Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines with renin angiotensin aldosterone system, clinical outcomes, and angiotensin (1-7) as a physiological treatment recommendation: hypothesis and theory article
, A., Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2025.1612442, Jul 2025
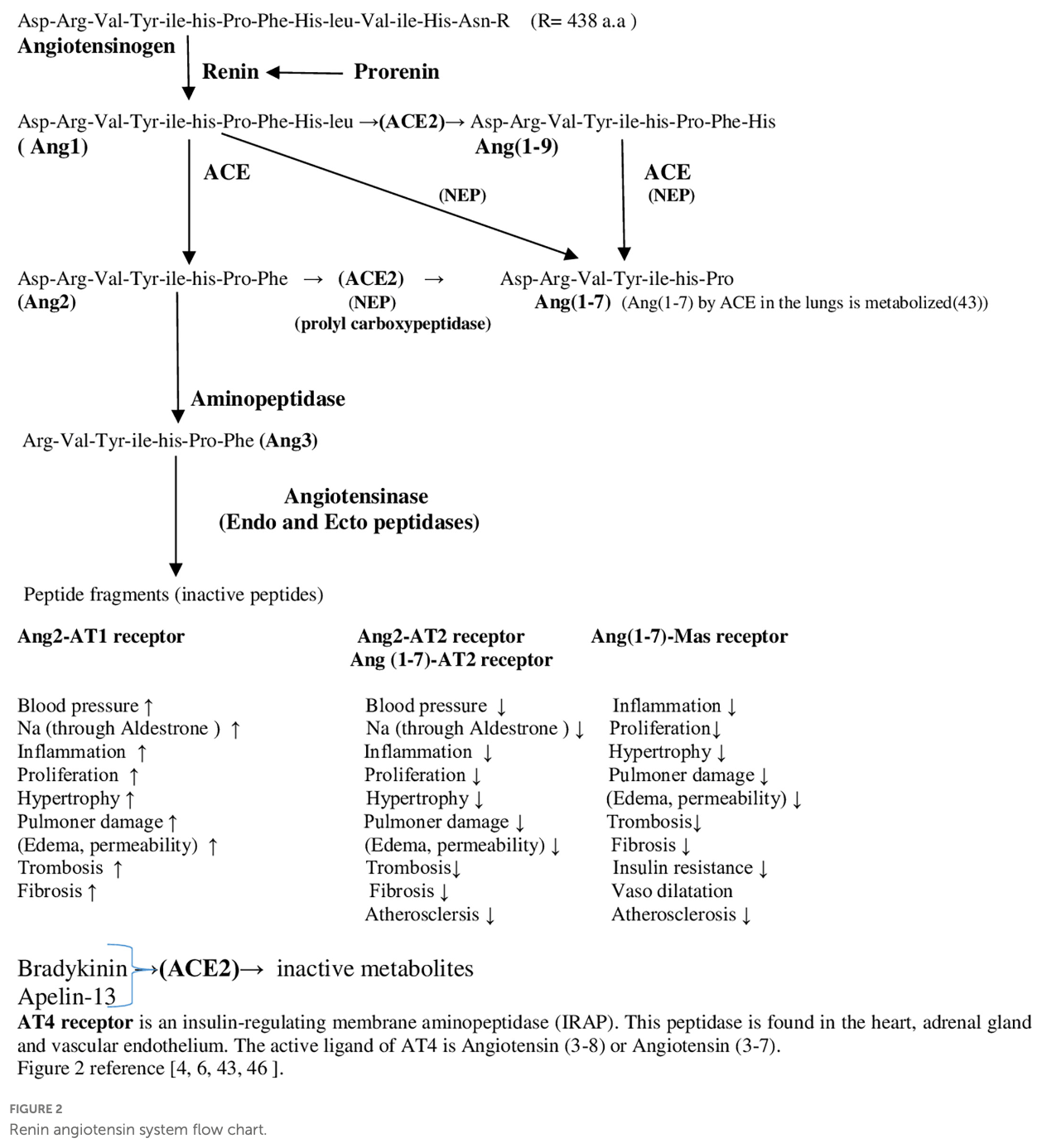
Review of the interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), highlighting how this interaction underlies COVID-19 pathology and complications. Author explains that SARS-CoV-2 binds to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), preventing it from converting angiotensin II (Ang2) to angiotensin 1-7 (Ang1-7), which disrupts the balance between vasoconstriction and vasodilation needed for proper tissue perfusion. This imbalance leads to hypoxia, tissue damage, cell death, and ultimately triggers cytokine storms and autoimmune responses that contribute to organ failure. Author suggests that administering Ang1-7 as a treatment could restore the disrupted RAAS balance, potentially preventing complications by improving perfusion, reducing hypoxia-induced cell death, and minimizing cytokine release.
Aktaş et al., 10 Jul 2025, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 1 author.
Contact: alirizaaktas71@gmail.com.
Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines with renin angiotensin aldosterone system, clinical outcomes, and angiotensin (1-7) as a physiological treatment recommendation: hypothesis and theory article
Frontiers in Medicine, doi:10.3389/fmed.2025.1612442
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has affected all of humanity since the first case was reported and spread rapidly around the world, creating a pandemic. Despite the repurposing of many drugs and the development of vaccines, effective treatment and protection are limited. In addition, SARS-CoV-2 continues to be a current public health problem with complications, identifying cases of long-term Covid syndrome, and detection of vaccine-related adverse events. It can be said that the most important factor underlying all these problems is that the interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is not completely understood despite extensive research. Although different disciplines have limited determinations from their own perspectives regarding the communication with RAAS, it has not been sufficiently expressed in a way to see the whole picture. In this study, it is tried to see the whole picture in the interaction of RAAS and SARS-CoV-2. It is detected inadequacies in treatments and interactions that may be design errors in vaccines. These determinations also show that our templates for producing treatments are not sufficient. For this reason, we have to develop our templates with what we have learned specifically about SARS-CoV-2. Considering the accuracy of our hypothesis on the SARS-CoV-2 -RAAS relationship, Ang(1-7) can be considered a strong option for treatment. Although the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic seems to be over, epidemics and even new pandemics are likely to occur with new mutations.
Author contributions ARA: Writing -original draft, Visualization, Conceptualization, Writing -review and editing, Methodology, Investigation.
Conflict of interest The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abassi, Assady, Khoury, Heyman, Letter to the editor: Angiotensinconverting enzyme 2: An ally or a Trojan horse? Implications to SARS-CoV-2-related cardiovascular complications, Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00215.2020
Abassi, Higazi, Kinaneh, Armaly, Skorecki et al., ACE2, COVID-19 infection, inflammation, and coagulopathy: Missing pieces in the puzzle, Front Physiol, doi:10.3389/fphys.2020.574753
Abassi, Knaney, Karram, Heyman, The lung macrophage in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A friend or a foe?, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01312
Abassi, Skorecki, Hamo-Giladi, Kruzel-Davila, Heyman, Kinins and chymase: The forgotten components of the renin-angiotensin system and their implications in COVID-19 disease, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol
Albashir, Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors and Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), South Med J, doi:10.14423/SMJ.0000000000001200
Amiral, Vissac, Seghatchian, Covid-19, induced activation of hemostasis, and immune reactions: Can an auto-immune reaction contribute to the delayed severe complications observed in some patients?, Transfus Apher Sci, doi:10.1016/j.transci.2020.102804
Andrade, Fde, Da Fonseca Pires, Millán, De Sousa et al., Proteomic white adipose tissue analysis of obese mice fed with a high-fat diet and treated with oral angiotensin-(1-7), Peptides, doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2014.07.023
Angeli, Zappa, Reboldi, Trapasso, Cavallini et al., Reninangiotensin system modulation with synthetic angiotensin (1-7) and angiotensin II Type 1 receptor-biased ligand in adults with covid-19: Two randomized clinical trials, J Biol Today's World, doi:10.35248/1745-7580.24.20.267
Arthur, Forrest, Boehme, Kennedy, Owens et al., Development of ACE2 autoantibodies after SARS-CoV-2 infection, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0257016
Bradley, Maioli, Johnston, Chaudhry, Fink et al., Histopathology and ultrastructural findings of fatal COVID-19 infections in Washington state: A case series, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31305-2
Braga, Silva-Aguiar, Battaglini, Peruchetti, Robba et al., The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: Role in pathogenesis and potential therapeutic target in COVID-19, Pharmacol Res Perspect, doi:10.1002/prp2.623
Briquez, Rouhani, Yu, Pyzer, Trujillo et al., Severe COVID-19 induces autoantibodies against angiotensin II that correlate with blood pressure dysregulation and disease severity, Sci Adv, doi:10.1126/sciadv.abn3777
Chams, Chams, Badran, Shams, Araji et al., COVID-19: A multidisciplinary review, Front Public Health, doi:10.3389/fpubh.2020.00383
Chappell, Diz, Gallagher, The renin-angiotensin system and the exocrine pancreas, JOP
Chen, Xu, Wang, Li, Shuai et al., New-onset autoimmune phenomena post-COVID-19 vaccination, Immunology, doi:10.1111/imm.13443
Chilamakuri, Agarwal, COVID-19: Characteristics and therapeutics, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells10020206
Contoli, Papi, Tomassetti, Rizzo, Vieceli et al., Blood interferon-α levels and severity, outcomes, and inflammatory profiles in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.648004
Cromer, Steain, Reynaldi, Schlub, Wheatley et al., Neutralising antibody titres as predictors of protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants and the impact of boosting: A meta-analysis, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00267-6
Dai, Zheng, Xu, Han, Xu et al., A universal design of betacoronavirus vaccines against COVID-19, MERS, and SARS, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.035.
Davis, Mccorkell, Vogel, Topol, Long COVID: Major findings, mechanisms and recommendations, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-022-00846-2
De Leeuw, Luttikhuis, Wellen, Müller, Calkhoven, Obesity and its impact on COVID-19, J Mol Med (Berl), doi:10.1007/s00109-021-02072-4
Draghici, Nguyen, Sonna, Ziraldo, Vanciu et al., COVID-19: Disease pathways and gene expression changes predict methylprednisolone can improve outcome in severe cases, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btab163
Ferrara, Vitiello, Scientific hypothesis for treatment of COVID-19's lung lesions by adjusting ACE/ACE2 imbalance, Cardiovasc Toxicol, doi:10.1007/s12012-021-09649-y
Foster, The functions of cytokines and their uses in toxicology, Int J Exp Pathol, doi:10.1046/j.1365-2613.2001.iep0082-0171-x
Fouriki, Fougère, Camaret, Rohner, Grazioli et al., Renin-angiotensin system blockers and the COVID-19 pandemic: At present there is no evidence to abandon renin-angiotensin system blockers, Front Pediatr, doi:10.3390/antiox9111129
Furuta, Komeno, Nakamura, Favipiravir (T-705), a broad spectrum inhibitor of viral RNA polymerase, Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci, doi:10.2183/pjab.93.027
Garcia, Barreras, Lewis, Pinilla, Sokoll et al., Cerebrospinal fluid in COVID-19 neurological complications: Neuroaxonal damage, anti-SARS-Cov2 antibodies but no evidence of cytokine storm, J Neurol Sci, doi:10.1016/j.jns.2021.117517
Ghareeb, Saleh, Nofal, Kaddah, Hassan et al., Potential therapeutic and pharmacological strategies for SARS-CoV2, J Pharm Investig, doi:10.1007/s40005-021-00520-4
Glende, Schwegmann-Wessels, Al-Falah, Pfefferle, Qu et al., Importance of cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains in the interaction of the S protein of SARS-coronavirus with the cellular receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2008.08.026
Glick, Barth, Macleod, Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms, J Pathol, doi:10.1002/path.2697
Group, Lundgren, Grund, Barkauskas, Holland et al., A neutralizing monoclonal antibody for hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2033130
Guo, Cao, Hong, Tan, Chen et al., The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak -An update on the status, Mil Med Res, doi:10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0
Gupta, Madhavan, Sehgal, Nair, Mahajan et al., Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19, Nat Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3
Gusev, Sarapultsev, Solomatina, Chereshnev, SARS-CoV-2-specific immune response and the pathogenesis of COVID-19, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms23031716
Hanley, Naresh, Roufosse, Nicholson, Weir et al., Histopathological findings and viral tropism in UK patients with severe fatal COVID-19: A post-mortem study, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30115-4
Hao, Yang, Zhang, Zhang, Chen et al., Angiotensin-(1-7) treatment mitigates right ventricular fibrosis as a distinctive feature of diabetic cardiomyopathy, Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00563.2014
Hargarten, Williamson, Epigenetic regulation of autophagy: A path to the control of autoimmunity, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.01864
Heurich, Hofmann-Winkler, Gierer, Liepold, Jahn et al., TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 cleave ACE2 differentially and only proteolysis by TMPRSS2 augments entry driven by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.02202-13
Heyman, Kinaneh, Abassi, The duplicitous nature of ACE2 in COVID-19 Disease, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103356
Hikmet, Méar, Edvinsson, Micke, Uhlén et al., The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues, Mol Syst Biol, doi:10.15252/msb.20209610
Hooper, Bernard, Pharmacogenetic treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome, Minerva Anestesiol
Howard, Travanty, Jeffers, Smith, Wennier et al., Aromatic amino acids in the juxtamembrane domain of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike glycoprotein are important for receptor-dependent virus entry and cell-cell fusion, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01805-07
Hu, Huang, Yin, The cytokine storm and COVID-19, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26232
Huppert, Matthay, Ware, Pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome, Semin Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1055/s-0039-1683996
Jafarzadeh, Chauhan, Saha, Jafarzadeh, Nemati, Contribution of monocytes and macrophages to the local tissue inflammation and cytokine storm in COVID-19: Lessons from SARS and MERS, and potential therapeutic interventions, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118102
Jiang, Yang, Zhang, Dong, Wang et al., Angiotensinconverting enzyme 2 and angiotensin 1-7: Novel therapeutic targets, Nat Rev Cardiol, doi:10.1038/nrcardio.2014.59
Jing, Wu, Xiang, Liu, Novakovic et al., Pathophysiological mechanisms of thrombosis in acute and long COVID-19, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.992384
Jordan, Zakowski, Tran, Smith, Gaultier et al., Compassionate use of tocilizumab for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa812
Kai, Kai, Interactions of coronaviruses with ACE2, angiotensin II, and RAS inhibitors-lessons from available evidence and insights into COVID-19, Hypertens Res, doi:10.1038/s41440-020-0455-8
Keese, Zheng, Yan, Bieback, Yard et al., Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect endothelial cells from hypoxic injury by suppressing terminal UPR in vivo and in vitro, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms242417197
Klaassen, Stankovic, Zukic, Kotur, Gasic et al., Functional prediction and comparative population analysis of variants in genes for proteases and innate immunity related to SARS-CoV-2 infection, Infect Genet Evol, doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104498
Kruglikov, Scherer, The role of adipocytes and adipocyte-like cells in the severity of COVID-19 infections, Obesity, doi:10.1002/oby.22856
Kuba, Imai, Penninger, Multiple functions of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and its relevance in cardiovascular diseases, Circ J, doi:10.1253/circj.cj-12-1544
Lamadrid, Alonso-Peña, Segundo, Arias-Loste, Crespo et al., Innate and adaptive immunity alterations in metabolic associated fatty liver disease and its implication in COVID-19 severity, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.651728
Leng, Zhu, Hou, Feng, Yang et al., Transplantation of ACE2-mesenchymal stem cells improves the outcome of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, Aging Dis, doi:10.14336/AD.2020.0228
Levine, Mizushima, Virgin, Autophagy in immunity and inflammation, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature09782
Li, Chen, Zhou, Li, Zhang et al., Ferroptosis and multi-organ complications in COVID-19: Mechanisms and potential therapies, Front Genet, doi:10.3389/fgene.2023.1187985
Li, Li, Zhang, Wang, Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues, Infect Dis Poverty, doi:10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x
Liu, Xing, Liang, Luo, Zhang et al., Reversal of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension by hypoxia-inducible overexpression of angiotensin-(1-7) in pulmonary endothelial cells, Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev, doi:10.1016/j.omtm.2020.04.008
Lleo, Invernizzi, Selmi, Coppel, Alpini et al., Autophagy: Highlighting a novel player in the autoimmunity scenario, J Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2007.06.003
Lodge, Nitschke, Kimhofer, Coudert, Begum et al., NMR spectroscopic windows on the systemic effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on plasma lipoproteins and metabolites in relation to circulating cytokines, J Proteome Res, doi:10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00876
Ma, Su, Yue, Zou, Zhu et al., The effect of oxidative stress-induced autophagy by cadmium exposure in kidney, liver, and bone damage, and neurotoxicity, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms232113491
Madjunkov, Dviri, Librach, A comprehensive review of the impact of COVID-19 on human reproductive biology, assisted reproduction care and pregnancy: A Canadian perspective, J Ovarian Res, doi:10.1186/s13048-020-00737-1
Maiuolo, Mollace, Gliozzi, Musolino, Carresi et al., The contribution of endothelial dysfunction in systemic injury subsequent to SARS-Cov-2 infection, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms21239309
Meftahi, Jangravi, Sahraei, Bahari, The possible pathophysiology mechanism of cytokine storm in elderly adults with COVID-19 infection: The contribution of inflame-aging, Inflamm Res, doi:10.1007/s00011-020-01372-8
Monteil, Kwon, Prado, Hagelkrüys, Wimmer et al., Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infections in engineered human tissues using clinical-grade soluble human ACE2, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.004
Murphy, Hossain, Swiderski, Chee, Naim et al., Mas receptor activation slows tumor growth and attenuates muscle wasting in cancer, Cancer Res, doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1207
Müller, Raj, Muth, Meyer, Kallies et al., Human coronavirus EMC does not require the SARS-coronavirus receptor and maintains broad replicative capability in mammalian cell lines, mBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.00515-12
Nile, Nile, Qiu, Li, Jia et al., COVID-19: Pathogenesis, cytokine storm and therapeutic potential of interferons, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.05.002
Nistor, Dillman, Cytokine network analysis of immune responses before and after autologous dendritic cell and tumor cell vaccine immunotherapies in a randomized trial, J Transl Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-020-02328-6
Oosthuizen, Sturrock, Exploring the impact of ACE inhibition in immunity and disease, J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst, doi:10.1155/2022/9028969
Oudit, Kassiri, Jiang, Liu, Poutanen et al., SARScoronavirus modulation of myocardial ACE2 expression and inflammation in patients with SARS, Eur J Clin Invest, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2009.02153.x
Peiró, Moncada, Substituting angiotensin-(1-7) to prevent lung damage in SARS-CoV-2 infection?, Circulation, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047297
Pilkington, Pepperrell, Hill, A review of the safety of favipiravir -A potential treatment in the COVID-19 pandemic?, J Virus Erad
Pisetsky, Pathogenesis of autoimmune disease, Nat Rev Nephrol, doi:10.1038/s41581-023-00720-1
Radzikowska, Ding, Tan, Zhakparov, Peng et al., Distribution of ACE2, CD147, CD26, and other SARS-CoV-2 associated molecules in tissues and immune cells in health and in asthma, COPD, obesity, hypertension, and COVID-19 risk factors, Allergy, doi:10.1111/all.14429
Reddy, Asante, Liu, Parikh, Liebler et al., Circulating angiotensin peptides levels in Acute respiratory distress syndrome correlate with clinical outcomes: A PILOT STUDY, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0213096
Rouse, Sehrawat, Immunity and immunopathology to viruses: What decides the outcome?, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri2802
Salle, Coronavirus-induced autoimmunity, Clin Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2021.108694
Santos, Sampaio, Alzamora, Motta-Santos, Alenina et al., The ACE2/angiotensin-(1-7)/MAS axis of the renin-angiotensin system: Focus on angiotensin-(1-7), Physiol Rev, doi:10.1152/physrev.00023.2016
Sette, Crotty, Adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.007
Shanmugaraj, Siriwattananon, Wangkanont, Phoolcharoen, Perspectives on monoclonal antibody therapy as potential therapeutic intervention for Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19), Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol, doi:10.12932/AP-200220-0773
Sharma, Sultan, Ding, Triggle, A review of the progress and challenges of developing a vaccine for COVID-19, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.585354
Singh, Yi, On the origin and evolution of SARS-CoV-2, Exp Mol Med, doi:10.1038/s12276-021-00604-z
Souza, Amorim, Sesti-Costa, Coimbra, Brunetti et al., Neutralisation of SARS-CoV-2 lineage P.1 by antibodies elicited through natural SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination with an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine: An immunological study, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00129-4
Sreekumar, Kuthe, Tripathi, Patil, Ravikumar, Integrated computational approach towards identification of HSPG and ACE2 mimicking moieties for SARS-CoV-2 inhibition, J Mol Liq, doi:10.1016/j.molliq.2022.120566
Swenson, Swenson, Pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome and COVID-19 lung injury, Crit Care Clin, doi:10.1016/j.ccc.2021.05.003
Synowiec, Szczepański, Barreto-Duran, Lie, Pyrc, Severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): A systemic infection, Clin Microbiol Rev, doi:10.1128/CMR.00133-20
Tai, He, Zhang, Pu, Voronin et al., Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine, Cell Mol Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0400-4
Tragni, Preziusi, Laera, Onofrio, Mercurio et al., Modeling SARS-CoV-2 spike/ACE2 protein-protein interactions for predicting the binding affinity of new spike variants for ACE2, and novel ACE2 structurally related human protein targets, for COVID-19 handling in the 3PM context, EPMA J, doi:10.1007/s13167-021-00267-w
Trayhurn, Hypoxia and adipose tissue function and dysfunction in obesity, Physiol Rev, doi:10.1152/physrev.00017.2012
Turner, Khan, Putrino, Woodcock, Kell et al., Long COVID: Pathophysiological factors and abnormalities of coagulation, Trends Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1016/j.tem.2023.03.002
Varagic, Ahmad, Nagata, Ferrario, ACE2: Angiotensin II/angiotensin-(1-7) balance in cardiac and renal injury, Curr Hypertens Rep, doi:10.1007/s11906-014-0420-5
Verdecchia, Cavallini, Spanevello, Angeli, The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection, Eur J Intern Med, doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2020.04.037
Vono, Garcia, Spinetti, Madeddu, Oxidative stress in mesenchymal stem cell senescence: Regulation by coding and noncoding RNAs, Antioxid Redox Signal, doi:10.1089/ars.2017.7294
Wallukat, Hohberger, Wenzel, Fürst, Schulze-Rothe et al., Functional autoantibodies against G-protein coupled receptors in patients with persistent Long-COVID-19 symptoms, J Transl Autoimmun, doi:10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100100
Wan, Shang, Graham, Baric, Li, Receptor recognition by the novel coronavirus from wuhan: An analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS coronavirus, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00127-20
Weisblum, Schmidt, Zhang, Dasilva, Poston et al., Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants, Elife, doi:10.7554/eLife.61312
Xia, Domains and functions of spike protein in sars-Cov-2 in the context of vaccine design, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13010109
Zhang, Lv, Jiang, Liu, Yan et al., Advances in developing ACE2 derivatives against SARS-CoV-2, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00011-3
Zhang, Sun, Han, Huang, Sheng et al., Neutrophil autophagy and NETosis in COVID-19: Perspectives, Autophagy, doi:10.1080/15548627.2022.2099206
Zhuang, Li, Uhal, Yian, Apoptosis-dependent acute pulmonary injury after intratracheal instillation of angiotensin II, Sheng Li Xue Bao
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2025.1612442",
"ISSN": [
"2296-858X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2025.1612442",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has affected all of humanity since the first case was reported and spread rapidly around the world, creating a pandemic. Despite the repurposing of many drugs and the development of vaccines, effective treatment and protection are limited. In addition, SARS-CoV-2 continues to be a current public health problem with complications, identifying cases of long-term Covid syndrome, and detection of vaccine-related adverse events. It can be said that the most important factor underlying all these problems is that the interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is not completely understood despite extensive research. Although different disciplines have limited determinations from their own perspectives regarding the communication with RAAS, it has not been sufficiently expressed in a way to see the whole picture. In this study, it is tried to see the whole picture in the interaction of RAAS and SARS-CoV-2. It is detected inadequacies in treatments and interactions that may be design errors in vaccines. These determinations also show that our templates for producing treatments are not sufficient. For this reason, we have to develop our templates with what we have learned specifically about SARS-CoV-2. Considering the accuracy of our hypothesis on the SARS-CoV-2 - RAAS relationship, Ang(1-7) can be considered a strong option for treatment. Although the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic seems to be over, epidemics and even new pandemics are likely to occur with new mutations.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fmed.2025.1612442"
],
"article-number": "1612442",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aktaş",
"given": "Ali Rıza",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Front. Med.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-10T05:31:59Z",
"timestamp": 1752125519000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-10T05:32:01Z",
"timestamp": 1752125521000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-10T06:10:02Z",
"timestamp": 1752127802596,
"version": "3.41.2"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
10
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2025-07-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1752105600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1612442/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
7,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1128/CMR.00133-20",
"article-title": "Severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2): A systemic infection.",
"author": "Synowiec",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e133",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Rev.",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s12276-021-00604-z",
"article-title": "On the origin and evolution of SARS-CoV-2.",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "537",
"journal-title": "Exp Mol Med.",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14423/SMJ.0000000000001200",
"article-title": "Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors and Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).",
"author": "Albashir",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "51",
"journal-title": "South Med J.",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2020.04.037",
"article-title": "The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection.",
"author": "Verdecchia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Eur J Intern Med.",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/msb.20209610",
"article-title": "The protein expression profile of ACE2 in human tissues.",
"author": "Hikmet",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e9610",
"journal-title": "Mol Syst Biol.",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00023.2016",
"article-title": "The ACE2/angiotensin-(1-7)/MAS axis of the renin-angiotensin system: Focus on angiotensin-(1-7).",
"author": "Santos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "505",
"journal-title": "Physiol Rev.",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/prp2.623",
"article-title": "The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system: Role in pathogenesis and potential therapeutic target in COVID-19.",
"author": "Braga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e00623",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Res Perspect.",
"key": "B7",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10020206",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Characteristics and therapeutics.",
"author": "Chilamakuri",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "206",
"journal-title": "Cells.",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40005-021-00520-4",
"article-title": "Potential therapeutic and pharmacological strategies for SARS-CoV2.",
"author": "Ghareeb",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "J Pharm Investig.",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40779-020-00240-0",
"article-title": "The origin, transmission and clinical therapies on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak - An update on the status.",
"author": "Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Mil Med Res.",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13167-021-00267-w",
"article-title": "Modeling SARS-CoV-2 spike/ACE2 protein-protein interactions for predicting the binding affinity of new spike variants for ACE2, and novel ACE2 structurally related human protein targets, for COVID-19 handling in the 3PM context.",
"author": "Tragni",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "149",
"journal-title": "EPMA J.",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13010109",
"article-title": "Domains and functions of spike protein in sars-Cov-2 in the context of vaccine design.",
"author": "Xia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "109",
"journal-title": "Viruses.",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.007",
"article-title": "Adaptive immunity to SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19.",
"author": "Sette",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "861",
"journal-title": "Cell.",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.61312",
"article-title": "Escape from neutralizing antibodies by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein variants.",
"author": "Weisblum",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e61312",
"journal-title": "Elife.",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00267-6",
"article-title": "Neutralising antibody titres as predictors of protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants and the impact of boosting: A meta-analysis.",
"author": "Cromer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e52",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe.",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.004",
"article-title": "Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infections in engineered human tissues using clinical-grade soluble human ACE2.",
"author": "Monteil",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "Cell.",
"key": "B16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(23)00011-3",
"article-title": "Advances in developing ACE2 derivatives against SARS-CoV-2.",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e369",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe.",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033130",
"article-title": "A neutralizing monoclonal antibody for hospitalized patients with Covid-19.",
"author": "ACTIV-3/TICO Ly-CoV555 Study Group, Lundgren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med.",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12932/AP-200220-0773",
"article-title": "Perspectives on monoclonal antibody therapy as potential therapeutic intervention for Coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19).",
"author": "Shanmugaraj",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10",
"journal-title": "Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol.",
"key": "B19",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2055-6640(20)30016-9",
"article-title": "A review of the safety of favipiravir - A potential treatment in the COVID-19 pandemic?",
"author": "Pilkington",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "J Virus Erad.",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2183/pjab.93.027",
"article-title": "Favipiravir (T-705), a broad spectrum inhibitor of viral RNA polymerase.",
"author": "Furuta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "449",
"journal-title": "Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci.",
"key": "B21",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fpubh.2020.00383",
"article-title": "COVID-19: A multidisciplinary review.",
"author": "Chams",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "383",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health.",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btab163",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Disease pathways and gene expression changes predict methylprednisolone can improve outcome in severe cases.",
"author": "Draghici",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2691",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics.",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Pharmacogenetic treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome.",
"author": "Hooper",
"first-page": "624",
"journal-title": "Minerva Anestesiol.",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ccc.2021.05.003",
"article-title": "Pathophysiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome and COVID-19 lung injury.",
"author": "Swenson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "749",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Clin.",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa812",
"article-title": "Compassionate use of tocilizumab for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia.",
"author": "Jordan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3168",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis.",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/imm.13443",
"article-title": "New-onset autoimmune phenomena post-COVID-19 vaccination.",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "386",
"journal-title": "Immunology.",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "165",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fgene.2023.1187985",
"article-title": "Ferroptosis and multi-organ complications in COVID-19: Mechanisms and potential therapies.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1187985",
"journal-title": "Front Genet.",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abn3777",
"article-title": "Severe COVID-19 induces autoantibodies against angiotensin II that correlate with blood pressure dysregulation and disease severity.",
"author": "Briquez",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eabn3777",
"journal-title": "Sci Adv.",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0257016",
"article-title": "Development of ACE2 autoantibodies after SARS-CoV-2 infection.",
"author": "Arthur",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0257016",
"journal-title": "PLoS One.",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2021.108694",
"article-title": "Coronavirus-induced autoimmunity.",
"author": "Salle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108694",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol.",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "226",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.transci.2020.102804",
"article-title": "Covid-19, induced activation of hemostasis, and immune reactions: Can an auto-immune reaction contribute to the delayed severe complications observed in some patients?",
"author": "Amiral",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "102804",
"journal-title": "Transfus Apher Sci.",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13048-020-00737-1",
"article-title": "A comprehensive review of the impact of COVID-19 on human reproductive biology, assisted reproduction care and pregnancy: A Canadian perspective.",
"author": "Madjunkov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "140",
"journal-title": "J Ovarian Res.",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/15548627.2022.2099206",
"article-title": "Neutrophil autophagy and NETosis in COVID-19: Perspectives.",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "758",
"journal-title": "Autophagy.",
"key": "B34",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jns.2021.117517",
"article-title": "Cerebrospinal fluid in COVID-19 neurological complications: Neuroaxonal damage, anti-SARS-Cov2 antibodies but no evidence of cytokine storm.",
"author": "Garcia",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "117517",
"journal-title": "J Neurol Sci.",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "427",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tem.2023.03.002",
"article-title": "Long COVID: Pathophysiological factors and abnormalities of coagulation.",
"author": "Turner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "321",
"journal-title": "Trends Endocrinol Metab.",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.992384",
"article-title": "Pathophysiological mechanisms of thrombosis in acute and long COVID-19.",
"author": "Jing",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "992384",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100100",
"article-title": "Functional autoantibodies against G-protein coupled receptors in patients with persistent Long-COVID-19 symptoms.",
"author": "Wallukat",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100100",
"journal-title": "J Transl Autoimmun.",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphys.2020.574753",
"article-title": "ACE2, COVID-19 infection, inflammation, and coagulopathy: Missing pieces in the puzzle.",
"author": "Abassi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "574753",
"journal-title": "Front Physiol.",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00129-4",
"article-title": "Neutralisation of SARS-CoV-2 lineage P.1 by antibodies elicited through natural SARS-CoV-2 infection or vaccination with an inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine: An immunological study.",
"author": "Souza",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e527",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe.",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00846-2",
"article-title": "Long COVID: Major findings, mechanisms and recommendations.",
"author": "Davis",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "133",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol.",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104498",
"article-title": "Functional prediction and comparative population analysis of variants in genes for proteases and innate immunity related to SARS-CoV-2 infection.",
"author": "Klaassen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104498",
"journal-title": "Infect Genet Evol.",
"key": "B42",
"volume": "84",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrcardio.2014.59",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and angiotensin 1-7: Novel therapeutic targets.",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "413",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Cardiol.",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11906-014-0420-5",
"article-title": "ACE2: Angiotensin II/angiotensin-(1-7) balance in cardiac and renal injury.",
"author": "Varagic",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "420",
"journal-title": "Curr Hypertens Rep.",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpheart.00563.2014",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-(1-7) treatment mitigates right ventricular fibrosis as a distinctive feature of diabetic cardiomyopathy.",
"author": "Hao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "H1007",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "308",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0213096",
"article-title": "Circulating angiotensin peptides levels in Acute respiratory distress syndrome correlate with clinical outcomes: A PILOT STUDY.",
"author": "Reddy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0213096",
"journal-title": "PLoS One.",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1253/circj.cj-12-1544",
"article-title": "Multiple functions of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and its relevance in cardiovascular diseases.",
"author": "Kuba",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "301",
"journal-title": "Circ J.",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01805-07",
"article-title": "Aromatic amino acids in the juxtamembrane domain of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike glycoprotein are important for receptor-dependent virus entry and cell-cell fusion.",
"author": "Howard",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2883",
"journal-title": "J Virol.",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.00515-12",
"article-title": "Human coronavirus EMC does not require the SARS-coronavirus receptor and maintains broad replicative capability in mammalian cell lines.",
"author": "Müller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e515",
"journal-title": "mBio.",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02202-13",
"article-title": "TMPRSS2 and ADAM17 cleave ACE2 differentially and only proteolysis by TMPRSS2 augments entry driven by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus spike protein.",
"author": "Heurich",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1293",
"journal-title": "J Virol.",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14336/AD.2020.0228",
"article-title": "Transplantation of ACE2- mesenchymal stem cells improves the outcome of patients with COVID-19 pneumonia.",
"author": "Leng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "216",
"journal-title": "Aging Dis.",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.585354",
"article-title": "A review of the progress and challenges of developing a vaccine for COVID-19.",
"author": "Sharma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "585354",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00127-20",
"article-title": "Receptor recognition by the novel coronavirus from wuhan: An analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS coronavirus.",
"author": "Wan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e127",
"journal-title": "J Virol.",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2008.08.026",
"article-title": "Importance of cholesterol-rich membrane microdomains in the interaction of the S protein of SARS-coronavirus with the cellular receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2.",
"author": "Glende",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "215",
"journal-title": "Virology.",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "381",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00011-020-01372-8",
"article-title": "The possible pathophysiology mechanism of cytokine storm in elderly adults with COVID-19 infection: The contribution of inflame-aging.",
"author": "Meftahi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "825",
"journal-title": "Inflamm Res.",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0400-4",
"article-title": "Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine.",
"author": "Tai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "613",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol Immunol.",
"key": "B56",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22856",
"article-title": "The role of adipocytes and adipocyte-like cells in the severity of COVID-19 infections.",
"author": "Kruglikov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1187",
"journal-title": "Obesity (Silver Spring).",
"key": "B57",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31305-2",
"article-title": "Histopathology and ultrastructural findings of fatal COVID-19 infections in Washington state: A case series.",
"author": "Bradley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "320",
"journal-title": "Lancet.",
"key": "B58",
"volume": "396",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30115-4",
"article-title": "Histopathological findings and viral tropism in UK patients with severe fatal COVID-19: A post-mortem study.",
"author": "Hanley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e245",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe.",
"key": "B59",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21239309",
"article-title": "The contribution of endothelial dysfunction in systemic injury subsequent to SARS-Cov-2 infection.",
"author": "Maiuolo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9309",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci.",
"key": "B60",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23031716",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2-specific immune response and the pathogenesis of COVID-19.",
"author": "Gusev",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1716",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci.",
"key": "B61",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118102",
"article-title": "Contribution of monocytes and macrophages to the local tissue inflammation and cytokine storm in COVID-19: Lessons from SARS and MERS, and potential therapeutic interventions.",
"author": "Jafarzadeh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "118102",
"journal-title": "Life Sci.",
"key": "B62",
"volume": "257",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpheart.00215.2020",
"article-title": "Letter to the editor: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: An ally or a Trojan horse? Implications to SARS-CoV-2-related cardiovascular complications.",
"author": "Abassi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "H1080",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.",
"key": "B63",
"volume": "318",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00548.2020",
"article-title": "Kinins and chymase: The forgotten components of the renin-angiotensin system and their implications in COVID-19 disease.",
"author": "Abassi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "L422",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.",
"key": "B64",
"volume": "320",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2022/9028969",
"article-title": "Exploring the impact of ACE inhibition in immunity and disease.",
"author": "Oosthuizen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9028969",
"journal-title": "J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst.",
"key": "B65",
"volume": "2022",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Apoptosis-dependent acute pulmonary injury after intratracheal instillation of angiotensin II.",
"author": "Zhuang",
"first-page": "715",
"journal-title": "Sheng Li Xue Bao.",
"key": "B66",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103356",
"article-title": "The duplicitous nature of ACE2 in COVID-19 Disease.",
"author": "Heyman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103356",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine.",
"key": "B67",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41440-020-0455-8",
"article-title": "Interactions of coronaviruses with ACE2, angiotensin II, and RAS inhibitors-lessons from available evidence and insights into COVID-19.",
"author": "Kai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "648",
"journal-title": "Hypertens Res.",
"key": "B68",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12012-021-09649-y",
"article-title": "Scientific hypothesis for treatment of COVID-19’s lung lesions by adjusting ACE/ACE2 imbalance.",
"author": "Ferrara",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "498",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Toxicol.",
"key": "B69",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01312",
"article-title": "The lung macrophage in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A friend or a foe?",
"author": "Abassi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1312",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B70",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0968-3",
"article-title": "Extrapulmonary manifestations of COVID-19.",
"author": "Gupta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1017",
"journal-title": "Nat Med.",
"key": "B71",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2613.2001.iep0082-0171-x",
"article-title": "The functions of cytokines and their uses in toxicology.",
"author": "Foster",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "171",
"journal-title": "Int J Exp Pathol.",
"key": "B72",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cytogfr.2020.05.002",
"article-title": "COVID-19: Pathogenesis, cytokine storm and therapeutic potential of interferons.",
"author": "Nile",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "66",
"journal-title": "Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.",
"key": "B73",
"volume": "53",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.648004",
"article-title": "Blood interferon-α levels and severity, outcomes, and inflammatory profiles in hospitalized COVID-19 patients.",
"author": "Contoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "648004",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B74",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40249-020-00662-x",
"article-title": "Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 cell receptor gene ACE2 in a wide variety of human tissues.",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Poverty.",
"key": "B75",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-020-02328-6",
"article-title": "Cytokine network analysis of immune responses before and after autologous dendritic cell and tumor cell vaccine immunotherapies in a randomized trial.",
"author": "Nistor",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "176",
"journal-title": "J Transl Med.",
"key": "B76",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26232",
"article-title": "The cytokine storm and COVID-19.",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "250",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol.",
"key": "B77",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00876",
"article-title": "NMR spectroscopic windows on the systemic effects of SARS-CoV-2 infection on plasma lipoproteins and metabolites in relation to circulating cytokines.",
"author": "Lodge",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "J Proteome Res.",
"key": "B78",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.omtm.2020.04.008",
"article-title": "Reversal of hypoxic pulmonary hypertension by hypoxia-inducible overexpression of angiotensin-(1-7) in pulmonary endothelial cells.",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "975",
"journal-title": "Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev.",
"key": "B79",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00017.2012",
"article-title": "Hypoxia and adipose tissue function and dysfunction in obesity.",
"author": "Trayhurn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Physiol Rev.",
"key": "B80",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms232113491",
"article-title": "The effect of oxidative stress-induced autophagy by cadmium exposure in kidney, liver, and bone damage, and neurotoxicity.",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13491",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci.",
"key": "B81",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.01864",
"article-title": "Epigenetic regulation of autophagy: A path to the control of autoimmunity.",
"author": "Hargarten",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1864",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B82",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41581-023-00720-1",
"article-title": "Pathogenesis of autoimmune disease.",
"author": "Pisetsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Nephrol.",
"key": "B83",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaut.2007.06.003",
"article-title": "Autophagy: Highlighting a novel player in the autoimmunity scenario.",
"author": "Lleo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "61",
"journal-title": "J Autoimmun.",
"key": "B84",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature09782",
"article-title": "Autophagy in immunity and inflammation.",
"author": "Levine",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "323",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "B85",
"volume": "469",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/ars.2017.7294",
"article-title": "Oxidative stress in mesenchymal stem cell senescence: Regulation by coding and noncoding RNAs.",
"author": "Vono",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "864",
"journal-title": "Antioxid Redox Signal.",
"key": "B86",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0039-1683996",
"article-title": "Pathogenesis of acute respiratory distress syndrome.",
"author": "Huppert",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "31",
"journal-title": "Semin Respir Crit Care Med.",
"key": "B87",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/path.2697",
"article-title": "Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms.",
"author": "Glick",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "J Pathol.",
"key": "B88",
"volume": "221",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molliq.2022.120566",
"article-title": "Integrated computational approach towards identification of HSPG and ACE2 mimicking moieties for SARS-CoV-2 inhibition.",
"author": "Sreekumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "120566",
"journal-title": "J Mol Liq.",
"key": "B89",
"volume": "367",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.035",
"article-title": "A universal design of betacoronavirus vaccines against COVID-19, MERS, and SARS.",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "722",
"journal-title": "Cell.",
"key": "B90",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri2802",
"article-title": "Immunity and immunopathology to viruses: What decides the outcome?",
"author": "Rouse",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "514",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol.",
"key": "B91",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047297",
"article-title": "Substituting angiotensin-(1-7) to prevent lung damage in SARS-CoV-2 infection?",
"author": "Peiró",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1665",
"journal-title": "Circulation.",
"key": "B92",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14429",
"article-title": "Distribution of ACE2, CD147, CD26, and other SARS-CoV-2 associated molecules in tissues and immune cells in health and in asthma, COPD, obesity, hypertension, and COVID-19 risk factors.",
"author": "Radzikowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2829",
"journal-title": "Allergy.",
"key": "B93",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.651728",
"article-title": "Innate and adaptive immunity alterations in metabolic associated fatty liver disease and its implication in COVID-19 severity.",
"author": "Lamadrid",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "651728",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol.",
"key": "B94",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.peptides.2014.07.023",
"article-title": "Proteomic white adipose tissue analysis of obese mice fed with a high-fat diet and treated with oral angiotensin-(1-7).",
"author": "Andrade",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "56",
"journal-title": "Peptides.",
"key": "B95",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms242417197",
"article-title": "Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells protect endothelial cells from hypoxic injury by suppressing terminal UPR in vivo and in vitro.",
"author": "Keese",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "17197",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci.",
"key": "B96",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1207",
"article-title": "Mas receptor activation slows tumor growth and attenuates muscle wasting in cancer.",
"author": "Murphy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "706",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res.",
"key": "B97",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2362.2009.02153.x",
"article-title": "SARS-coronavirus modulation of myocardial ACE2 expression and inflammation in patients with SARS.",
"author": "Oudit",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "618",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Invest.",
"key": "B98",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fped.2020.594127",
"article-title": "Case report: Case series of children with multisystem inflammatory syndrome following SARS-CoV-2 infection in Switzerland.",
"author": "Fouriki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "594127",
"journal-title": "Front Pediatr.",
"key": "B99",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15082",
"article-title": "Renin-angiotensin system blockers and the COVID-19 pandemic: At present there is no evidence to abandon renin-angiotensin system blockers.",
"author": "Danser",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "Hypertension.",
"key": "B100",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.peptides.2020.170428",
"article-title": "The role of kallikrein-kinin and renin-angiotensin systems in COVID-19 infection.",
"author": "Carvalho",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "170428",
"journal-title": "Peptides.",
"key": "B101",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox9111129",
"article-title": "The pivotal role of adipocyte-na K peptide in reversing systemic inflammation in obesity and COVID-19 in the development of heart failure.",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1129",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel).",
"key": "B102",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00109-021-02072-4",
"article-title": "Obesity and its impact on COVID-19.",
"author": "de Leeuw",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "899",
"journal-title": "J Mol Med (Berl).",
"key": "B103",
"volume": "99",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The renin-angiotensin system and the exocrine pancreas.",
"author": "Chappell",
"first-page": "33",
"journal-title": "JOP.",
"key": "B104",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejim.2021.09.007",
"article-title": "The pivotal link between ACE2 deficiency and SARS-CoV-2 infection: One year later.",
"author": "Angeli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "Eur J Intern Med.",
"key": "B105",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2023.3546",
"article-title": "Renin-angiotensin system modulation with synthetic angiotensin (1-7) and angiotensin II Type 1 receptor-biased ligand in adults with covid-19: Two randomized clinical trials.",
"author": "Self",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1170",
"journal-title": "JAMA.",
"key": "B106",
"volume": "329",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-024-01369-0",
"article-title": "Angiotensin-(1-7) infusion in COVID-19 patients admitted to the ICU: A seamless phase 1-2 randomized clinical trial.",
"author": "Martins",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "Ann Intensive Care.",
"key": "B107",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18103/mra.v12i9.5704",
"article-title": "Suspected causes of the specific intolerance profile of spike-Based COVID-19 vaccines (review/analysis).",
"author": "Lehmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Eur Soc Med.",
"key": "B108",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.35248/2322-3308-12.4.004",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2-spike interactions with the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system -consequences of adverse reactions of vaccination.",
"author": "Lehmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "J Biol Today’s World.",
"key": "B109",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.35248/1745-7580.24.20.267",
"article-title": "Impact of SARS-CoV-2 spikes on safety of spike-based COVID-19 vaccinations.",
"author": "Lehmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1000267",
"journal-title": "Immunome Res.",
"key": "B110",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2024"
}
],
"reference-count": 110,
"references-count": 110,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1612442/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Interaction of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines with renin angiotensin aldosterone system, clinical outcomes, and angiotensin (1-7) as a physiological treatment recommendation: hypothesis and theory article",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "12"
}