Intravenous ravulizumab in mechanically ventilated patients hospitalised with severe COVID-19: a phase 3, multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial
et al., The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6, ALXN1210-COV-305, NCT04369469, Mar 2023
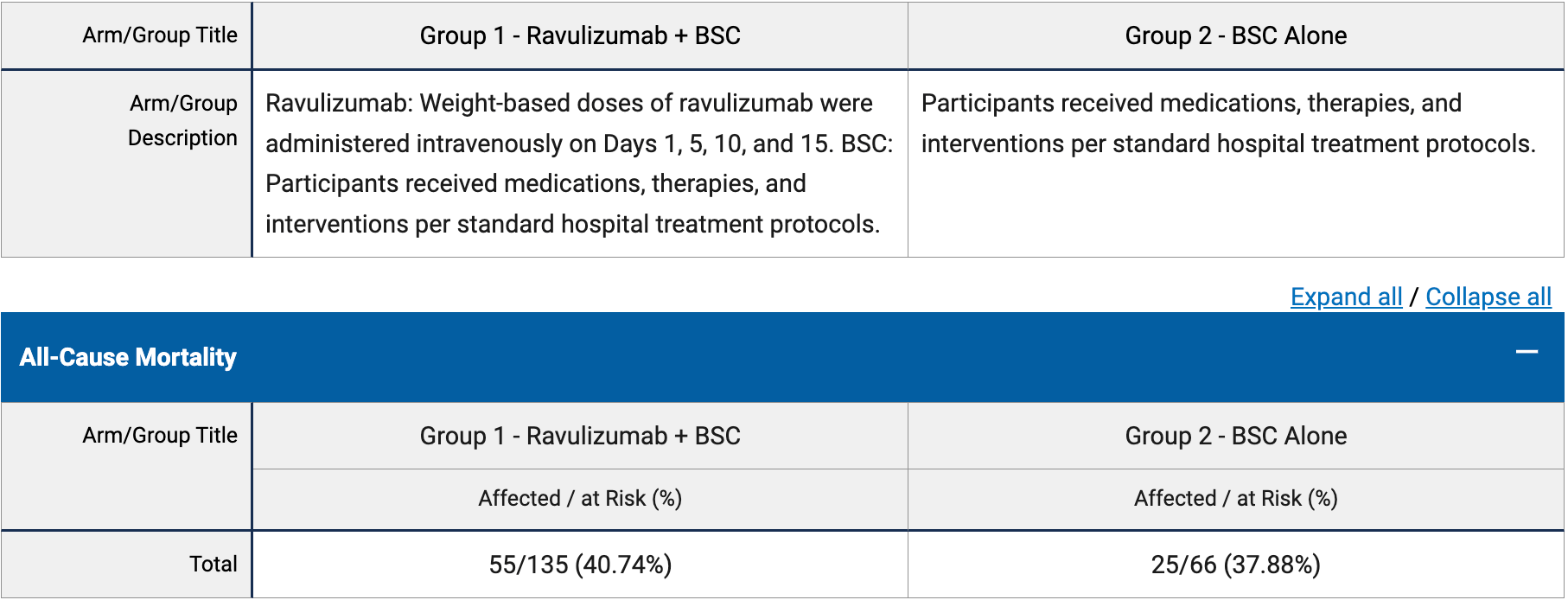
RCT 201 mechanically ventilated patients with severe COVID-19 showing no significant difference in mortality with ravulizumab. The study was terminated early due to futility.
|
risk of death, 7.6% higher, RR 1.08, p = 0.76, treatment 55 of 135 (40.7%), control 25 of 66 (37.9%), day 90.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Annane et al., 20 Mar 2023, Randomized Controlled Trial, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, mean age 63.0, 14 authors, study period 10 May, 2020 - 13 January, 2021, average treatment delay 12.4 days, trial NCT04369469 (history) (ALXN1210-COV-305).
Contact: austin.kulasekararaj@nhs.net.
Intravenous ravulizumab in mechanically ventilated patients hospitalised with severe COVID-19: a phase 3, multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial
The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, doi:10.1016/s2213-2600(23)00082-6
Background The complement pathway is a potential target for the treatment of severe COVID-19. We evaluated the safety and efficacy of ravulizumab, a terminal complement C5 inhibitor, in patients hospitalised with severe COVID-19 requiring invasive or non-invasive mechanical ventilation.
Methods This phase 3, multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial (ALXN1210-COV-305) enrolled adult patients (aged ≥18 years) from 31 hospitals in France, Japan, Spain, the UK, and the USA. Eligible patients had a confirmed diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 that required hospitalisation and either invasive or non-invasive mechanical ventilation, with severe pneumonia, acute lung injury, or acute respiratory distress syndrome confirmed by CT scan or x-ray. We randomly assigned participants (2:1) to receive intravenous ravulizumab plus best supportive care (BSC) or BSC alone using a web-based interactive response system. Randomisation was in permuted blocks of six with stratification by intubation status. Bodyweight-based intravenous doses of ravulizumab were administered on days 1, 5, 10, and 15. The primary efficacy endpoint was survival based on all-cause mortality at day 29 in the intentionto-treat (ITT) population. Safety endpoints were analysed in all randomly assigned patients in the ravulizumab plus BSC group who received at least one dose of ravulizumab, and in all randomly assigned patients in the BSC group. The trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT04369469, and was terminated at interim analysis due to futility. Findings Between May 10, 2020, and Jan 13, 2021, 202 patients were enrolled in the study and randomly assigned to ravulizumab plus BSC or BSC. 201 patients were included in the ITT population (135 in the ravulizumab plus BSC group and 66 in the BSC group). The ravulizumab plus BSC group comprised 96 (71%) men and 39 (29%) women with a mean age of 63•2 years (SD 13•23); the BSC group comprised 43 (65%) men and 23 (35%) women with a mean age of 63•5 years (12•40). Most patients (113 [84%] of 135 in the ravulizumab plus BSC group and 53 [80%] of 66 in the BSC group) were on invasive mechanical ventilation at baseline. Overall survival estimates based on multiple imputation were 58% for patients receiving ravulizumab plus BSC and 60% for patients receiving BSC (Mantel-Haenszel analysis: risk difference -0•0205; 95% CI -0•1703 to 0•1293; one-sided p=0•61). In the safety population, 113 (89%) of 127 patients in the ravulizumab plus BSC group and 56 (84%) of 67 in the BSC group had a treatmentemergent adverse event. Of these events, infections and infestations (73 [57%] vs 24 [36%] patients) and vascular disorders (39 [31%] vs 12 [18%]) were observed more frequently in the ravulizumab plus BSC group than in the BSC group. Five patients had serious adverse events considered to be related to ravulizumab. These events were bacteraemia, thrombocytopenia, oesophageal haemorrhage, cryptococcal pneumonia, and pyrexia (in one patient each)...
Data sharing Alexion, AstraZeneca Rare Disease will consider requests for disclosure of clinical study participant-level data provided that participant privacy is assured by methods such as data de-identification, pseudonymisation, or anonymisation (as required by applicable law), and if such disclosure was included in the relevant study informed consent form or similar documentation. Qualified academic investigators can request participant-level clinical data and supporting documents (statistical analysis and protocol) pertaining to Alexion-sponsored studies. Further details regarding data availability and instructions for requesting information are available in the Alexion Clinical Trials Disclosure and Transparency Policy at https://alexionclinicaltrials.com/Disclosure-and-Transparency-Policy. The data request form is available at https://alexion.com/contact-alexion/medical-information.
References
Ackermann, Verleden, Kuehnel, Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Annane, Heming, Grimaldi-Bensouda, Eculizumab as an emergency treatment for adult patients with severe COVID-19 in the intensive care unit: a proof-of-concept study, EClinicalMedicine
Apellis, Apellis provides update of APL-9 for severe COVID-19
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19-final report, N Engl J Med
Carvelli, Meziani, Dellamonica, Avdoralimab (anti-C5aR1 mAb) versus placebo in patients with severe COVID-19: results from a randomized controlled trial (FOR COVID Elimination [FORCE]), Crit Care Med
De Latour, Bergeron, Lengline, Complement C5 inhibition in patients with COVID-19-a promising target?, Haematologica
De Latour, Brodsky, Ortiz, Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic effects of ravulizumab and eculizumab on complement component 5 in adults with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria: results of two phase 3 randomised, multicentre studies, Br J Haematol
De Leeuw, Van Damme, Declercq, Efficacy and safety of the investigational complement C5 inhibitor zilucoplan in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: an open-label randomized controlled trial, Respir Res
Diurno, Numis, Porta, Eculizumab treatment in patients with COVID-19: preliminary results from real life ASL Napoli 2 Nord experience, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci
Gralinski, Sheahan, Morrison, Complement activation contributes to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus pathogenesis, MBio
Holter, Pischke, De Boer, Systemic complement activation is associated with respiratory failure in COVID-19 hospitalized patients, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Horita, Fukumoto, Global case fatality rate from COVID-19 has decreased by 96•8% during 2•5 years of the pandemic, J Med Virol
Jiang, Zhao, Song, Blockade of the C5a-C5aR axis alleviates lung damage in hDPP4-transgenic mice infected with MERS-CoV, Emerg Microbes Infect
Jodele, Fukuda, Mizuno, Variable eculizumab clearance requires pharmacodynamic monitoring to optimize therapy for thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, Biol Blood Marrow Transplant
Kramer, Prinz, Fichtner, Janus kinase inhibitors for the treatment of COVID-19, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Lim, Van Amstel, De Boer, Complement activation in COVID-19 and targeted therapeutic options: a scoping review, Blood Rev
Llitjos, Bredin, Lascarrou, Increased susceptibility to intensive care unit-acquired pneumonia in severe COVID-19 patients: a multicentre retrospective cohort study, Ann Intensive Care
Magro, Mulvey, Berlin, Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: a report of five cases, Transl Res
Mansour, Palma, Ulaf, Safety and outcomes associated with the pharmacological inhibition of the kininkallikrein system in severe COVID-19, Viruses
Mceneny-King, Monteleone, Kazani, Ortiz, Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of ravulizumab in adults with severe coronavirus disease 2019, Infect Dis Ther
Pharmaceuticals, NDA/BLA multi-disciplinary review and evaluation BLA 761108. Ultomiris (ravulizumab)
Rondeau, Scully, Ariceta, The long-acting C5 inhibitor, ravulizumab, is effective and safe in adult patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome naive to complement inhibitor treatment, Kidney Int
Ruggenenti, Marco, Cortinovis, Eculizumab in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) requiring continuous positive airway pressure ventilator support: retrospective cohort study, PLoS One
Sheridan, Yu, Zhang, Design and preclinical characterization of ALXN1210: a novel anti-C5 antibody with extended duration of action, PLoS One
Skendros, Germanidis, Mastellos, Complement C3 inhibition in severe COVID-19 using compstatin AMY-101, Sci Adv
Smith, Pace, Ortiz, Kazani, Rottinghaus, A phase 3 openlabel, randomized, controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of intravenously administered ravulizumab compared with best supportive care in patients with COVID-19 severe pneumonia, acute lung injury, or acute respiratory distress syndrome: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial, Trials
Tsai, Lai, Chen, Lee, The efficacy and safety of complement C5a inhibitors for patients with severe COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther
Vincent, De Mendonça, Cantraine, Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: results of a multicenter, prospective study, Crit Care Med
Vlaar, Witzenrath, Van Paassen, Anti-C5a antibody (vilobelimab) therapy for critically ill, invasively mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 (PANAMO): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial, Lancet Respir Med
Wang, Xiao, Guo, Li, Shen, The role of C5a in acute lung injury induced by highly pathogenic viral infections, Emerg Microbes Infect
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s2213-2600(23)00082-6",
"ISSN": [
"2213-2600"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6",
"alternative-id": [
"S2213260023000826"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Intravenous ravulizumab in mechanically ventilated patients hospitalised with severe COVID-19: a phase 3, multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Lancet Respiratory Medicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00423-X"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Annane",
"given": "Djillali",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pittock",
"given": "Sean J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kulkarni",
"given": "Hrishikesh S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pickering",
"given": "Brian W",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khoshnevis",
"given": "Matt R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Siegel",
"given": "Jason L",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Powell",
"given": "Charles A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Castro",
"given": "Pedro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fujii",
"given": "Tomoko",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dunn",
"given": "Derek",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smith",
"given": "Keisha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mitter",
"given": "Sanjay",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kazani",
"given": "Shamsah",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kulasekararaj",
"given": "Austin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet Respiratory Medicine",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet Respiratory Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com",
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-21T00:34:28Z",
"timestamp": 1679358868000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-01T14:00:11Z",
"timestamp": 1714572011000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-22T01:39:05Z",
"timestamp": 1719020345254
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 11,
"issue": "12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "12",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1701388800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1701388800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1701388800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1701388800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1701388800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1701388800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1701388800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2213260023000826?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2213260023000826?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1051-1063",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.28231",
"article-title": "Global case fatality rate from COVID-19 has decreased by 96·8% during 2·5 years of the pandemic",
"author": "Horita",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib1",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100590",
"article-title": "Eculizumab as an emergency treatment for adult patients with severe COVID-19 in the intensive care unit: a proof-of-concept study",
"author": "Annane",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib2",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2010540117",
"article-title": "Systemic complement activation is associated with respiratory failure in COVID-19 hospitalized patients",
"author": "Holter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "25018",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci USA",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib3",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3324/haematol.2020.260117",
"article-title": "Complement C5 inhibition in patients with COVID-19—a promising target?",
"author": "Peffault de Latour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2847",
"journal-title": "Haematologica",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib4",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2015432",
"article-title": "Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in COVID-19",
"author": "Ackermann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "120",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib5",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/emi.2015.28",
"article-title": "The role of C5a in acute lung injury induced by highly pathogenic viral infections",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e28",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib6",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.01753-18",
"article-title": "Complement activation contributes to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus pathogenesis",
"author": "Gralinski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e01753",
"journal-title": "MBio",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib7",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41426-018-0063-8",
"article-title": "Blockade of the C5a-C5aR axis alleviates lung damage in hDPP4-transgenic mice infected with MERS-CoV",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib8",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.trsl.2020.04.007",
"article-title": "Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID-19 infection: a report of five cases",
"author": "Magro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Transl Res",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib9",
"volume": "220",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Eculizumab treatment in patients with COVID-19: preliminary results from real life ASL Napoli 2 Nord experience",
"author": "Diurno",
"first-page": "4040",
"journal-title": "Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib10",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0261113",
"article-title": "Eculizumab in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) requiring continuous positive airway pressure ventilator support: retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Ruggenenti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib11",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0195909",
"article-title": "Design and preclinical characterization of ALXN1210: a novel anti-C5 antibody with extended duration of action",
"author": "Sheridan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib12",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.kint.2020.01.035",
"article-title": "The long-acting C5 inhibitor, ravulizumab, is effective and safe in adult patients with atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome naive to complement inhibitor treatment",
"author": "Rondeau",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1287",
"journal-title": "Kidney Int",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib13",
"volume": "97",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bjh.16711",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic effects of ravulizumab and eculizumab on complement component 5 in adults with paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria: results of two phase 3 randomised, multicentre studies",
"author": "Peffault de Latour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "476",
"journal-title": "Br J Haematol",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib14",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-020-04548-z",
"author": "Smith",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "639",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib15",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-021-00425-7",
"article-title": "Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of ravulizumab in adults with severe coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "McEneny-King",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1045",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib16",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Horby",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib17",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00003246-199811000-00016",
"article-title": "Use of the SOFA score to assess the incidence of organ dysfunction/failure in intensive care units: results of a multicenter, prospective study",
"author": "Vincent",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1793",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib18",
"volume": "26",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19—final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib21",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Janus kinase inhibitors for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Kramer",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib22",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1637",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib23",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbmt.2015.10.002",
"article-title": "Variable eculizumab clearance requires pharmacodynamic monitoring to optimize therapy for thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation",
"author": "Jodele",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "307",
"journal-title": "Biol Blood Marrow Transplant",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib24",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.blre.2022.100995",
"article-title": "Complement activation in COVID-19 and targeted therapeutic options: a scoping review",
"author": "Lim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Blood Rev",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib25",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(22)00297-1",
"article-title": "Anti-C5a antibody (vilobelimab) therapy for critically ill, invasively mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 (PANAMO): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial",
"author": "Vlaar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1137",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib26",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-022-02126-2",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of the investigational complement C5 inhibitor zilucoplan in patients hospitalized with COVID-19: an open-label randomized controlled trial",
"author": "De Leeuw",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "202",
"journal-title": "Respir Res",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib27",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000005683",
"article-title": "Avdoralimab (anti-C5aR1 mAb) versus placebo in patients with severe COVID-19: results from a randomized controlled trial (FOR COVID Elimination [FORCE])",
"author": "Carvelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1788",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib28",
"volume": "50",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abo2341",
"article-title": "Complement C3 inhibition in severe COVID-19 using compstatin AMY-101",
"author": "Skendros",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Adv",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib29",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13020309",
"article-title": "Safety and outcomes associated with the pharmacological inhibition of the kinin-kallikrein system in severe COVID-19",
"author": "Mansour",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "309",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib30",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14787210.2022.2150165",
"article-title": "The efficacy and safety of complement C5a inhibitors for patients with severe COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Tsai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib32",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-021-00812-w",
"article-title": "Increased susceptibility to intensive care unit-acquired pneumonia in severe COVID-19 patients: a multicentre retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Llitjos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Ann Intensive Care",
"key": "10.1016/S2213-2600(23)00082-6_bib33",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 30,
"references-count": 30,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2213260023000826"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Intravenous ravulizumab in mechanically ventilated patients hospitalised with severe COVID-19: a phase 3, multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "11"
}