The relationship between vitamin D and the severity of COVID-19
et al., Bratislava Medical Journal, doi:10.4149/bll_2021_034, Feb 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Prospective study of 204 patients with COVID-19-like pneumonia in Turkey, 42 outpatients (mild cases), and 162 inpatients (serious cases), showing significantly higher risk of severe cases with vitamin D deficiency.
This is the 47th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of severe case, 68.6% lower, RR 0.31, p = 0.005, high D levels 82 of 119 (68.9%), low D levels 80 of 85 (94.1%), NNT 4.0, inverted to make RR<1 favor high D levels, odds ratio converted to relative risk, >10μg/L, per standard deviation increase in levels.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Basaran et al., 12 Feb 2021, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
The relationship between vitamin D and the severity of COVID-19
Bratislava Medical Journal, doi:10.4149/bll_2021_034
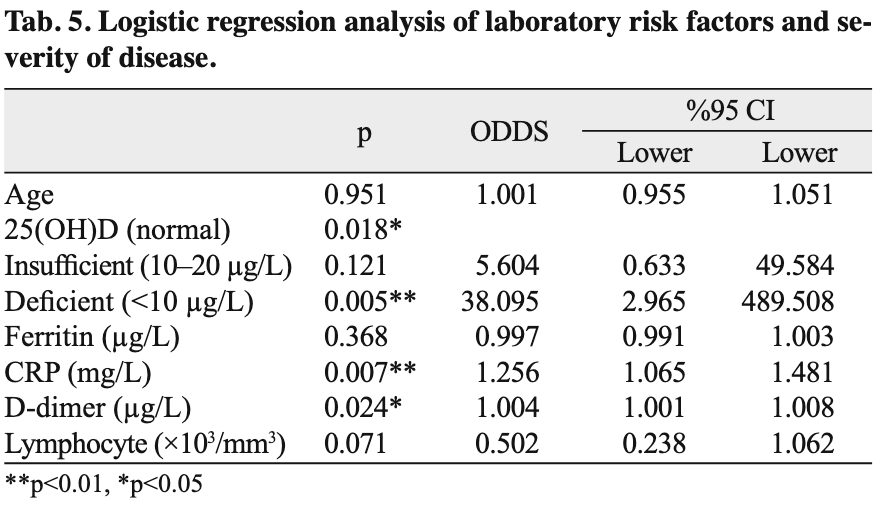
AIM: Vitamin D, which has immunomodulatory effect, can reduce risk of infections and concentrations of proinfl ammatory cytokines. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between the levels of vitamin D and severity of COVID-19. METHODS: A total of 204 patients with COVID-19 disease were enrolled in the study. All patients had viral pneumonia, which was confi rmed with chest computer tomography. All cases were divided in two groupsmild (outpatients); and serious (inpatients)-according to their clinical and laboratory data. Serum vitamin D levels were measured by chemiluminescence method. RESULTS: Vitamin D defi ciency was found in 41.7 % (n = 85) of cases and insuffi ciency was found in 46.0 % (n = 94), while in 12.3 % (n = 25) of cases normal vitamin D levels were found. The odds of having a serious clinical outcome were increased for vitamin D insuffi ciency patients 5.604 times (%95 CI:0.633-49.584) and for vitamin D defi ciency patients 38.095 times (%95 CI:2.965-489.50) for each standard deviation decrease in serum 25(OH)D. CONCLUSION: Adequate levels of vitamin D could suppress infl ammation and reduce the severity of COVID-19. Vitamin D supplementation may have an important role in decreasing the impact of the pandemic (Tab. 5, Fig. 2, Ref. 27
References
Alipio, Vitamin D Supplementation Could Possibly Improve Clinical Outcomes of Patients Infected with Coronavirus, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3571484
Barlow, Svoboda, Mackellar, Antiviralactivity and increased host defense against infl uenza infection elicited by the human cathelicidin LL-37, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0025333
Blondonm, Rodabough, Budrys, The effect of calcium plus vitamin D supplementation on the risk of venous thromboembolism. From the Women's Health Initiative Randomized Controlled Trial, ThrombHaemost, doi:10.1160/TH14-05-0478
Bolland, Avenell, Grey, Should adults take vitamin D supplements to prevent disease?, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.i6201
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Ebadi, Montano-Loza, Perspective: improving vitamin D status in the management of COVID-19, Eur J ClinNutr, doi:10.1038/s41430-020-0661-0
El Hassoun, Valaskova, Polak, Hulin, Few Insights on the problem of COVID-19, Bratisl Med J, doi:10.4149/BLL_2020_078
Giannis, Ziogasia, Gianni, Coagulation disorders in coronavirus infected patients: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-1, MERS-CoV and lessons from the past, J Clin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104362
Gombart, Pierre, Maggini, A Review of Micronutrients and the Immune System-Working in Harmony to Reduce the Risk of Infection, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12010236
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Evidence that Vitamin D Supplementation Could Reduce Risk of Infl uenza and COVID-19 Infections and Deaths, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12040988
Hastie, Mackay, Ho, Vitamin D concentrations and CO-VID-19 infection in UK Biobank, Diabetes MetabSyndr, doi:10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.050
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Ilie, Stefanescu, Smith, The role of vitamin D in the prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 infection and mortality
Kong, Zhu, Shi, VDR attenuates acute lung injury by blocking Ang-2-Tie-2 pathway and renin-angiotensin system, Mol Endocrinol, doi:10.1210/me.2013-1146
Laird, Mcnulty, Ward, Vitamin D defi ciency is associated with infl ammation in older Irish adults, J ClinEndocrinolMetab2014, doi:10.1210/jc.2013-3507
Li, Geng, Peng, Meng, Lu, Molecular immune pathogenesis and diagnosis of COVID-19, J Pharm Anal, doi:10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.001
Mohammad, Mishra, Ashraf, Emerging Role of Vitamin D and its Associated Molecules in Pathways Related to Pathogenesis of Thrombosis, Biomolecules, doi:10.3390/biom9110649
Ni, Tian, Xiang, Yu, Characteristics of infl ammatory factors and lymphocyte subsets in patients with severe COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26070
Rhodes, Subramanian, Laird, Kenny, Editorial: low population mortality from COVID-19 in countries south of latitude 35 degrees North supports vitamin D as a factor determining severity, Aliment PharmacolTher, doi:10.1111/apt.15777
Tang, Li, Wang, Sun, Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia, J ThrombHaemost, doi:10.1111/jth.14768
Vanherwegen, Gysemans, Mathieu, Regulation of Immune Function by Vitamin D and Its Use in Diseases of Immunity, Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am, doi:10.1016/j.ecl.2017.07.010
Weir, Thenappan, Bhargava, Chen, Does vitamin D defi ciency increase the severity of COVID-19?
Wu, He, Low Vitamin D Levels Are Associated with the Development of Deep Venous Thromboembolic Events in Patients With-Ischemic Stroke, Clin Appl ThrombHemost, doi:10.1177/1076029618786574
Yormaz, Ergun, Tulek, The evaluation of prognostic value of acute phase reactants in the COVID-19, Bratisl Med J, doi:10.4149/BLL_2020_103
Zhao, Ran, Jiang, D Alleviates Rotavirus Infection through a Microrna-155-5p Mediated Regulation of the TBK1/IRF3 Signaling Pathway In Vivo and In Vitro, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms20143562
Zhou, She, Wang, Ma, Utility of Ferritin, Procalcitonin, and Creactive Protein in Severe Patients with 2019 Novel Coronavirus Disease, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-18079/v1+
Zhou, Yu, Du, Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.4149/bll_2021_034",
"ISSN": [
"1336-0345"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.4149/bll_2021_034",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Basaran",
"given": "N.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Adas",
"given": "M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gokden",
"given": "Y.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Turgut",
"given": "N.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yildirmak",
"given": "T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Guntas",
"given": "G.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Bratislava Medical Journal",
"container-title-short": "BLL",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-16T01:38:03Z",
"timestamp": 1613439483000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-16T01:38:10Z",
"timestamp": 1613439490000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-04T19:10:51Z",
"timestamp": 1712257851737
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 6,
"issue": "03",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "03",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
}
},
"member": "2638",
"original-title": [],
"page": "200-205",
"prefix": "10.4149",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021
]
]
},
"publisher": "AEPress, s.r.o.",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.elis.sk/index.php?page=shop.product_details&flypage=flypage.tpl&product_id=7119&category_id=171&option=com_virtuemart"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Earth and Planetary Sciences",
"General Environmental Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The relationship between vitamin D and the severity of COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "122"
}
