Feb 23 |
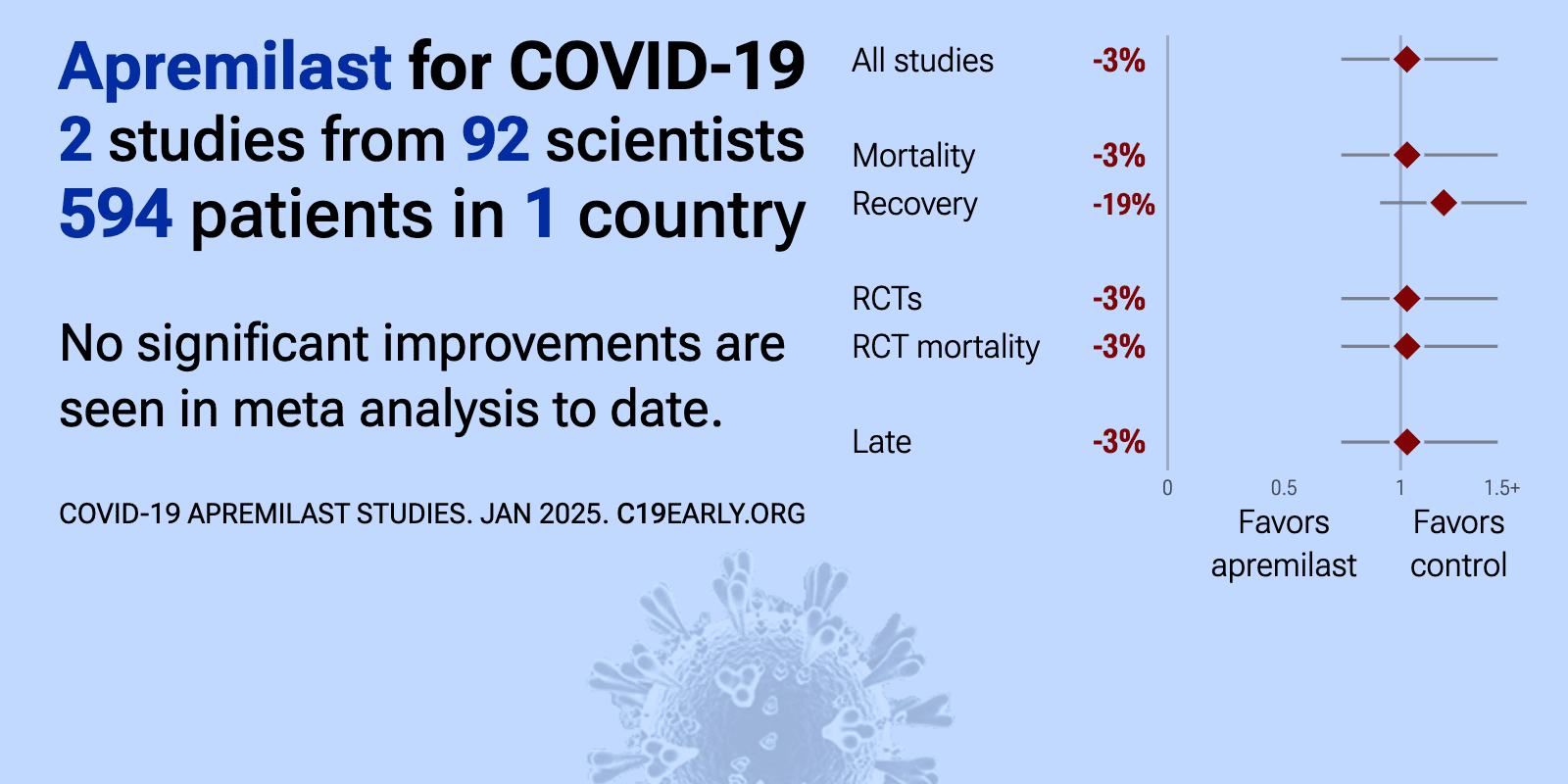
Meta-analysis of apremilast studies | |
| Meta-analysis of apremilast studies | ||
Nov 8 2024 |
et al., Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters, doi:10.1186/s11658-024-00659-6 | The role of reactive oxygen species in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-COV-2) infection-induced cell death |
| Review of the effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on cell death pathways in SARS-CoV-2 infection. SARS-CoV-2 induces oxidative stress and ROS generation which can lead to several types of regulated cell death including NETosis, ferro.. | ||
Mar 3 2023 |
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101889 | Report of the first seven agents in the I-SPY COVID trial: a phase 2, open label, adaptive platform randomised controlled trial |
| 5% higher mortality (p=0.85) and 28% worse recovery (p=0.22). RCT severe COVID-19 patients showing no significant difference in outcomes with apremilast. | ||
Apr 7 2022 |
, NCT04590586 | Industry Alliance Platform Trial to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of Multiple Candidate Agents for the Treatment of COVID-19 in Hospitalized Patients |
| 1% higher mortality (p=1), 8% worse improvement (p=0.73), 11% lower hospital discharge (p=0.56), and 11% worse recovery (p=0.58). RCT 384 hospitalized patients showing no significant difference with apremilast treatment. | ||