Evaluation of the Effect of Zinc, Quercetin, Bromelain and Vitamin C on COVID-19 Patients
et al., International Journal of Diabetes Management, doi:10.61797/ijdm.v2i2.259, NCT04468139, Oct 2023
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
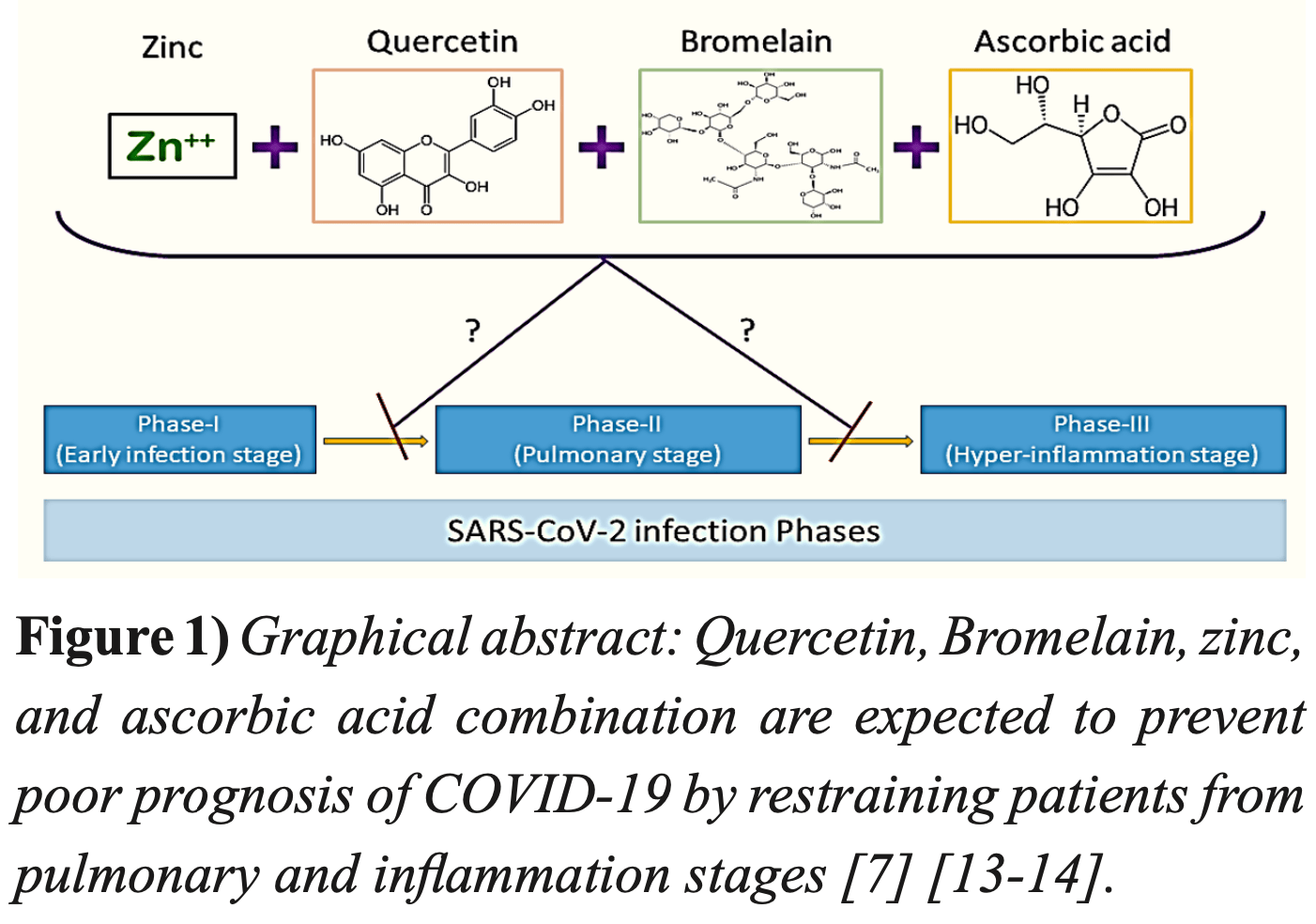
Case series of 22 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing that a combination of quercetin 800mg, bromelain 165mg, zinc acetate 50mg and vitamin C 1g daily for 3-5 days was safe when given with other treatments.
Authors include in silico molecular docking analysis showing that the natural compounds quercetin and bromelain bind strongly to the active site of human cathepsin L protein, indicating they may act as inhibitors. Quercetin exhibited a binding energy of -5.15 kcal/mol with 5 hydrogen bonds and 1 pi-interaction. Bromelain had a binding energy of -5.65 kcal/mol with 7 hydrogen bonds. As human cathepsin L is involved in inflammatory pathways, the results suggest quercetin and bromelain could potentially help prevent COVID-19 progression to severe inflammation and cytokine storm.
Ahmed et al., 6 Oct 2023, Saudi Arabia, peer-reviewed, mean age 49.3, 6 authors, study period June 2020 - September 2020, trial NCT04468139 (history).
Contact: drmedahmed@gmail.com.
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19 ) is an infectious disease caused by a new strain of coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2. There are three phases of COVID-19: early infection stage, pulmonary stage, and hyper-inflammation stage. It is essential to prevent lung or other organ injuries by preventing phase-II and phase-III using pharmacological or non-pharmacological treatments. This case series study aims to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Quercetin, Bromelain, zinc, and vitamin C combination supplements in patients with COVID-19. In this study, twenty-two patients diagnosed (mean age 49.27, 68.18% male) with COVID-19 in Imam Abdulrahman Alfaisal Hospital in Riyadh have administrated Quercetin 800 mg, Bromelain 165 mg, zinc acetate 50 mg, and vitamin C 1 g once daily as supplements for 3 to 5 days. The mean levels of WBC, ANC, ALC, AMC, and AST, D dimer were measured to investigate the safety of the used treatment. we planned to measure how long stay at the hospital, Chemistry profiles like D dimer, serum ferritin, CRP, serum zinc, and interleukin 6 as planned in the protocol and measured not done for all parameters like zinc, and interleukin 6 were not done as unavailable facilities at lab of hospital Their mean values were normal among all included patients before and after taking the supplements. Therefore, the oncedaily administration of these supplements was found to be safe for patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 and may prevent the poor prognosis of the disease. Randomized clinical trials are needed in the future to ensure the efficacy of Quercetin, Bromelain, zinc, and vitamin C combination. The study was registered at clinicaltrials.gov
Ethical Approval Institutional review board (IRB) was obtained from the Saudi Ministry of Health on June 7, 2020, with the central IRB log number: 20-95M.
Authors' Contributions (Amr Ahmed wrote the protocol of the study, and follow-up of cases at the hospital for patients which was included in the study to finish the study and follow-up of treatment, Heba Abdelseed taking consent from patients, Dr. Abdullah Alkattan, lab results, and statistics, Eman Aslsalameen, lab results collection). Yousef Albalawi follows up on cases during the study and files cases, and Hassan Shoura revises the protocol)
References
Aucoin, Cooley, Saunders, The effect of quercetin on the prevention or treatment of COVID-19 and other respiratory tract infections in humans: a rapid review, Adv Integr Med
Chandler, Mynott, Bromelain protects piglets from diarrhoea caused by oral challenge with K88 positive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, Gut
Chiow, Phoon, Putti, Evaluation of antiviral activities of Houttuynia cordata Thunb. extract, quercetin, quercetrin and cinanserin on murine coronavirus and dengue virus infection, Asian Pac J Trop Med
Jasso-Miranda, Herrera-Camacho, Flores-Mendoza, Antiviral and immunomodulatory effects of polyphenols on macrophages infected with dengue virus serotypes 2 and 3 enhanced or not with antibodies, Infect Drug Resist
Larson, Symons, Jalili, Quercetin: a Treatment for Hypertension?-a Review of efficacy and mechanisms, Pharmaceuticals
Nezami, Yamamoto, Nezami, Biological disruptive therapies as counter measures for unpredictable biological insults, a case for successful treatment of COVID 19, Advances in Infectious Diseases
Pavan, Jain, Shraddha, Properties and therapeutic application of bromelain: a review, Biotechnol Res Int
Qiu, Kroeker, He, Prophylactic efficacy of quercetin 3-β-O-d-Glucoside against Ebola virus Infection, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Rathnavelu, Alitheen, Sohila, Potential role of bromelain in clinical and therapeutic applications, Biomed Rep
Sagar, Rathinavel, Lutz, Bromelain inhibits SARS-CoV-2 infection in VeroE6 cells, BioRxiv
Verma, Meena, Paul, Role of bromelain as herbal anti inflammatory compound using in vitro and in vivo model of colitis, J Autoimmune Dis
Winter, On the pharmacology of bromelain: an update with special regard to animal studies on dose dependent effects, Planta Med
Wong, He, Siragam, Antiviral activity of quercetin-3-β-O-D-glucoside against Zika virus infection, Virol Sin
Wu, Li, Li, Quercetin as an antiviral agent inhibits Influenza A Virus (IAV) entry, Viruses
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.61797/ijdm.v2i2.259",
"ISSN": [
"2564-324X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.61797/ijdm.v2i2.259",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is an infectious disease caused by a new strain of coronavirus. There are three phases of COVID-19: early infection stage, pulmonary stage and hyper-inflammation stage respectively. It is important to prevent lung or other organs injuries by preventing phase-II and phase-III via pharmacological or non-pharmacological treatments. This was a case series study done on twenty-two patients confirmed to be infected with SARS-CoV-2 and diagnosed with COVID-19. Patients in this study have been used quercetin 800 mg, bromelain 165 mg, zinc acetate 50 mg and ascorbic acid 1 g once daily as supplements for 3 to 5 days during SARS-CoV-2 infection. The aim of this study is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of quercetin, bromelain, zinc and ascorbic acid combination supplements on patients with COVID-19. The mean levels of WBC, ANC, ALC, AMC and AST were normal among all included patients before and after taking quercetin, bromelain, zinc and ascorbic acid supplements (P-value >0.05). Quercetin 800 mg, bromelain 165 mg, zinc acetate 50 mg and ascorbic acid 1 g once daily supplements were safe for patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 and may prevent poor prognosis. Randomized clinical trials needed in the future to ensure the efficacy of quercetin, bromelain, zinc and vitamin C combination.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ahmed",
"given": "Amr",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Abdelseed",
"given": "Heba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shora",
"given": "Hassan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Albalawi",
"given": "Yousef",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aslsalameen",
"given": "Eman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alkattan",
"given": "Abdullah",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Diabetes Management",
"container-title-short": "Int J Diabetes Manag",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-30T14:56:19Z",
"timestamp": 1703948179000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-30T14:56:19Z",
"timestamp": 1703948179000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-31T00:28:40Z",
"timestamp": 1703982520565
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
30
]
]
}
},
"member": null,
"original-title": [],
"page": "29-37",
"prefix": "10.61797",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
30
]
]
},
"publisher": null,
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://researchlakejournals.com/index.php/IJDM/article/view/259"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Evaluation of the Effect of Zinc, Quercetin, Bromelain and Vitamin C on COVID-19 Patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "2"
}
ahmed5
