Effect of high-dose Spirulina supplementation on hospitalized adults with COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial
et al., Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1332425, IRCT20210216050373N1, Apr 2024
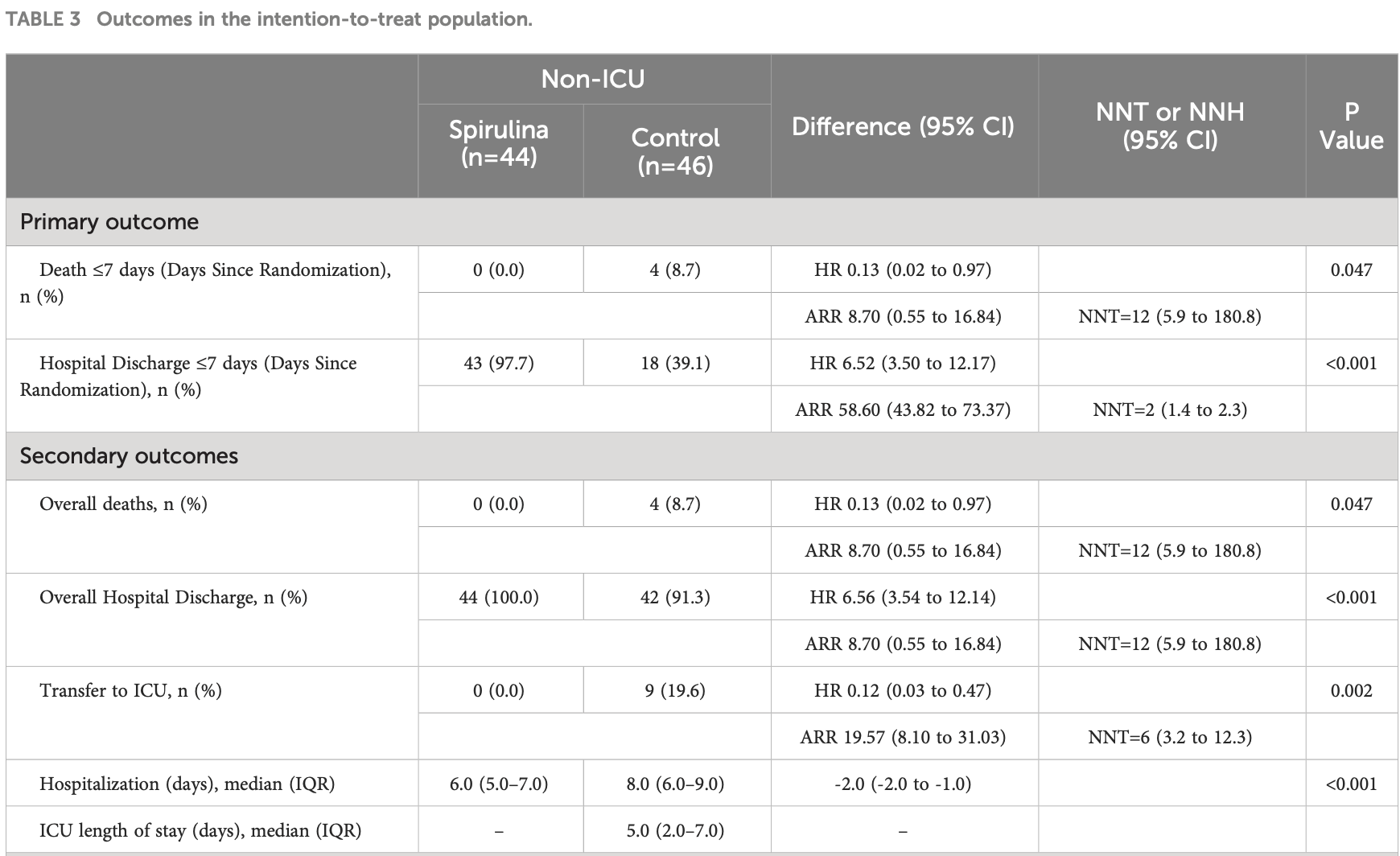
RCT 189 hospitalized COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality and faster recovery with spirulina. Spirulina treatment also resulted in greater reductions in inflammatory markers such as IL-6, TNF-a, IP-10, CRP, ESR, and ferritin. All patients received remdesivir. Spirulina contains many components including calcium spirulan, a sulfated polysaccharide shown to inhibit the replication of various enveloped viruses in vitro, and many nutrients showing benefits for COVID-19 including vitamins A, C, and D, selenium, and zinc.
|
risk of death, 84.8% lower, HR 0.15, p < 0.001, treatment 47, control 52, adjusted per study, combined.
|
|
risk of death, 87.0% lower, HR 0.13, p = 0.04, treatment 0 of 44 (0.0%), control 4 of 46 (8.7%), NNT 12, adjusted per study, Non-ICU, overall mortality.
|
|
risk of death, 84.0% lower, HR 0.16, p = 0.002, treatment 0 of 47 (0.0%), control 15 of 52 (28.8%), NNT 3.5, adjusted per study, ICU, overall mortality.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 75.4% lower, HR 0.25, p = 0.003, treatment 47, control 52, adjusted per study, combined.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 84.8% lower, HR 0.15, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 44 (0.0%), control 4 of 46 (8.7%), NNT 12, adjusted per study, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, Non-ICU, overall discharge.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 61.4% lower, HR 0.39, p < 0.001, treatment 0 of 47 (0.0%), control 37 of 52 (71.2%), NNT 1.4, adjusted per study, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, ICU, overall discharge.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Aghasadeghi et al., 8 Apr 2024, Randomized Controlled Trial, Iran, peer-reviewed, mean age 45.8, 26 authors, study period June 2021 - February 2022, trial IRCT20210216050373N1.
Contact: a_alinaghi@sina.tums.ac.ir.
Effect of high-dose Spirulina supplementation on hospitalized adults with COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial
Frontiers in Immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1332425
Objective: Spirulina (arthrospira platensis) is a cyanobacterium proven to have anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and antioxidant effects. However, the effect of highdose Spirulina supplementation on hospitalized adults with COVID-19 is currently unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of highdose Spirulina platensis for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Study Design: We conducted a randomized, controlled, open-label trial involving 189 patients with COVID-19 who were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to an experimental group that received 15.2g of Spirulina supplement plus standard treatment (44 non-intensive care unit (non-ICU) and 47 ICU), or to a control group that received standard treatment alone (46 non-ICU and 52 ICU). The study was conducted over six days. Immune mediators were monitored on days 1, 3, 5, and 7. The primary outcome of this study was mortality or hospital Frontiers in Immunology frontiersin.org 01
Ethics statement This study is a multicenter, randomized controlled trialapproved by the Research Ethics Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences (IR.TUMS.IKHC.REC.1399.481) and the Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (IRCT) registry team. The s tu dy pro t oco l is re gi stered w ith IRCT u n d e r IRCT20210216050373N1, available at https://irct.ir/trial/54375. All patients gave written informed consent before starting the study.
Author contributions
Conflict of interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1332425/ full#supplementary-material
References
Arjmand, Alavi-Moghadam, Roudsari, Rezaei-Tavirani, Rahim et al., COVID-19 pathology on various organs and regenerative medicine and stem cell-based interventions, Front Cell Dev Biol, doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.675310
Ayehunie, Belay, Baba, Ruprecht, Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by an aqueous extract of Spirulina platensis (Arthrospira platensis), J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol, doi:10.1097/00042560-199805010-00002
Bansal, Mahapure, Bhurwal, Gupta, Hassanain et al., Mortality benefit of remdesivir in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.606429
Batista, De Albuquerque, Vasconcelos, Bezerra, Da et al., Probiotics and prebiotics: potential prevention and therapeutic target for nutritional management of COVID-19?, Nutr Res Rev, doi:10.1017/s0954422421000317
Belay, Biology and industrial production of Arthrospira (Spirulina)
Bergandi, Apprato, Silvagno, Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of combined phycocyanin and palmitoylethanolamide in human lung and prostate epithelial cells, Antioxidants, doi:10.3390/antiox11020201
Bhimraj, Morgan, Shumaker, Lavergne, Baden et al., Infectious diseases society of america guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa478
Billiau, Matthys, Interferon-g: a historical perspective, Cytokine Growth factor Rev, doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.02.004
Chen, Chang, Kuo, Huang, Hu et al., Well-tolerated Spirulina extract inhibits influenza virus replication and reduces virus-induced mortality, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/srep24253
Dehghan, Ghanbari, Heidari, Shahrbabaki, Zakeri, Use of complementary and alternative medicine in general population during COVID-19 outbreak: A survey in Iran, J Integr Med, doi:10.1016/j.joim.2021.11.004
Deleu, Machiels, Raes, Verbeke, Vermeire, Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: An overlooked therapy for IBD?, EBioMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103293
El-Saadony, Shehata, Saad, Aldhumri, Ouda, Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Spirulina platensis extracts and biogenic selenium nanoparticles against selected pathogenic bacteria and fungi, Saudi J Biol Sci, doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.046
Elfar, Billa, Lim, Chew, Cheah et al., Advances in delivery methods of Arthrospira platensis (spirulina) for enhanced therapeutic outcomes, Bioengineered, doi:10.1080/21655979.2022.2100863
Fajgenbaum, June, Cytokine storm, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMra2026131
Finamore, Palmery, Bensehaila, Peluso, Antioxidant, immunomodulating, and microbial-modulating activities of the sustainable and ecofriendly spirulina, Oxid Med Cell Longev, doi:10.1155/2017/3247528
Gao, Liu, Wan, Wang, Cheng et al., Phycocyanin prevents methylglyoxal-induced mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in INS-1 cells by Nrf2, Food Funct, doi:10.1039/C5FO01548K
Gouda, Tadda, Zhao, Farmanullah, Chu et al., Microalgae bioactive carbohydrates as a novel sustainable and eco-friendly source of prebiotics: emerging health functionality and recent technologies for extraction and detection, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2022.806692
Hariharan, Hakeem, Radhakrishnan, Reddy, Rela, The role and therapeutic potential of NF-kappa-B pathway in severe COVID-19 patients, Inflammopharmacology, doi:10.1007/s10787-020-00773-9
Hayashi, Hayashi, Maeda, Kojima, Calcium spirulan, an inhibitor of enveloped virus replication, from a blue-green alga Spirulina platensis, J Nat Prod, doi:10.1021/np960017o
Hirahashi, Matsumoto, Hazeki, Saeki, Ui et al., Activation of the human innate immune system by Spirulina: augmentation of interferon production and NK cytotoxicity by oral administration of hot water extract of Spirulina platensis, Int Immunopharmacol, doi:10.1016/s1567-5769(01)00166-7
Hu, Li, Pakpour, Wang, Pan et al., Dose effects of orally administered spirulina suspension on colonic microbiota in healthy mice, Front Cell Infect Microbiol, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2019.00243
Ishii, Katoch, Okuwaki, Hayashi, Influence of dietary Spirulina platensis on IgA level in human saliva, J Kagawa Nutr Univ
Jabczyk, Nowak, Hudzik, Zubelewicz-Szkodzińska, Microbiota and its impact on the immune system in COVID-19-A narrative review, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm10194537
Jiang, Zhao, Zhou, Xiang, Gutierrez-Castrellon et al., Inflammatory pathways in COVID-19: Mechanism and therapeutic interventions, MedComm, doi:10.1002/mco2.154
Jin, Hu, Li, Yu, Xiao et al., Noncanonical NF-kB pathway controls the production of type I interferons in antiviral innate immunity, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2014.02.006
Jirjees, Saad, Hano, Hatahet, Obaidi et al., COVID-19 treatment guidelines: do they really reflect best medical practices to manage the pandemic?, Infect Dis Rep, doi:10.3390/idr13020029
Karkos, Leong, Karkos, Sivaji, Da, Spirulina in clinical practice: evidence-based human applications, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, doi:10.1093/ecam/nen058
Kim, Lee, Cho, Moon, Inhibitory effect of mast cell-mediated immediate-type allergic reactions in rats by spirulina, Biochem Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/s0006-2952(97)00678-3
Laurent, Yang, Rendeiro, Nilsson-Payant, Carrau et al., Sensing of SARS-CoV-2 by pDCs and their subsequent production of IFN-I contribute to macrophage-induced cytokine storm during COVID-19, Sci Immunol, doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.add4906
Li, Fan, Lai, Han, Li et al., Coronavirus infections and immune responses, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.25685
Li, Yu, Li, Liu, Jiao et al., Phycocyanin attenuates pulmonary fibrosis via the TLR2-MyD88-NF-kB signaling pathway, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-06021-5
Liu, Qin, Li, Phycocyanin: Anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism, BioMed Pharmacother, doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113362
Liu, Zhang, Joo, Sun, NF-kB signaling in inflammation, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23
Liu, Zhang, Yang, Ma, Li et al., The role of interleukin-6 in monitoring severe case of coronavirus disease 2019, EMBO Mol Med, doi:10.15252/emmm.202012421
Mao, Van De Water, Gershwin, Effects of a Spirulina-based dietary supplement on cytokine production from allergic rhinitis patients, Med Food, doi:10.1089/jmf.2005.8.27
Mccarty, Clinical potential of Spirulina as a source of phycocyanobilin, J Med Food, doi:10.1089/jmf.2007.621
Mueller, Tamura, Crowley, Degrado, Haider et al., Inflammatory biomarker trends predict respiratory decline in COVID-19 patients, Cell Rep Med, doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100144
Munster, Koopmans, Van Doremalen, Van Riel, De, A novel coronavirus emerging in China -key questions for impact assessment, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMp2000929
Neyrinck, Taminiau, Walgrave, Daube, Cani et al., Spirulina protects against hepatic inflammation in aging: an effect related to the modulation of the gut microbiota?, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu9060633
Ngo-Matip, Pieme, Azabji-Kenfack, Moukette, Korosky et al., Impact of daily supplementation of Spirulina platensis on the immune system of naïve HIV-1 patients in Cameroon: a 12-months single blind, randomized, multicenter trial, Nutr J, doi:10.1186/s12937-015-0058-4
Parvizi, Forouhari, Shahriarirad, Shahriarirad, Bradley et al., Prevalence and associated factors of complementary and integrative medicine use in patients afflicted with COVID-19, BMC Complementary Med Therapies, doi:10.1186/s12906-022-03722-x
Peiris, Chu, Cheng, Chan, Hung et al., Clinical progression and viral load in a community outbreak of coronavirus-associated SARS pneumonia: a prospective study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(03)13412-5
Peng, Zhang, Yao, Kwok, Zhang, Probiotics as adjunctive treatment for patients contracted COVID-19: current understanding and future needs, Front Nutr, doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.669808
Piovan, Battaglia, Filippini, Costa, Facci et al., Preand early post-treatment with arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) extract impedes lipopolysaccharide-triggered neuroinflammation in microglia, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.724993
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Crawford, Mcginn et al., Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York city area, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6775
Saini, Sanyal, Cell cycle regulation and apoptotic cell death in experimental colon carcinogenesis: intervening with cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, Nutr Cancer, doi:10.1080/01635581.2015.1015743
Sayah, Berkane, Guermache, Sabri, Lakhal et al., Interleukin-6, procalcitonin and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: Potential immuneinflammatory parameters to identify severe and fatal forms of COVID-19, Cytokine, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155428
Sibiya, Ghazi, Chuturgoon, The potential of spirulina platensis to ameliorate the adverse effects of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART), Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu14153076
Singh, Gandhi, Bhattacharya, Tandon, Tiwari, Cyanometabolites: molecules with immense antiviral potential, Arch Microbiol, doi:10.1007/s00203-023-03514-y
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, Jama, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Wu, Liu, Miron, Klıḿováb, Kucǎ, The antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory activities of Spirulina: an overview, Arch Toxicol, doi:10.1007/s00204-016-1744-5
Yang, Lee, Kim, Spirulina platensis inhibits anaphylactic reaction, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/s0024-3205(97)00668-1
Yeoh, Zuo, Lui, Zhang, Liu et al., Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19, Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323020
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30566-3
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2024.1332425",
"ISSN": [
"1664-3224"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1332425",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p><jats:italic>Spirulina</jats:italic> (<jats:italic>arthrospira platensis</jats:italic>) is a cyanobacterium proven to have anti-inflammatory, antiviral, and antioxidant effects. However, the effect of high-dose <jats:italic>Spirulina</jats:italic> supplementation on hospitalized adults with COVID-19 is currently unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of high-dose <jats:italic>Spirulina platensis</jats:italic> for SARS-CoV-2 infection.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Study Design</jats:title><jats:p>We conducted a randomized, controlled, open-label trial involving 189 patients with COVID-19 who were randomly assigned in a 1:1 ratio to an experimental group that received 15.2g of <jats:italic>Spirulina</jats:italic> supplement plus standard treatment (44 non-intensive care unit (non-ICU) and 47 ICU), or to a control group that received standard treatment alone (46 non-ICU and 52 ICU). The study was conducted over six days. Immune mediators were monitored on days 1, 3, 5, and 7. The primary outcome of this study was mortality or hospital discharge within seven days, while the overall discharge or mortality was considered the secondary outcome.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Within seven days, there were no deaths in the <jats:italic>Spirulina</jats:italic> group, while 15 deaths (15.3%) occurred in the control group. Moreover, within seven days, there was a greater number of patients discharged in the <jats:italic>Spirulina</jats:italic> group (97.7%) in non-ICU compared to the control group (39.1%) (HR, 6.52; 95% CI, 3.50 to 12.17). Overall mortality was higher in the control group (8.7% non-ICU, 28.8% ICU) compared to the <jats:italic>Spirulina</jats:italic> group (non-ICU HR, 0.13; 95% CI, 0.02 to 0.97; ICU, HR, 0.16; 95% CI, 0.05 to 0.48). In non-ICU, patients who received <jats:italic>Spirulina</jats:italic> showed a significant reduction in the levels of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-10, and IP-10 as intervention time increased. Furthermore, in ICU, patients who received <jats:italic>Spirulina</jats:italic> showed a significant decrease in the levels of MIP-1α and IL-6. IFN-γ levels were significantly higher in the intervention group in both ICU and non-ICU subgroups as intervention time increased. No side effects related to <jats:italic>Spirulina</jats:italic> supplements were observed during the trial.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>High-dose <jats:italic>Spirulina</jats:italic> supplements coupled with the standard treatment of COVID-19 may improve recovery and remarkably reduce mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Clinical Trial Registration</jats:title><jats:p><jats:ext-link>https://irct.ir/trial/54375</jats:ext-link>, Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials number (IRCT20210216050373N1)</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.3389/fimmu.2024.1332425"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Aghasadeghi",
"given": "Mohammad Reza",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zaheri Birgani",
"given": "Mohammad Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jamalimoghadamsiyahkali",
"given": "Saeedreza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hosamirudsari",
"given": "Hadiseh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moradi",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jafari-Sabet",
"given": "Majid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sadigh",
"given": "Nooshin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rahimi",
"given": "Pooneh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tavakoli",
"given": "Rezvan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hamidi-Fard",
"given": "Mojtaba",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bahramali",
"given": "Golnaz",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parmoon",
"given": "Zohal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Arjmand Hashjin",
"given": "Sina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mirzajani",
"given": "Ghasem",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kouhkheil",
"given": "Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Roshangaran",
"given": "Somayeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khalaf",
"given": "Samineh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khademi Nadoushan",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gholamiyan Yousef Abad",
"given": "Ghazaleh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shahryarpour",
"given": "Nima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Izadi",
"given": "Mohammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zendedel",
"given": "Abolfazl",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jahanfar",
"given": "Shayesteh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Dadras",
"given": "Omid",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "SeyedAlinaghi",
"given": "SeyedAhmad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hackett",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Frontiers in Immunology",
"container-title-short": "Front. Immunol.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"frontiersin.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T04:37:26Z",
"timestamp": 1712551046000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T04:37:32Z",
"timestamp": 1712551052000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-09T00:33:28Z",
"timestamp": 1712622808518
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
]
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1712534400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1332425/full",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1965",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.3389",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Frontiers Media SA",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25685",
"article-title": "Coronavirus infections and immune responses",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "B1",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMp2000929",
"article-title": "A novel coronavirus emerging in China - key questions for impact assessment",
"author": "Munster",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B2",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "B3",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30566-3",
"article-title": "Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B4",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"article-title": "Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York city area",
"author": "Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Jama",
"key": "B5",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/idr13020029",
"article-title": "COVID-19 treatment guidelines: do they really reflect best medical practices to manage the pandemic",
"author": "Jirjees",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Rep",
"key": "B6",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa478",
"article-title": "Infectious diseases society of america guidelines on the treatment and management of patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Bhimraj",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "ciaa478",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "B7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.606429",
"article-title": "Mortality benefit of remdesivir in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Bansal",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Med (Lausanne)",
"key": "B8",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mco2.154",
"article-title": "Inflammatory pathways in COVID-19: Mechanism and therapeutic interventions",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "MedComm (2020)",
"key": "B9",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra2026131",
"article-title": "Cytokine storm",
"author": "Fajgenbaum",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "B10",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/emmm.202012421",
"article-title": "The role of interleukin-6 in monitoring severe case of coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EMBO Mol Med",
"key": "B11",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155428",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6, procalcitonin and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: Potential immune-inflammatory parameters to identify severe and fatal forms of COVID-19",
"author": "Sayah",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cytokine",
"key": "B12",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2021.675310",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pathology on various organs and regenerative medicine and stem cell-based interventions",
"author": "Arjmand",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Dev Biol",
"key": "B13",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.add4906",
"article-title": "Sensing of SARS-CoV-2 by pDCs and their subsequent production of IFN-I contribute to macrophage-induced cytokine storm during COVID-19",
"author": "Laurent",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci Immunol",
"key": "B14",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100144",
"article-title": "Inflammatory biomarker trends predict respiratory decline in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Mueller",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep Med",
"key": "B15",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(03)13412-5",
"article-title": "Clinical progression and viral load in a community outbreak of coronavirus-associated SARS pneumonia: a prospective study",
"author": "Peiris",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "B16",
"volume": "361",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12937-015-0058-4",
"article-title": "Impact of daily supplementation of Spirulina platensis on the immune system of naïve HIV-1 patients in Cameroon: a 12-months single blind, randomized, multicenter trial",
"author": "Ngo-Matip",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "70",
"journal-title": "Nutr J",
"key": "B17",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu14153076",
"article-title": "The potential of spirulina platensis to ameliorate the adverse effects of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)",
"author": "Sibiya",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3076",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B18",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/9781118567166.ch17",
"article-title": "Biology and industrial production of Arthrospira (Spirulina)",
"author": "Belay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "B19",
"volume-title": "Handbook of microalgal culture:",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/21655979.2022.2100863",
"article-title": "Advances in delivery methods of Arthrospira platensis (spirulina) for enhanced therapeutic outcomes",
"author": "ElFar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Bioengineered",
"key": "B20",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ecam/nen058",
"article-title": "Spirulina in clinical practice: evidence-based human applications",
"author": "Karkos",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "531053",
"journal-title": "Evid Based Complement Alternat Med",
"key": "B21",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jmf.2007.621",
"article-title": "Clinical potential of Spirulina as a source of phycocyanobilin",
"author": "McCarty",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Med Food",
"key": "B22",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0006-2952(97)00678-3",
"article-title": "Inhibitory effect of mast cell-mediated immediate-type allergic reactions in rats by spirulina",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Biochem Pharmacol",
"key": "B23",
"volume": "55",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0024-3205(97)00668-1",
"article-title": "Spirulina platensis inhibits anaphylactic reaction",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "B24",
"volume": "61",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/jmf.2005.8.27",
"article-title": "Effects of a Spirulina-based dietary supplement on cytokine production from allergic rhinitis patients",
"author": "Mao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "Med Food",
"key": "B25",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"article-title": "Influence of dietary Spirulina platensis on IgA level in human saliva",
"author": "Ishii",
"first-page": "27",
"journal-title": "J Kagawa Nutr Univ",
"key": "B26",
"volume": "30",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1567-5769(01)00166-7",
"article-title": "Activation of the human innate immune system by Spirulina: augmentation of interferon production and NK cytotoxicity by oral administration of hot water extract of Spirulina platensis",
"author": "Hirahashi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "B27",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2002"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/np960017o",
"article-title": "Calcium spirulan, an inhibitor of enveloped virus replication, from a blue-green alga Spirulina platensis",
"author": "Hayashi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "J Nat Prod",
"key": "B28",
"volume": "59",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00042560-199805010-00002",
"article-title": "Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by an aqueous extract of Spirulina platensis (Arthrospira platensis)",
"author": "Ayehunie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7",
"journal-title": "J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol",
"key": "B29",
"volume": "18",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep24253",
"article-title": "Well-tolerated Spirulina extract inhibits influenza virus replication and reduces virus-induced mortality",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B30",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00203-023-03514-y",
"article-title": "Cyanometabolites: molecules with immense antiviral potential",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "164",
"journal-title": "Arch Microbiol",
"key": "B31",
"volume": "205",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2014.02.006",
"article-title": "Noncanonical NF-κB pathway controls the production of type I interferons in antiviral innate immunity",
"author": "Jin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "B32",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-020-00773-9",
"article-title": "The role and therapeutic potential of NF-kappa-B pathway in severe COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Hariharan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "91",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "B33",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2017/3247528",
"article-title": "Antioxidant, immunomodulating, and microbial-modulating activities of the sustainable and ecofriendly spirulina",
"author": "Finamore",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Oxid Med Cell Longev",
"key": "B34",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-017-06021-5",
"article-title": "Phycocyanin attenuates pulmonary fibrosis via the TLR2-MyD88-NF-κB signaling pathway",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5843",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "B35",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/01635581.2015.1015743",
"article-title": "Cell cycle regulation and apoptotic cell death in experimental colon carcinogenesis: intervening with cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors",
"author": "Saini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutr Cancer",
"key": "B36",
"volume": "67",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/C5FO01548K",
"article-title": "Phycocyanin prevents methylglyoxal-induced mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in INS-1 cells by Nrf2",
"author": "Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Food Funct",
"key": "B37",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.724993",
"article-title": "Pre- and early post-treatment with arthrospira platensis (Spirulina) extract impedes lipopolysaccharide-triggered neuroinflammation in microglia",
"author": "Piovan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol",
"key": "B38",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113362",
"article-title": "Phycocyanin: Anti-inflammatory effect and mechanism",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "BioMed Pharmacother",
"key": "B39",
"volume": "153",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.046",
"article-title": "Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Spirulina platensis extracts and biogenic selenium nanoparticles against selected pathogenic bacteria and fungi",
"author": "Abdel-Moneim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Saudi J Biol Sci",
"key": "B40",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00204-016-1744-5",
"article-title": "The antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory activities of Spirulina: an overview",
"author": "Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Arch Toxicol",
"key": "B41",
"volume": "90",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"key": "B42",
"unstructured": ""
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox11020201",
"article-title": "Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of combined phycocyanin and palmitoylethanolamide in human lung and prostate epithelial cells",
"author": "Bergandi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "201",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants (Basel)",
"key": "B43",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sigtrans.2017.23",
"article-title": "NF-κB signaling in inflammation",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "B44",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323020",
"article-title": "Gut microbiota composition reflects disease severity and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Yeoh",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "698",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "B45",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103293",
"article-title": "Short chain fatty acids and its producing organisms: An overlooked therapy for IBD",
"author": "Deleu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "B46",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10194537",
"article-title": "Microbiota and its impact on the immune system in COVID-19-A narrative review",
"author": "Jabczyk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4537",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "B47",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2021.669808",
"article-title": "Probiotics as adjunctive treatment for patients contracted COVID-19: current understanding and future needs",
"author": "Peng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "B48",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/s0954422421000317",
"article-title": "Probiotics and prebiotics: potential prevention and therapeutic target for nutritional management of COVID-19",
"author": "Batista",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nutr Res Rev",
"key": "B49",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fnut.2022.806692",
"article-title": "Microalgae bioactive carbohydrates as a novel sustainable and eco-friendly source of prebiotics: emerging health functionality and recent technologies for extraction and detection",
"author": "Gouda",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Nutr",
"key": "B50",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9060633",
"article-title": "Spirulina protects against hepatic inflammation in aging: an effect related to the modulation of the gut microbiota",
"author": "Neyrinck",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "633",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "B51",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2019.00243",
"article-title": "Dose effects of orally administered spirulina suspension on colonic microbiota in healthy mice",
"author": "Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Front Cell Infect Microbiol",
"key": "B52",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.02.004",
"article-title": "Interferon-γ: a historical perspective",
"author": "Billiau",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "97",
"journal-title": "Cytokine Growth factor Rev",
"key": "B53",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12906-022-03722-x",
"article-title": "Prevalence and associated factors of complementary and integrative medicine use in patients afflicted with COVID-19",
"author": "Parvizi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Complementary Med Therapies",
"key": "B54",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.joim.2021.11.004",
"article-title": "Use of complementary and alternative medicine in general population during COVID-19 outbreak: A survey in Iran",
"author": "Dehghan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "J Integr Med",
"key": "B55",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 55,
"references-count": 55,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1332425/full"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Immunology",
"Immunology and Allergy"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of high-dose Spirulina supplementation on hospitalized adults with COVID-19: a randomized controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/crossmark-policy",
"volume": "15"
}