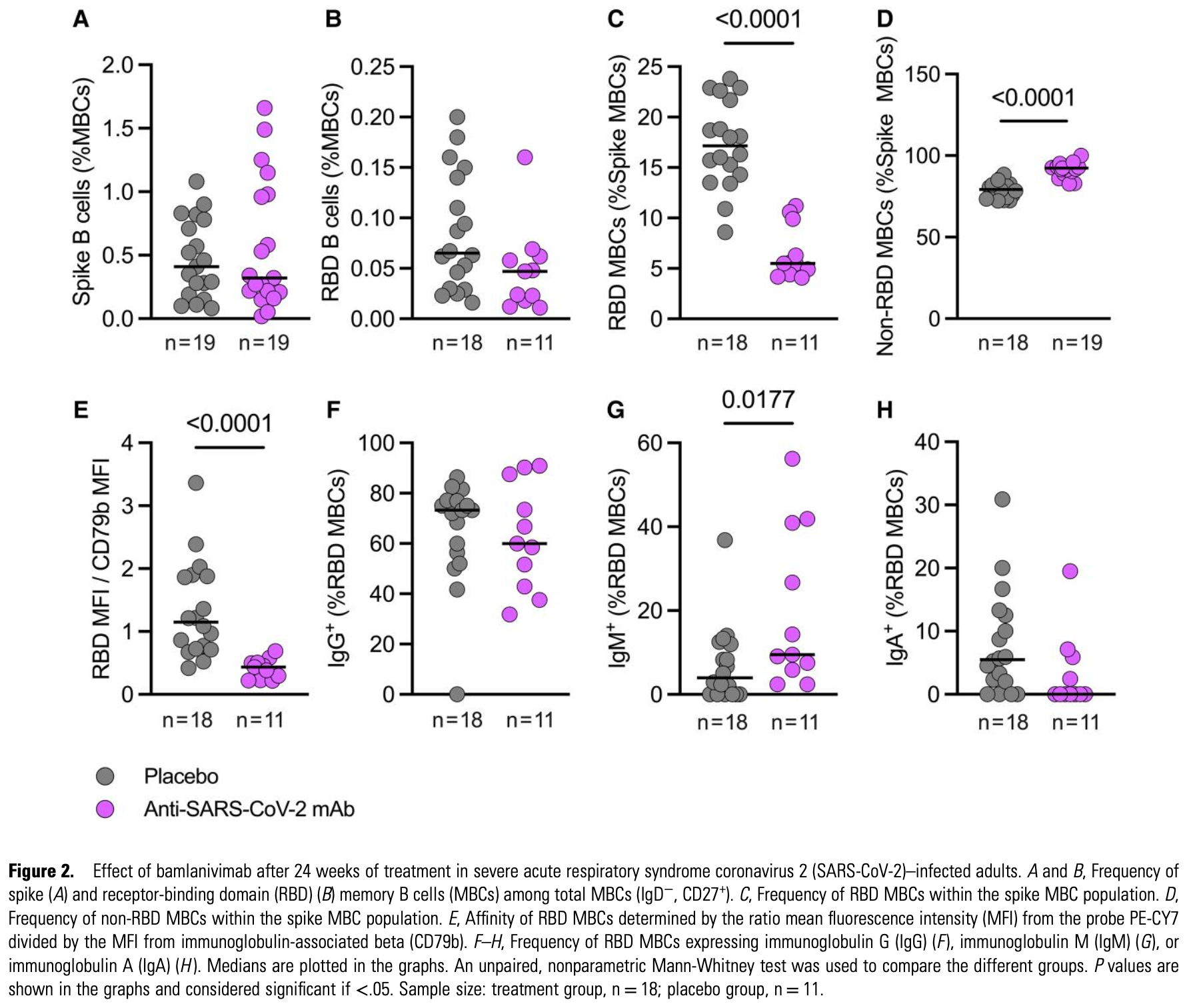
Analysis of 46 COVID-19 patients showing that bamlanivimab treatment altered epitope recognition by memory B cells, indicating antibody feedback. Bamlanivimab reduced the frequency and affinity of RBD-specific memory B cells compared to placebo at 24 weeks and after subsequent vaccination.
The results suggest that, while mAb treatment may provide immediate protection against the targeted virus, it may aso alter immune memory. Specifically, it may reduce memory B-cell responses to the exact viral epitope targeted by the antibody, which may result in a less robust immune response to the same virus or closely related variants.
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
Bloom et al., 22 Jul 2024, peer-reviewed, 27 authors.
Contact: camila.coelho@mssm.edu, shane@lji.org.
SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibody Treatment Followed by Vaccination Shifts Human Memory B-Cell Epitope Recognition, Suggesting Antibody Feedback
The Journal of Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiae371
Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have been studied in humans, but the impact on immune memory of mAb treatment during an ongoing infection remains unclear. We evaluated the effect of infusion of the anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) mAb bamlanivimab on memory B cells (MBCs) in SARS-CoV-2-infected individuals. Bamlanivimab treatment skewed the repertoire of MBCs targeting spike toward non-RBD epitopes. Furthermore, the relative affinity of RBD MBCs was weaker in mAb-treated individuals compared to placebo-treated individuals over time. Subsequently, after mRNA coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination, MBC differences persisted and mapped to a specific reduction in recognition of the class II RBD site, the same RBD epitope recognized by bamlanivimab. These findings indicate a substantial role of antibody feedback in regulating MBC responses to infection, and single mAb administration can continue to impact MBC responses to additional antigen exposures months later.
MBC Specificities We assessed the impact of mAb treatment on MBCs in greater detail by examining RBD MBC epitope specificity. SARS-CoV-2 RBD and spike antibody epitopes have been extensively characterized [27] [28] [29] [30] . We designed RBD epitope probe constructs by incorporating point mutations disrupting
Supplementary Data Supplementary materials are available at The Journal of Infectious Diseases online ( http://jid.oxfordjournals.org/ ). Supplementary materials consist of data provided by the author that are published to benefit the reader. The posted materials are not copyedited. The contents of all supplementary data ipants, site staff, site investigators, members of the ACTIV-2/ A5401 Study Team, the ACTIV-
References
Addetia, Park, Starr, Structural changes in the SARS-CoV-2 spike E406W mutant escaping a clinical monoclonal antibody cocktail, Cell Rep
Alsoussi, Malladi, Zhou, SARS-CoV-2 Omicron boosting induces de novo B cell response in humans, Nature
Benschop, Tuttle, Zhang, The anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody bamlanivimab minimally affects the endogenous immune response to COVID-19 vaccination, Sci Transl Med
Boucau, Chew, Choudhary, Monoclonal antibody treatment drives rapid culture conversion in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Cell Rep Med
Brouwer, Caniels, Van Der Straten, Potent neutralizing antibodies from COVID-19 patients define multiple targets of vulnerability, Science
Chew, Moser, Daar, Antiviral and clinical activity of bamlanivimab in a randomized trial of nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19, Nat Commun
Choudhary, Chew, Deo, Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 escape mutations during bamlanivimab therapy in a phase II randomized clinical trial, Nat Microbiol
Dougan, Nirula, Azizad, Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Dugan, Guthmiller, Arevalo, Preexisting immunity shapes distinct antibody landscapes after influenza virus infection and vaccination in humans, Sci Transl Med
Fan, Cohen, Park, Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies elicited by mosaic RBD nanoparticles bind conserved sarbecovirus epitopes, Immunity
Greaney, Loes, Crawford, Comprehensive mapping of mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain that affect recognition by polyclonal human plasma antibodies, Cell Host Microbe
Greaney, Starr, Barnes, Mapping mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 RBD that escape binding by different classes of antibodies, Nat Commun
Greaney, Starr, Bloom, An antibody-escape estimator for mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain, Virus Evol
Greaney, Starr, Gilchuk, Complete mapping of mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain that escape antibody recognition, Cell Host Microbe
Hastie, Li, Bedinger, Defining variant-resistant epitopes targeted by SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: a global consortium study, Science
Heyman, Regulation of antibody responses via antibodies, complement, and Fc receptors, Annu Rev Immunol
Kaku, Bergeron, Ahlm, Recall of preexisting cross-reactive B cell memory after Omicron BA.1 breakthrough infection, Sci Immunol
Kaku, Starr, Zhou, Evolution of antibody immunity following Omicron BA.1 breakthrough infection, Nat Commun
Koutsakos, Ellebedy, Immunological imprinting: understanding COVID-19, Immunity
Pape, Dileepan, Kabage, High-affinity memory B cells induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection produce more plasmablasts and atypical memory B cells than those primed by mRNA vaccines, Cell Rep
Pape, Maul, Dileepan, Paustian, Gearhart et al., Naïve B cells with high-avidity germlineencoded antigen receptors produce persistent IgM+ and transient IgG+ memory B cells, Immunity
Pape, Taylor, Maul, Gearhart, Jenkins, Different B cell populations mediate early and late memory during an endogenous immune response, Science
Ramirez, Grifoni, Weiskopf, Bamlanivimab therapy for acute COVID-19 does not blunt SARS-CoV-2-specific memory T cell responses, JCI Insight
Ramirez, Lopez, Faraji, Early antiviral CD4 and CD8 T cell responses are associated with upper respiratory tract clearance of SARS-CoV-2, doi:10.1101/2023.10.25.564014
Robbiani, Gaebler, Muecksch, Convergent antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in convalescent individuals, Nature
Röltgen, Nielsen, Silva, Immune imprinting, breadth of variant recognition, and germinal center response in human SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination, Cell
Schaefer-Babajew, Wang, Muecksch, Antibody feedback regulates immune memory after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination, Nature
Schiepers, Van 't Wout, Greaney, Molecular fate-mapping of serum antibody responses to repeat immunization, Nature
Shiakolas, Kramer, Johnson, Efficient discovery of SARS-CoV-2-neutralizing antibodies via B cell receptor sequencing and ligand blocking, Nat Biotechnol
Smith, Active immunity produced by so called balanced or neutral mixtures of diphtheria toxin and antitoxin, J Exp Med
Starr, Greaney, Dingens, Bloom, Complete map of SARS-CoV-2 RBD mutations that escape the monoclonal antibody LY-CoV555 and its cocktail with LY-CoV016, Cell Rep Med
Sun, Ramos, Coelho, Asymptomatic or symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection plus vaccination confers increased adaptive immunity to variants of concern, iScience
Tarke, Coelho, Zhang, SARS-CoV-2 vaccination induces immunological T cell memory able to crossrecognize variants from Alpha to Omicron, Cell
Tas, Koo, Lin, Antibodies from primary humoral responses modulate the recruitment of naive B cells during secondary responses, Immunity
Wang, Schmidt, Weisblum, mRNA vaccine-elicited antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and circulating variants, Nature
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Zhang, Mateus, Coelho, Humoral and cellular immune memory to four COVID-19 vaccines, Cell
Zhang, Meyer-Hermann, George, Germinal center B cells govern their own fate via antibody feedback, J Exp Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiae371",
"ISSN": [
"0022-1899",
"1537-6613"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiae371",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have been studied in humans, but the impact on immune memory of mAb treatment during an ongoing infection remains unclear. We evaluated the effect of infusion of the anti–severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike receptor-binding domain (RBD) mAb bamlanivimab on memory B cells (MBCs) in SARS-CoV-2–infected individuals. Bamlanivimab treatment skewed the repertoire of MBCs targeting spike toward non-RBD epitopes. Furthermore, the relative affinity of RBD MBCs was weaker in mAb-treated individuals compared to placebo-treated individuals over time. Subsequently, after mRNA coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination, MBC differences persisted and mapped to a specific reduction in recognition of the class II RBD site, the same RBD epitope recognized by bamlanivimab. These findings indicate a substantial role of antibody feedback in regulating MBC responses to infection, and single mAb administration can continue to impact MBC responses to additional antigen exposures months later.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Vaccine Innovation, La Jolla Institute for Immunology"
}
],
"family": "Bloom",
"given": "Nathaniel",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Vaccine Innovation, La Jolla Institute for Immunology"
},
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases and Global Public Health, Department of Medicine, University of California, San Diego , La Jolla"
}
],
"family": "Ramirez",
"given": "Sydney I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology"
},
{
"name": "Center for Vaccine Research and Pandemic Preparedness, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai , New York, New York"
}
],
"family": "Cohn",
"given": "Hallie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine , Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Parikh",
"given": "Urvi M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine , Pennsylvania"
}
],
"family": "Heaps",
"given": "Amy",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases and HIV Medicine, Department of Medicine, Case Western Reserve School of Medicine , Cleveland, Ohio"
}
],
"family": "Sieg",
"given": "Scott F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7443-0527",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of Washington , Seattle"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Greninger",
"given": "Alex",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Biostatistics in AIDS Research, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health , Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Ritz",
"given": "Justin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5601-9112",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Biostatistics in AIDS Research, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health , Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Moser",
"given": "Carlee",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine"
}
],
"family": "Eron",
"given": "Joseph J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology"
}
],
"family": "Bajic",
"given": "Goran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles"
}
],
"family": "Currier",
"given": "Judith S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Eli Lilly and Company , San Diego"
}
],
"family": "Klekotka",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine"
}
],
"family": "Wohl",
"given": "David A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Lundquist Institute at Harbor, University of California, Los Angeles Medical Center , Torrance"
}
],
"family": "Daar",
"given": "Eric S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School , Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Biostatistics in AIDS Research, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health , Boston, Massachusetts"
}
],
"family": "Hughes",
"given": "Michael D",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Medicine, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles"
}
],
"family": "Chew",
"given": "Kara W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases and Global Public Health, Department of Medicine, University of California, San Diego , La Jolla"
}
],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Davey M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Center for Vaccine Innovation, La Jolla Institute for Immunology"
},
{
"name": "Division of Infectious Diseases and Global Public Health, Department of Medicine, University of California, San Diego , La Jolla"
}
],
"family": "Crotty",
"given": "Shane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7885-9996",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology"
},
{
"name": "Center for Vaccine Research and Pandemic Preparedness, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai , New York, New York"
},
{
"name": "Precision Immunology Institute, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai , New York, New York"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Coelho",
"given": "Camila H",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"name": "for the Accelerating COVID-19 Therapeutic Interventions and Vaccines–2/A5401 (ACTIV-2/A5401) Study Team",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hosey",
"given": "Lara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roa",
"given": "Jhoanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patel",
"given": "Nilam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Erhardt",
"given": "Bill",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adams",
"given": "Stacey",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-19T05:42:12Z",
"timestamp": 1721367732000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-15T14:56:16Z",
"timestamp": 1731682576000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000060",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000002",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100012264",
"award": [
"75N93019C00065"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100012264",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "NIH"
},
{
"award": [
"U54CA267776"
],
"name": "NIH Faculty Institutional Recruitment for Sustainable Transformation"
},
{
"award": [
"AI142742"
],
"name": "Collaborative Center for Human Immunology"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100020189",
"award": [
"T32 AI007036"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100020189",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "John and Mary Tu Foundation"
},
{
"name": "La Jolla Institute for Immunology institutional funds"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100002112",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100002112",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "A. P. Giannini Foundation"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-11-16T05:26:18Z",
"timestamp": 1731734778049,
"version": "3.28.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "5",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
22
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "5",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
22
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
15
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/pages/standard-publication-reuse-rights",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-22T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1721606400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/infdis/jiae371/58689853/jiae371.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/article-pdf/230/5/1187/60683867/jiae371.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/article-pdf/230/5/1187/60683867/jiae371.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1187-1196",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
22
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
22
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
15
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
11,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00163-5",
"article-title": "Casirivimab and imdevimab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "665",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B1",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "238",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B2",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2102685",
"article-title": "Bamlanivimab plus etesevimab in mild or moderate Covid-19",
"author": "Dougan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B3",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-32551-2",
"article-title": "Antiviral and clinical activity of bamlanivimab in a randomized trial of non-hospitalized adults with COVID-19",
"author": "Chew",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4931",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B4",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100678",
"article-title": "Monoclonal antibody treatment drives rapid culture conversion in SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Boucau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100678",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep Med",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B5",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abn3041",
"article-title": "The anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody bamlanivimab minimally affects the endogenous immune response to COVID-19 vaccination",
"author": "Benschop",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabn3041",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B6",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05609-w",
"article-title": "Antibody feedback regulates immune memory after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination",
"author": "Schaefer-Babajew",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "735",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B7",
"volume": "613",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.709",
"article-title": "Regulation of antibody responses via antibodies, complement, and Fc receptors",
"author": "Heyman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "709",
"journal-title": "Annu Rev Immunol",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B8",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2022.07.020",
"article-title": "Antibodies from primary humoral responses modulate the recruitment of naive B cells during secondary responses",
"author": "Tas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1856",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B9",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1201730",
"article-title": "Different B cell populations mediate early and late memory during an endogenous immune response",
"author": "Pape",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1203",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B10",
"volume": "331",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.11.2.241",
"article-title": "Active immunity produced by so called balanced or neutral mixtures of diphtheria toxin and antitoxin",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "241",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B11",
"volume": "11",
"year": "1909"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1084/jem.20120150",
"article-title": "Germinal center B cells govern their own fate via antibody feedback",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "457",
"journal-title": "J Exp Med",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B12",
"volume": "210",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-05715-3",
"article-title": "Molecular fate-mapping of serum antibody responses to repeat immunization",
"author": "Schiepers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "482",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B13",
"volume": "615",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06025-4",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Omicron boosting induces de novo B cell response in humans",
"author": "Alsoussi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "592",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B14",
"volume": "617",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-38345-4",
"article-title": "Evolution of antibody immunity following Omicron BA.1 breakthrough infection",
"author": "Kaku",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2751",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B15",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.abq3511",
"article-title": "Recall of preexisting cross-reactive B cell memory after Omicron BA.1 breakthrough infection",
"author": "Kaku",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabq3511",
"journal-title": "Sci Immunol",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B16",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2023.04.012",
"article-title": "Immunological imprinting: understanding COVID-19",
"author": "Koutsakos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "909",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B17",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abd3601",
"article-title": "Preexisting immunity shapes distinct antibody landscapes after influenza virus infection and vaccination in humans",
"author": "Dugan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "eabd3601",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B18",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.163471",
"article-title": "Bamlanivimab therapy for acute COVID-19 does not blunt SARS-CoV-2-specific memory T cell responses",
"author": "Ramirez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e163471",
"journal-title": "JCI Insight",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B19",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-24435-8",
"article-title": "Mapping mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 RBD that escape binding by different classes of antibodies",
"author": "Greaney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4196",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B20",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.11.007",
"article-title": "Complete mapping of mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain that escape antibody recognition",
"author": "Greaney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "44",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B21",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.015",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 vaccination induces immunological T cell memory able to cross-recognize variants from Alpha to Omicron",
"author": "Tarke",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "847",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B22",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-022-01254-1",
"article-title": "Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 escape mutations during bamlanivimab therapy in a phase II randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Choudhary",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1906",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B23",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.10.25.564014",
"author": "Ramirez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109823",
"article-title": "High-affinity memory B cells induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection produce more plasmablasts and atypical memory B cells than those primed by mRNA vaccines",
"author": "Pape",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "109823",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B25",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2018.04.019",
"article-title": "Naïve B cells with high-avidity germline-encoded antigen receptors produce persistent IgM+ and transient IgG+ memory B cells",
"author": "Pape",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1135",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B26",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc5902",
"article-title": "Potent neutralizing antibodies from COVID-19 patients define multiple targets of vulnerability",
"author": "Brouwer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "643",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B27",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abh2315",
"article-title": "Defining variant-resistant epitopes targeted by SARS-CoV-2 antibodies: a global consortium study",
"author": "Hastie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "472",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B28",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2022.10.019",
"article-title": "Neutralizing monoclonal antibodies elicited by mosaic RBD nanoparticles bind conserved sarbecovirus epitopes",
"author": "Fan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2419",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B29",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2456-9",
"article-title": "Convergent antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 in convalescent individuals",
"author": "Robbiani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "437",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B30",
"volume": "584",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2021.02.003",
"article-title": "Comprehensive mapping of mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain that affect recognition by polyclonal human plasma antibodies",
"author": "Greaney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "463",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B31",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ve/veac021",
"article-title": "An antibody-escape estimator for mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain",
"author": "Greaney",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "veac021",
"journal-title": "Virus Evol",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B32",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03324-6",
"article-title": "mRNA vaccine-elicited antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and circulating variants",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "616",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B33",
"volume": "592",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112621",
"article-title": "Structural changes in the SARS-CoV-2 spike E406W mutant escaping a clinical monoclonal antibody cocktail",
"author": "Addetia",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "112621",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B34",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41587-022-01232-2",
"article-title": "Efficient discovery of SARS-CoV-2-neutralizing antibodies via B cell receptor sequencing and ligand blocking",
"author": "Shiakolas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1270",
"journal-title": "Nat Biotechnol",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B35",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2021.100255",
"article-title": "Complete map of SARS-CoV-2 RBD mutations that escape the monoclonal antibody LY-CoV555 and its cocktail with LY-CoV016",
"author": "Starr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100255",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep Med",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B36",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.018",
"article-title": "Immune imprinting, breadth of variant recognition, and germinal center response in human SARS-CoV-2 infection and vaccination",
"author": "Röltgen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1025",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B37",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2022.105202",
"article-title": "Asymptomatic or symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection plus vaccination confers increased adaptive immunity to variants of concern",
"author": "Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105202",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B38",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.05.022",
"article-title": "Humoral and cellular immune memory to four COVID-19 vaccines",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2434",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2024111514553793800_jiae371-B39",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 39,
"references-count": 39,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/jid/article/230/5/1187/7717844"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibody Treatment Followed by Vaccination Shifts Human Memory B-Cell Epitope Recognition, Suggesting Antibody Feedback",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "230"
}