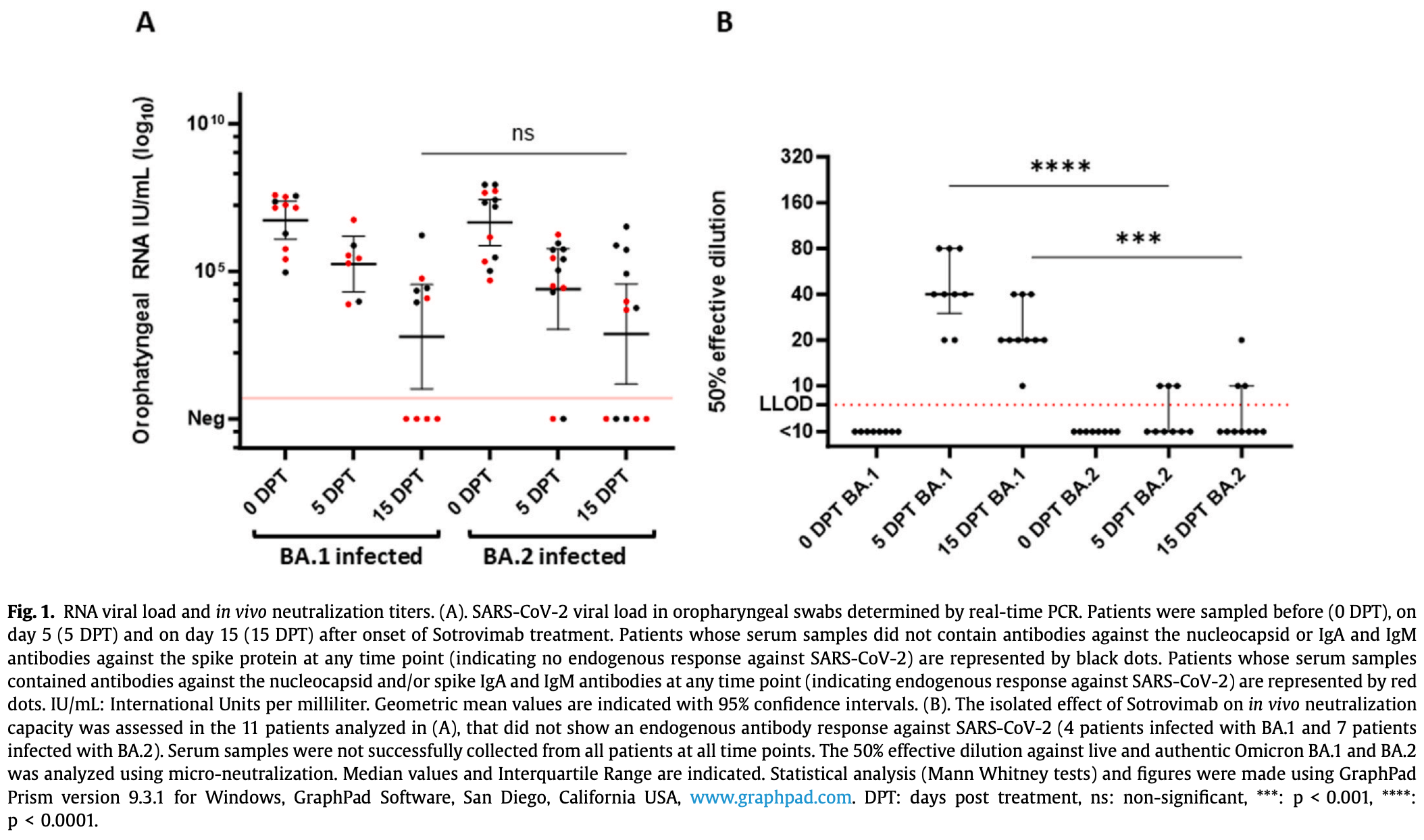
Sotrovimab lost neutralization efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 subvariants but remained clinically effective: Were monoclonal antibodies against COVID-19 rejected too early?
et al., Journal of Infection and Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512, Aug 2024
Sotrovimab for COVID-19
45th treatment shown to reduce risk in
August 2022, now with p = 0.00048 from 29 studies, recognized in 42 countries.
Efficacy is variant dependent.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 14 outpatients treated with sotrovimab showing that while sotrovimab lost in vitro neutralization efficacy against omicron subvariants BA.1 and BA.2, it remained clinically effective in reducing viral load in patients who did not have an endogenous antibody response. The results suggest that monoclonal antibodies should have potentially remained available for certain patient groups despite the strong recommendations against their use issued by health authorities in late 2022 and early 2023, which were largely based on in vitro neutralization results. Authors hypothesize that the immune stimulation induced by monoclonal antibodies, beyond just neutralization, may be beneficial for some patients.
Efficacy is variant dependent. In Vitro studies predict lower efficacy for BA.11-3, BA.4, BA.54, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5.24, XBB.2.9, CH.1.15, and no efficacy for BA.26, XBB, XBB.1.5, ХВВ.1.9.17, XBB.1.16, BQ.1.1.45, and CL.15. US EUA has been revoked.
1.
Liu et al., Striking Antibody Evasion Manifested by the Omicron Variant of SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.14.472719.
2.
Sheward et al., Variable loss of antibody potency against SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 (Omicron), bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.19.473354.
3.
VanBlargan et al., An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by several therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.12.15.472828.
4.
Haars et al., Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Sublineages and Spike Protein Mutations Conferring Resistance against Monoclonal Antibodies in a Swedish Cohort during 2022–2023, Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms11102417.
5.
Pochtovyi et al., In Vitro Efficacy of Antivirals and Monoclonal Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Lineages XBB.1.9.1, XBB.1.9.3, XBB.1.5, XBB.1.16, XBB.2.4, BQ.1.1.45, CH.1.1, and CL.1, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines11101533.
Bang et al., 12 Aug 2024, Denmark, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Sotrovimab lost neutralization efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 subvariants but remained clinically effective: Were monoclonal antibodies against COVID-19 rejected too early?
Journal of Infection and Public Health, doi:10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512
We read with interest the article by Behzad et al. [1
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
Behzad, Ali, Niinuma, Butler, Alqahtani, Real world effectiveness of sotrovimab in preventing COVID-19-related hospitalisation or death in patients infected with Omicron BA.2, J Infect Public Health
Cai, Diallo, Rosenthal, Ren, Flores et al., AZD3152 neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 historical and contemporary variants and is protective in hamsters and well tolerated in adults, Sci Transl Med
Driouich, Bernadin, Touret, Lamballerie, Nougairède, Activity of Sotrovimab against BQ.1.1 and XBB.1 Omicron sublineages in a hamster model, Antivir Res
Drysdale, Gibbons, Singh, Rolland, Lavoie et al., Realworld effectiveness of sotrovimab for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection during Omicron BA.2 subvariant predominance: a systematic literature review, Infection
Hérate, Touret, Dereuddre-Bosquet, Donati, Relouzat, Sotrovimab retains activity against SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant BQ.1.1 in a nonhuman primate model, Heliyon
Stadler, Burgess, Schlub, Khan, Chai et al., Monoclonal antibody levels and protection from COVID-19, Nat Commun
Supernova Phase, trial of sipavibart long-acting antibody met primary endpoints in preventing COVID-19 in immunocompromised patient population
Uraki, Kiso, Iida, Imai, Takashita et al., Characterization and antiviral susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2, Nature
Wilhelm, Widera, Grikscheit, Toptan, Schenk et al., Limited neutralisation of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.1 and BA.2 by convalescent and vaccine serum and monoclonal antibodies, eBioMedicine
Zhang, Stacey, Agostino, Tugg, Marzok et al., Beyond neutralization: Fc-dependent antibody effector functions in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nat Rev Immunol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512",
"ISSN": [
"1876-0341"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512",
"alternative-id": [
"S1876034124002466"
],
"article-number": "102512",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Sotrovimab lost neutralization efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 subvariants but remained clinically effective: Were monoclonal antibodies against COVID-19 rejected too early?"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of Infection and Public Health"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of King Saud Bin Abdulaziz University for Health Sciences."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bang",
"given": "Line Lundegaard",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madsen",
"given": "Lone Wulff",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pedersen",
"given": "Rune Micha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nilsson",
"given": "Anna Christine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2189-9823",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Johansen",
"given": "Isik Somuncu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andersen",
"given": "Thomas Emil",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Infection and Public Health",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Infection and Public Health",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-07T02:24:28Z",
"timestamp": 1722997468000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-12T19:33:58Z",
"timestamp": 1723491238000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100024075",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Region of Southern Denmark"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-13T04:40:05Z",
"timestamp": 1723524005614
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1725148800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-09-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1725148800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1722384000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1876034124002466?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1876034124002466?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "102512",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2023.11.029",
"article-title": "Real world effectiveness of sotrovimab in preventing COVID-19–related hospitalisation or death in patients infected with Omicron BA.2",
"author": "Behzad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "315",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512_bib1",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s15010-023-02098-5",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of sotrovimab for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection during Omicron BA.2 subvariant predominance: a systematic literature review",
"author": "Drysdale",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Infection",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512_bib2",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104158",
"article-title": "Limited neutralisation of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.1 and BA.2 by convalescent and vaccine serum and monoclonal antibodies",
"author": "Wilhelm",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "eBioMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512_bib3",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04856-1",
"article-title": "Characterization and antiviral susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2",
"author": "Uraki",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"issue": "7917",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512_bib4",
"volume": "607",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16664",
"article-title": "Sotrovimab retains activity against SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant BQ.1.1 in a non-human primate model",
"author": "Hérate",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512_bib5",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2023.105638",
"article-title": "Activity of Sotrovimab against BQ.1.1 and XBB.1 Omicron sublineages in a hamster model",
"author": "Driouich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Antivir Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512_bib6",
"volume": "215",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512_bib7",
"unstructured": "Zhang A, Stacey HD, D’Agostino MR, Tugg Y, Marzok A, Miller MS. Beyond neutralization: Fc-dependent antibody effector functions in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Rev Immunol; 2022 [Internet] [cited 2023 Sep 13]; Available from: 〈https://www.nature.com/articles/s41577-022-00813-1〉."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512_bib8",
"unstructured": "Therapeutics and COVID-19: living guideline, 16 September 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022 (WHO/2019-nCoV/therapeutics/2022.5). Available from: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/362843/WHO-2019-nCoV-therapeutics-2022.5-eng.pdf."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-40204-1",
"article-title": "Monoclonal antibody levels and protection from COVID-19",
"author": "Stadler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4545",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512_bib9",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.ado2817",
"article-title": "AZD3152 neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 historical and contemporary variants and is protective in hamsters and well tolerated in adults",
"author": "Cai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "753",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512_bib10",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512_bib11",
"unstructured": "SUPERNOVA Phase I.I.I. trial of sipavibart long-acting antibody met primary endpoints in preventing COVID-19 in immunocompromised patient population [Internet]. 2024 [cited 2024 Jul 8]. Available from: 〈https://www.astrazeneca.com/media-centre/press-releases/2024/supernova-trial-met-covid-19-prevention-endpoint.html〉."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.jiph.2024.102512_bib12",
"unstructured": "F.D.A. (Food and Drug Administration). Fact sheet for patients, parents, and caregivers Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) of PEMGARDA (pemivibart) for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) [Internet]. [cited 2024 Jul 15]. Available from: 〈https://www.fda.gov/media/177069/download〉."
}
],
"reference-count": 12,
"references-count": 12,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1876034124002466"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Sotrovimab lost neutralization efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 subvariants but remained clinically effective: Were monoclonal antibodies against COVID-19 rejected too early?",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "17"
}